Uterine polyps are formed due to pathological growth of the uterine mucosa. They can be in any quantity: from one to many, on a stalk or on a wide base. The clinical picture depends on the degree of damage, the duration of the disease and the number of polyps.
Diagnosis requires a gynecological examination with a number of instrumental and laboratory tests.
At CELT you can get advice from a gynecologist.
- Cost of initial consultation - 3,000
- Cost of consultation with ultrasound - 4,200
Make an appointment
What it is?
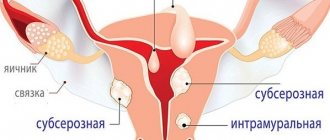
Polyps form in the endometrium (the layer of cells lining the inside of the uterus). It is the endometrium that changes over the course of the menstrual cycle and is responsible for the attachment of a fertilized egg at the very beginning of pregnancy. The resulting polyps look like separate hills. They stand out against the background of the mucous membrane and look like tubercles. Their size can vary from very small to several centimeters. They are always connected to the wall of the uterus by a stalk or base. If many tumors are detected, the disease is called polyposis.
In most cases, endometrial polyps do not extend beyond the uterus. In some cases, they are found in the cervical canal and vagina, spreading through the cervix.
Polyps can develop in girls and women of any age group. The main danger of the disease is that polyps can be precancerous growths. Therefore, in the absence of contraindications for surgery, removal of polyps is indicated.
Bloody discharge after surgery
Due to trauma to the uterine mucosa after surgery, spotting and spasmodic pain may be observed for several days from the place where the polyp in the uterus was removed.
Bloody discharge can be observed for several days, but heavy bleeding can only be a concern in the first hours after surgery.
How does a polyp affect menstruation?
Menstruation after removal of an endometrial polyp in the uterus is irregular and may differ significantly from normal menstruation. The restoration of the cycle usually occurs within a month and a half, but it can be regulated within three to four months. The consequences of removing a polyp in the uterus will depend on whether there was a violation of the surgical technique or other complications directly during the manipulation.
Classification
Since a polyp is a derivative of the endometrium, the same thing can happen to the neoplasm that sometimes happens to other tissues: infection, necrotization, and the formation of ulcers. Structurally, the neoplasm consists of the following components: epithelium (integumentary tissue), stroma and blood vessels.
Depending on which tissue predominates in the structure, the following types of polyps are distinguished:
- glandular;
- fibrous;
- adenomatous;
- mixed glandular-fibrous.
The glandular type of polyps is more common in young girls. Polyps of mixed type, in addition to glandular tissue, also contain connective tissue. They are more common in adulthood. Fibrous neoplasms are predominantly composed of connective tissue. Adenomatous neoplasms are the most dangerous in terms of degeneration into cancer. Therefore, they try to remove them immediately after detection.
In addition to the listed types, a placental form is isolated, in which case the polyp is formed after childbirth or artificial or spontaneous termination of pregnancy. As the name implies, the polyp comes from the placenta, part of which for some reason was not removed from the body. This form of the disease has more pronounced symptoms: prolonged bleeding appears, and infection often occurs.
Diagnosis of uterine polyposis
The disease is diagnosed in four ways:
- transvaginal ultrasound;
- scraping;
- hysteroscopy;
- MRI.
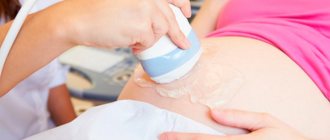
Polyp on ultrasound
Thanks to ultrasound, you can find out whether there is a disease, and determine with little certainty the type of tumor: benign or malignant. Such a study can be carried out even with severe thickening of the endometrium.
Cancer can also be diagnosed by curettage of the uterus, especially with glandular polyposis: they are easily removed and further histological examination of the material allows the final diagnosis to be determined. Fibrous structures may be missed due to the very strong and dense structure.
At the moment, a modern and effective way to diagnose and simultaneously remove any neoplasms in the field of gynecology is hysteroscopy, which provides accurate data regarding intrauterine pathology. During the procedure, it is guaranteed to completely remove endometrial polyposis, even if it has a dense structure, that is, a fibrous component.
If the disease is diagnosed at a young age in the patient, you can try to treat it with pills. The success of this method is not guaranteed, but it may work for a glandular polyp. The prescribed medications are taken for no more than three months. Completed the course, but no results? A more constructive treatment will be selected for you.
The main method is hysteroscopy, which helps to remove the polyp and minimize relapses. After removing the glandular formation, doctors prescribe hormonal therapy.
If the patient had a fibrous type of polyp, then she should be observed by a doctor who can monitor the activity of the herpes virus and HPV, as well as other “hidden” infections that can cause the recurrence of the disease.
In order to prove the effectiveness of such a diagnostic method as MRI, a large study was conducted in Berlin in 2008. About 335 patients with polyposis who were diagnosed using ultrasound were involved. Subsequently, they underwent an MRI of the pelvis, after which they underwent hysteroscopy followed by histological examination.
As a result, it was possible to prove the high accuracy of MRI, and in addition, evaluation criteria were determined that indicated the malignant type of formations. But in addition to MRI, doctors still recommend hysteroscopy for young patients of reproductive age with subsequent examination of the removed tissue. This is necessary to obtain more reliable information regarding the presence or absence of cancer cells.
Causes
In the mechanism of development of the disease, the leading role is played by the influence of hormones and inflammatory diseases, which lead to changes in endometrial cells.
There are a number of diseases against which polyposis most often develops:
- ovarian diseases;
- disruption of estrogen production.
Against the background of these diseases, endometrial hyperplasia first develops, that is, pathological growth of mucosal tissue, then polyps form. Polyposis is often combined with other diseases caused by an imbalance of hormones in the body: fibroids, uterine fibroids, mastopathy, ovarian cysts.
The development of pathological changes in the endometrium can be provoked by inflammation or infection, as well as any trauma to the uterine tissue (they occur as a result of operations, after abortions by curettage, as well as as a result of prolonged wearing of an intrauterine device).
In addition to the causes, there are also risk factors - these are conditions that cannot directly provoke the development of the disease, but increase the likelihood of its occurrence in the future.
Risk factors include:
- arterial hypertension
- diabetes
- overweight
- thyroid diseases
- autoimmune diseases
Due to a number of risk factors, there are rules for prevention. One of these rules is timely treatment of chronic diseases.
Signs of formations
There is no reliable information about the reasons for the appearance of polyps. There are several possible causes of the formation of focal endometrial hyperplasia, including:
- Hormonal dysfunction (formed when there is a large amount of estrogens and a lack of progesterone in the second phase of the menstrual cycle). This is why polyps are most often diagnosed between the ages of forty and fifty, shortly before menopause;
- Infections - chronic inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs: previous endometritis (inflammation of the intrauterine membrane), cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix), salpingo-oophoritis (inflammation of the uterine appendages);
- Endometrial trauma (abortion, diagnostic curettage);
- Obesity;
- Thyroid diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Stress.
Symptoms
Regardless of size and shape, polyps cause similar symptoms. The first stage of the disease is asymptomatic. The second stage is bleeding. Sometimes they can be associated with the menstrual cycle, sometimes they occur randomly. The nature of menstruation changes - they become profuse, and outside of menstruation bloody discharge appears. The main danger of such symptoms is that blood loss can lead to the development of anemia. Its signs: weakness, dizziness, pallor, pathological fatigue, loss of strength.
If the polyps are large, then the list of standard symptoms includes discharge of mucous leucorrhoea, as well as pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen. Discomfort may occur depending on the phase of the cycle. In addition, discomfort appears during sexual intercourse.
It is important for women of reproductive age to know that uterine polyps can lead to miscarriage or premature birth, and if treatment is completely ignored, they can also cause infertility. In addition to treatment, prevention is also required, which consists of timely examinations by a gynecologist, as well as the correction of chronic diseases.
The symptoms of this disease may be similar to those of other diseases of the reproductive system, so a full examination is required to make a diagnosis.
Forecast
Uterine polyps are prone to recurrence. Therefore, after their removal, a woman needs to visit a gynecologist for a preventive visit twice a year.
In 1.5% of cases, recurrent growths of the uterus are susceptible to malignant degeneration. According to statistics, adenomatous polyps are most often associated with the development of endometrial cancer. Based on this, after the course of treatment, patients remain at the dispensary with a gynecologist for observation.
If uterine polyposis is left untreated, infertility and anemia develop. The presence of such a pathology in the anamnesis provokes miscarriages, which is of particular importance when planning pregnancy.
Treatment
The most effective treatment method is endoscopic surgery to remove polyps. This surgical treatment is considered optimal for two reasons: endoscopy is minimally invasive, which means the risk of complications is minimized, and removal allows you to solve the problem immediately. Doctors offer such a radical method because polyposis does not go away on its own - over time, polyps can only increase in size or number.
If an adenomatous polyp is detected or “malignancy” has begun, then a more radical operation is required - removal of part or all of the uterus.
The prognosis is favorable if removed in a timely manner. The main danger is relapse. Prevention - timely treatment of diseases of the reproductive system, annual gynecological examination.
You can undergo a full examination, consult with competent specialists and begin effective treatment at the CELT multifunctional clinic. Trust your health to the best specialists.
Preparing for polypectomy
Women undergoing polypectomy require careful preparation. At the Yusupov Hospital, patients can undergo all the necessary examinations and undergo the appropriate tests. Preparation for removal of a polyp in the uterus includes:
- Consultation with a gynecologist, therapist, anesthesiologist;
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Vaginal smears for flora and cytology;
- Electrocardiogram and fluorography.
In the presence of an active inflammatory process, surgery is performed only after a course of appropriate therapy.
Make an appointment
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist with ultrasound examination (primary) | 4 200 |
| Endometrial aspiration biopsy | 2 000 |
| Hysteroscopy (diagnostic, therapeutic) | 47 500 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions