PCR diagnosis of latent infections
or
Polymerase chain reaction
diagnostics is a highly accurate method of gene diagnostics for identifying various types of infectious and hereditary diseases in a patient, both in the chronic stage and long before the onset of the disease.
How the research works
During the analysis process, the material is placed in a special device, heated and cooled. The accuracy of the obtained values depends on the correct change in temperature conditions.
Using the PCR method you can determine:
- HIV;
- Viral hepatitis;
- Mononucleosis (infectious);
- Cytomegalovirus;
- For STDs (ureaplasma);
- Herpes;
- Candidiasis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Tick-borne encephalitis.
Most diagnostic centers offer a PCR test for 12 infections, but the diagnostic capabilities at the Health Laboratory are wider, so it is possible to perform a PCR test for 14 and even 15 infections.
Preparing for the examination
Various biological fluids are used as samples for PCR analysis: saliva, urine, blood, urethral secretions, and in difficult cases, even pleural and cerebrospinal fluid. But most often you have to take a smear test.
How to prepare for a PCR test depends on the biological sample that is to be sent for testing.
If the test involves saliva or a throat swab, the patient must refrain from eating, drinking, or taking medications for four hours before the test.
If you need to donate blood, then this is done, as with an ordinary general analysis, on an empty stomach, and the day before the examination it is advisable to refrain from fatty foods and alcohol.
Before donating urine, women and men should prepare by slightly tightening personal hygiene standards: for women, it is advisable to put a tampon after washing, and for men, it is advisable to thoroughly rinse all skin folds.
When examining semen or vaginal smears, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse for two to three days.
Decoding the results
The results obtained are assessed only individually for each person, taking into account the patient’s chronic diseases and developmental pathologies. The decoding is based on quantitative indicators of pathogenic microorganisms. Analyzing the data obtained, the doctor will determine:
- The severity of the disease;
- The stage of its development;
- Prescribe a course of treatment taking into account the required dosages and duration of medication use.
A negative result indicates the absence of manifestations of infections and viruses. A positive test indicates the presence of infection. The minimum values of the indicator indicate that the patient is a carrier and requires observation.
This diagnosis is carried out for everyone with complaints of discharge and urogenital symptoms.
- When planning a pregnancy and when registering a pregnant woman;
- Before surgery;
- It is recommended that all women undergo testing once a year due to the fact that the infection can be hidden.
- Before IVF to exclude causes of rejection of the fertilized egg.
- In men after vacation, when they had unprotected sex.
You can take PCR tests at the clinic in Mytishchi, which has its own laboratory equipped with modern equipment. An appointment with a gynecologist can be made by calling the number provided. Information on prices for various types of diagnostics is presented on the Health Laboratory website.
List of tests for hidden infections
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS
Chlamydia
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 010001 | Chlamydia trachomatis DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; prostate secretion; urine | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | |
| 010003 | Chlamydia trachomatis DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; urine; vaginal smear | count | 1-3 k.d. | 900.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 010005 | Chlamydia trachomatis DNA | discharge from the conjunctiva of the eyes; oropharyngeal swab | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Mycoplasmas
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 010101 | Mycoplasma hominis DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; prostate secretion; urine | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 010104 | Mycoplasma hominis DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract | count | 1-3 k.d. | 600.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 010102 | Mycoplasma genitalium DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; prostate secretion; urine | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 010110 | Mycoplasma genitalium DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; urine; vaginal smear | count | 1-3 k.d. | 900.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 010107 | U.urealyticum/U. Parvum DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; urine; prostate secretion | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 010109 | U.urealyticum/U. Parvum DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract | count | 1-3 k.d. | 600.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Gardnerellas
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 010201 | Gardnerella vaginalis DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Treponema
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 010301 | Treponema pallidum DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Neisseri
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 010401 | Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; urine; prostate secretion | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 010404 | Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; urine; vaginal smear | count | 1-3 k.d. | 900.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
FUNGAL INFECTIONS AND PROTOZOOS
Candida
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 020001 | Candida albicans DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Toxoplasma
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 020101 | Toxoplasma gondii DNA | cerebrospinal fluid; amniotic fluid | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 020102 | Toxoplasma gondii DNA | blood with EDTA | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Trichomonas
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 020201 | Trichomonas vaginalis DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; prostate secretion; urine | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 020202 | Trichomonas vaginalis DNA | scraping from the urogenital tract; urine; vaginal smear | count | 1-3 k.d. | 900.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Cytomegalovirus
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 030601 | DNA Cytomegalovirus | scraping from the urogenital tract; urine | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 030603 | DNA Cytomegalovirus | blood with EDTA | count | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 030604 | DNA Cytomegalovirus | blood with EDTA (plasma) | count | 1-5 k.d. | 1200.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 030605 | DNA Cytomegalovirus | oropharyngeal swab; amniotic fluid; cerebrospinal fluid | count | 1-3 k.d. | 600.00 rub. | 0 |
Herpes simplex virus
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 030701 | DNA Herpes simplex virus type I/II | scraping from the urogenital tract | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 030702 | DNA Herpes simplex virus type I/II | blood with EDTA | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 030703 | DNA Herpes simplex virus type 1/2 | oropharyngeal swab; discharge of vesicular rashes and erosive and ulcerative lesions; cerebrospinal fluid | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 600.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Herpes virus type VI
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 030801 | DNA Human herpes virus type VI | oropharyngeal swab; cerebrospinal fluid | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 030803 | DNA Human herpes virus type VI | blood with EDTA | count | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Epstein-Barr virus
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 030901 | Epstein-Barr virus DNA | oropharyngeal swab; cerebrospinal fluid | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 030903 | Epstein-Barr virus DNA | blood with EDTA | count | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ |
Varicella-Zoster virus
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 031001 | Varicella-Zoster virus DNA | oropharyngeal swab; cerebrospinal fluid; amniotic fluid | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031002 | Varicella-Zoster virus DNA | blood with EDTA | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Papillomavirus
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 031201 | HPV DNA types 16 and 18 | in men: urethra; foreskin; in women: cervical canal; Cervix | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031203 | HPV DNA types 6 and 11 | in men: urethra; foreskin; in women: cervical canal; Cervix | quality | 1 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031206 | High-risk HPV DNA (types 16,18,31,33,35,39,45,51,52,56, 58,59,68) | in women: cervical canal; Cervix | count | 1-5 k.d. | 1000.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031207 | HPV DNA types 16 and 18 | in women: cervical canal; Cervix | count | 1-5 k.d. | 700.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031208 | High-risk HPV DNA (types 16,18,31,33,35,39,45,51,52,56, 58,59,68) | in men: urethra; foreskin; in women: cervical canal; Cervix | quality | 1-3 k.d. | 300.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031209 | High-risk HPV DNA (types 16,18,31,33,35,39,45,51,52,56, 58,59) | in men: urethra; foreskin; in women: cervical canal; Cervix | gene. | 3-7 k.d. | 1500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031210 | Extended HPV test (with determination of the amount and type of virus) | scraping from the cervical canal | comp. | 3-7 k.d. | 1500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031211 | HPV-PAP test (expanded set of HPV tests with determination of the amount and type of virus and PAP test) | scraping from the cervical canal (glass + test tube) | comp. | 3-7 k.d. | 3500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031212 | HPV-PAP test liquid (extended set of HPV tests with determination of the amount and type of virus and PAP test) | liquid scraping from the cervical canal | comp. | 3-7 k.d. | 4000.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031213 | Extended liquid HPV test (with determination of the amount and type of virus) | liquid scraping from the cervical canal | comp. | 3-7 k.d. | 2000.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 031214 | Pap test liquid | liquid scraping from the cervical canal | — | 3-7 k.d. | 3000.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
ZIKA virus
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 032501 | Zika virus RNA | blood with EDTA + saliva + urine | quality | 1-5 k.d. | 4000.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 032502 | Zika virus RNA | ejaculate | quality | 1-5 k.d. | 1500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
| 032503 | Zika virus RNA | amniotic fluid | quality | 1-5 k.d. | 1500.00 rub. | 0 ₽ | 0 |
Tick-borne infections
| Code | Name of the study | Biological material | Result | ****Execution period | Price | ***CIT | Note |
| 170401 | DNA/RNA TBEV/B.burgdorferi sl/A.phagocytophillum/E.chaffeensis, E.muris | ixodid tick | quality | 1-2 k.d. | 2000.00 rub. | 0 ₽ |
All our services and prices
Prices for services
| Service name | Price |
| Sexually transmitted infections (STIs using PCR): chlamydia, toxoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, urogenital herpes, gardnerellosis, candidiasis (for 1 infection) | 320 rub. |
See all prices
| Service name | Price |
| Sexually transmitted infections (STIs using PCR): chlamydia, toxoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, urogenital herpes, gardnerellosis, candidiasis (for 1 infection) | 320 rub. |
- We work seven days a week
- Convenient reception schedule until 20:00
- No queues
- Experienced, highly qualified doctors
+ 7 (495) 374-777-0
Make an appointment
Cost of PCR diagnostics of latent infections
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner | 1800 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner | 1300 rub. |
| Primary appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist (candidate of medical sciences; doctor of medical sciences) | 1900 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist (candidate of medical sciences; doctor of medical sciences) | 1400 rub. |
| Primary appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist | 1800 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with the obstetrician-gynecologist | 1300 rub. |
| Primary appointment with a urologist-andrologist | 1800 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a urologist-andrologist | 1300 rub. |
| Taking blood from a vein | 300 rub. |
General rules for collecting PCR analysis 12
In general, when collecting biomaterial from the urethra:
- the external opening is pre-treated with a swab moistened with sterile saline solution;
- if there is purulent discharge, a scraping is taken either immediately or approximately 20 minutes after urination;
- if there is no discharge, first massage the urethra with a probe;
- sampling is usually carried out with rotational movements after inserting the probe to a depth of 1 - 1.5 cm in women, 3 - 4 cm in men;
- in children it is carried out only from the external opening;
From the vulva and vaginal vestibule:
- the sampling is carried out with a sterile cotton swab;
- in case of inflammation of the Bartholin glands, they are punctured;
From the vagina:
- sampling is carried out from the posterior fornix or altered areas;
From the cervical canal:
- first remove mucus with a cotton swab and treat the cervix with sterile saline;
- inserting the probe to a depth of 5 to 15 mm;
- in case of erosive lesions, material is taken from the border area of the changed/healthy tissue;
- the probe is removed strictly without touching the vaginal walls;
From the uterus:
- the sampling is carried out with a special syringe-like instrument;
From the uterine appendages:
- samples (tissue, exudate, pus) are taken during surgery or by transvaginal puncture.
Urine is tested for infection before starting antibiotics after thorough hygienic treatment of the genitals.
Approximately 5 ml of average portion is collected.
In men, when diagnosing prostatitis, three portions of urine (the first and middle, as well as the last, collected after prostate massage) and prostate secretions are examined separately.
Prostate secretion with a volume of about 1 ml is collected after massage into a dry tube.
If it is not possible to obtain prostatic juice, analyze the first portion of urine (10 ml) obtained after prostate massage.
To test for syphilis using the PCR method, material is taken from the lymph nodes and affected areas.
Since for most STIs the hematogenous route of spread in the body is not the main one, blood for PCR diagnostics is not used for all infections.
It is possible to detect HIV and hepatitis viruses using blood PCR.
In case of long-term persistence of positive seroreactions (results of tests for antibodies/antigens in the blood) for syphilis after full therapy, PCR can be used to detect Treponema DNA sections in the blood.
In a situation where blood is being tested, no special preparation is required.
As a rule, the analysis is done on an empty stomach.
If the number of analyzed objects is below the sensitivity limit of standard test systems (which happens when performing blood PCR), the sample can first be concentrated.
In all cases, the study is carried out only after stopping the use of topical drugs and after complete removal of the active substances from the body.
In order to monitor the effectiveness of therapy, the analysis is done 2 weeks after the end of treatment (if there are no symptoms).
The method is highly sensitive and can detect DNA residues even from non-viable pathogenic microorganisms.
Therefore, it is recommended to repeat the control study one month from the date of the last medication.
What is PCR 12 test?
In medicine, PCR diagnostics are especially effective in detecting infectious diseases, including STIs (infections with predominant sexual transmission).
Many laboratories offer comprehensive examinations for the most common sexually transmitted infections.
For example, Invitro has a similar profile (PCR for 12 infections + smear for flora).
However, depending on the researcher, the set of analyzes may differ.
If a doctor prescribes an examination for sexually transmitted infections, you should ask in advance what infections are included in the “PCR 12” profile in this laboratory.
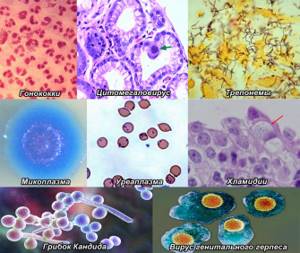
In most cases, the list of diagnosed pathogenic microorganisms includes the identification of:
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasmas;
- ureaplasma;
- candid;
- gonococci;
- gardnerell;
- trichomonas;
- herpes viruses (types I and II);
- cytomegalovirus;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- human papillomaviruses (HPV) of different types and groups;
- HIV;
- hepatitis B and C viruses.
Not all of the above may be included in a profile.
Somewhere, the detection of viruses of different types (herpes simplex types I and II, HPV types 16 and 18) is considered to be separate studies, and no analysis is carried out for HIV or hepatitis.
Somewhere the study for EBV, etc. is not included.