Although x-ray itself is a harmful procedure that is contraindicated for a child, it is children who are most often prescribed it when examining the nasopharynx. This is due to the fact that endoscopic methods for children are unacceptable due to the risk of damaging the nasopharyngeal cavity, and more modern studies, such as MRI and CT, require prolonged immobility.
X-ray of the nasopharynx in children: rules of implementation
The Russian Ministry of Health categorically does not recommend X-raying a child without special indications, including when it comes to the nasopharynx. Therefore, without serious justification, the doctor does not prescribe this type of research: it is applicable only in cases where the consequences of inaction cause more damage to health than a small dose of radiation. Usually the procedure is carried out with the participation of a parent, who monitors the child’s behavior and ensures his immobility. The parent, who is next to the child under the beam of the X-ray unit, wears a leaded rubber apron. Of course, the child himself is provided with similar radiation protection. If the mother is next to the child, she must be sure that she is not pregnant, since X-rays can cause pathologies in the fetus, especially in the early stages.
Reasons for holding
Most often, an X-ray examination is needed for suspected adenoids, injuries, or congenital anomalies. In this case, a referral is issued by the attending physician. However, there are still a number of symptoms that should alert parents. Your child needs specialist advice and possibly a nasal x-ray if the following symptoms are present:
- prolonged nasal congestion;
- headaches, especially in the frontal part;
- redness of the area around the nose, swelling;
- pain in the nose after ARVI, flu;
- copious discharge from the nostrils, bleeding;
- impaired breathing;
- lacrimation.
X-rays of the nose are done in children not only to make a diagnosis, but also during treatment to assess its effectiveness or before surgery.
How is a nose x-ray done?
The study does not require preparation and takes approximately 2-5 minutes. The procedure is painless and is usually performed in two projections in a lying or standing position. At the moment when the photo is taken, you cannot move. In order for radiography to take place as quickly as possible and without the need to repeat failed images, the smallest patients are gently immobilized, and sometimes light sedatives are used. The child's eyes, thyroid gland and genitals are covered with personal protective equipment. Newborns are covered completely, except for the examination area.
Contraindications
This study has no contraindications. You should only discuss possible restrictions with your doctor if you have recently had an X-ray or CT scan.
Is the procedure harmful?
X-rays are harmful to the human body because they ionize molecules. However, now medicine uses equipment that provides an extremely low dose of radiation and a very short-term exposure. Modern radiography is almost harmless if done for a fee, because municipal institutions often have outdated equipment installed. After each procedure, the dose received is recorded in the patient’s chart. It should not exceed 1 mSv per year (for children). The device used in the SM-Clinic minimizes radiation exposure to 0.03-0.1 mSv (depending on the study area). Even if repeated quite often, the test will not harm the child’s health.
When is a child's nasopharynx x-ray prescribed?
An X-ray of the nasopharynx is prescribed to a child for injuries and fractures of the nose, suspected deviated nasal septum and inflammatory diseases that are difficult to diagnose in any other way. The most common reason for ordering an x-ray of the nasopharynx in a child is adenoids. This is also one of the effective diagnostic methods when foreign bodies enter the nasopharyngeal cavity.
What diseases are visible on x-rays?
Standard x-ray of the nasopharynx
cannot be called the most informative research method, however, if a child’s nasal bones or septum are damaged, it is effective: it shows displacements of bones and cartilage, as well as their fragments and cracks. An X-ray of the nasopharynx of a child with adenoids is done with contrast, since in standard mode they are practically invisible in the images. This procedure allows you to confirm enlarged tonsils and other inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx. Most rarely, neoplasms are discovered as a result of the examination.
X-ray of the sinuses: why and how they are done - MEDSI
Table of contents
- Indications for the study
- Contraindications to the procedure
- How the research is carried out
- Normal x-ray picture
- What can a radiologist find?
- Advantages and disadvantages of sinus x-rays
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
X-ray
is a widely used type of examination using a special device that uses a special type of radiation. It allows you to visualize any pathologies, neoplasms, polyps or injuries. This type of examination also allows you to check how successful treatment or recovery from injury is.
Indications for the study
The doctor prescribes an X-ray of the nose in the following cases:
- Constant headaches concentrated in the upper part of the head and eye sockets
- Trauma to the nose, jaw, forehead
- Persistent nasal congestion
- The appearance of sudden discomfort in the eye area, bridge of the nose against a background of high fever and purulent discharge
- Periodic bleeding from the nose
This examination may also be prescribed before dental surgery in the upper jaw.
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses allows you to identify diseases and disorders such as:
- Malignant and benign neoplasms, cysts and polyps
- Ethmoiditis
- Frontit
- Sinusitis
- Injuries and fractures of the bone walls of the paranasal sinus
Contraindications to the procedure
The following contraindications exist for the use of this examination:
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding
- The patient's age is less than seven years (except for situations accompanied by purulent inflammation or a fracture of the sinus wall)
- Frequency of use - no more than two to three times a year
- Allergy to iodine (if a contrast study is necessary)
If indicated, MRI or ultrasound can be used instead of x-rays of the sinuses.
The radiation exposure of this method is low, so there are few restrictions on its use.
How the research is carried out
The procedure for performing an x-ray of the nasal sinuses is as follows:
- Before the procedure, it is necessary to remove various metal objects: jewelry, dentures, glasses, etc., to avoid image distortion
- The patient is placed lying or sitting on a special couch, which fixes the position of the head during the analysis
- The patient's upper body is then covered with an apron, which prevents it from being exposed to radiation.
- After this, within a few minutes a picture is taken in four projections:
- Side view - shows the boundaries of the frontal, maxillary and sphenoid sinuses; at the same time, the patient opens his mouth and touches the screen with his chin
- Chinocranial projection - allows you to examine the sphenoid and the walls of the frontal sinus
- Waters position - demonstrates the structure of the anterior part of the cells of the ethmoid sinus and the floor of the orbit, the maxillary sinuses; the patient presses his chin to the screen and throws his head back
- Posteroanterior projection - shows the ethmoid and frontal sinuses from above; the patient tilts his head forward and leans his forehead and nose against the screen
- If necessary, an examination with contrast can be performed - in this case, an iodine-containing solution is injected into the sinuses
The results of the study should be viewed by a qualified specialist who can correctly interpret the images.
Normal x-ray picture
By reviewing the X-ray results, your doctor can determine if there are any abnormalities. In normal condition, the image should show the following elements:
- The triangular nasal cavity with the nasal turbinates and passages should be symmetrically divided in half by a septum, with the turbinates appearing as shadow areas and the passages as lightened
- The triangular maxillary sinuses should have clear boundaries and be located on both sides of the cavity
- The space between the eye sockets displays the ethmoid sinus, separated by thin walls
- The frontal sinuses are visible above the eye sockets, which may have bony septa and different shapes
What can a radiologist find?
The examination result shows various abnormalities that indicate illness or injury. These are violations such as:
- A light, round spot outside the sinus border indicates the appearance of a cyst or other similar neoplasm
- Thickening of the walls, accompanied by a narrowing of the sinus lumen, is a sign of a chronic inflammatory process
- Fracture or distortion of the shape of the bone wall, dense fragments are a sign of injury
- Dense neoplasm - indicates the presence of a tumor
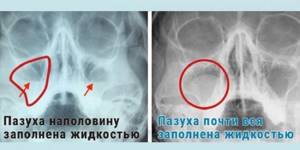
- Thickening of the mucous membrane, fluid in the sinus - these are signs of an acute inflammatory process
When conducting a contrast study, signs of sinusitis are also determined: both acute and chronic.
Advantages and disadvantages of sinus x-rays
Like any other diagnostic method, x-rays of the nose have positive and negative sides:
- Pros:
- Painless
- No surgical or endoscopic intervention
- Can be used by children from 7 years of age
- Minimum radiation dose
- Qualitatively demonstrates the formation of fluid in the sinuses
- The ethmoid sinus is not visible clearly and accurately
- Does not allow assessing the severity of inflammation
- Diagnostics may be hampered by overlapping bones on the image.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- MEDSI clinics conduct more than fifty types of radiographic examinations, including x-rays of the nose
- Only new generation expert-level systems with a low or individually calculated radiation dose are used, which ensure the accuracy and quality of the result
- To examine children, only the safest equipment with a minimum level of radiation is used.
- The results of the study are interpreted by an experienced radiographer.
- If necessary (trauma, acute inflammation, etc.), an urgent examination may be performed
- When making a complex diagnosis, a medical council is involved, which consists of specialists of different profiles
- If you are worried about headaches and difficulty breathing, do not wait for complications, make an appointment with an experienced MEDSI specialist by calling 8 (495) 7-800-500
How is the examination carried out?
The progress of the procedure largely depends on the type of X-ray unit and the age of the child. Before the examination, jewelry and other objects that may distort the image are removed from the child. The doctor then places the child on a couch or in front of an x-ray machine in a position comfortable for viewing. After the small patient is in the required position, he is asked not to move or breathe. The picture is taken within a few seconds, and its quality directly depends on the child’s behavior. 5-7 minutes after the completion of the X-ray of the child’s nasopharynx, the parents will receive an image.
Conducting research
We are sometimes asked the question of where to get an x-ray. In fact, there are a huge number of options, because this procedure can even be attended free of charge with a referral from the attending physician. If you prefer to be treated in private clinics, then you will have to pay for an x-ray, but it will still cost quite cheap compared to other diagnostic procedures.
The nasopharynx can be successfully visualized on photographs of the skull in various projections. Such an examination can be done quite quickly, and it does not require any special preparation. Of course, X-rays have their contraindications, for example, during pregnancy and lactation, but this does not apply to children. Patients who are too young may also be prohibited from undergoing X-rays due to unnecessary risks. Here are the main conditions according to which diagnostics are carried out:
- The patient must first lie down on a special table and press his head against the cassette. The doctor will immediately correct the position of the child’s head and ask him not to move.
- All metal objects must be removed, and this also applies to metal elements on clothing.
- At the specialist’s command, the child will have to hold his breath, but the picture will not take much time, and after a few seconds he will be allowed to breathe.
In the lateral projection, many sinuses can be seen, but if it is necessary to diagnose a paranasal problem, then other projections will be required. The fact is that in most situations, adults are given several different images for maximum information content, but when performing the procedure on a child, the specialist must minimize training as much as possible, so quite often some projections have to be neglected.
Note! Much also depends on the radiation dose, to reduce which it is necessary to use only modern digital equipment; in no case should you perform radiography on a child using an old film machine, because in this case the training will be many times longer.
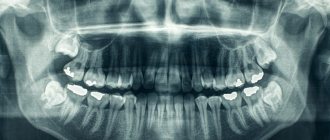
Decoding the results
Darkening of the paranasal sinus indicates sinusitis; sinusitis is also expressed in darkening of the structure in the sinus area. The lumen of the nasopharynx allows you to determine the degree of hypertrophy of the tonsils. Cysts are visible on x-rays of the nasopharynx as oval or round formations, but this is rare for a child. Even less common are neoplasms that are recognizable by their jagged edges and dark shadows.
Sinusitis on x-ray
To be examined and get a transcript of the results from the photo, you need to contact a radiologist. Signs of the inflammatory process on an x-ray depend on the form of sinusitis:
- Purulent. The photographs in 2 projections show the contrast of the black color of the paranasal sinuses with the white infiltrate.
- Polypous. Such a neoplasm is visible on X-ray as a bulge on a stalk, which is located on the wall of the maxillary sinus.
- Odontogenic. X-ray darkening is visible in the sinuses and sockets of the teeth, the bones of the upper jaw are thickened.
Sinusitis in the picture has the following features:
- discrepancy between the sinuses and eye sockets in color;
- uneven edges, thickened walls of the maxillary sinuses;
- infiltrate;
- white areas with a clear line against the background of an oval darkening (this is what an accumulation of fluid looks like);
- circles in the sinuses with clear boundaries and smooth edges (tumors, cysts).
Contraindications for X-raying the nasopharynx in a child
An X-ray of the nasopharynx is rarely prescribed to a child, only if there is no possibility of a standard medical examination, and the situation requires clarification. Before prescribing a test, the doctor weighs the pros and cons. However, as a rule, the harm from an advanced stage of illness or blindly prescribed treatment is much greater than from a small dose of radiation. It is advisable not to do x-rays of the nasopharynx in children under one year of age, who are especially susceptible to radiation. Due to their small size, their organs are located very close to each other. In this regard, the effect of radiation on neighboring organs during the study increases by 2-3 times. It is worth noting that the lowest dose of radiation is provided by the most modern equipment, which, in addition, is also more informative.
Is there an alternative to examination?
An alternative to an X-ray of the nasopharynx for a child can be echosinusoscopy - a method of ultrasound diagnostics of the nasal sinuses, which opens up a view of the nasopharynx area. However, this study, which combines ultrasound and endoscopic methods, is not suitable for a child who cannot remain motionless for a long time and tolerate discomfort. MRI of the nasopharynx
also requires remaining motionless for a long time. Therefore, despite being highly informative, these examinations cannot replace an x-ray of the nasopharynx for your child.
Contraindications for diagnosis
It is strictly not recommended for women to undergo the procedure during pregnancy, since it has long been known about the negative impact of X-rays on the development of the embryo.
It is also worth refusing the procedure if the patient has dental, facial or cranial metal prostheses. They try to refuse this type of study if patients are diagnosed with cancer.
X-rays have no special contraindications, but it is still recommended to consult a doctor.
Classification of sinusitis
Sinusitis has two main forms - catarrhal and purulent. The forms are distinguished by the composition of the discharge from the sinuses. In the catarrhal form, the discharge has an aseptic composition; in the purulent form, it has pathogenic microflora.
The pathology is also classified according to the route of infection:
- hematogenous - through the blood;
- rhinogenic – a consequence of pathological processes in the nasal cavity;
- odontogenic – the result of the development of caries on the upper molars;
- traumatic – the result of fractures and injuries.
Chronic sinusitis, depending on the changes that occur, is divided into two types:
- exudative – pus is actively formed and secreted;
- productive – the mucous membrane undergoes changes (necrosis, polyps, atrophy).
Blockage of small openings inside the nasal sinuses, in addition to inflammation, forms true and pseudocysts.