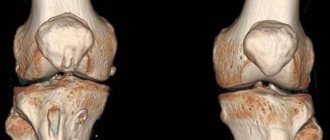
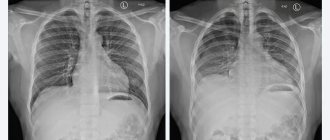
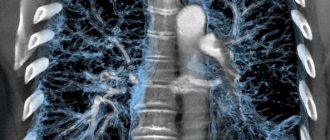
Magnetic resonance imaging of the foot is used to identify possible congenital or acquired abnormalities of a part of the lower limb. Despite its relatively modest size in relation to other functional areas of the body, it is the foot that acts as a support when walking. It consists of 26 bones, which have a complex structure. If at least one of the bones fails or nearby tissues and blood vessels are damaged, this leads to a significant deterioration in the quality of life.
Due to the fact that classical examination methods such as x-rays or ultrasound are not able to provide high-quality visualization, people turn to MRI of the foot for help. Some people mistakenly believe that this testing format can only provide data on possible damage to bone structures. But what an MRI shows is much broader. We are talking about depicting the surrounding soft tissues, which are muscles, tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, and nerves. The study can also reflect the picture of joint health.
What is an MRI of the ankle?
MRI of the ankle is a study that consists of layer-by-layer scanning and determination of changes that occur in cells. This is a reliable and informative diagnostic method that provides high accuracy and detail. Diagnostics are carried out under the influence of electromagnetic waves in a constant magnetic field. The examination is prescribed to identify abnormalities, inflammation, injuries and tissue destruction. The procedure is non-invasive and safe, performed in hospitals and outpatient settings.
How is the examination performed?
At the diagnostic center, the patient lies down on a retractable table, after which one or both feet are secured with special straps. Next, the table slides into the device and diagnostics begins. You will be able to find out what a CT scan of the foot shows after the procedure is completed.
Features of CT with contrast
In this case, preparation for the study will be required. A special substance is administered immediately before the examination. Before this, you will need to be tested for allergies to the drug. Tomography of the ankle joints with contrast is performed if cancer is suspected.
What does an ankle MRI show?
Using magnetic resonance imaging, you can examine the structure of the ankle and see the condition:
- bones;
- cartilage;
- ligaments;
- soft tissues;
- blood vessels and nerves.
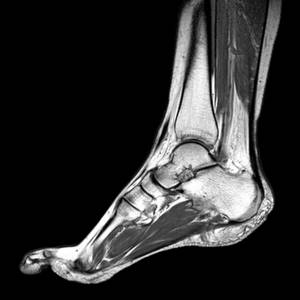
This is an effective way to visualize the fibula, tibia, calcaneus and talus, as well as muscles and tendons. The image is obtained in three planes: side, front and horizontal.
Advantages of the technique
Content:
- Advantages of the technique
- Indications and contraindications
- How is the reception going?
- How to decipher the conclusion?
The most important advantage of the method is the ability to visualize even small anatomical formations. They cannot be found on an x-ray image due to the poor detail of the latter.
Also, many patients are interested in what is better: computed tomography or MRI. But CT involves the use of x-rays, which can negatively affect health. In addition, the study often needs to be carried out using a contrast agent, which can be a significant allergen and can turn into toxins when accumulated in cells. Magnetic resonance imaging has no radiation exposure to the body, and a contrast agent used when necessary has a different allergic effect, since the base is made up of other substances.
The examination principle is based on sequential scanning of a given structural formation. Each equipment model has its own average step for capturing an image. Usually it does not exceed 5 millimeters, which is less than that of a classic computed tomography machine. This allows you to get an improved final quality of “pictures”.
Also, some patients are interested in the question of whether they can use both popular diagnostic formats to confirm the results. In most cases, deciphering the MRI report is sufficient. If the doctor suspects a pathology of bone tissue and blood vessels, then it would be useful to do a CT scan or angiography. But, as evidenced by reviews from numerous patients, MRI is usually sufficient.
Parents of children usually highly value the technique for its non-invasive approach, which means painlessness for the baby. But doctors prefer magnetic resonance scanning due to the fact that it provides information on almost all structures of the lower parts of the legs at once.
Moreover, if you calculate how much one generalized procedure costs and add up the cost of ultrasound, x-ray and CT, then a single analysis will be much cheaper. It will even require less time than three different diagnostics.
In addition to obtaining information about problems in the foot itself, the result will tell you about the condition of the ankle joint, which is difficult to achieve from other diagnostic analogues.
But even a standard bone fracture cannot always be studied thoroughly using X-rays, which is especially important for shrapnel injuries. Hence the desire to use a special tomograph that will detect even the slightest anomalies that other imaging options cannot cope with.
Indications for MRI of the ankle joint
People are referred for the procedure if:
- arthritis;
- arthrosis;
- gout;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- suspected fluid accumulation.
Indications for an MRI of the foot or ankle are sports injuries: ruptures of tendons, ligaments, bone cracks, dislocations. The procedure shows developmental disorders, tumors and metastases, and allows for postoperative observation.
Indications and contraindications
It is generally accepted in society that the main reason for issuing a referral for an MRI is the suspicion of oncological neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature. But the capabilities of new generation medical equipment are much broader, as they help to establish the characteristics of a tumor of any etiology. At the same time, the image will tell you about the exact location of the lesion, the degree of damage to surrounding tissues and structures.
High-fidelity imaging will also shed light on the condition after:
- fracture;
- sprains;
- dislocation;
- pinched nerve.
Sometimes doctors send patients for examination who have pain in the foot area, but the source of its origin could not be determined by other means. For the same reason, a person can ask their doctor for an appointment for a procedure if they have severe pain in the ankle area for no apparent reason.
Persistent swelling, as well as any restrictions on the normal mobility of the specified part of the lower limb, indicate the need to undergo this high-tech testing.
If the patient is already registered with a surgeon or traumatologist, then from time to time he will have to go under a magnetic resonance scanner. Completion of the study will be part of a program for monitoring the health and dynamics of recovery of those who have the following ailments:
- arthritis;
- arthrosis;
- problems with blood circulation.
Even the most minor heel abnormalities will be clearly visible. But not everyone will be able to undergo such a useful examination. Those who suffer from a fear of closed spaces may experience some discomfort when entering the CT scanner tunnel.
Unlike computed tomography, magnetic scanning lasts an order of magnitude longer, which can cause panic.
This can be avoided by visiting clinics that use open-type devices. And when examining particularly complex patients, the doctor can decide on the spot to put the victim into medicated sleep or prescribe general anesthesia.
Such a radical solution is explained by the fact that only complete immobility during the manipulation can guarantee excellent quality of the final image.
The risk group of those who, in urgent need, may be prescribed sedatives for the test, in addition to those suffering from claustrophobia, includes:
- children;
- aged people;
- patients with mental disorders;
- people with uncontrolled seizure disorder.

For the same reason, MRI is carefully prescribed to patients in extremely serious condition, since it is unclear how they will behave in an unfamiliar environment. Even open side surfaces do not always help here.
An absolute contraindication is the presence of metal components in the body. This could be either a pacemaker or some kind of bone substitute like a support pin. Moreover, electrical devices installed in the body, such as internal hearing aids, are prohibited, even taking into account the fact that the lower limb will be examined. But for metal supports such strictness is not provided. If they do not interact with the territory of influence of the magnetic field, then an absolute contraindication turns into a relative one.
In practice, this means that when benefits predominate, all possible harm is neutralized. The final decision in such problematic scenarios should be made by the treating specialist, knowing the characteristics of his patient.
The category of other relative prohibitions includes:
- renal failure;
- liver failure;
- breastfeeding period.
All of the above only covers situations where the doctor insists on the mandatory use of the contrast stage. The danger lies in the fact that when the components of the contrast solution accumulate in the body, they turn into toxins. When the kidneys and liver do not have time to remove the elements of the drug, this negatively affects the general condition of the body.
Despite the fact that the dosage of the medicine is harmless for healthy people, for newborns during lactation, milk with its components can turn into the cause of an unknown ailment. Therefore, experts insist on avoiding breastfeeding for at least two days after the procedure. All this time the milk needs to be expressed and poured out.
But during pregnancy you won’t be able to get off so easily. This is especially true for the early stages of fetal development, when it is better to replace MRI with a more gentle analogue - ultrasound.
The final contraindication also affects contrast. We are talking about an allergic reaction. If the patient is not sure how the body will react to an unfamiliar drug, then it is worth insisting on conducting a control allergy test. Depending on the result, a decision will be made: use another version of the study, or replace the drug or take antihistamines.
How is an ankle MRI done?
Before the examination, the patient must remove all metal products, including removable dentures, piercings, and jewelry. During the procedure, the person lies on a special mobile base, the body position is fixed with bolsters and belts. While an MRI of the foot is being done, you cannot move. The joint is placed in the tomograph area for careful examination. A three-dimensional reconstruction of the joint surface is performed, and the condition of the soft tissues is also determined. The computer takes several pictures showing thin sections of the area being examined.
How is the reception going?
To obtain high-quality images, technicians use the capabilities of an innovative device - a magnetic resonance imaging scanner. Its action is based on the physical properties of the electromagnetic field, which explains the name of the technique itself. The detectors detect the reverse reaction of hydrogen ions contained in the tissues of the foot being examined.
Since all tissues have different indicators of hydrogen atoms, which is explained by their different structuring, visualization takes on detailed outlines.
Externally, the tomograph looks like a capsule, into which a medical couch with a patient is placed. The area to be studied is placed in a special coil with built-in sensors. After activating the tomograph, an electromagnetic field is generated inside the capsule.
To get a quality result, you will have to wait about half an hour. But such a wait is worth it, since it does not involve violating the integrity of the tissues. Due to almost zero harm for the majority of potential patients, the technique is widely used even for diagnosing diseases among children.
Upon completion of the manipulation, the radiologist will provide the patient with tomograms, which are successive thin sections made in different projections. All data is recorded on a digital medium, to which a written conclusion is attached.
The procedure does not require a special preparatory stage. The only exception is the use of contrast, which indicates the need to abstain from eating approximately five hours before the scheduled appointment.
The doctor will warn you in advance that during the examination you should wear only clothes that do not have metal components, and also remove jewelry. But sometimes private diagnostic rooms offer visitors to change into disposable gowns for convenience. In inpatient hospitals, people are given special cotton pajamas with ties or buttons.
MRI of the foot with contrast
In some cases, for good visualization of tissues with a similar structure, a conventional, native study is not enough. Then contrast enhancement is applied.
As a contrast, drugs based on gadolinium salts, a rare earth metal, are used. These drugs are inert and do not cause allergic reactions or toxic effects on the kidneys. The contrast is injected intravenously and spreads through the bloodstream to the area under study. Considering that the blood supply to pathological lesions differs from normal tissues, this makes them more contrasting against the general background. In this way, tumors, inflammatory diseases, circulatory disorders and other pathologies are visualized.