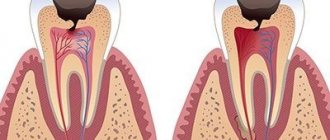
Tooth root granuloma is a limited inflammation of the periodontium, which is a small round formation located in the area of the tooth root. The disease manifests itself in most cases in response to a complicated course of periodontal inflammation. The peculiarity of the disease is the latent symptoms in the initial period and the manifestation of severe pain with the progression of the inflammatory process.
Granuloma is presented in the form of a compacted node at the tooth root, in the periodontium. This name is given to formations up to 5 mm in size. Nodes that are larger (up to 1 cm) are classified as cystogranulomas.
Make an appointment with a therapist by phone+7(985)532-21-01
Education is the pathological epicenter. Starting from a tooth root granuloma, inflammation spreads, gradually destroying the tooth. The disease requires treatment or tooth extraction. Otherwise, the process continues to progress and will lead to complications in other organs. Most often, the pathology spreads to the muscles of the face, neck, and heart area.
How does a dental root granuloma form?
The process of development of pathological formation includes 3 stages:
- Development of dental disease leading to complications. Progression of inflammation with the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms in the dental pulp. The pathological process, developing in connective tissues, leads to cell death over time.
- Pathology continues to develop. The infectious environment ends up in bone tissue. The result of the process is the formation of a neoplasm that transforms into the described granuloma.
- Against the background of bone tissue detachment from the infectious focus, a compacted connective tissue capsule is formed in the local area. In the resulting environment, complicated inflammation occurs, which leads to the rapid proliferation of bacterial microorganisms. At this time, the tissue grows rapidly, bacteria turn into purulent mucus. When visiting a doctor at the current stage, the specialist diagnoses acute granuloma.
The disease significantly undermines the human immune system. As the pathology develops, the tooth begins to loosen - the roots of the element are exposed.
Periodontal pockets, pathological formations between the gum and dental tissue, can also lead to the development of the disease. The cause of cavities is hard tartar.
The pocket holds a lot of bacteria, which leads to the formation of a gap between the gum and the socket. It becomes a “transport” for infection that penetrates into the root of the tooth. Subsequent growth of tissue at the base of the tooth root and filling of the cavity with pus is a granuloma.
Causes of dental granuloma
Experts divide all the causes of granuloma into two groups: primary and secondary.
Main provoking factors
We are talking about factors that are key conditions for the development of the pathological process. Among them:
- advanced caries;
- untreated pulpitis formed as a result of inflammation of the connective tissue;
- fracture of the tooth, leading to the penetration of infection into the element of the dentition;
- periodontal inflammation;
- inappropriate antiseptic treatment of the tooth following removal of the element or therapy.
Minor provoking factors
The group of secondary causes includes factors that can, but are not required to lead to the formation of granuloma. Among them:
- constant stress;
- physical stress;
- sudden change in climatic conditions;
- hypothermia of the body;
- serious cold.
The development of the disease can also be triggered by poor-quality therapy (canal filling, etc.). Often the appearance of inflammation is preceded by tooth extraction and a complete lack of infection prevention after manipulation.
The area of the removed element tightens the tissue, and after microbes enter the cavity, the inflammatory process of the periodontium begins to develop. In the absence of preventive measures, the granuloma quickly grows, filling with pus. If treatment is neglected, the formation moves along the gum - infective endocarditis occurs, often leading to death.
It is possible that granulomas may appear when primary teeth are removed in children. Accordingly, the development of the disease in childhood cannot be ruled out.
Urgent dental care for the development of purulent inflammation
We already wrote above that dental granuloma develops asymptomatically for a long time and this form is called chronic. But if a person experiences severe stress, catches a cold, a malfunction occurs in the immune system of his body - the granuloma will turn into an acute form, in which purulent inflammation can begin to actively develop. Its signs are excruciating pain that does not subside after taking pharmaceutical painkillers, swelling of the gums and cheeks, and increased body temperature.
Naturally, with such symptoms, you need to urgently contact the dentist to get emergency help. Treatment will depend on where the pus is located and accumulates:
- If the pus is in the granuloma itself, then assistance to the patient will consist of opening the tooth to ensure the outflow of pus through the root canals;
- If there is swelling on the gum and cheek, this indicates that the pus could go into the mucous membrane or periosteum and then the doctor will have to make an incision in the gum to drain it.
If you go to the dentist with a granuloma of a tooth that is completely destroyed, it would be advisable to remove such a tooth. But at the same time, it is important that the tooth extraction procedure is carried out efficiently and not only the tooth is extracted, but also the granuloma. If the tumor remains in the socket, alveolitis may develop - a rather serious and unpleasant complication.
If you have had a tooth with a granuloma removed, you must properly care for your teeth and oral cavity after this operation. You should:
- Temporarily stop drinking too hot food/drinks, alcohol, smoking;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia of the body and for this purpose do not visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, be sure to dress according to the weather;
- Eliminate stress and physical activity;
- Eat soft and warm foods for a week, trying not to chew on the side of the jaw on which the extracted tooth was located.
Be sure to take all medications and carry out all procedures prescribed by your doctor! If, within 3-4 days after the removal of a tooth with a granuloma, pain and swelling do not go away, contact the clinic immediately. The persistence of pain and swelling may indicate that the inflammatory process continues for some reason.
After tooth extraction during the treatment of granulomas, prosthetics and dental implantation are carried out no earlier than six months later. Such a pause in treatment is necessary for the complete restoration of all tissues in the area of tooth extraction.
Symptoms of granuloma on the root of the tooth
In the initial stage of the disease, the patient does not notice specific symptoms. The first sign that indicates a pathological phenomenon is a sharp pain syndrome.
An additional symptom of the disease is the sensation of a foreign object in the mouth. The role of a foreign object in the oral cavity is played by overgrown tissue. It can be easily felt with your tongue.
If the patient can see a granuloma, you should prepare for the following symptoms of pathology:
- redness, swelling of the gums;
- inflammatory process in the mouth, accompanied by unstable hyperthermia;
- change in enamel color (darkens);
- discharge of pus from under the gums;
- feeling unwell, migraine;
- flux.
Swelling and redness can be observed on several sides of the tooth (internal, palatal, behind the lips). If you press on the affected area, the pain increases sharply, the pain is bursting, and progresses over time.
To summarize: the basic symptom is acute pain observed against the background of tissue swelling. Then the patient notes significant changes in body temperature.
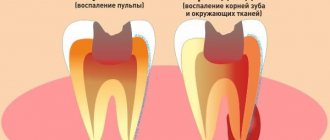
Types, signs and symptoms of periodontitis
According to the Russian classification, there are several forms of inflammatory processes developing in the periodontium.
- Spicy.
- Chronic.
- Separately, it is customary to highlight exacerbations of chronic inflammation of the tooth root.
Signs and symptoms of acute periodontitis
The main symptom of this form of the disease is sharp, aching, sometimes unbearable pain. In this case, the pain is clearly localized in the area of the diseased tooth and is permanent. If the patient did not receive dental care on time, the pain quickly intensifies, becomes tearing and pulsating, which in most cases indicates that the primary inflammation has turned purulent.
The period during which an acute form of tooth root inflammation can last is from several days to 2 weeks. In this case, two successive stages are distinguished.
- 1st (phase of periodontal intoxication). Severe, persistent aching pain is the main sign indicating the beginning of the development of the inflammatory process. Often the patient feels heaviness in the area of the affected tooth and complains of a dull pain, which sharply intensifies when trying to bite.
- 2nd (exudative). In this phase, inflammation of the tooth root is characterized by very strong pain that does not subside without the use of analgesics for almost a minute. Unbearable pain is now caused not only by biting, but even by a slight touch of the tip of the tongue to the affected tooth. Most patients complain of the feeling that the diseased tooth is “pushing out”, which to some extent corresponds to reality, since it acquires increased mobility. In the exudative stage, the adjacent soft tissues may swell and the lymph nodes may become inflamed.
Chronic inflammation of the tooth root
Diagnosing the chronic form in a timely manner is difficult for two reasons. First, many patients do not have the signs and symptoms characteristic of acute apical periodontitis, and complaints may be misleading. Secondly, the clinical picture of chronic periodontal inflammation is in many ways similar to other diseases, for example, some complex types of pulpitis.
The following signs and symptoms may indicate the development of chronic tooth root inflammation.
- There is usually no constant or prolonged pain, but severe discomfort is often felt when pressing and biting on the affected tooth.
- A weak, intermittent feeling of heaviness and fullness, intensifying from time to time.
- Bad breath.
- Change in tooth color (not to be confused with carious stains).
- The occurrence of fistulas.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes, their pain.
- Unpleasant sensations when pressing on the gums.
During a diagnostic examination, the dentist usually identifies a deep cavity, the probing of which causes severe pain in the patient. The diagnosis is made based on the X-ray obtained.
How is granuloma on a tooth diagnosed?
The dentist makes the diagnosis. The patient undergoes an x-ray. With a granuloma on an x-ray, a specialist notes darkening at the tooth root.
In a hospital, the patient may be prescribed radiovisiography, a type of x-ray that provides a reduced dose of radiation. In this case, the situation is assessed not on an x-ray, but on a monitor. Accordingly, the diagnostic method is classified as digital.
The most favorable outcome is diagnosing granuloma at an early stage of development. Pathology is often determined during the treatment of other dental diseases. The specialist notes swelling of the gums, which is very painful. A doctor may also suspect a granuloma based on the protruding bone at the apex of the tooth.
Particular attention is paid to patients whose oral cavity has crowns and pulpless teeth, since the diagnosis of “granuloma” in these categories of patients is made much more often.
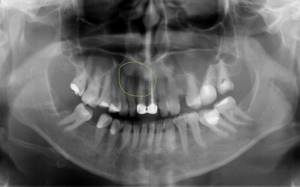
How does the procedure work?
We use modern digital pantomographs. Their advantages include:

low radiation exposure, which allows repeated examinations to monitor the effectiveness of prosthetics and therapy;- the ability to obtain a digital image, which can be optionally recorded on any medium (disk, USB flash drive), sent to the attending physician by e-mail;
- ability to enlarge the image of the area of interest.
Before starting the study, you are asked to remove all jewelry (they can distort a panoramic photo of your teeth) and put on special devices to protect the body from excess radiation doses. The position of the pantograph plate is then adjusted based on the patient’s height. X-rays can also be performed in a sitting position (for example, if a person cannot stand on his or her feet for health reasons). At the request of the radiologist, you should bite down on a special plate - this is necessary to center the jaw. If it is necessary to visualize the temporomandibular joint, an x-ray is taken in two projections: with the mouth open and with the mouth closed.
During operation of the pantomograph, remain motionless. Sometimes, to improve visualization, you are asked to tilt or turn your head. The procedure itself takes no more than 5 minutes (including the time required for preparation). After another 10–15 minutes, a transcript is given to you along with a printed image, and, upon request, an external medium with a recording of the radiograph.
How to cure dental granuloma
For a patient with granuloma, therapy is indicated at the first stage of pathology development. He visits the dentist, undergoes x-rays, then follows all the specialist’s recommendations and remains calm during the necessary manipulations.
The treatment course for this type of pathology may include:
- Conservative treatment.
- Surgical intervention.
- Traditional therapy.
The first two methods are most effective in the fight against granuloma. They are held within the walls of the clinic. Traditional methods of therapy are applicable only as supportive measures.
Conservative method
The therapeutic approach involves the prescription of antibacterial agents, sulfa drugs, and tooth filling. This approach makes it possible to stop inflammation and preserve the element of the dentition.
Antibiotics are designed to quickly stop the progress of inflammation, eliminate the pathogenic environment, and cleanse the tooth of infection. At the same time, the patient rinses the mouth with antiseptic agents. They help relieve pain.
In case of deep caries, an inflammatory phenomenon is observed in the pulp - the doctor carries out canal cleaning and removal of the infectious focus. Then the doctor puts the drug into the tooth cavity and performs a temporary filling. After a certain period, a permanent filling is installed in this place.
In severe cases of the disease, therapeutic methods of treatment are powerless - surgical therapy is indicated for the patient.
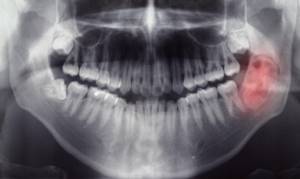
Surgery
The essence of the operation is to open the gums and remove purulent discharge through drainage. This method eliminates inflammation. As an additional measure, they resort to prescribing antibacterial drugs, analgesics and antiseptics. The prognosis after surgery is favorable.
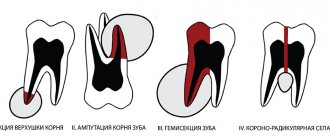
The surgical treatment of dental granuloma involves one of the following procedures:
- Gum opening and drainage.
- Removal of the apex of the tooth root.
- Hemisection of the tooth.
- Removal of an element of the dentition.
If there is a pocket on the gum or a gap on the tooth, the cyst is dissected and the accumulated substance is removed from the cavity.
Root resection
Medical manipulation consists of the following stages:
- Violation of the integrity of the shell.
- Cleaning the channel.
- Filling the cavity with the drug.
- Elimination of formation (granuloma) and the apex of the tooth.
- Replacement of unsuitable fabric with artificial material.
- Installation of a seal.
Hemisection of tooth
A therapeutic measure is resorted to if there are a large number of tooth roots and the disease is extremely neglected - it is not possible to preserve the root part. The process consists of 4 stages:
- Removal of the root and the crown part of the tooth in contact with it.
- Filling the cavity with material.
- Placement of the crown.
- Monitoring the clinical picture after surgery using radiography.
Removal of a tooth
If it is not possible to save the tooth, they resort to removing it. Indications for manipulation are:
- prolonged pain;
- formed gum canal;
- dental crack (vertical);
- complete destruction of the element or its crown;
- visualization of root perforation;
- obstruction of the root canals.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional therapy can alleviate the patient’s condition by reducing the manifestation of concomitant symptoms: Below are several effective traditional medicine recipes:
- Tincture of propolis and calamus. Prepare calamus root and dry propolis (30 g each). Pour the components with alcohol or vodka and leave in a dark, cool place for 14 days. Use as a rinse.
- Herbal decoctions. Sage, chamomile, and eucalyptus can be used as raw materials. Use for mouth rinsing.
Treatment methods
As already noted, in modern dentistry, preference is given to conservative treatment. However, it is often impossible to fully treat tooth root inflammation without surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
This is a complex methodology that includes several types of activities:
- mechanical cleaning of channels
- disinfection of canals using medications
- Temporary filling with medication
Conservative therapy includes the prescription of antibiotics for inflammation of the tooth root.
Surgery
Involves the operation:
- removal of 1/3 of the root tip
- removal of part of the root (hemisection)
- removal of a tooth from the dental socket
Important: Doctors try to save teeth using all conservative treatment methods available today, since they are successful in 70-90% of cases.
Complications with dental granuloma
Lack of appropriate treatment for granuloma can lead to the following complications:
- Complete tooth loss. The root is destroyed, the inflammatory process is transferred to the soft tissues.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw.
- Formation of a cyst-like formation.
- Malignant tumors.
- Involvement of other organs and systems in the infectious process (sinusitis, pyelonephritis, etc.).
- Penetration of purulent discharge into the skull (meningitis, encephalitis, etc. develops).
- Migrating granuloma. The skin on the patient's face bulges, abscesses and fistulas form.
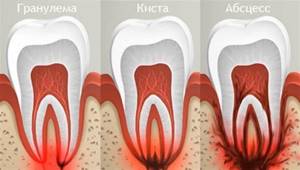
Preventive measures
Prevention of the disease is complex. The actions of a person who wants to prevent the formation of granulomas require compliance with the following medical recommendations:
- Following the rules of personal hygiene (daily brushing of teeth, rinsing the mouth).
- Timely treatment of bleeding gums.
- Regular visits to the dentist (at least 2 times a year).
- Timely change of toothbrushes to prevent infection in the mouth.
- Attentive attitude to your own health - reaction to pain, discomfort in the oral cavity, timely contact with a specialist.
- Complete cure of dental diseases.
- Use of medicated toothpastes for preventive purposes.
- Regular rinsing of the mouth with herbal decoctions.
- Including foods that are sources of calcium and vitamins in your daily diet.
Is it possible to cure dental granuloma?
The prognosis for treatment of granuloma depends on the stage of development of the pathology and the chosen therapeutic strategy. When organizing treatment at the first stage of the clinical picture, the prognosis is always favorable. Positive results are obtained with timely treatment of granuloma in children.
If treatment is started at the stage of formation of purulent discharge, the success of therapy depends on the location of the inflammatory process. If it is the root part, the prognosis is rarely favorable - the tooth is removed. If pus collects only in the gums, after surgery and a course of antibiotics the patient makes a full recovery.
Lack of timely treatment can cause the patient's death. The pus, bypassing the muscle tissue, reaches the heart area - sepsis appears, leading to death.
To summarize, it is worth emphasizing that granuloma is a truly serious pathology. The appearance of the first signs of the disease is a reason to visit the dentist and begin treatment. Otherwise, the progression of inflammation will lead to irreversible complications.
Make an appointment with a therapist by phone+7(985)532-21-01
Treatment of wisdom tooth caries if it hurts
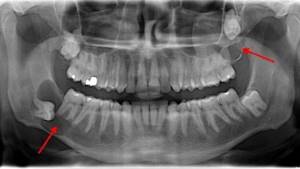
Removal of a wisdom tooth cyst
Tetracycline teeth treatment, whitening, veneers
Tooth root caries treated or removed
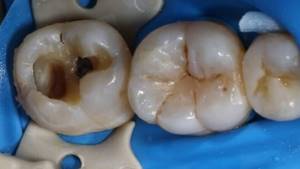
Treatment of average dental caries from 6,000 rubles - sign up at the clinic of the Central Administrative District of Moscow
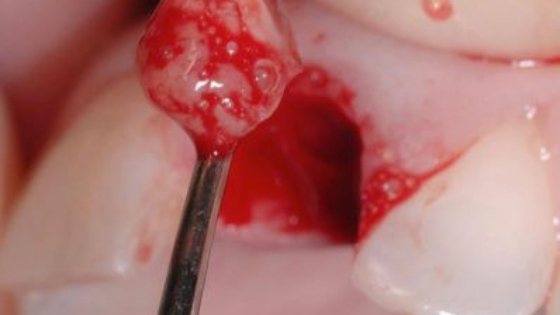
Tooth granuloma, what is this disease and how to cure it
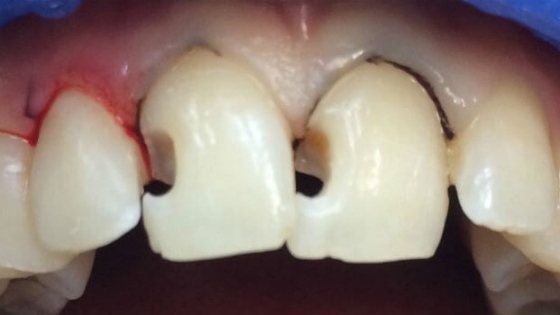
Treatment of caries between the front teeth
Stages of periodontitis treatment
How many times you will have to come to the doctor to treat inflammation at the root of the tooth depends directly on the form of the disease, in remission or during an exacerbation. The course of treatment is also influenced by the method chosen by the doctor. Often, therapy requires a course consisting of several stages of treatment and a visit to the dentist. Until the inflammatory process is eliminated, the tooth cannot be filled, so you will have to visit your doctor several times:
- Preparatory stage. Diagnosis of the condition of the tooth root using x-rays
- When removing the old filling, the tooth is drilled to open access to the canals and remove the nerve
- Channels are expanded to the required size
- Treating the canals with antiseptic drugs and applying medication
- A temporary filling is installed
- At the next visit, the temporary filling is removed and the canals are treated with antiseptic. This stage can last for weeks, or even months - the process will be repeated until the inflammatory focus is completely eliminated and the number of visits will depend on this
- A permanent filling is placed and x-rays are taken again for control.
In addition to the procedures performed in the clinic, the patient must undergo antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy. At home, he should do warm rinses with special antiseptic solutions (herbal, medicinal - as recommended by a doctor).