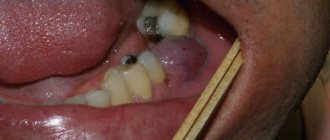
If a gynecologist has diagnosed you with an ovarian cyst, do not be alarmed: as a rule, these formations are benign and do not pose a danger; surgery is not required. Often they do not need to be treated at all and disappear on their own within a few months. It is enough to periodically visit a gynecologist and undergo an ultrasound examination.
- What types of ovarian cysts are there?
- When is laparoscopy performed?
- When is laparoscopy not performed?
- Benefits of laparoscopy
- Preparation
- How is laparoscopy performed?
- Postoperative period
- Complications
- Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst?
Sometimes ovarian cysts still have to be removed. Operations can be performed without an incision, through several punctures in the abdominal wall - laparoscopically. Euroonco employs expert-level gynecological surgeons who have extensive experience in performing such interventions. Come for a consultation with our specialist: he will tell you whether surgery is necessary in your case, and prescribe an examination that will help distinguish a benign neoplasm from a malignant one.
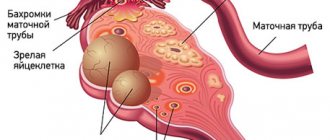
A cyst is not a specific disease. This term refers to any pathological cavity with fluid. The reasons for its formation are different. According to statistics, ovarian cysts are diagnosed in every tenth woman. They most often occur during puberty and menopause. Some girls have them from birth.
What types of ovarian cysts are there?
All ovarian cysts are divided into two large groups: functional , which occur in most cases, and pathological , which doctors have to deal with much less frequently.
Functional cysts are the result of disturbances during the menstrual cycle. Usually they do not cause complications and disappear on their own. They come in three types:
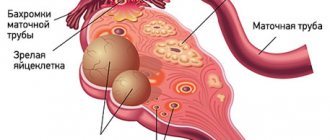
- Follicular . follicle matures in a woman’s ovaries . Normally, it should open and release the oocyte. If this does not happen and the follicle continues to grow, it turns into a cyst.
- Corpus luteum cysts . After the follicle releases the egg, it turns into a special gland - the corpus luteum . It produces the hormones estrogen and progesterone. If pregnancy does not occur, the corpus luteum atrophies. And if fluid accumulates in it, it turns into a cyst.
- Theca-luteal cysts often develop as a side effect of infertility treatment with hormonal drugs.
Pathological ovarian cysts are not associated with the menstrual cycle. They are always characterized by the appearance of “wrong” cells that should not be present normally. The most common types of pathological cysts:
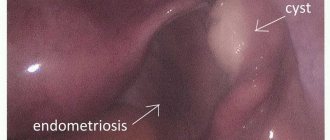
- Endometrioid . This is a form of endometriosis, a condition in which endometrial tissue (the lining of the uterus) gets into unusual places and grows there. In the ovaries, it can form cavities with fluid. They often appear as “chocolate” cysts filled with dark blood.
- Dermoid cysts , or teratomas , are a special type of benign tumors made from embryonic cells. There may be different tissues inside them, for example, skin, hair, nails. Dermoid cysts become malignant very rarely.
- Cystadenomas are benign neoplasms of epithelial cells. Usually they are filled with contents of a mucous or watery nature.
For more information about malignant cysts, please visit the ovarian cancer page on our website.
How to normalize stool after surgery?
To eliminate constipation after ovarian laparoscopy, you need to follow a special diet. The following foods should be excluded from the diet: bread, persimmon, pomegranate, strong tea, sweets. The menu should include boiled beets, cabbage, carrots, dried fruits, apricots, plums, honey.
Treatment for constipation also includes taking laxatives. After laparoscopy, you should avoid products with senna and other components that provoke spasms. It is better to give preference to plant-based complexes. These include Fitomucil Norm. It contains the pulp of the fruit of the domestic plum and the shell of the seeds of the plantain variety Plantago Psyllium. The product acts gently and does not cause diarrhea, bloating, flatulence, or cramps. You can buy the drug at a pharmacy. Instructions for use are on the package.
When is laparoscopy performed?
If the ovarian cyst is small, does not cause symptoms and does not look cancerous, it can be left alone. No surgery needed. The gynecologist will prescribe periodic examinations and control ultrasounds. Moreover, postmenopausal women will have to do this more often, because they have a higher risk of malignant tumors.
Are there effective medications?
In some cases, hormonal contraceptives may be helpful. They help prevent the formation of new cysts in the ovaries, but do not affect the growth of existing ones. If a woman is bothered by pain, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). But this is only symptomatic treatment. The only way to get rid of the formation is surgery.
If the cyst is “problematic,” then the doctor will definitely say that it needs to be removed. Indications for surgery:
- Large size of formation. In most cases, ovarian cysts have a diameter of 1–3 cm. Very rarely they reach 15–30 cm.
- Presence of symptoms: abdominal pain, pelvic pain, bloating, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, heavy periods, vaginal bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle. A large cyst can compress the intestines and bladder. This leads to problems with stool and urination.
- Suspicion of a malignant nature of the cyst - the risks are increased in postmenopausal women.
- Continued growth over 2–3 menstrual cycles.
- Pathological ovarian cyst.
What happens if the cyst is not removed?
If the doctor said that the cyst needs to be removed, then delaying the operation is primarily dangerous for postmenopausal women. They, as we have already mentioned, have a higher risk that the formation may turn out to be malignant. And with cancer, time is critical. The later treatment is started, the lower the chances that it will be successful and that remission will be achieved. The prognosis worsens and survival rate decreases.
At the Euroonko clinic you can receive treatment for ovarian cancer according to modern standards. Our doctors perform operations of any complexity; we have access to all the latest generation antitumor drugs registered in Russia. We work according to modern European, American, Israeli treatment protocols. For ovarian cancer complicated by peritoneal carcinomatosis, we use an innovative technique - hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC).
With benign ovarian cysts, serious complications can also occur, although they are rare. Large cysts may rupture. In this case, severe bleeding develops into the abdominal cavity, and severe abdominal pain occurs.
As the cyst grows, the risk of ovarian torsion increases. Due to compression of the blood vessels, it stops receiving blood supply, severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting occur. The result may be necrosis (death) of the ovary, and it will have to be removed urgently.
If you experience symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or a fever of more than 38 degrees, you should immediately seek medical help.
Postoperative period - the first month after surgery
In the first month after surgery, the functions and general condition of the body are restored. Careful adherence to medical recommendations is the key to full recovery of health. The main areas of rehabilitation are adherence to physical activity, diet, drug treatment, and wound care.
Compliance with physical activity
Any surgical intervention is accompanied by anesthesia and tissue trauma, which requires restoration of the body. The usual rehabilitation period after laparoscopic cholecystectomy ranges from 7 to 28 days (depending on the nature of the patient’s activity). Despite the fact that 2-3 days after the operation the patient feels satisfactory and can walk freely, walk on the street, even drive a car, we recommend staying at home and not going to work for at least 7 days after the operation, which is required for the body to recover. . At this time, the patient may feel weakness and increased fatigue.
After surgery, it is recommended to limit physical activity for a period of 1 month (do not carry weights of more than 3-4 kilograms, exclude physical exercises that require tension in the abdominal muscles). This recommendation is due to the peculiarities of the formation of the scar of the muscular aponeurotic layer of the abdominal wall, which reaches sufficient strength within 28 days from the moment of surgery. 1 month after surgery there are no restrictions on physical activity.
Diet
Compliance with the diet is required for up to 1 month after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. It is recommended to exclude alcohol, easily digestible carbohydrates, fatty, spicy, fried, spicy foods, and regular meals 4-6 times a day. New foods should be introduced into the diet gradually; 1 month after surgery, dietary restrictions may be lifted on the recommendation of a gastroenterologist.
Drug treatment
Minimal medical treatment is usually required after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Pain syndrome after surgery is usually mild, but some patients require the use of analgesics for 2-3 days. Usually these are ketanov, paracetamol, ethol fort.
In some patients, it is possible to use antispasmodics (no-spa or drotaverine, buscopan) for 7-10 days.
Taking ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursofalk) can improve the lithogenicity of bile and eliminate possible microcholelithiasis.
Taking medications should be carried out strictly as directed by the attending physician in an individual dosage.
Preparation
Ovarian cysts are usually detected during an ultrasound examination. In order to better assess the size, location and internal structure of the neoplasm, the condition of the ovary, they usually resort to not only transabdominal (through the abdominal wall), but also transvaginal (using a special sensor inserted into the vagina) ultrasound.
In rare cases, usually when a malignant nature of the formation is suspected, computed tomography and diagnostic laparoscopy are prescribed. of cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) in the blood testifies in favor of cancer . But this analysis is unreliable, since a positive result can be obtained for uterine fibroids, endometriosis and inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
Based on the examination results, the doctor advises the woman and explains which treatment tactics will be optimal in her case. If laparoscopic surgery is indicated, a date for hospitalization is set. You need to undergo a preoperative examination. It usually includes the following diagnostic methods:
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood test for hormone levels.
- Tests for infections.
- Cervical smears - cytological, flora.
- Blood clotting study.
- Determination of blood group AB0, Rh factor.
- Electrocardiography.
- X-ray of the lungs.
Laparoscopic removal of ovarian cysts is performed under general anesthesia - endotracheal anesthesia. The woman is hospitalized in the hospital the day before surgery. You can’t eat anything for 8 hours before surgery, and you can’t drink anything in the morning. Some time before anesthesia, premedication : the woman is given drugs that help her relax and calm down.
Rehabilitation methods after laparoscopic intervention
The main indications for prescribing physiotherapeutic procedures after laparoscopy include restoration of the functions of tissues dissected during surgery, acceleration of the process of resorption of scar formations and adhesions; pain relief, anti-inflammatory treatment.
After gynecological operations, electrophoresis and galvanization may be prescribed. Ultrasound therapy is widely used. Heat treatment in the form of paraffin and ozokerite applications is used for MT obstruction. The anti-inflammatory effect is achieved by the use of sinusoidal modulated currents and magnetic therapy.
An important role in the complex treatment of gynecological diseases is given to sanatorium-resort therapy, which helps restore the patency of the fallopian tubes, reduce and disappear inflammatory infiltrates, normalize secretory functions and generally improve the woman’s condition.
How is laparoscopy performed?
Laparoscopic intervention is performed through several punctures in the abdominal wall. Through one of them, in the navel area, a laparoscope - an instrument with a miniature video camera. It broadcasts an enlarged image onto the screen. For better visualization during surgery, the abdominal cavity is filled with gas.
Special laparoscopic instruments are inserted through additional punctures, and the cyst is removed with the help of them.
Depending on the specific situation, the scope of the operation varies:
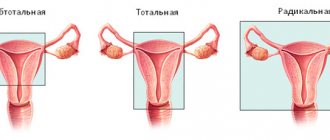
- Often it is possible to remove only the cyst, preserving the ovary.
- In some cases, it is necessary to remove the entire ovary - to perform an oophorectomy (oophorectomy) - while the second ovary can be saved. This has to be done if a malignant tumor is suspected, or if the cyst is in an “inconvenient” location, when it is difficult to remove it separately.
- In rare cases, both ovaries may have to be removed. This operation is performed only in extreme cases, especially in women of reproductive age, since menopause occurs after removal of both sex glands. The levels of female sex hormones decrease, and this can lead to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, hot flashes, etc.
Don't hesitate to ask your doctor questions before surgery. Ask what is the likelihood that during the operation you will have to remove both ovaries, what negative consequences this threatens, and how to cope with them.
Complications
Laparoscopic operations are associated with a low risk of complications. As after any surgical intervention, in rare cases, infection and suppuration in the area of surgical sutures and bleeding are possible. If you are concerned about severe pain, vaginal bleeding, or increased body temperature, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Adhesions may occur after surgery. Very rarely, during surgery, damage to neighboring organs (intestines, bladder) is possible.
At the Euroonko clinic, operations are performed by experienced gynecological surgeons. Our operating room is equipped with modern equipment, multifunctional laparoscopic stands from leading manufacturers. This helps to minimize risks and perform the operation as safely as possible.
After removal, the cyst may recur, in the same ovary or on the other side. Only removal of both ovaries helps to completely eliminate relapse. But such an operation leads to menopause and undesirable consequences, so it is resorted to only in extreme cases.
Reviews and results
This diet is balanced, healthy and can be followed consistently. Restrictions apply to fatty, fried foods, canned food, smoked foods, and sweets that are not healthy foods. Having benign formations, and not wanting to undergo surgery, women should especially carefully monitor their health - lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right and avoid sun exposure. Reviews note that such a diet is easily tolerated and is beneficial for all family members.
- “...The ovarian teratoma was removed as planned; the operation lasted 1 hour 50 minutes. I left for two days: there was pressure in my heart, there was weakness. A month later the cycle was restored, but my periods were very heavy. The doctor said that everything will be restored, since the second ovary is clean, there is no inflammation. After a month I feel good, I try to eat right, because before that I had constipation - I ate few vegetables and did not drink enough water. They told me to avoid constipation and to keep my intestines working like clockwork. The stool is now normal. It’s not difficult to follow the diet, but I’m a little tired of boiled and under-salted food”;
- “... They removed the cyst, they also discovered adhesions after the removal of the appendix and the removal of the left tube (hydrosalpings). In general, I have all the gynecological pathologies. It's good that I'm not at childbearing age. The difference in the strip operation and in the laparoscopic one is noticeable - I got up in the morning, there are no drains, no stitches need to be removed. Now I’m watching my diet, especially since some adhesions could not be cut and I need to avoid constipation. Yes, and you need to eat right as you age. I got to this point only after the third operation. I started cooking meals in a double boiler, I eat more vegetables than before, I eliminated yeast bread and bake bread from grain flour. I add bran, flax seeds and sesame to many dishes. It’s good that my family supports me and enjoys eating many healthy dishes”;
- “... Endometrioid formations were discovered in both ovaries - she agreed to undergo surgery. I didn’t waste time on treatment with hormonal drugs. I agreed to an expensive laparoscopic operation. On the same day, 2 hours later, I was already moving around the ward. The next morning the stitches were processed and I went home. For two days, due to the injected gas, my stomach was distended. No painkillers were required at home. The threads were self-absorbing. Now 3 weeks have passed, the scars are almost invisible. I eat according to a diet - boiled and steamed, vegetables, sour milk, bread. I had never abused meat before, but after the operation I completely stopped wanting to eat it. Now it has “attacked” fish and vegetables.”
Is it possible to get pregnant after removing an ovarian cyst?
You can get pregnant even with an ovarian cyst. Most often, they do not interfere with pregnancy, but they can make it difficult to conceive a child.
If during surgery only the cyst is removed or at least one ovary is left, the woman’s fertility is preserved. She may become pregnant in the future. Of course, you need to understand that reproductive function is affected not only by surgery. The ovarian reserve (the number of eggs in the ovaries - it constantly decreases with age) and concomitant diseases play a role.
Get a consultation with a doctor at the Euroonko clinic. Our doctor will tell you whether treatment is needed in your case, what type of surgery is indicated for you, and what is the likelihood that you will be able to conceive and carry a pregnancy in the future.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of PCOS is carried out individually in each individual case. The choice of tactics depends on the age, the complaints, the severity of symptoms and their combination, the woman’s reproductive plans, and the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
In general, treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome is complex. It includes:
- weight loss and correction of metabolic disorders;
- infertility treatment;
- treatment of skin manifestations of hyperandrogenism - increased hair growth (hirsutism) and alopecia;
- restoration and normalization of the menstrual cycle;
- improvement of psychological state.
Losing excess weight and correcting metabolic disorders
First of all, you need to change your lifestyle :
- Quit smoking, normalize your sleep schedule.
- In case of increased BMI, reduce the daily calorie intake to 1200-1500 kcal/day. However, the benefits of any specific diet have not yet been proven.
- Teenagers are recommended to engage in intense physical activity of at least 60 minutes a day, women 18-64 years old - at least 150 minutes a week (walking or cycling, household chores, games, sports, etc.). Exercises to strengthen major muscle groups should be performed at least two days a week. It is optimal to walk at least 10,000 steps daily, including daily exercise and 30 minutes of intense physical activity [1]. For this purpose, it will be useful to use a fitness bracelet.
It is also important to correct obesity . If weight decreases by less than 5% within three months due to lifestyle changes, then drug therapy for obesity is prescribed. The drugs used today are:
- orlistat - blocks the breakdown and further absorption of fats in the intestines;
- sibutramine - affects the central nervous system, accelerates the feeling of fullness after eating and increases energy expenditure;
- Liraglutide is an effective drug for subcutaneous administration, has a hypoglycemic effect without the risk of excessive reduction, can improve blood lipids and moderately reduce high blood pressure. The drug has a natural mechanism for the body to regulate appetite and food consumption, and prevents the development of cardiovascular diseases [16].
Surgery of the stomach and/or intestines can be performed to reduce weight in women with PCOS and obesity [1]. Today, bariatric surgery is considered the most effective treatment for obesity [15].
An antihyperglycemic agent such as metformin can be prescribed to adolescents with PCOS, adult women with a BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2, and patients at high risk of developing prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus [1].
Infertility treatment
First of all, the following drugs are recommended for the treatment of infertility:
- Letrozole - prevents androgens from being converted into estrogens, leading to a decrease in estrogen levels, a compensatory increase in FSH with subsequent development and maturation of the dominant follicle.
- Clomiphene citrate - stimulates the production of FSH and LH, causing maturation of the dominant follicle.
- Metformin - makes tissues more sensitive to insulin, reducing insulin resistance - a key point in the development of PCOS. It can be used as a stand-alone drug to stimulate ovulation in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome, obesity or normal weight, and also as an addition to clomiphene citrate if the latter is insufficiently effective [17].
- Gonadotropins are hormone preparations that mimic the natural peaks of LH and FSH necessary for the final maturation of follicles and ovulation [18]. These include:
- FSH, LH and their combination - human (obtained by special purification of the urine of women during menopause) or recombinant (synthesized by special producer cells into which the DNA of the hormone is built);
- urinary or recombinant hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is a pregnancy hormone, similar in structure to LH, which can stimulate ovulation [1].
Gonadotropins can be used in conjunction with metformin, but only after excluding pathology of the uterus, fallopian tubes and male infertility [1]. Treatment is expensive.
In the process of stimulating ovulation, ultrasound monitoring of the state of the endometrium and follicle maturation (it is safe to have less than three mature follicles), observation by an obstetrician-gynecologist and hormonal control must be carried out. This is necessary to avoid the development of possible complications:
- ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome - an excessive reaction of the body in which the size of the ovaries increases due to their severe swelling and multiple cysts;
- multiple pregnancy, etc. [1][18].
Secondarily, the following treatment methods are recommended:
- Conservative treatment with gonadotropins in women who have not responded to therapy with clomiphene citrate in combination with metformin.
- Laparoscopic operations on the ovaries are performed in the absence of effect from drug therapy [19]. These include drilling and wedge resection of the ovaries.
Ovarian drilling (“perforating”) is a laparoscopic destruction of polycystic formations. Leads to the restoration of ovulation due to the mechanical destruction of the thickened ovarian membrane, which prevents the egg from leaving the follicle. Thus, drilling contributes to:
- reducing the amount of androgens and increasing the production of FSH;
- a decrease in the level of anti-Mullerian hormone, the excess of which disrupts the normal maturation of the dominant follicle;
- improving blood supply to the ovaries and blood delivery of FSH and LH, necessary for ovulation [19].
Drilling can be the main method of treatment in the presence of adhesions between the pelvic organs, obstruction of the fallopian tubes and other pathologies.
Drilling methods:
- diathermocauterization - creating incisions on the ovaries using heating with an electrode inserted through small holes in the bikini and navel areas;
- electrocautery - the formation of holes 3-15 mm deep using high-temperature heating with an electrode;
- laser vaporization - evaporation of tissue under the influence of a laser.
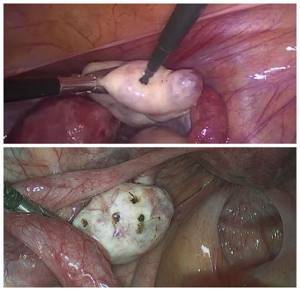
Wedge resection of the ovary is practically not used today due to the risk of developing adhesions, tubal infertility and a decrease in the ovarian reserve - the number of follicles with egg precursors. Laparoscopic drilling has a lower risk of decreased ovarian reserve and ovarian function [1][19].
Thirdly , if after the operation the long-awaited pregnancy does not occur within a year, assisted reproductive technologies are recommended:
- IVF is in vitro fertilization, i.e. “in vitro fertilization.” To begin with, superovulation is carried out - the maturation of a large number of follicles with eggs is stimulated. Then the follicles are punctured and the eggs are collected, after which they are placed in test tubes and 100,000 sperm are injected into them. As a result of successful fertilization, the embryo is transferred into the uterine cavity for further development of pregnancy.
- IVF in combination with ICSI - intracytoplasmic sperm injection. It differs from conventional IVF in that only one sperm is injected into the egg. This method of fertilization is carried out when the partner has a lack of sperm in the semen (azoospermia) or a sharp decrease in the fertilizing ability of the sperm. In this case, sperm is collected naturally or using puncture of the testicle and its appendages [1][6].
In the case of IVF, gonadotropins are often used in conjunction with analogues of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, a hormone of the hypothalamus that regulates the production of FSH and LH by the pituitary gland. Moreover, additional use of metformin can reduce the risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome and increase the chances of pregnancy [1][26].
Before stimulating ovulation in an IVF program (with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist) or in a natural cycle, it is necessary to increase the pregnancy rate. For this purpose, it is more advisable to use progestogens [22].
Treatment of hirsutism and alopecia
If PCOS is not associated with infertility, combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are first prescribed. They contain minimal doses of ethinyl estradiol (20-30 mcg) or natural estrogens (for example, Qlaira).
So far, no advantage of one type of COC has been proven over others, including in the treatment of hirsutism. However, COCs containing 35 mcg ethinyl estradiol and cyproterone acetate, which were previously actively prescribed in the initial stages of treatment of PCOS (Diane-35, Chloe, Modell Pure), are now not recommended for use as first-line drugs [1].
When prescribing COCs, contraindications and restrictions are assessed according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization. This takes into account the woman’s age, smoking, the presence of superficial and deep venous disorders, metabolic pathologies, cardiovascular diseases, mutations in the blood coagulation system, etc. [20].
The hair growth cycle on the scalp lasts 2-6 years, and on the body skin - 3-6 months. Male sex hormones prolong the growth cycle of body hair and shorten it in scalp hair [4][6]. Therefore, the result of therapy will be noticeable no earlier than after 6-12 months. If during this period of treatment with COCs and the use of cosmetic procedures (photoepilation), the manifestations of hirsutism have not decreased, then antiandrogens can be added to therapy - drugs aimed at reducing the level or activity of androgens in the body. Such drugs include:
- spironolactone;
- cyproterone acetate;
- finasteride;
- flutamide is not recommended for the treatment of hirsutism due to its toxic effect on the liver [5].
In combination with COCs, antiandrogens are used to treat androgenetic alopecia in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. They can be prescribed in case of intolerance to COCs or the presence of contraindications to them [1]. During treatment with antiandrogens, it is recommended to use effective methods of contraception, since pregnancy with a male fetus can lead to disruption of its hormonal development.
The effectiveness of treating PCOS with inositol (in any form) is also discussed in the literature [1][21].
Restoration and normalization of the menstrual cycle
To restore the regularity of the menstrual cycle in patients without hyperandrogenism, who are not planning pregnancy and do not need contraception, treatment with progestins is recommended. For example, in the second phase of the cycle, progesterone preparations are used - duphaston, utrozhestan, kraynon gel[21].
Improved psychological state
- psychological therapy;
- cosmetological treatment of acne under the supervision of a dermatocosmetologist;
- If necessary, antidepressants are used to treat depressive disorders or anxiolytics to relieve anxiety and fear. In this case, it is necessary to select a drug that has a minimal effect on body weight [1].