Ultrasound of the genitourinary system is the basis for diagnosing almost all diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract.
In addition, it is very informative when examining the reproductive system in men. Ultrasound examination is indispensable for the early detection of urological diseases. Medical examinations are carried out by specialists with extensive practical experience using expert-class equipment, and the price of services is affordable. You can sign up for an ultrasound in a clinic or call doctors to conduct it at home - it will be carried out using portable equipment that guarantees the same accurate results as stationary ones.
| No. | Service name | Price |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space | ||
| 1 | Abdominal cavity (small complex). Liver, gall bladder, bile ducts, pancreas, spleen . | 1500 |
| 2 | Abdominal cavity (large complex). Liver, spleen, gallbladder, bile ducts, pancreas, kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters. | 2000 |
| 3 | Onkopoisk. Diagnosis of abdominal and retroperitoneal cancer with color Doppler mapping. | 3500 |
| 4 | Liver. | 800 |
| 5 | Gallbladder and bile ducts. | 800 |
| 6 | Liver, gall bladder and bile ducts. | 1000 |
| 7 | Determination of gallbladder function with load. The examination includes examination of the abdominal cavity. (Have 2 chicken eggs or 100g of chocolate or 2 bananas with you). | 2200 |
| 8 | Pancreas. | 800 |
| 9 | Spleen. | 800 |
| 10 | Color duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava. | 1500 |
| 11 | Kidneys , adrenal glands, ureters. | 1100 |
| 12 | Adrenal glands. | 800 |
| 13 | Renal vessels and abdominal aorta (duplex scanning of veins and arteries). | 1800 |
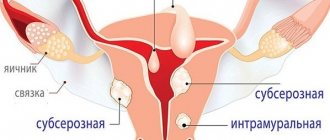
| Ultrasound of the female pelvic organs | ||
| 14 | (Uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries, retrouterine space). Transvaginally. // With Doppler analysis. | 1500 // 2100 |
| 15 | Ultrasound of the pelvis. (Ovaries (appendages), uterus, bladder). Transabdominal. // With Doppler analysis. | 1100 // 1700 |
| 16 | Ultrasound of the pelvis. (Uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries, retrouterine space, bladder). Complex - transvaginal and transabdominal. // With Doppler | 1900 // 2500 |
| 17 | (Uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries, retrouterine space). Transrectal. TRUSY for girls. // With Doppler. | 1900 // 2500 |
| 18 | Folliculometry - 1 study Monitoring follicle maturation. | 1000 |
| 19 | Folliculometry with measurement of endometrial thickness - 1 study | 1200 |
| 20 | Folliculometry with measurement of endometrial thickness - 4 visits during the cycle (from the 8th day of the cycle, every 2-3 days) | 2900 |
| 21 | Ultrasound of the pelvic vessels (Doppler study of blood flow in the uterus and appendages). Transvaginally. | 1700 |
| 22 | Hysterosalpingoscopy with recording on DVD. Ultrasound of fallopian tube patency - ultrasonic echohysterosalpingoscopy. | 4900 |
| 23 | Ultrasound before and after medical abortion for 14 days. (Included in the cost of medical abortion). | For free |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland (prostate), kidneys, bladder, scrotum. | ||
| 24 | Prostate. Transabdominal. | 1100 |
| 25 | Prostate, seminal vesicles. Transrectal examination. TRUSY. | 1800 |
| 26 | Prostate, bladder, determination of residual urine. Transabdominal. Small complex. | 1700 |
| 27 | Prostate, bladder, determination of residual urine, kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters. Transabdominal. Large complex. | 2300 |
| 28 | Bladder. | 800 |
| 29 | Bladder with determination of residual urine. | 1100 |
| 30 | Bladder with assessment of ureteral emissions. | 1500 |
| 31 | Organs of the scrotum. // with Doppler. | 1100 // 1700 |
| 32 | Penis with Doppler study. | 2200 |
| 33 | Comprehensive ultrasound of children under 1 year of age (abdominal and kidney organs, echo kg of the heart, hip joints, brain) | 6400 |
| Additional services. | ||
| 34 | Brief commentary from an ultrasound diagnostic doctor. | For free |
| 35 | Printing an ultrasound image on a thermal printer, 1-2 images. // 3rd and subsequent photos | Free // 50 rub. |
| 36 | The use of color Doppler mapping (CDC) for additional diagnosis of pathological changes in organs. | 600 |
| 37 | Ultrasound video recording on DVD. | 500 |
| 38 | You can order ultrasound of any organs, blood vessels, children’s ultrasound and other studies at home, see the page “Ultrasound at home” | |
What is this
All patients in modern reality are so accustomed to the ultrasound examination procedure that they take it for granted. But, unfortunately, not everyone fully understands what it is. Such diagnostics are carried out in Nizhny Novgorod and other Russian cities based on data obtained by reflecting ultrasonic waves from the organ being examined. The result can be viewed on the monitor screen. Moreover, the picture is available to both the medical specialist and the patient.
The ultrasound doctor not only contemplates the image, but also skillfully deciphers it, which greatly helps the specialists or therapists whose help the patients turned to. The cost of the procedure cannot be compared with the benefits that this examination brings to obtain an accurate diagnosis.
The bladder ultrasound procedure in children is carried out in the same way as in adults; there are no age restrictions for this diagnostic method. There are no painful sensations during the examination, but there is some discomfort associated with overfilling of the examined organ. This diagnostic method completely eliminates the possibility of infection, as could happen when collecting urine with a catheter.
The postoperative period is not a contraindication for such a procedure; on the contrary, research in this way will help to monitor the progress of the recovery of the operated organ. To obtain the most complete picture of the study, proper preparation for an ultrasound of the bladder is necessary.
Ultrasound methods of functional diagnostics in urological practice
SonoAce Ultrasound Magazine
Contains current clinical information on ultrasonography and is aimed at ultrasound doctors, published since 1996.
Introduction
One of the greatest achievements of recent decades has been the introduction of ultrasound research methods into medicine. Currently, ultrasound diagnostics is widely used in clinical practice in various disciplines. The role of ultrasound echo scanning is especially great in identifying space-occupying formations of parenchymal organs and visualizing stones of various locations, including X-ray negative ones.
It should be noted that having the above advantages, ultrasound is currently used to a large extent to identify morphological changes. The use of the method in the functional assessment of the kidneys and urinary tract has not yet found proper distribution. To some extent, this is due to the fact that normal, non-dilated urinary tracts are not visualized during conventional ultrasound examination and begin to be clearly visible on ultrasonograms only when they are overfilled with urine.
The emerging trend towards the development of a functional direction using various pharmacological stress tests suggested the possibility of using diuretics, beta-agonists and drugs that act on the arterial component of the renal blood flow. These drugs cause increased functional load on the kidneys and urinary tract. To identify hidden insufficiency and reserve capabilities of the hemodynamics of the kidneys and upper urinary tract, we used furosemide, ginipral and vazaprostan. Thus, the introduction into practice of ultrasound and Dopplerography with stress tests has allowed us to reconsider many issues of ultrasound diagnostics of the kidneys and upper urinary tract in some diseases.
results
We conducted 15,822 ultrasound examinations, including 5,280 pharmacoultrasound examinations, 252 pharmacoecho-Doppler examinations, and 2,344 functional ultrasound examinations of the bladder and urethra.
When visualizing the renal parenchyma, ultrasound reveals the size of the organ and the echogenicity of its structure, which makes it possible to diagnose solid or liquid formations, a wrinkled kidney, and stones. With conventional ultrasound, it is impossible to determine the structural features of the pyelocaliceal system, assess the functional state of the urinary tract, and the adequacy of the intrarenal blood flow of various segments of the kidney. Such information can be obtained using pharmacoechography and pharmacoechodopplerography using various drugs.
Our studies have shown that pharmacoechography with furosemide allows us to indirectly assess the functional capacity of the kidneys and upper urinary tract, establish their reserve capacity and hidden functional failure, which is extremely important in choosing a rational type of treatment for various diseases of the kidneys and upper urinary tract and monitoring its effectiveness. Based on the analysis of the results obtained, it was found that with undisturbed passage of urine through the upper urinary tract, the clarity of the image and the size of the cups and pelvis do not change after administration of the diuretic or dilate to 0.5-1 cm and disappear within 7 minutes. Based on this, we can assume good functional abilities of the upper urinary tract. In case of impaired urine passage in response to polyuria, retention changes in the pyelocaliceal system are revealed echographically. The increase in the size of the cups and pelvis occurs quickly and persists for a relatively long time. Based on these data, one can judge about impaired urine passage or a decrease in the reserve capacity of the upper urinary tract. An increase in the size of the pelvis by more than 20% for 20 minutes or more indicates a violation of urine passage (Fig. 1, 2). The high information content, safety and relative simplicity of pharmacoechography with furosemide allowed us to widely use this research method in the diagnosis of hidden urodynamic disorders of the upper urinary tract in various kidney diseases.
Rice. 1.
Pharmacoultrasonogram of the kidney with furosemide with undisturbed urine passage.
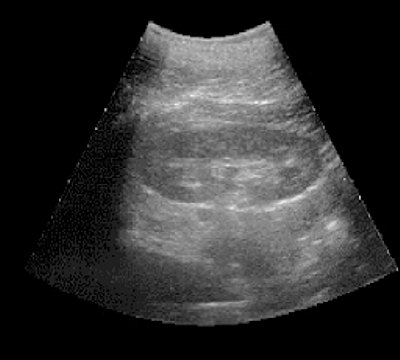
A)
Initial data.
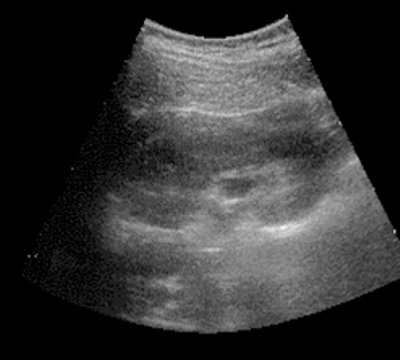
b)
3 minutes after administration of furosemide.
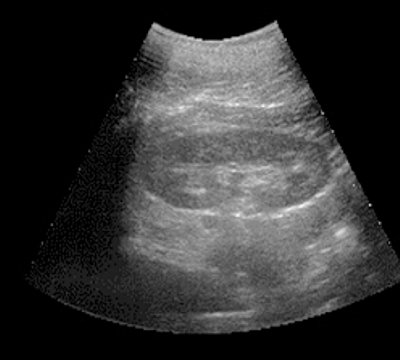
V)
7 minutes after administration of furosemide.
Rice. 2.
Pharmacoultrasonogram of the kidney with furosemide in case of impaired urine passage.
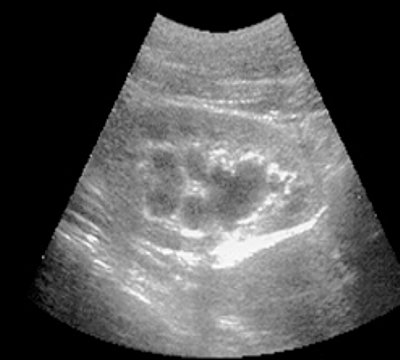
A)
Initial data.
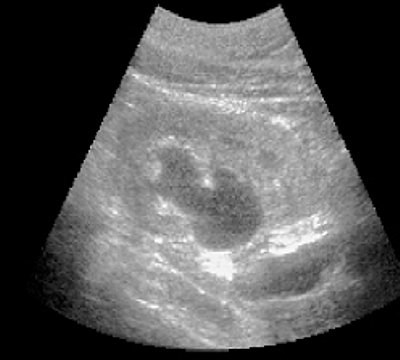
b)
20 minutes after administration of the diuretic.
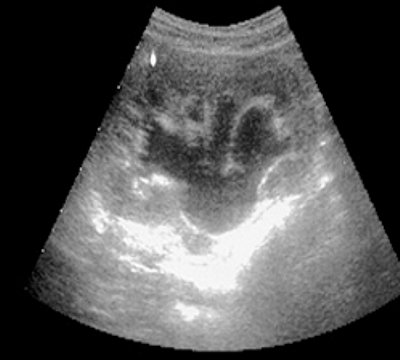
V)
40 minutes after administration of the diuretic.
Pharmacoechography acquires particular importance in assessing the dynamic processes occurring in the upper urinary tract when examining pregnant women, when X-ray radiological studies are contraindicated, as well as in patients with intolerance to X-ray contrast agents. In such cases, information about the functional state of the upper urinary tract determines the volume of surgical treatment.
Pharmacoultrasound examination in some cases makes it possible to make a differential diagnosis between renal sinus cysts and hydronephrotic transformation.
We used pharmacoultrasonography with a diuretic to improve the diagnosis of papillary tumor of the collecting system. As already noted, even with undisturbed urine passage, a short-term response of the pyelocaliceal system to the administration of furosemide occurs. Thus, with ultrasound scanning of the kidney in various planes at the time of the physiologically expanded pyelocaliceal system, we were able to visualize a space-occupying formation in the pelvis, which was not visualized with conventional echo scanning.
Ultrasound assessment of the bladder and prostate is widely used in the diagnosis of various diseases of these organs. If you create an increased functional load on the bladder wall by “physiologically” overfilling it, you can obtain information about the distensibility of the detrusor, which, in combination with an assessment of the act of urination, provides information about the functional state of the bladder, determining indications for conservative or surgical treatment tactics for bladder outlet obstruction. With ultrasound descending polycystoscopy, it is possible to determine the degree of infiltration of the bladder wall by the tumor process, its mobility, which is important to know in the case of an upcoming radical operation. I would like to note that the study must begin on an empty bladder, after which drug-induced polyuria is created, and constant ultrasound monitoring with video recording is required to monitor the dynamics of bladder filling and straightening of its walls (Fig. 3, 4).
Rice. 3.
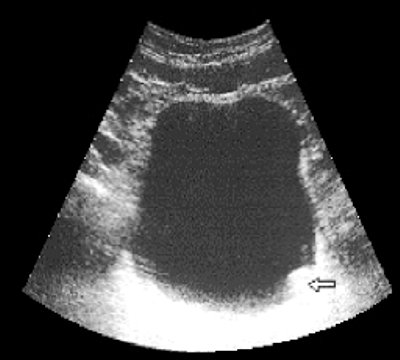
Ultrasound polycystogram for a bladder tumor (arrow) stage T1. The walls of the bladder straighten evenly (a, b - different moments of filling time).
Rice. 4.
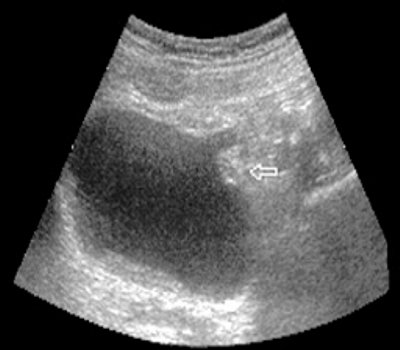
Ultrasound polycystogram for a bladder tumor (arrow) stage T3. Asymmetry of the walls of the bladder due to limited mobility of the left wall (a, b - different moments of filling).
Until recently, visualization of the urethra was carried out mainly either by X-ray using a contrast agent or by invasive instrumental methods - by urethroscopy. The increased capabilities of ultrasound scanning using various sensors in real time with video recording have made it possible to perform ultrasound cystourethroscopy at the time of urination, and Dopplerography of urine flow and uroflowmetry performed simultaneously - to obtain maximum information and give a functional assessment of the act of urination. It should be emphasized that all ultrasound functional research methods must be recorded on videotape, which allows analysis of the data obtained by repeated viewing of video materials (Fig. 5).
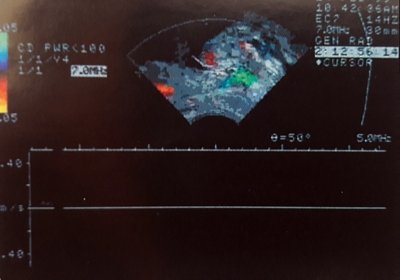
Rice. 5.
Fragment of a video recording of Doppler ultrasound assessment of urine flow in the prostatic urethra using a rectal sensor.
The combination of ultrasonic voiding cystourethroscopy with color Doppler mapping of urine flow, as well as the combination of ultrasonic voiding cystourethroscopy with uroflowmetry, makes it possible to expand the diagnostic capabilities of determining functional disorders of the urodynamics of the lower urinary tract under physiological conditions, to identify their causes and determine their localization.
conclusions
The foregoing allows us to assert that the development of functional ultrasound diagnostic methods is the basis for a new direction in urology - the use of ultrasound methods with various pharmacological loads, which contribute not only to improving the diagnosis of the disease, but also to assessing the functional state of the kidneys and urinary tract. The enormous significance of such information is obvious, not only for diagnostic purposes, but also for choosing treatment tactics, and in some patients, for assessing the results of treatment and determining the prognosis.
We believe that functional ultrasound diagnostic studies allow us to approach the deciphering of some aspects of the pathogenesis of urological diseases, which can become a theoretical and practical basis for studying treatment results. A close and in-depth study of this section of our specialty convinces us of the broad perspective that functional ultrasound diagnostics creates in the further development of modern urology.
Literature
- Amosov A.V. Diagnostic value of ultrasound scanning for kidney disease. Diss. Ph.D. honey. Sci. - M., 1982.
- Amosov A.V. Ultrasound methods of functional diagnostics in urological practice. Diss. Dr. med. Sci. - M., 1999.
- Amosov A.V., Imnaishvili G.M. Pharmacoechography // Materials of the VIII All-Russian Congress of Urologists. - 1988. - P. 215-216.
- Amosov A.V., Khalifa M. Functional ultrasound examination of the bladder and urethra//Sb. scientific works of the Astrakhan Scientific Society of Urologists. - Astrakhan, 1991. - pp. 22-25.
- Amosov A.V. Functional ultrasound diagnostics of the bladder and urethra//Regional scientific and practical conference of urologists. - Tula, 1992. - pp. 62-72.
- Darenkov A.F., Ignashin N.S. Ultrasound examinations in urology. - M., 1994.
- Ignashin N.S. Ultrasonography in the diagnosis and treatment of urological diseases. - M.: Vidar, 1996.
- Pytel Yu.A., Alyaev Yu.G., Demidov V.N., Amosov A.V., Chabanov V.A. Possibilities of ultrasound scanning in the differential diagnosis of uric acid stones and papillary kidney tumors // Urology and Nephrology. - 1981. - N6. — P. 8-12.
- Khitrova A.N. Differential diagnosis of renal sinus cysts and hydronephrosis using the method of complex ultrasound examination. Diss. Ph.D. honey. Sci. - M., 1995.
SonoAce Ultrasound Magazine
Contains current clinical information on ultrasonography and is aimed at ultrasound doctors, published since 1996.
Indications
First of all, let's determine who this examination method is indicated for. For undergoing an ultrasound of the bladder in women, the male population and children, there are the following indications:
- Pain in the suprapubic part of the body.
- Increased urge to urinate.
- Presence of bloody substances in the urine.
- Atypical urine color.
- Visual observation of flakes or sedimentary particles in the urine.
- Difficulty passing urine.
- Reducing the amount of urine.
- The likelihood of stone formations in the bladder.
An ultrasound of the bladder in men may be prescribed if it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis of prostate problems. If doctors suspect the presence of inflammation or adenoma of this organ, then most likely you will be referred for an ultrasound examination.
When there is a need for a more detailed gynecological examination, an ultrasound of the bladder in women will help in diagnosing the exact disease.
The essence of the technique
Ultrasonic waves are neither visible nor audible to humans. They are able to pass through the skin and internal organs and be reflected from them. This is the basis of ultrasound diagnostics. Ultrasound can be used to examine the entire body.
Ultrasound MBC is an examination of the urinary system. It includes:
- kidneys;
- bladder;
- ureters;
- urinary canal.
If necessary, the doctor prescribes an additional examination of the genital structures. Examination of the genitourinary system includes the uterus and tubes in women, and the prostate in men.
Goals and objectives of the survey
The main goal of the diagnostic procedure is to clarify the patient’s disease. By undergoing this painless procedure, many important characteristics of the bladder can be determined.
The challenges facing ultrasound of the bladder in children and adults:
- search for tumor formations;
- clarification of the presence of stones and sand;
- identification of the inflammatory process in the mucous membranes;
- identification of foreign fragments in the bladder;
- determination of anatomical anomalies of this organ and other components of the urinary system;
- exclusion/detection of urine reflux into the ureters.
The cost of the examination does not change depending on the number of problems solved; the price is the same - for the entire procedure. These tasks can be overcome only with proper preparation for an ultrasound scan of the bladder.
Obtained results
The result of the examination depends on the disease. To determine whether a person has a genitourinary pathology, you need to know the normal criteria.
- The kidneys are bean-shaped, the size in an adult is 12x5 cm. In children under one year, the kidney size is 5.5x3 cm, after 10 years the size becomes the same as in adults. The organ has clear contours and its structure is homogeneous.
- A full bladder has an oval shape, the wall thickness is 0.3-0.5 cm. After emptying, no more than 40 ml of urine should remain. The wall is smooth, without thickening or recesses.
- The ureters are smooth, not tortuous. Width no more than 0.8 cm.
- The prostate has the shape of a chestnut, width 2-4 cm, length 3-5 cm. The determined mass is no more than 2.4 g.
- The uterus is pear-shaped, 4-5 cm long. The contours are smooth, the structure is uniform.
With various diseases of the genitourinary organs, deviations from normal indicators are observed:
- Pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis. These are inflammatory kidney diseases. The organ enlarges and becomes darker in the picture.
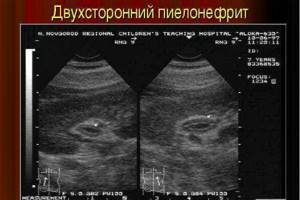
- Urolithiasis disease. White spots - stones - are found inside the kidney or bladder.
- Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder. Its wall thickens, after emptying more than 40 ml of urine remains.
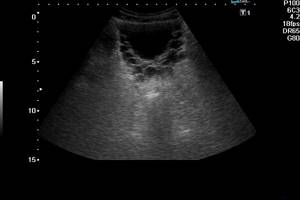
- Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland. The gland enlarges and looks darker in the picture.
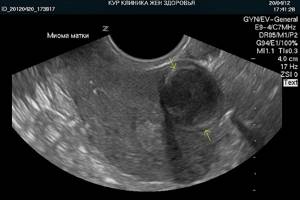
- Uterine fibroids are a benign tumor of the muscle wall. Can reach gigantic sizes. In the picture it looks like a thickening of the wall.
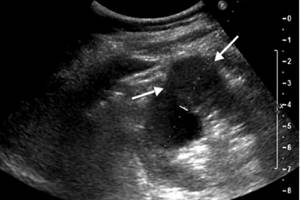
- Malignant tumors are found in any genitourinary organ. They have unclear contours and abundant blood supply. The picture shows dark or light spots.
Ultrasound is used to detect displacement of the genitourinary organs, their underdevelopment or absence.
Additionally, read the article: interpretation of ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women.
Preparatory activities
The attending physician who referred you for an ultrasound examination will always tell you how to prepare for the procedure. Filling of the examined organ is the main condition for performing an ultrasound of the bladder in men and women. How can this be done?
First, drink plenty of fluids at least 60 minutes before the procedure. Moreover, it is not recommended to drink milk, and in no case should you get carried away with water with gases. Plain water, compote, or tea are best suited for filling the bladder. The second way is to wait... Try not to empty your bladder for a long time (at least three hours). If you are invited to the office in the morning, then you can not urinate the night before and wait until you visit a specialist. As a last resort, do not visit the toilet after four o'clock in the morning and before the morning trip to the ultrasound specialist.
Preparation for a bladder ultrasound, done properly, will make this examination not a waste of time, but the most informative and useful procedure.
Indications for use
The doctor will send you for an ultrasound of the genitourinary system if:
- renal colic;
- suspected kidney inflammation;
- changes in urine tests;
- injuries of the lumbar region;
- suspected kidney tumors;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- suspected kidney development abnormalities;
- preventive examination.
Complaints of frequent or painful urination, blood in the urine, and incontinence indicate problems with the prostate or bladder.
In this case, an ultrasound of the genitourinary system is also performed. An examination of only the prostate can be prescribed in case of male infertility, identifying abnormalities in the spermogram. An important indication for prostate ultrasound is an increase in PSA (prostate-specific antigen) levels. This indicates possible prostate cancer.
Progress of the examination
The normal procedure time is about twenty minutes. During this period, the specialist will do all the necessary manipulations:
- Invite the patient to remove obstructive clothing or expose the abdomen.
- Helps the person to sit on the couch facing themselves (lying on their back).
- Apply a special gel composition to the abdominal area.
- Using an ultrasound sensor, it will “examine” the patient’s abdomen.
- Based on the obtained image of the bladder, it will decipher the data and print out these readings.
There are other ways to carry out this manipulation. Ultrasound of the bladder in women can be performed transvaginally by inserting a special sensor of the device into the vagina (necessarily in a condom). Preparing for an ultrasound of the bladder performed in this way does not free women from the not entirely pleasant procedure of filling this organ.
Representatives of the male population with a large supply of fatty deposits or cirrhosis of the liver (if there is fluid inside the abdominal cavity) are “difficult” patients for a routine (external) ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system.
Ultrasound of the bladder in men in this situation is done transrectally. An ultrasound transducer is placed in the rectum and data about the bladder is scanned through the rectal wall. In Nizhny Novgorod, as in other regional clinics, such diagnostic activities are not uncommon. The cost of the examination is reasonable, affordable for the middle segments of the population.
How to prepare for the examination
Typically, an ultrasound of the genitourinary system is performed through the anterior abdominal wall.
To prepare for the procedure, 3 days before the examination you should exclude from your diet foods that increase gas formation - cabbage, grapes, legumes, carbonated drinks, and fatty foods. To improve digestion these days, it is advisable to use Mezim. If this is not enough and the stomach is bloated, use Espumisan or sorbents. The examination is carried out on a full bladder. To do this, drink about a liter of water an hour before the examination or simply do not go to the toilet for 3-4 hours.
In difficult cases, the examination is carried out through the vagina in women or through the rectum (it will need to be emptied first) in men. The doctor will tell you more about everything.