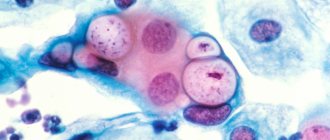
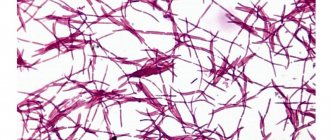
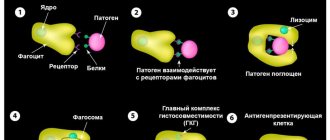
Coccobacilli are a special type of bacteria that belongs to the pathogenic flora in the smear. Their presence in a smear from the genital tract is not normal and may indicate the development of bacterial vaginosis and sexually transmitted diseases in a woman.
What does coccal, bacillary and coccobacillary flora mean in a smear in women, including during pregnancy, what are the causes of abundant and poor microflora, how to treat this condition?
Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult with a qualified healthcare practitioner. The information is for informational purposes only and does not replace medical care.
What does such flora mean in gynecological analysis?
Under certain factors, the ratio of microorganisms changes, the beneficial flora is displaced or dies. The health of the female reproductive system is undermined due to developing pathologies (dysbacteriosis, STDs).
In a healthy woman, the vaginal microflora is represented by 90% lactic acid bacteria (Dederlein bacilli), 10% by bifidobacteria. Less than 0.5-1% is the proportion of opportunistic microorganisms (Escherichia coli, fungi).
This ratio does not allow pathogenic microbes to negatively affect women's health.
Kokkovaya
What do cocci mean in a smear on the flora in women? Coccal flora is classified as opportunistic and includes a wide group of microorganisms.
The most common representatives of microflora:
- staphylococci;
- meningococci;
- streptococci;
- gonococci.
If cocci are found in a flora smear, the most dangerous are the first two microbes due to their ability to cause severe infectious diseases that affect the intestines, brain, and other organs.
Gonococci provoke the development of sexually transmitted diseases. The peculiarity of the coccal flora is its high resistance to antibiotics and heat.
How to get rid of toothache quickly at home? Read our article. What is the best way for women to wash themselves: you will find advice from a gynecologist in this material.
Treatment of urinary incontinence in older women is discussed in detail in this publication.
Bacillary
Bacillary flora in a smear - what is it? The variety of microflora includes both beneficial and pathogenic rod-shaped microorganisms.
Useful flora smears include bacilli in the form of large Dederlein rods (beneficial lactobacilli). Their benefit is in the production of lactic acid.
Lactic acid maintains optimal biocenosis in the vagina, preventing the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi.
Dangerous representatives of bacilli in a flora smear include small rod flora - gram-negative microbes that can cause inflammatory reactions and dysbiosis of the genital tract.
Small rod flora reduces general and local immunity, slowing down the healing process.
Coccobacillary
Coccobacillary flora in a smear - what is it? Coccobacillary flora is characterized by a significant lack of beneficial microbes and the presence of a large number of bacteria, combining two types of pathogenic microorganisms - bacilli and cocci.
Coccobacillary flora can be represented by chlamydia, Haemophilus influenzae, and Gardnerella.
Such microorganisms cause serious diseases that are difficult to treat - chlamydia, hemophilus influenzae, colpitis, gardnerellosis.
If coccobacillary microflora is detected, you should seek medical help .
conclusions
Remember that timely diagnosis, medication and folk therapy can cope with this disease. But self-treatment will lead to chronic pathologies.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Variants of norm and deviations
When such microflora is detected in a smear, the leading role is given to the number of pathogens.
Ideally, the number of Dederlein sticks should be more than 95-99%. This is a variant of the norm, indicating the absence of fungal and infectious lesions of the genital organs.
The number of coccobacilli in a flora smear can be characterized as:
- insignificant - less than 0.5-1%;
- moderate - from 2 to 8%;
- increased - from 8-10 to 50%;
- abundant - more than 50% or complete absence of lactobacilli.
The absence or meager content of coccobacillary flora is a variant of the norm.
If the bacilli flora is abundantly present in a gynecological smear, this is an alarming sign, accompanied by deviations in women’s health: mucous or purulent discharge, abdominal pain, discomfort, and menstrual irregularities.
Composition of normal vaginal microflora
The gold standard for diagnosis in gynecology is the examination of a smear taken from the posterior vaginal vault and cervical canal. Normally the following can be found:
- 1Döderlein acidophilus bacilli (lactobacteria). Normally, their number should be at least 85-95% of the entire flora or 106-108 copies in the sample.
- 2Bifidobacteria (about 10%).
- 3Peptostreptococci, eubacteria, prevotella, bacteroides, fusobacteria and other anaerobic bacteria (5%).
- 4Other cocci and fungi (in small quantities).
- 5Epithelium (not much, its quantity depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle).
- 6Leukocytes (up to 10 cells).
This ratio of microorganisms can maintain a slightly acidic environment for a long time, allows you to fight pathogenic bacteria, provides natural hydration and local immunity. The state of the vaginal microflora is assessed using laboratory methods and has its own conditional classification.
Additional diagnostics
The main way to confirm excess coccobacillary flora is to take a smear for laboratory testing .
A smear is taken from the vagina and cervix. This is necessary to identify the degree of activity of the pathology.
Additional diagnostic methods are used:
- colposcopy for the purpose of diagnostic examination of the vulva, vagina, and its walls to identify changes in the mucosa;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs to identify the condition of the inner layer of the uterus;
- PCR diagnostics of the infectious agent;
- general blood test as an indicator of general condition.
The results of all diagnostic procedures are brought together and analyzed, then a diagnosis is made indicating the cause of the disease .
What can a low number of leukocytes in a woman’s blood mean? Our article will answer the question. Cutting pain in the left lower abdomen in women - what does it signal? Find out in this publication.
If a woman has pain in the lower abdomen on the right, what are the possible causes? Read in this material.
Coccobacillary flora in men
As mentioned above, it is men who can become distributors of coccobacilli without even knowing it.
If in a woman an excess of the norm of coccobacillary flora can be determined by unusual vaginal discharge and a feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen, then in men there are no such symptoms.
Men's smears cannot contain microorganisms that are natural to the vaginal microflora.
An analysis that does not contain bacterial flora, such as cocci and bacilli, is considered ideal. In men, a smear is taken from the urogenital canal.
The biomaterial is placed on a glass slide and then dried. The sample remains valid for about seven days.
Various reasons can provoke an increase in coccobacillary flora in men, the most common of which are:
- promiscuous sex life;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- early sexual life;
- masturbation with dirty hands.
Coccobacilli are divided into groups. In men, pneumococcal discharge most often occurs from the respiratory tract. Streptococci and staphylococcal microorganisms live on the skin.
In the tests, in addition to coccobacilli, fungi, E. coli and other microorganisms are detected.
There are very rare cases when only coccobacillary microflora is present in a man’s urogenital smear.
A significant number of coccobacilli in the analysis indicates the presence of a chronic infection in the body.
Other possible reasons for the development of coccobacillary flora in men may be poor nutrition, decreased protective functions of the body, and hypothermia.
A long course of antibiotic treatment, which is prescribed to rid the body of infections, leads to the suppression of healthy microflora in men.
The result of such treatment in many cases is dysbiosis. To exclude possible complications, antibiotic therapy is carried out only under the supervision of a physician.
The detection of coccobacillary flora in a person’s smear is a serious reason for prescribing blood and urine testing, which will confirm or refute information about the patient’s infection with sexually transmitted infections.
If the test results are positive, then this diagnostic method will determine whether the infection has managed to penetrate the urogenital tract and spread to other organs.
Only after confirming the diagnosis will the specialist be able to choose an effective direction for treatment.
Treatment of pathology
It is necessary to treat coccobacillary flora , otherwise adverse health consequences may develop, the most dangerous of which is infertility.
Therapy is prescribed after the examination results and includes:
- suppression and destruction of pathogenic microorganisms with antibiotics and antiseptics;
- colonization with the “correct” microflora;
- restoration of local and general immunity.
At the first stage, the following is prescribed:
- Metronidazole (if Gardnerella is present) - 500 mg twice a day, course of administration is 7 days;
- Ceftriaxone intramuscularly (for chlamydia, gonococci) - 0.5 g twice a day for a course of 7-10 days;
- Terzhinan (for vaginal dysbiosis) in the form of vaginal tablets - one piece at a dosage of 500 mg at night for a course of 10 days;
- Amoxiclav orally 0.5 g 2 times a day for a course of 7 days.
The next stage is no less important; its goal is to create an optimal biocenosis in the vagina.
Gynecologists prefer to prescribe drugs in the form of suppositories containing lactobacilli. Their advantage is their rapid effect, the delivery of active substances directly to the problem area.
The most effective drugs are Acylact, Vaginorm-S, Vagilak.
Tampons soaked in a solution of Lactobacterin and Bifidumbacterin are no less effective. The course to restore the flora lasts at least 14 days.
The third stage is aimed at increasing local and general immunity. The use of immunomodulators (topically and orally, in the form of injections) for 10-14 days will correct the immune capabilities towards strengthening.
The following medications are used:
- Genferon or Viferon (suppositories);
- Interferon (intramuscular);
- Wobenzym (oral).
Drugs used and treatment regimens for coccal and bacillary flora
The course of treatment consists of taking antibacterial agents, antibiotics, and immunomodulators. During pregnancy, medications are selected individually in order to avoid the negative impact of medicinal components on the developing organism. It is important to note that in the presence of coccobacillary infection, it is guaranteed that the woman’s sexual partner is infected, and therefore both of them need to be treated. To eliminate the disease, experts prescribe Metronidazole, together You can use gel and ointment with clindamycin. The effectiveness of such drugs is 95%, they are safer compared to tablet analogues. In some cases, to treat dysbiosis, it is enough to adjust the diet, introduce more plant products, fermented milk products with an average percentage of fat content into the diet. Probiotics can be prescribed as an adjuvant - “Linex” ", "Bifidumbacterin", "Lactobacterin", "Trilact". To improve the condition of the immune system, you need to take multivitamin complexes, eat more vegetables, berries and fruits. The list of folk remedies that can suppress the spread of pathogenic flora includes:
- Douching with herbal decoctions - chamomile, calendula, celandine. Perform the procedure for no more than 5-7 days; be sure to consult a doctor before starting the session.
- Vaginal suppositories with sea buckthorn oil and other essential extracts can be purchased at a pharmacy; the composition of the products is considered safe and has a positive effect on improving the functionality of the reproductive organs.
- Therapeutic tampons with sea buckthorn oil, honey, celandine can be prepared at home, however, before using them, it is important to have an informative conversation with your doctor.
To avoid relapse, it is necessary to pay more attention to the hygiene of the genital organs, to reconsider the means that can cause a violation of the acidity of the microflora. When having sexual intercourse, you need to use condoms, avoid casual sex, and undergo regular preventive examinations with a gynecologist. You should not self-medicate to avoid serious complications in a woman’s reproductive system. Coccobacillary flora does not always indicate serious diseases and pathological changes, so if any deviations from the norm are detected, you should not panic.
Prevention
To prevent imbalances in the microflora of the genital tract, it is necessary to eliminate, if possible, all provoking factors:
- Eliminate hormonal imbalance (HRT for menopause, oral contraceptives as indicated).
- Maintain daily intimate hygiene, as well as during menstruation and sex. Avoid douching without a doctor's prescription.
- Use condoms.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, be active, play sports or exercise, eat right, avoid frequent use of antibiotics, protect your body from infections.
- One of the methods of prevention is also regular visits to the gynecologist and treatment of chronic diseases not only of the reproductive system, but also of other organs.
What symptoms may be observed?
Active reproduction of coccal flora will sooner or later lead to the appearance of clinical symptoms of the disease. Signs of an inflammatory process in the vagina are nonspecific, that is, they cannot be used to determine which cocci are multiplying in the genital tract.
A woman may suspect a change in the composition of the microflora based on the following symptoms:
- Itching, irritation, burning of the genital tract - these symptoms may be absent.
- Change in the nature of vaginal discharge (yellow, white, gray or greenish, copious, thick).
- Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse and in the lower abdomen.
- Unpleasant and pungent odor, but may be absent.
The symptoms of colpitis are quite vivid, it is impossible not to notice them. If you ignore the signs of the disease, the infection can lead to the following complications:
- 1Nonspecific cervicitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervix).
- 2 Endometritis, salpingoophoritis (appear when local or general immunity decreases).
- 3Cystitis and pyelonephritis often develop against the background of vulvovaginitis and have a chronic course with frequent relapses. They are associated with sexual intercourse, during which flora is carried from the genital tract into the urethra.
- 4Attachment of pathogenic flora (Trichomonas, Candida fungi, chlamydia). Disruption of the microflora contributes to the transmission of STIs in the presence of an infected sexual partner.
- 5Complications of normal pregnancy.