Author: Strokina O.A., therapist, functional diagnostics doctor. February 2021.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is the standard, most common and already familiar method for examining the internal organs and tissues of the abdomen. In terms of information content, it may lag behind more modern technologies (CT and MRI), but in terms of safety and painlessness, it is significantly superior to them. Therefore, the abdominal ultrasound procedure is prescribed without restrictions to children, even newborns, and pregnant women.
Indications
Who can prescribe an abdominal ultrasound and why?
You can do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity at your own request, or with a referral from a general practitioner, gastroenterologist, hepatologist, etc.
Indications for the procedure are:
- pain in the abdomen (location does not matter);
- the presence of specific complaints characteristic of problems with the liver and gall bladder: bitter taste in the mouth;
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- jaundice.
- signs of diseases of the stomach and/or duodenum:
- bursting pain in the stomach after eating;
- belching, heartburn;
- nagging pain in the pit of the stomach,
- hungry or night pain in the epigastrium (upper abdomen).
There are no contraindications to ultrasound.
Contraindications
As with almost any medical procedure, there are a number of contraindications for performing an abdominal ultrasound. These include:
- hyperthermia;
- infectious diseases in the acute phase;
- open wounds in the peritoneum;
- skin diseases with exudation localized in the area under study;
- severe general condition of the patient.
Pregnancy, contrary to popular belief, is not a contraindication to the procedure. The study is completely safe for the health of the woman and fetus and cannot cause deterioration in well-being.
Constant improvement of diagnostic equipment has made it possible to carry out the procedure within pediatric practice over the past two decades. If pathology of the abdominal organs is suspected, the examination can be carried out even on newborn children.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs in a medical setting provides the opportunity to most accurately identify the cause of the existing pathology, make the correct diagnosis and, as a result, receive prescriptions for effective therapy.
Diet
The diet before an abdominal ultrasound requires a complete exclusion from the diet of dairy products, black bread, fresh vegetables and fruits, juices, legumes, sauerkraut, fatty meats, sweet confectionery, coffee, alcohol, and carbonated drinks.
The diet should be fractional, i.e. often (every 3-4 hours), but in small portions. The amount of liquid you drink is not limited.
On the recommendation of a doctor, as an addition to the diet, you can take medications that improve digestion and help reduce gas formation (Activated carbon, Espumisan, Festal, Pancreatin, Mezim-forte).
Note: an enema before an abdominal ultrasound is necessary for those people who suffer from chronic constipation.
12 hours before the start of the procedure, you can put a laxative suppository (Bisacodyl), and only if it is ineffective, cleanse the intestines with an enema. On the eve of the study, a light dinner is allowed (until 20.00), during which it is not advisable to eat meat and fish dishes (dietary ones too!). On the day of the procedure, if the ultrasound is scheduled for the morning, you cannot have breakfast. If the examination is carried out after 15.00, then you can eat something light in the morning (before 11.00).
Activated charcoal must be taken before an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity - 2 hours before diagnosis, 5-10 tablets per dose.
Important! Smoking before an abdominal ultrasound, as well as drinking water, sucking hard candies, and chewing gum is strictly prohibited. If you are taking vital medications or shortly before the ultrasound appointment you underwent irrigoscopy, FGDS, or colonoscopy, be sure to warn your doctor about this. Your doctor may give you additional recommendations before an abdominal ultrasound or reschedule the examination for another day.
Methodology of the procedure
An examination of the abdominal cavity is carried out in an outpatient or inpatient setting, in a specially equipped room.
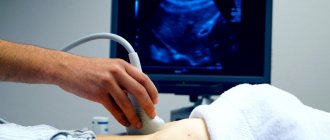
The patient lies on the couch, on his back. The ultrasound doctor applies a special hypoallergenic gel to the skin of the patient’s abdomen (to improve contact) and the device’s sensor, then begins the examination. In some areas of the abdomen, the sensor, under pressure from the doctor’s hand, seems to go deeper inside, providing the closest possible distance to the organ. A person does not feel pain during these movements if the abdominal wall is completely relaxed and there is no inflammatory process or pain syndrome in the corresponding areas of the abdomen.
Sometimes, to improve visibility of the area being examined, for example, the liver and spleen hidden under the costal arch, it will be necessary to take a deep breath and hold your breath. At this moment, the organs move slightly downward, which facilitates their better visualization.
The duration of the procedure is 15-40 minutes. Immediately after the end of the study, the patient can return to their usual rhythm of life.
There are no complications with ultrasound.
Abdominal ultrasound: what it is, indications, stages of preparation for the procedure, which organs are examined
Abdominal (transabdominal) ultrasound examination
is a type of ultrasound that is performed using a special device - a convex sensor. It uses a frequency of up to 7.5 MHz and can scan tissue to a depth of 25 centimeters.
This examination helps to see the internal organs and their structure, determine the presence of any diseases and pathologies, as well as neoplasms (including cancer). Its results are more accurate than other ultrasound methods.
The examination proceeds as follows:
- The patient lies on the couch on his back or on his side, depending on the indications. During pregnancy, a woman should lie on her side
- Clothing in the abdominal area should be removed or raised.
- The doctor lubricates the surface of the abdomen with a special gel to increase the area of contact between the sensor and the skin. This allows you to achieve more accurate results
- The sonologist (ultrasound specialist) then moves the device over the area being examined.
- The information obtained during the process is transmitted to the monitor and recorded on the computer.
A distinctive feature of abdominal ultrasound is that the procedure is completely painless, safe and suitable for patients of any gender and age.
Since it is carried out using a sensor that receives information when it comes into contact with the wall of the abdominal cavity, no invasive methods are required. Thanks to this, there is not only the need for anesthesia, but also the patient’s nervous tension before the procedure.
This is especially important if a child is to be tested. He may be afraid of any physical intervention, which may cause problems during the examination.
This analysis allows you to examine not just one organ, but several neighboring ones, which helps the doctor see the full picture of the condition of the abdominal cavity.
The entire procedure lasts no more than twenty minutes.
In what cases is research required?
Abdominal ultrasound is used both to establish or clarify the diagnosis, and for preventive purposes. Using this study, you can identify diseases such as:
- Hepatitis
- Cholecystitis
- Cirrhosis
- Tissue necrosis
- Inflammation of various types
- Pathologies
- Splenic infarction
- Prostatitis
- Pyelonephritis
- Cystitis
- Endometriosis
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Abnormalities in the development of the uterus
- Trauma, hemorrhage, abscess
Also, this type of analysis allows us to identify the presence of various neoplasms in the abdominal organs:
- Tumor (benign and malignant)
- Adenoma
- Cyst
- Stones in the bladder and kidneys
- Uterine fibroids
An abdominal ultrasound is required to prevent various problems in such cases as:
- Pregnancy (from 2nd trimester)
- Monitoring the effectiveness of disease treatment
- General prevention of age-related and other diseases
What organs can this type of ultrasound examine?
These are the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system and others, namely:
- Liver
- Kidneys
- Bladder
- Stomach
- Pancreas
- Uterus
- Ovaries
- Prostate
- Intestines
- Spleen
- Gallbladder
Why is pelvic ultrasound performed abdominally for pregnant women?
This is necessary to identify possible problems in the development of the fetus and general monitoring of the situation as a whole. This analysis allows you to check the following readings:
- Condition of the uterus and its cervix
- Gestational age
- Fetal position
- Volume of amniotic fluid
- Condition of the organs and limbs of the unborn child
- Condition and quality of the placenta
All these details allow you to find out about possible anomalies at an early stage and quickly solve problems that arise without harm to the mother and fetus.
Also, the need for ultrasound examinations for women during pregnancy is enshrined in legislative acts.
In what cases is this test prescribed for men?
There are a number of symptoms for which a doctor prescribes a pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe for a male patient. Here are the main ones:
- Frequent and unpleasant urination
- Pain and discomfort in the groin area, perineum, scrotum
- Potency disorders
- Inability to urinate
- Unusual discharge from the urethra (blood and other)
Remember, if at least one of these signs appears, you should immediately contact the clinic!
Stages of preparation for the examination
Unlike other types of ultrasound examination, pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe
requires special preparation. It is necessary for the result to be as accurate as possible, otherwise it may be distorted.
It is important that at the time of such analysis the following parameters are met:
- Gases from the intestines must be eliminated
- There should be no food residues in the gastrointestinal tract
- The bladder should be filled with water
On the eve and directly during the procedure, it is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol or smoke.
When there are obvious disorders (bleeding, etc.) that require urgent diagnosis, it is impossible to carry out the necessary preparation. In all other cases it must be there.
How to achieve the absence of gases?
Flatulence and bloating can interfere with the test results, as the image will be distorted. Therefore, people who experience these phenomena frequently (and others - for preventive purposes) are advised to avoid a number of foods and drinks before the study - to stick to a diet. Its features are described in detail below.
Also, immediately before the examination, it is necessary to take medications that help remove gases from the body. The attending physician can advise the most appropriate medications in each case individually.
Removing food from the gastrointestinal tract
An abdominal pelvic ultrasound should be performed on an empty stomach. Therefore, the following conditions must be met:
- The last meal on the eve of the test should be no later than six o'clock in the evening
- It is allowed to use an enema (but not on an empty stomach!)
- The use of drugs that facilitate and accelerate gastrointestinal emptying is allowed (it is recommended to discuss with your doctor)
- You should not eat food before the test
Full bladder
An hour and a half before the procedure, you must drink at least half a liter of liquid, since the bladder must be full before the procedure. This is important for the accuracy of the diagnosis. You can use both purified water and tea or compote.
Features of training for women
When preparing to study the female body, you should remember that the procedure is best timed to coincide with the first phase of the cycle, in the first week after the end of monthly bleeding.
This is due to the fact that during “critical days” the walls of the uterus become denser and the bleeding itself makes it difficult to determine the presence of minor formations in the tissues of this organ.
Sometimes it may be necessary to conduct several ultrasounds at different periods of the cycle to clarify the diagnosis.
If urgent diagnosis is necessary, this analysis can be performed during menstruation, but after that the procedure should be repeated again.
Preparation for children
Before an abdominal ultrasound, much fewer requirements are placed on the child. Accordingly, there are not many restrictions. All of them are related to age:
- In children under 3 years of age, the last meal should be 3 hours before the test and fluid intake should be 50 minutes before the test.
- A child over three years old can be fed 8 hours and given water an hour before the test.
Diet
One of the most important stages of preparation for an abdominal pelvic ultrasound is diet. It is recommended to switch to a special diet no later than three days before the test. It is advisable to do this even earlier (a week in advance), but this is not always possible.
What food is prohibited?
It is necessary to exclude products that contribute to gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract or can otherwise affect the results of the study, namely:
- Milk and dairy products
- Fatty meat and fish
- Flour products (bread, buns, etc.)
- Sweets (sweets, chocolate)
- Coffee
- Alcohol
- Legumes (lentils, beans, peas, etc.)
- Spices (cinnamon, cumin)
- Uncooked fruits and vegetables (cherries, apples, pears, corn, cabbage, potatoes, etc.)
- Fast food
- Carbonated drinks
These products contain various polysaccharides, lactose, fructose. All of them irritate the intestines and, when broken down, release large amounts of gases.
Smoking is also prohibited and chewing gum is not recommended. In both processes, excessive air is swallowed, which then interferes with the examination.
What can you eat?
You can eat healthy foods, especially steamed ones, with a minimum amount of oil and spices:
- Boiled beef, poultry
- Fish (sea, lean)
- Porridge (rice, buckwheat, barley)
- Hard cheeses with low fat content
- Tea (can be lightly sweetened, but not heavily brewed)
- Boiled eggs (one per day)
All these products are easily digestible and do not require a long time to digest.
It is recommended to eat often, but in small portions. You cannot drink food with water.
Contraindications
There are no obvious contraindications to abdominal pelvic ultrasound. There are a number of restrictions that are associated with a woman’s menstrual cycle.
Difficulties during ultrasound may arise if there is a serious rash, extensive eczema or other complex large skin disorders in the area being examined.
Restrictions due to the cycle in women
- It is recommended to conduct the study in the first week after the end of menstruation
- If there has been any surgical intervention or abortion, an analysis must be carried out immediately after bleeding is completed.
- The second half of the cycle is used to diagnose endometriosis
- To determine fibroids - in the first half
If urgent diagnosis is necessary, it is possible to conduct an ultrasound examination during menstruation. But subsequently it is recommended to do a repeat analysis after its completion.
Abdominal ultrasound results
An ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity is interpreted by an ophthalmologist immediately after the examination. The time can vary from several minutes to 2 hours. The conclusion is given to the patient or sent to the doctor’s office who issued a referral for the procedure.
Abdominal ultrasound is normal
- the size, shape and structure of the abdominal organs (liver, pancreas and spleen) are not impaired;
- the contours of the organs are clear, even, the capsule is well differentiated;
- there is no tissue growth and fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- the aortic diameter is normal, the walls are not changed;
- the gallbladder is unchanged, there are no stones, the ducts are not dilated;
- the kidneys are of normal bean-shaped shape, without the presence of stones, no disturbance in the outflow of urine was detected.
Ultrasound can be used to accurately determine:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- fatty hepatosis (fatty infiltration of the liver);
- all inflammatory processes;
- gallstones or kidney stones;
- mechanical damage (rupture) of internal organs (gallbladder, spleen);
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites, blood);
- tumor formations of the liver, pancreas, kidneys, adrenal glands, pelvic organs;
- metastases to the listed organs, lymph nodes.
If any pathological conditions are detected on ultrasound, the doctor will immediately inform the patient about it. And since no diagnosis is ever made based on the results of a single examination, additional diagnostics may be needed to control and clarify:
- X-ray of the abdominal organs
- FGDS (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) for more detailed visualization of the stomach, duodenum, and esophagus;
- to confirm tumor formations: computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- to identify stones in the gall bladder: radiotope scanning of the gallbladder and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography;
- biopsy (if a fluid-filled cyst is detected to determine the composition of the contents and the degree of malignancy);
- colonoscopy or irrigoscopy (to study the condition of the large intestine).
Advantages of the method
- Almost all the most important internal organs are examined at one time;
- diseases localized in the organ cavity (for example, gallstones), inflammation of the walls, ulcers, abscesses, fistulas, tumors, extra-organ pathologies (which are located outside the organ itself, for example, cysts), diseases of the lymph nodes (infectious and drug-induced lymphadenopathy and etc.);
- safety for the patient, no radiation exposure;
- low price for MRI of the abdominal cavity: the cost of examining one organ is approx. 500 rub.
Where is an abdominal ultrasound performed?
An abdominal ultrasound can be performed at any diagnostic center, private or public, since today almost all medical institutions are equipped with ultrasound diagnostic devices.
When making your choice, pay attention to the institution’s profile. Still, it is better to do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity where there is a highly qualified gastroenterologist on staff, who, if any pathology is detected, will supervise you until complete recovery.
Sources:
- Volkov V.N. Basics of ultrasound diagnostics. — GSMU, Department of Oncology, Radiation Diagnostics and Radiation Therapy.
Why is an ultrasound prescribed?
At the first suspicion of intra-abdominal diseases, doctors write out a referral for an ultrasound scan. This allows you to detect anomalies such as:
migration of cancerous processes – metastasis;- tumor processes in the pancreas;
- liver cancer;
- cystic formations;
- tissue degeneration, abscesses, internal hemorrhages;
- benign neoplasms;
- pathological accumulation of fluid in the retroperitoneal space.
In order to “catch” the disease at an early stage and quickly take the necessary therapeutic measures, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations, including with the help of ultrasound.