Prices | Why do | Ultrasound with Doppler | Preparation | How is it carried out | Possible results | Ultrasound of the prostate Pre-registration for ultrasound by phone
Ultrasound of the scrotum
allows you to obtain information about the condition of the testicles and surrounding tissues.
An ultrasound machine converts high-frequency sound waves to produce black-and-white images. Normal and abnormal tissues transmit different types of signals and appear differently on a video monitor. This allows you to analyze the benignity and malignancy of formations, as well as their density, boundaries and sizes.
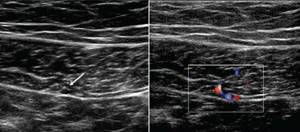
Ultrasound of the scrotum with Dopplerography of the vessels of the testicles and spermatic cords
During the study, the scrotal tissues are scanned in detail, and the vessels of the testicles and spermatic cords are assessed using Doppler. Doppler shows the speed and completeness of movement inside the vessels and cords. You may see a blockage or critical narrowing.
Conducted by doctor andrologist, urologist Konstantin Anatolyevich Menshchikov.
Comprehensive andrological ultrasound using an expert-class device
(prostate gland, bladder, scrotal organs) with conclusion
Price 4200 rub.
Ultrasound of the scrotum and inguinal lymph nodes
Price 3500 rubles
Where it can be done:
Moscow, Begovaya str., 7; m. Begovaya
Phone: +7 495 199-7554
+ MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
Normal indicators
The testicles of an adult man should normally be in the form of rounded formations with a smooth surface, fine-grained structure, and average echo density. In an adult man, the length of the testicles is 3-5 cm and the width is 2-3 cm. In normal conditions, the testicles have fluid around them. There shouldn't be too much of it. The testicles of boys have low echo density, which by the time of puberty become the same as those of an adult man. The doctor’s guide to the accuracy and reliability of the procedure is the mediastinum, a line of high echogenicity. It is detected during puberty in the sagittal plane in the testicles of boys. During echography, the appendage is highlighted in the longitudinal plane. It looks like a club and runs along the posterior edge of the testicle, but not all men have a clearly defined border. It is also not visible in small boys. An appendage that has a head, body and tail extends from each gonad. The vas deferens is a continuation of the tail and enters the spermatic cord. This in turn is connected to the abdominal cavity by the inguinal canal. Connected to the seminal vesicles, in the form of the ejaculatory duct it goes into the prostate gland, opening further in the urethra.
Inguinal canal on ultrasound
The inguinal canal is studied in B-mode for cryptorchidism and to identify abnormalities of the vaginal process of the peritoneum.
Against the background of fatty tissue, the anterior wall of the inguinal canal, formed by the aponeurosis of the external oblique abdominal muscle, stands out as a separate bright structure and emphasizes the anterior contour of the spermatic cord. The transversalis fascia, constituting the posterior wall, is associated with the peritoneum, highlighting the opposite contour of the cord. The inguinal canal is easier to visualize in men, as the heterogeneous tubular structures of the spermatic cord surrounded by hyperechoic fat are clearly visible.
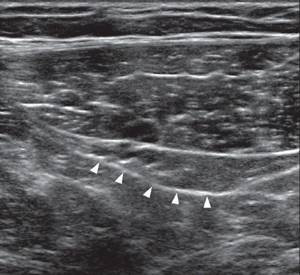
When searching for the internal ring of the inguinal canal, the reference point is the inferior epigastric artery, which passes accompanied by a vein near the medial edge of the peritoneal infundibulum of the processus vaginalis. The sensor is placed transversely just below the navel and lowered along the inferior epigastric artery until a convex hyperechoic linear structure appears behind the rectus abdominis muscle - this is the upper part of the inguinal canal.
| Photo. A, The inferior epigastric arteries and veins (asterisks) arise from the external iliac arteries just above the inguinal ligament (IL), pass posterior to the inguinal canal (IC), and medial to the edge of the deep inguinal ring (D) enter the posterior portions of the rectus abdominis muscle (R). B — With CDK, the epigastric artery and veins (arrow) are clearly visible on the transverse section of the rectus abdominis muscle on the right, just below the navel. | ||
| ||
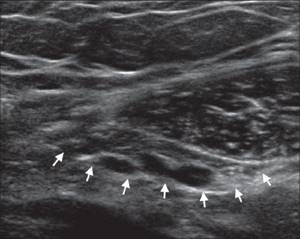
| Photo. A, B - When the epigastric vessels leave the rectus abdominis muscle and are directed posterolaterally to the external iliac vessels, an arcuate hyperechoic linear structure (triangles) appears behind the rectus abdominis muscle - this is the upper part of the inguinal canal. On ultrasound, the deep ring of the inguinal canal is visible better in men (A) than in women (B). B - Lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels, when scanning parallel to the inguinal ligament, a hypoechoic abdominal infundibulum of the vaginal process (arrows) is visible - this is the internal ring of the inguinal canal. | ||
|
|
|
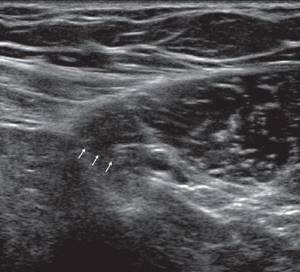
The outer ring of the inguinal canal is recognized by a change in the direction of the acoustic structures of the Thomsonian and superficial fascia, which in this place move to the spermatic cord. This transition is clearly visible when scanning the cord at the root of the scrotum.
The length of the inguinal canal in children of the first year of life varies between 0.5-2.5 cm. With age, it lengthens and becomes narrower.
Indications for ultrasound of the scrotum
The following conditions should be indications for ultrasound of the scrotum:
- diagnosis of epididymitis, orchitis, orchiepididymitis;
- suspicion of a tumor;
- varicose veins of the inguinal canal venous vessels (varicocele), torsion of the spermatic cord;
- dropsy of the testicles (hydrocele);
- various injuries;
- diagnosis of infertility;
- necrotic processes in the scrotum of various etiologies, including non-inflammatory cysts;
A specialist also prescribes an ultrasound of the scrotum in cases of detecting a hernia and analyzing the hernial sac, monitoring existing infections, leukemia, lymphoma, suspected testicular atrophy, pain in the scrotum, etc.
If there is a possibility of diseases such as varicocele, torsion of the spermatic cord, trauma, tumors, Doppler examination of the vessels of the scrotum is prescribed.
Ultrasound of the scrotum in children is performed in cases of delayed psychosomatic or physical development, obesity, underweight, gigantism or dwarfism, pathology of hair growth, and congenital heart disease.
What is vascular ultrasound?
In acute conditions, there is a need to study blood flow in the scrotal organs. For this purpose, ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound is used. A special sensor allows you to clearly see the direction of blood flow and its intensity. This study is most relevant for suspected obstruction of the vas deferens. A vascular pattern can be observed on the monitor screen. Identification of areas of increased blood supply to tissues or, conversely, areas that do not receive sufficient nutrition, helps to diagnose neoplasms and inflammatory processes even at an early stage.
Doppler ultrasound is a very effective diagnostic method for erectile dysfunction. The study allows us to exclude the vascular nature of the condition. To learn how to prepare for a scrotal Doppler ultrasound, consult your doctor.
Pathologies
Ultrasound of the scrotum is a reliable diagnostic method that allows you to identify the entire range of pathologies of the male genital organs.
- Diagnosis of cryptorchidism: (absence of testicles in the scrotum, their localization in the abdominal cavity) is a consequence of genetic pathology, observed in every 600 boys. Size smaller than age, lack of grain, poor blood flow.
- A heterogeneous altered structure is visualized as a tumor. Small formations are diagnosed, this increases the patient’s chances of recovery.
- Calcification (small stone).
- Cysts are often unilateral hollow formations.
- With infection, orchitis develops. The organ increases in size due to the presence of edema, but its structure is preserved, and heterogeneous echo density is noted.
- A limited round formation that has a uniform density is an abscess.
- The presence of fluid between the membranes of the testicle is dropsy.
- Diagnosis of varicocele.
- Testicular trauma - testicular rupture, the presence of blood in the scrotum area and between the membranes, some hematomas.
What will a testicular ultrasound show?
During the procedure, the doctor evaluates:
- organ structure, shape, size of the testicles, clarity of contours;
- echogenicity;
- amount of free liquid;
- whether there are new formations in the area of study, and if so, then their number, density and structure;
- The vascular network and its symmetry are assessed.
If a detailed analysis of blood vessels is necessary, Doppler is used. Using an ultrasound scan of the scrotum and testicles, the following pathologies can be diagnosed: Cryptorchidism - absence of a testicle. During an ultrasound in such a situation, the doctor clarifies the location of the disappeared testicle. With such problems in the male body, the testicle is most often retained in the abdominal cavity. It is usually found in the inguinal canal. As a rule, it is reduced and does not have a clear contour, the structure is heterogeneous. Varicocele is another pathology that can be detected using ultrasound. This problem is associated with varicose veins of the seminal canal and requires immediate treatment as it can lead to infertility in men. An ultrasound of the testicles with this disease clearly shows veins, the thickness of which exceeds 3 mm. Hydrocele or dropsy . With this pathology, fluid accumulates between the two layers of the testicular membranes. The disease can be acquired and manifest after injuries, inflammatory processes and surgical interventions, as well as congenital. Hydrocele is diagnosed by ultrasound without much difficulty. Sometimes this anomaly occurs in the form of a figure eight and is multi-chambered. Cystic neoplasms of the testicle and its epididymis can be congenital, then on ultrasound they usually appear as small formations, and the fluid contained in them is transparent. Acquired testicular cysts usually occur when a duct is blocked due to injury or inflammation. An ultrasound with this disease shows a formation that has clear, rounded shapes. Orchitis and orchiepididymitis - inflammation of the epididymis. Acute inflammation of testicular tissue (orchitis) - a sharply increased volume of gland, often accompanied by dropsy. Chronic orchiepididymitis - the size of the testicle is changed in one direction or another. Enlargement of the appendage is visible. This disease is provoked by microbial flora, which affects tissues with reduced immunity. Ultrasound of the testicle with orchitis clearly shows an enlargement of the epididymis, the structure of which is heterogeneous. Oncological processes in the testicle cannot be diagnosed with high accuracy using ultrasound. With this disease, it is necessary to perform an MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast or do a biopsy to identify the malignant nature of the disease. Most often, cancerous tumors are found in the right testicle. On ultrasound, the tumor will appear as a formation or several formations of an uneven shape, and the organ will be enlarged in size. An abscess is a formation that requires urgent treatment, sometimes even surgery. On an ultrasound scan of the scrotum and testicles, it is easy to distinguish it from a cyst and tumor, since this formation has an even contour. Tuberculosis of the testicle and appendages is, as a rule, a bilateral process and is manifested on ultrasound by multiple calcifications.
| Ultrasound service of pelvic organs | Price, rub | Promotion Price |
| Ultrasound of the bladder with determination of residual urine | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women and men with an abdominal sensor | 1200 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women with a vaginal probe | 1300 rub. | |
| Comprehensive pelvic ultrasound with abdominal and vaginal probe | 1400 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of folliculogenesis | 750 rub. | |
| Ultrasound cervicometry | 1100 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland with a rectal probe | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum (testicles, appendages) | 1000 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate and bladder with an abdominal probe | 1900 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the pelvis with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
How is the procedure performed?
It is diagnosed fairly quickly and takes about 20 minutes. If the specialist detects any abnormalities, the procedure may take an additional 10-15 minutes.
Before the procedure, the doctor interviews the patient, studies the medical history and proceeds to examine the area being examined. The scrotal ultrasound procedure is completely painless. A comprehensive examination of the scrotal organs (ultrasound of male organs) is carried out in a lying position. A man, lying on his back, should fix the penis with his hand, slightly pressing it to his stomach. The specialist lubricates the man’s organs with a gel intended for this procedure, and the sensor is placed at a certain point. It is necessary that the gel is at room temperature, this is how to prevent the retraction of the testicles into the inguinal canal. The doctor evaluates the size, wall thickness, echostructure of the testicles and appendages, and venous plexus. Then all deviations that the patient has are recorded. Local anesthesia is given for very painful genitals. The first testicle is examined, then the second, the sizes are correlated, and the structure is assessed. If an asymmetrical lesion is observed, the examination begins from the healthy side. The ultrasound report is given to the patient after the procedure.
Preparation for the examination and its implementation
How is an ultrasound of the scrotum done? The patient does not require any preparation other than maintaining personal hygiene of the intimate organs. You should stop smoking 1-2 hours before the procedure, because the nicotine present in cigarettes constricts blood vessels, and this will significantly affect the result.
To avoid discomfort during the examination, it is recommended to remove hair in the groin area, since the diagnosis uses a gel that may remain on the surface.
If an ultrasound of the scrotum in Moscow needs to be performed on a child, the parents need to mentally prepare the boy for the procedure. In children, fear may cause the testicles to retract, making examination difficult.
The procedure itself takes 20 minutes. With the patient lying on the couch, a special gel is applied to the area to be examined. This tool helps to form close contact between the sensor and the skin of the subject. The data obtained is recorded by a specialist and then sent to a doctor to make a diagnosis.
Scrotal ultrasound includes grayscale and color Doppler. Doppler evaluation is performed to demonstrate the waveform in the testicular artery and vein. Typically high frequency is used, and wide bandwidth becomes 17-5 MHz or 12-5 MHz.
Many scanning protocols begin by imaging a large field of view side by side, including both testicles, using grayscale and other Doppler colors. This allows you to determine echogenicity and perfusion. The physician examines and obtains longitudinal images of each testicle in the medial, oblique, and lateral portions, and transverse images of the superior, middle, and inferior poles of each testis. Each testicle must be measured sequentially in three parameters - length, height and width. Detailed examination of each testis in the sagittal and transverse planes can provide a more thorough diagnosis and evaluation. The final result includes checking the longitudinal and transverse images, including the head, body and tail.
Color and spectral Doppler analysis must be optimized in attempts to depict low-velocity venous flow. Specific assessment for testicular torsion is decided by additional color Doppler ultrasound of multiple vascular planes.
The scrotum should be examined for extrasticular disease such as hydrocele or scrotolitis. Any extra- or intrasticular pathology (diffuse or focal) should be characterized by a gray color. Ultrasound may be used to examine for the presence of cystic, solid, complex cystic, or calcific components.
The acquired images should be labeled with respect to lesion location (superior, middle, and inferior regions), image orientation (longitudinal and transverse), and patient position (supine, lateral, and standing).
Brief explanation of the results
If there are diseases, an ultrasound of the scrotum will reveal:
- Epididymitis - an increased size of the head of the penis, its altered structure, the tail and appendages are visible, fluid in the scrotum.
- Abscess of the appendage - the presence of space-occupying formations with uneven contours and reduced echogenicity, a focus of discharge with an uneven edge.
- Trauma - the contours of the testicles are uneven, the shape is irregular, the echostructure is heterogeneous, there is fluid at the site of injury.
- An appendage cyst is a round, clear formation, with fluid visible inside it, a septum in the cyst.
- Testicular tumor - irregular shape, voluminous formations of echo density, in the testicle itself and beyond.
- Infertility - cysts of the epididymis and spermatic cord, which compress the vas deferens.
Conducting research in children
The safety of the procedure allows it to be prescribed as a preventive or diagnostic measure even in childhood. An ultrasound of the scrotum of boys can detect possible problems, examine the cause of pain, or examine areas of swelling. There are no contraindications to ultrasound diagnostics, so the study is widely used to examine patients starting from birth.
An ultrasound of the child’s scrotum is performed to observe the formation of the organ. The information content of the procedure makes it possible to identify pathologies, if any. Eliminating diseases in childhood will have a positive effect for the future, so doctors use this preventive diagnostic technique.
Benefits of scrotal ultrasound
- Ultrasound examination is a non-invasive and painless procedure.
- It is affordable, convenient and very effective.
- When applying this procedure, no radiation sources are used.
- Ultrasound examination of the scrotum makes it possible to perfectly visualize the soft tissues of the male genital organs; during X-ray examination they are practically invisible.
- It does not have a negative impact on human health, so this procedure can be prescribed repeatedly.
- Ultrasound imaging is in real time, which is why it is used for needle biopsy and aspiration.
Ultrasound of the testicles is completely harmless. It has absolutely no side effects, no complications. The procedure is atraumatic (non-invasive). After the procedure is completed, you can safely continue to do your normal business and go to work.
Is Doppler ultrasound of the testicle safe?
To perform an ultrasound scan, it is not necessary to introduce additional stimulating or contrasting drugs by puncturing the skin of the scrotum. During the examination, the genitals are not exposed to harmful ionizing radiation. It follows that the procedure is safe and harmless. It can be prescribed to young children in the first year of life.
The frequency of ultrasound examination of the testicles can be any, because this examination is safe. This is important when it is necessary to periodically evaluate the condition of the scrotum during treatment, because, for example, such types of diagnostics as CT or MRI are not allowed to be used frequently.