To the reference Laryngoscopy is an examination of the larynx. Depending on the method of implementation, it can be direct, indirect and retrograde.
Author:
- Oganesyan Tigran Sergeevich
ENT pathology expert
(Voted by: )
Laryngoscopy is a method of examining the larynx using special instruments.
What types of laryngoscopy are there?
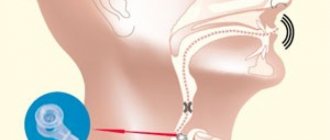
- Indirect laryngoscopy Performed by an ENT doctor at an appointment as part of a general examination of all ENT organs. For this purpose, a special laryngeal speculum is used, which is inserted into the oropharynx. With the help of a frontal reflector - a mirror, light is reflected from the lamp and illuminates the larynx.
- Direct laryngoscopy Using direct laryngoscopy, it is possible to examine the larynx in more detail and completely. It can be performed using either a flexible fiber laryngoscope or a rigid one. A rigid laryngoscope is usually used during surgical interventions.
- Direct transnasal laryngoscopy (performed with a flexible nasopharyngoscope) Direct laryngoscopy allows you to see more than the standard indirect method. Transnasal direct laryngoscopy is a more gentle method, performed using a flexible nasopharyngoscope, which is a thin flexible tube with a video camera at the end.
A nasopharyngoscope is a tool for visual examination of the pharyngeal and nasal cavities, as well as assessment of the biomechanics of breathing and swallowing processes. The ENT Plus clinic uses a flexible and ultra-thin nasopharyngoscope PENTAX (a brand of optical equipment used by the Japanese companies Hoya Corporation and Ricoh).This method has obvious advantages compared to classical methods. The nasopharyngoscope is inserted under local anesthesia into the nasal passage (hence the second name of the method - transnasal laryngoscopy), and a particularly good view of the larynx is obtained. Why does the result of an examination with a FLEXIBLE NASOPHARINGOSCOPE give a better picture to the doctor? It's simple: the patient is not tense, because when examining the larynx transnasally, its movements are more natural than when examining through the mouth (with direct laryngoscopy). The doctor can also observe swallowing movements and movements of the back of the tongue, which is important for understanding the overall clinical picture.
In addition, a flexible nasopharyngoscope allows obtaining high-resolution images in a small size, ensuring careful treatment of the patient and reliable diagnosis.
Bibliography
- Vasilenko Yu. S. Application of videolaryngoscopy and videolaryngostroboscopy in phoniatric practice / Yu. S. Vasilenko, G. F. Ivanchenko // Vestn. otorhinol. - 1991. - No. 3.-S. 38 - 40.
- Vasilenko Yu. S. Voice. Phoniatric aspects / Yu. S. Vasilenko. – M.: Energoizdat, 2002. – 480 p.
- Garashchenko T. I. Modern diagnostics and therapeutic endoscopy of the larynx and lower respiratory tract in children / T. I. Garashchenko, M. R. Bogomilsky // Obstruction of the larynx and trachea in children / St. Petersburg Pediatrician. Honey. Institute - St. Petersburg, 1996. - P. 62 - 66.
- Garashchenko T. I. The role of endoscopy in the diagnosis of diseases of the larynx / T. I. Garashchenko, E. S. Astakhova, E. Yu. Radzig // Ibid. – 2002. No. 1(1). — P. 24 — 25.
- Gracheva M. S. Human larynx / Gracheva M. S. // In the book. Children's voices. Experimental study. - M.: APN RSFSR, 1970. - P. 157 - 160.
- Lepekhina T.V. Assessment of the functional state of the vocal apparatus in children of different ages / T.V. Lepekhina // XVII Congress of the Union of European Phoniatricians: Abstracts. report – M., 1991. – P. 114 – 115.
- Shatskaya V.N. Development of a child’s voice / V.N. Shatskaya. – M.: APN RSFSR, 1963. – 341 p.
- Hirano M. Videostroboscopic examination of the larynx / M. Hirano, DM Bless. - San-Diego: Singular, 1993. - 249 p.
- Sataloff RT Professional voice: The Science and Art of Clinical Car / RT Sataloff. - New York, 1991. - P. 253 - 276.
What are the indications for these examination methods?
- Identifying the cause of voice changes such as hoarseness, dysphonia or aphonia;
- Identifying the cause of a sore throat or earache;
- Identifying the cause of difficulty swallowing, feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- Detection of damage to the larynx, narrowing or obstruction of the airway.
In general, indirect laryngoscopy is a standard procedure and is required for every patient during an examination of all ENT organs, regardless of the patient’s complaints. The purpose of such a diagnosis is to exclude hidden pathology of the larynx and oropharynx, which the patient himself may not pay attention to.
Advantages of visiting the ENT-PRACTIKA clinic
The ENT-PRACTIKA clinic provides specialized care to all groups of the population - from children to the elderly. Here they diagnose and treat all diseases of the ENT organs. Patients note the attentive attitude, high quality of medical services, reasonable prices for laryngoscopy and other procedures.
At the clinic you can get an initial consultation, therapeutic, surgical and physiotherapeutic treatment, and undergo all the procedures necessary for diagnosis, including CT scans and laboratory tests.
Are there any contraindications for laryngoscopy?
There are circumstances in which indirect laryngoscopy cannot be performed or must be performed so quickly that it cannot give a clear picture of the condition of the larynx. This applies primarily to young children, especially to children suffering from laryngeal papillomatosis.
Contraindications for direct laryngoscopy are ulcerative processes of the epiglottis, oropharyngeal cavity, pronounced aortic aneurysm, decompensated heart disease, large edema, severe arteriosclerosis, hypertension. For children, sharp stenotic breathing is a contraindication. However, such breathing is a contraindication for direct laryngoscopy in adults.
Let us note once again that for indirect laryngoscopy, doctors at the Lor Plus clinic use a flexible and very thin PENTAX nasopharyngoscope.
Endoscopic examination of the larynx and oropharynx with an ultra-thin flexible nasopharyngoscope is very effective when working with children, weakened patients, and people with a high gag reflex.
Rehabilitation and complications
Before laryngoscopy, you can find out in advance how it is tolerated. After a mirror check, no special rehabilitation is needed. Sometimes, when pressure is applied to the back of the throat, small attacks of nausea occur, which quickly pass. Rigid or flexible diagnosis may be accompanied by complications, although this is rare. When using a flexible hose, attacks of gag reflexes may also occur, but in most cases they are dulled by the action of anesthetics. After the procedure, local anesthesia creates a feeling of a swollen throat, and swallowing is a little difficult. These symptoms go away after the drugs wear off.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Rigid laryngoscopy is a little more complicated. Nothing is felt during the intervention itself, but side effects may occur afterward. For example, in rare cases, patient reviews indicate a sore throat, hoarse voice, and difficulty swallowing. Such effects should disappear after 1-2 days. If biomaterial was collected, blood is periodically released within 24 hours. It's not scary if it lasts no more than a day. Bleeding from the throat and a constant iron taste in the mouth for 2-3 days is a reason to urgently consult an ENT specialist.
After examination or treatment, especially the rigid method, patients are advised to refrain from drinking and eating until the effect of the anesthetic wears off. Smokers should definitely abstain from nicotine for another 8-12 hours. If there are complications, such as bleeding, you can smoke only with the doctor's permission. After restoration of all functions, it is advised to drink small sips of warm water, and only then eat.
Features of the device
The high efficiency, accuracy and information content of laryngoscopy contribute to expanding the scope of its use. Today, this procedure is adopted by all otolaryngologists and therapists interested in quick and accurate diagnosis to identify the disease at the initial stage in order to prescribe high-quality, effective treatment.
Modern laryngoscopes are safe to use. Thanks to the choice of lamps with “cold” light as a light source, they do not have thermal radiation. In addition, thanks to a competent, well-thought-out design, when using them, there is no possibility of pinching soft tissues or causing harm to the patient’s health.
The devices offered by the world's leading manufacturers are reliable and durable. The blades and handles of reusable devices are made of hard alloys that are resistant to abrasion and damage. Laser welding ensures maximum precision in the manufacturing process of the device and ensures the preservation of its integrity during operation, maintenance, and sterilization.
The ability to connect various attachments to the handle makes it possible to use the device for laryngoscopy of children and adults. Innovative methods of processing the materials from which they are made prevent the possibility of changing the geometric parameters of accessories during their use.
Development engineers are constantly improving existing models, modifying them, and creating newer, more modern devices. The improvement of medical instruments for otolaryngology is aimed at reducing inconvenience for the patient and the doctor during the necessary manipulations. To increase the information content of diagnostics, to make procedures simpler and more comfortable for both medical staff and the patient. Modern video and digital technologies also help with this.
Laryngoscope care
Since the device comes into contact not only with the surface of the patient’s body, but also with his mucous membranes, to prevent infection of patients, reusable devices must be thoroughly disinfected. To carry out these procedures, two methods are used: chemical or gas sterilization (ethylene oxide) with a temperature of about 75ºC. During processing, it is not recommended to disconnect or remove light sources (bulbs, LEDs) from the blade, as this can lead to failure of the electronic contact. As for the power source (battery, batteries) located in the handle, they must be disconnected and removed.
Chemical treatment of the blade must be carried out in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. The instructions supplied with the device usually indicate the name of the substance that can be used (for example, a solution of glutamine aldehyde), percentage concentration, exposure time and other features. Also, before chemical treatment, the blade must be cleaned of mucus, pus, and blood remaining on its surface. Otherwise, these biological substances may dry out and curl up. To remove them, you can simply wash the part with soap, avoiding any liquid getting on the electronic contacts. Pre-sterilization cleaning is monitored by performing an azopyram test.
The laryngoscope handle can be treated three times with alcohol (70%) or subjected to steam disinfection in an autoclave at 135ºC for about 10 minutes. in this case, be sure to remove the battery. But such processing shortens the life of electronic contacts.
It is not recommended to expose the laryngoscope to ultrasonic treatment or exposure to hot air. If, during disinfection, flakes appear in the solution, a sediment or plaque forms, then the drug should be replaced and not used in the future.