In the field of surgical intervention of gynecological diseases, the laparoscopy method is gaining popularity. This occurs due to minimal tissue trauma and rapid recovery after surgery.
At this time, almost 90% of all operations are carried out using this method.
The main indications for performing operations using the laparoscopic method are diseases such as:
- endometriosis;
- tubo-peritoneal infertility;
- ovarian hemorrhage;
- oncological neoplasms (uterus or ovaries);
- formations of benign etiology (also in the uterus or ovaries);
- ectopic pregnancy (fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity).
The laparoscopic method of surgical intervention is also used for other gynecological diseases. Another aspect of medicine where this method is used is sterilization, both temporary and permanent.
Services and prices
Removal of the fallopian tube for ectopic pregnancy (4 bed days)
65000 ₽
Sign up
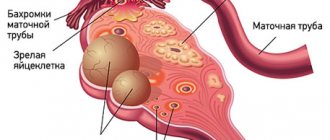
The uterus is a hollow organ located in the woman’s pelvis, which consists of a cervix, body and fundus, and one fallopian tube extends from each side of it. The fallopian tubes are the pathway from the ovary to the uterine cavity through which the egg passes. If pregnancy occurs, this is where fertilization normally occurs, and not in the uterus, as many people think.
Removing the fallopian tube is a difficult operation, leading to loss of some functions and partial disability. Therefore, intervention must be carried out strictly according to indications and only in cases where the problem cannot be solved in another way. This should be a joint decision between your healthcare provider and you. Before deciding to undergo surgery, you should discuss possible complications of the intervention, the prognosis for recovery after the procedure, as well as the consequences in case of refusal of surgical treatment.
What can you eat
During the first day after surgery for ectopic pregnancy, only drinking non-carbonated mineral water is allowed. Then gradually include easily digestible foods in the diet in small portions with a frequency of up to 6–7 times a day.
What to eat after laparoscopy of ectopic pregnancy to reduce the risk of complications:
- lean broth;
- jelly on fruits or berries;
- jelly or compote, weak tea, diluted juice;
- herbal decoctions;
- after three days, porridge is introduced (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice);
- then include pureed meat or fish products, but only boiled or steamed;
- cottage cheese mixed with low-fat cream;
- bread is replaced with crackers.
The doctor regulates the diet after laparoscopy based on the patient’s well-being. In their reviews on forums, women note that a gentle diet allows you to quickly restore the menstrual cycle and organ function.
Fertilization is a miracle
Indications for removal
- Ectopic tubal pregnancy
- Pyosalpinx
- Hydrosalpinx
- Tubal-peritoneal infertility
- Removal of the fallopian tubes in combination with hysterectomy
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious and extremely dangerous condition, which is one of the five causes of maternal mortality, requiring emergency surgical treatment. The most common type of ectopic pregnancy, more than 90% of all cases, is tubal pregnancy.
The fertilized egg is implanted into the wall of the fallopian tube and begins its development.
There are several possible outcomes for this condition. Implantation causes contraction of the fallopian tube, which can lead to expulsion of the fertilized egg. This condition is called tubal abortion and is accompanied by not severe but prolonged bleeding.
One of the most difficult outcomes is a breakup. The embryo grows rapidly and the chorionic villi successively destroy the layers of the wall of the fallopian tube. This leads to its destruction and is accompanied by massive bleeding into the abdominal cavity. This condition is an absolute indication for removal of the fallopian tube.
In case of early diagnosis, before complications develop, it is possible to perform organ-preserving surgery. However, some evidence argues against such tactics. It is believed that preservation of the fallopian tube leads to an increased risk of recurrent tubal pregnancy and the development of adhesions, which ultimately leads to removal of the organ.
Pyosalpinx is a purulent inflammation of the fallopian tube. At the beginning of the development of the pathological process, conservative therapy with antibiotics is used. However, in case of suppuration, surgical treatment is used. As a rule, pyosalpinx ends with the removal of the inflamed part of the organ, but in some cases the intervention may be limited to draining the abscess.
Hydrosalpinx is an accumulation of serous fluid in the cavity of the fallopian tube due to inflammation.
Tubal-peritoneal infertility . In the presence of inflammatory processes, the chances of getting pregnant and bearing a child are significantly reduced. The fallopian tube is the exact place where fertilization occurs. The development of pathological processes not only prevents the onset of pregnancy, but can also threaten the development of one that has already occurred.
For example, hydrosalpinx can lead to mechanical leaching of the embryo from the uterine cavity, as well as to a toxic effect on the endometrium and fertilized egg. Therefore, before IVF, it is recommended to remove the affected fallopian tube in order to increase the survival rate of embryos during transfer.
Removal of the fallopian tubes in combination with hysterectomy , fortunately, is performed infrequently. Reasons for radical surgery may include life-threatening uterine bleeding, malignant neoplasms of the pelvic organs, or severe cases of adenomyosis.
For what types of ectopic pregnancy is laparoscopy performed?
How is the operation performed?
VB pathology is classified into several types.
- Tubal pregnancy - the fertilized cell cannot travel to the uterus. Due to obstruction, it attaches to the pipe wall, where it begins to develop. It is registered in 97% of patients diagnosed with ectopic pregnancy.
- Abdominal - accidental entry of a wandering zygote into the peritoneal area, where it finds a place for implantation.
- Ovarian pregnancy - at the exit from the follicle, an active sperm is encountered along the path of the egg. After fertilization, it immediately attaches to the wall of the nearest ovary. Such ectopic pregnancy is registered in a maximum of 0.7% of all cases.
- Cervical is a very rare anomaly when the fertilized egg matures in the cervix. It is quickly recognized by the woman’s sensations or during examination.
Any type of ectopic pregnancy can be diagnosed or operated on laparoscopically.
How is the operation performed?
Most operations in modern gynecology are performed using laparoscopic access, which has a number of undeniable advantages for both the doctor and the patient. Laparoscopic operations are less traumatic, have a lower risk of complications, less pronounced postoperative pain syndrome, allow for quick rehabilitation and leave a minor cosmetic defect.
However, if there are contraindications, laparotomy is resorted to. The Pfannenstiel incision is chosen - this is a transverse incision in the lower third of the anterior abdominal wall of the abdomen. The surgeon resorts to choosing a more traumatic approach if there are contraindications to laparoscopic surgery, such as severe adhesions, suspicion of malignant neoplasm of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, or grade 3-4 purity of the vaginal smear.
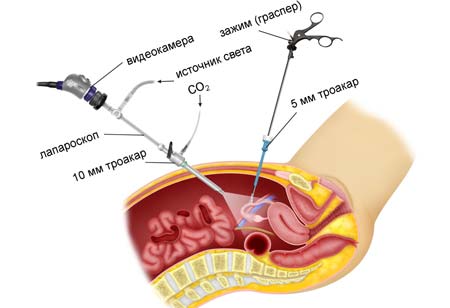
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The patient falls asleep and wakes up in her room. Laparoscopic access is carried out using three trocars, which are inserted through small holes with a diameter of up to 1.5 cm. The first, with a video camera, is located in the umbilical region, and the other two with manipulators in the right and left iliac regions.
The assisting surgeon fills the abdominal cavity with gas in a volume of 2-3 liters. This stage is called pneumoperitoneum and is necessary to create conditions for the operation of optics, with the help of which the surgeon navigates inside the abdominal cavity. In most cases, carbon dioxide is used as the safest. In addition, by acting on the respiratory center, it increases the vital capacity of the lungs and, as a result, reduces the risk of secondary complications from the respiratory system.
At the beginning of the operation, the surgeon examines the pelvic cavity, finds the affected part of the organ and immobilizes it. Clamps are applied to the fallopian tube and blood vessels. Then the affected part of the uterus is excised, and a hemostatic suture is placed on the vessels, which will stop the bleeding. Since the fallopian tube is directly connected to the uterine cavity, the resulting hole is closed with a sheet of peritoneum. This process is called peritonization. In case of purulent inflammation of the fallopian tube, the abdominal cavity is thoroughly washed. Drainage is installed through the posterior vaginal fornix. At the end of the surgical intervention, the surgeon inspects the pelvic cavity, removes the trocars and sutures the small incisions that remain from them.
Advantages
Today, the technique in most cases avoids organ removal. This is her main advantage. Other advantages of laparoscopy in gynecology:
- at the same time it is a diagnostic and treatment procedure;
- during diagnosis, it allows you to see what the examination did not show and immediately carry out treatment;
- refers to gentle organ-preserving methods of surgical intervention;
- takes minimal time;
- the possibility of natural pregnancy is higher than after laparotomy operations;
- Rehabilitation has been shortened and is much easier. Women return to their normal lifestyle faster;
- high precision and effectiveness;
- low risk of complications;
- low probability of damage to adjacent tissues, as with abdominal access;
- There is practically no postoperative bleeding;
- no scars remain on the body, as after laparotomy.
According to various statistics, the pregnancy rate after laparoscopy is high - from 80% to 99%.
Indications
- myomatous nodes;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes, determining its degree;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- cystic formations on the ovaries;
- adhesive process;
- infertility;
- study of the structure of the gonads and uterus if anatomical defects are suspected;
- endometriosis;
- contraindications for laparotomy surgery on the pelvic organs;
- chronic pelvic pain;
- control over previous treatment.
If it is not possible to find out why pregnancy does not occur, then laparoscopy is often used as a diagnostic and treatment method. Often, in one go, it is possible to establish the cause of infertility and eliminate it. Sometimes laparoscopic diagnosis is necessary before performing in vitro fertilization. Thus, with endometriotic lesions, the chances of successful IVF after surgery increase significantly. Laparoscopy is more informative than ultrasonography and hysteroscopy, so it is often used to clarify the diagnosis.
Laparoscopic access is prohibited for cardiovascular and pulmonary decompensation, bleeding disorders, severe obesity, diaphragmatic hernia, and ARVI.
Previously, pregnancy was an absolute contraindication. Nowadays, laparoscopy is often performed during gestation. The most common indications are gallbladder diseases requiring cholecystectomy (up to 48%), resection of the appendages (28-43%), appendectomy (16%). The results and forecasts are good. Laparoscopy during pregnancy is necessary in the following cases:
- ovarian torsion in the first trimester (1:5000);
- benign cyst (found in one in 80 pregnant women). However, the number of operations performed is 1:600, since more often a corpus luteum cyst occurs, which resolves on its own;
- malignant neoplasm;
- necrosis of the myoma node (rare).
During pregnancy, they resort to urgent laparoscopy due to the risk of malignancy (1-8%), torsion or rupture with bleeding (10-42%), and premature birth.
Contraindications
A contraindication to any surgical intervention is the unstable condition of the patient caused by hemorrhagic shock or a chronic disease in the stage of decompensation. Therefore, in case of emergency intervention, the patient’s readiness is assessed primarily by vital signs such as blood pressure, oxygen saturation, heart rate, and platelet levels. In the case of elective surgery, the patient and surgical team have the opportunity to prepare for the operation in advance. Patients with current acute infectious diseases or those suffered less than 4 weeks ago are not allowed to undergo surgery. The patient must first treat the disease and then undergo surgery.
Preparation
Preparation for any operation includes a number of instrumental and laboratory studies. For hospitalization for a planned surgical intervention in the gynecology department, a standard set of tests is required:
- Electrocardiogram
- Fluorography
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
- Vaginal smears for microflora and oncocytology
- General blood analysis
- General urine analysis
- Coagulogram (blood clotting indicators)
- Screening for infections (HIV, Hepatitis, Syphilis)
Also, due to the unfavorable epidemiological situation, you may need to take a smear test for coronavirus infection.
The evening before the intervention, a cleansing enema is performed. The operation is performed on an empty stomach, usually in the first half of the day. In some cases, the doctor prescribes additional medications or discontinues medications that the patient is taking.
Rehabilitation period
The rehabilitation period after laparoscopic intervention is minimal. Already on the first day after surgery, the patient can get up and perform minimal physical activity. This prevents the development of thromboembolic complications. If drainage was installed during the operation, it is removed 2-3 days after the intervention.
For several days after the operation, a small amount of bloody discharge from the vagina may be present, which is normal. In the postoperative period, complications such as bleeding and the development of an infectious process may occur.
However, you should not be afraid of this. Complications are possible after any procedure. The task of medical personnel and the patient is to jointly reduce these risks to a minimum. To prevent postoperative infections, antibiotic therapy with broad-spectrum drugs is used for a week after the intervention.
Recommendations after discharge are in most cases individual, depending on the reason for removal of the fallopian tube. Some patients are prescribed oral contraceptives for a period of 3-6 months. And in the case of an ectopic pregnancy, they often resort to repeat diagnostic laparoscopy after 3 months.
Discharge after ectopic pregnancy
Discharge with blood after an ectopic pregnancy indicates the onset of menstruation if twenty-five to thirty days have passed after the operation. If discharge after an ectopic pregnancy begins earlier, this indicates the onset of uterine bleeding. If there is no discharge after an ectopic pregnancy for more than a month, then a hormonal imbalance is possible. In these cases, an urgent visit to the doctor is required. If the discharge after an ectopic pregnancy has an unpleasant odor, a pasty state is an indicator of the presence of infection and examination is required.
Is it possible to get pregnant
The issue of being able to get pregnant and bear a child is extremely important for many women. The chances of pregnancy depend on the extent of resection that was performed during surgery. If the fallopian tube was removed on only one side, then pregnancy is possible naturally. In the case where the removal of the affected part of the organ was bilateral, pregnancy cannot occur naturally.
However, this does not mean that a woman will never be able to give birth to a child. Most tubal removal surgeries do not involve the uterus or ovaries. IVF techniques allow a woman to become pregnant. A woman's egg is collected by aspiration from the ovary. A man, the future father of a baby, donates sperm. The role of the fallopian tube is taken on by a fertility doctor. In the laboratory, special conditions are created for the fertilization of an egg outside the body. The embryo then grows and develops for several days. This period corresponds to the journey of the zygote through the fallopian tube to the uterus. On the 4-5th day, embryos are implanted into the uterus, where implantation of the embryo and its subsequent development occur naturally.
Back to list of articles
Diagnostic laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes
According to statistics, approximately 40% of cases of infertility in couples are caused by diseases of the female reproductive system. Very often (about 40%) the cause is tubal obstruction. Hence the logical answer to the question: “Why is tubal laparoscopy done?” The procedure allows you to visualize the uterine appendages (fallopian tubes and ovaries), assess their condition, and accurately determine the real cause of infertility. Modern endoscopic equipment makes it possible to examine the internal organs in detail in good lighting, enlarge the image to study small details, which provides high information content and diagnostic value of the study.
In addition to assessing the patency of the fallopian tubes, laparoscopy is the “gold” standard for diagnosing endometriosis, a condition in which elements of the uterine mucosa (endometrium-like cells) are found in atypical places (tubes, ovaries, retrocervical space, peritoneum, etc.). Ultrasound is not always informative in identifying this disease, especially when it comes to superficial lesions.