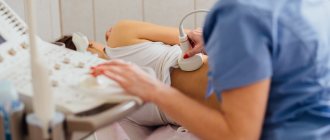
This study is widely used to diagnose pathologies of the urinary system. Unlike other techniques, such as X-rays with contrast, an ultrasound does not inject drugs into the patient or expose the body to radiation. Renal ultrasound is a painless, effective and bloodless method for diagnosing the kidneys.
THE COST OF AN ULTRASOUND OF A KIDNEY IN OUR CLINIC IS 1000 rubles. Kidney ultrasound + liver ultrasound - 1600 rubles.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
An ultrasound of the kidneys can be done using new equipment at the Diana Clinic. The examination and interpretation of the kidney ultrasound will be performed by a highly qualified doctor. The results will be delivered to you.
Why do you need to monitor the condition of your kidneys and adrenal glands?
The content of the article
Impaired functioning of the kidneys and adrenal glands is the cause of the development of a number of dangerous pathological conditions. Kidney disease is also a common complication of infectious diseases, pregnancy, diabetes and other diseases.
Ultrasound examination of the kidneys reveals structural disorders of organ tissue and malfunctions in the functioning of the entire urinary system. Examining the kidneys and adrenal glands using high-frequency sound waves gives doctors a complete picture with detailed visualization in real time. What is important is that the price of kidney ultrasound is affordable for every patient.
The Diana Clinic offers ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands using the latest modern ultrasound machine, which generates ultrasound waves of optimal amplitude and frequency to obtain high-quality color images. Our specialists have many years of experience working with ultrasound techniques using SonoAce X8 equipment of a high expert level. The individual approach and professionalism of the clinic staff will minimize the discomfort of visiting a medical facility and save your time.
Indications for ultrasound of the kidneys
Kidney ultrasound is prescribed for the following conditions:
- headaches accompanied by increased blood pressure;
- swelling of the limbs and face;
- difficulty urinating;
- abnormalities in blood and urine tests indicating renal pathologies;
- suspected nephritis - inflammation of the kidneys;
- the appearance of blood and purulent “flakes” in the urine;
- urolithiasis;
- lower back pain accompanied by fever, weakness and chills;
- suspected abnormalities in the development and location of the kidneys (prolapse, doubling);
- pathologies of the renal vessels;
- suspected renal failure;
- injuries of the lumbar region;
- metabolic diseases accompanied by damage to kidney tissue;
- suspected tumors and cancer metastases.
Often, an ultrasound of the kidneys is prescribed together with an ultrasound examination of the bladder and pelvic organs. To diagnose renal vascular diseases, Doppler ultrasound (USDG) is additionally prescribed.
When is an adrenal ultrasound prescribed?
The examination is recommended for patients in the following cases:
- infertility in women
, as well as other hormonal problems (menstrual irregularities, excessive hair growth); - general weakness;
- suspicion of a tumor or other inflammatory process;
- high blood pressure;
- sudden weight gain;
- injuries and damage to the adrenal glands;
- decreased potency in men.
What can be seen on a kidney ultrasound
The list of pathological conditions that can be identified during the diagnostic process is huge. Ultrasound examination of the kidneys clearly shows:
- Dystrophic changes in tissues;
- Kidney inflammation;
- Cysts and tumors, abscesses, diverticula;
- Kidney prolapse;
- Narrowing or widening of the ureters;
- Presence of stones, sand, air, liquid;
- Urethrocele;
- Transplant rejection.
- Nephroptosis, signs of pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis.
Important! Only small stones up to 4 mm in size can be detected with ultrasound accuracy.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the kidneys
To prevent gas accumulated in the intestines from distorting the result, two days before the examination the following are excluded from the diet: black bread, legumes, sauerkraut, soda, alcohol, and fatty broths. You can eat lean fish, cheese, poultry, dried white bread and one egg per day. 8 hours before the diagnosis you need to abstain from food. Water and still drinks can be drunk in unlimited quantities.
An enema before a kidney ultrasound is done only as directed by a doctor. People suffering from constipation should take a laxative the day before. For increased gas formation, activated carbon, Espumisan or chamomile tincture are indicated.
Preparation for ultrasound of the kidneys in pregnant women
The preparatory stage before diagnosing kidneys in pregnant women is practically no different from ultrasound for the rest of the group of people. Firstly, approximately 3 days before the expected date of the ultrasound, the woman needs to adhere to a certain diet and temporarily give up foods that increase gas formation in the intestines (the list of foods is listed above).
Immediately 6 hours before the kidney test, you must take the usual dosage of Espumisan or another drug with similar effects. This is necessary to reduce the manifestation of flatulence and obtain more accurate results.
The bladder should be full during the examination, so you should try not to visit the toilet for three hours before the ultrasound. If you can’t stand it, you can empty your bladder, but after that be sure to drink a glass of still water.
How is a kidney ultrasound examination performed?
The procedure is carried out with the patient lying on his back, side or standing. A gel is applied to the examination area to improve the conductivity of ultrasound.
First, the ureters are examined, starting from the bladder, and then the kidneys themselves. At some stages of the procedure, the patient is asked not to breathe or, conversely, to inflate his stomach.
A picture of the condition of the kidneys appears on the monitor, and the doctor diagnoses the presence or absence of pathologies. If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed additional examinations.
Diagnostic technique
Ultrasound of the adrenal glands is performed transabdominally, that is, through the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. The patient is placed on the couch in a prone or supine position. The position should be comfortable and relaxed. If necessary, the doctor will ask the patient to roll over on his side or stand up straight. The lower back and stomach are freed from clothing.
To carry out the procedure, a special gel is applied to the area under study. It performs two functions:
- lubricating, that is, it improves the sliding of the ultrasound machine sensor over the skin;
- conductive: the gel enhances contact of the sensor with the skin, helping to reduce interference.
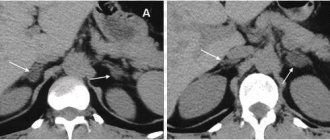
According to the research scheme, the doctor first finds the right kidney, the right lobe of the liver and the inferior vena cava with a sensor. The extreme points of these organs limit the area in which the right adrenal gland is located.
To obtain the most informative image of the adrenal glands, the doctor may ask you to take a deep breath and hold your breath for a while.
To examine the left adrenal gland, the patient is turned over on his right side, and the area of its location is found between the lower edge of the spleen and the upper pole of the kidney.
The technique of conducting an ultrasound examination of the adrenal glands is to detect their location and scan it for the presence of pathologies. In most cases, it is pathological changes or formations that will be displayed on the device’s monitor, while healthy glands may not normally be visualized. If ultrasound diagnostics did not reveal pathological changes, this is explained by the following feature: a healthy organ is not always visualized, but it is possible to see an enlargement or neoplasm of the adrenal gland in almost all cases. This is due to the fact that the size of the glands is very small, and they are not always amenable to visualization using ultrasound.
Contraindications for ultrasound of the kidneys
There are no absolute contraindications for ultrasound examination of the kidneys. However, there are a number of factors that reduce the informativeness of the diagnosis. These include:
- Intolerance to the components of the gel, which is used to apply to the skin and ensures its contact with the ultrasound sensor.
- Skin diseases. An ultrasound is a procedure in which the doctor passes a special sensor over the lumbar region. An obstacle to this procedure can be skin diseases and lesions, such as wounds, cuts, deep scratches, burns, lichen, pyoderma, furunculosis, etc.
- General health of the patient.
The state of human health is considered a relative contraindication. The ultrasound is performed in the lying position on the side, back and stomach. Difficulties arise when a person cannot be in a horizontal position due to various circumstances. The patient's excess weight also affects the information content of the study. The image in this case is unclear due to the thickness of the fat layer.
Where can I get high-quality ultrasound diagnostics in Fryazino?
The medical clinic in Fryazino employs experienced, professional specialists who perform high-quality ultrasound diagnostics using modern high-tech equipment. The examinations are carried out using the HITACHI ALOKA PROSOUND ALPHA 7 device. An appointment for an ultrasound scan is carried out at any time convenient for the patient, and our administrative assistants will tell you in detail how to prepare for the examination procedure.
Medical is located in Fryazino at the following address: st. Lesnaya 2
tell friends
Who interprets the results?
Most patients expect that during an ultrasound scan the specialist will explain to them in detail all the imaging parameters and make a clear and definitive diagnosis. This is certainly a misconception. Only a urologist can draw any conclusions and establish a diagnosis after drawing up a complete picture of the disease based on a study of symptoms, medical history, laboratory tests, ultrasound results and other diagnostic methods.
The ultrasound doctor gives the patient only general information about the condition of the organ and refers him to a urologist with a text printout of the study results.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands
Many patients ask what indicators they should pay attention to.
Quantity.
No matter how strange it may sound, the number of kidneys must be indicated in the final ultrasound report. The fact is that there is a small percentage of people who have one kidney from birth or as a result of organ removal. In addition, if a specialist uses the term “hypoplasia,” it should mean underdevelopment or functional inferiority of the organ. Less common is duplication of one or both kidneys at once, which should also be indicated in the study results.
Dimensions.
If you experience nagging pain in the lumbar region and difficulty urinating, accompanied by pain (especially during pregnancy), it is very important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and conduct an ultrasound. In pregnant women, kidneys in normal condition should not differ in size from the usual indicators for adults.
Knowing the normal size of the kidneys, you can approximately determine the presence or absence of pathologies. In an adult, the kidneys have the following parameters:
| Length | 10-12 cm |
| Thickness | 4-5 cm |
| Width | 5-6 cm |
| Thickness of parenchyma (kidney tissue) | 1-2-3 mm |
In children, the size of the kidneys varies depending on age. From birth until reaching 80 cm in height, the thickness of the kidneys remains unchanged, only the width and length change. At this age, normal kidney characteristics look like this:
| Length | 4.5-6.2 cm |
| Thickness | 4 cm |
| Width | 2.2-2.5 cm |
| Thickness of parenchyma (kidney tissue) | 0.9-1.8 cm |
It should be remembered that the size of any organ may have individual characteristics for each individual person, and if the deviation from normal values is insignificant, this does not indicate the presence of a disease. For example, in those patients who have only one kidney, its size is increased even with normal functioning.
The protocol may indicate the “antero-posterior” dimensions of the kidney, which are normally up to 15 mm. The kidneys should have the same size or differ by no more than 2 cm. Deviations from the norm occur both in the direction of reduction of the organ (tissue atrophy) and in the form of its enlargement (cysts and tumors).
In what cases is ultrasound examination of the adrenal glands performed?
As a rule, ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands is performed simultaneously.
Indications for performing a diagnostic study are:
- Rapid weight gain;
- Sudden changes in blood pressure;
- The appearance of general weakness and loss of performance;
- Kidney injury;
- Suspicion of the presence of an oncological neoplasm;
- In case of violation of the reproductive function of the body;
- When pain appears in the head area, which is regular;
- With difficulty urinating and darkening of the color of urine;
- If there is pain in the lumbar spine for a long time;
- If any of the above symptoms are accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- In addition, ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands and retroperitoneum may be performed to monitor the results of treatment or as part of a preoperative examination.
Position of organs
In the diagnostic protocol, the most common phrase is “the left kidney is slightly higher than the right,” which is the norm, since the liver slightly displaces the right organ. The term “nephroptosis” means prolapse of one of the kidneys and is usually characterized as left- or right-sided.
Additional characteristics of kidney health in healthy people
The shape of the organ is a bean, the outer contour is smooth and clear, the difference in size is acceptable no more than 2 cm. The presence of pathologies is indicated by such signs as: uneven contours, increased echogenicity. They indicate the presence of a tumor or stone.
Parenchyma thickness
Parenchyma is the surface tissue of the kidneys, the structural unit of which is the nephron. It is this structure that serves as the body’s natural filter. Normally, the thickness of the parenchyma should be 15-25 mm, but with age it decreases due to degenerative processes, and for a 60-year-old patient, even 11 mm can be considered a variant of the norm.
Thickening of the parenchyma can be observed in acute edematous inflammatory conditions (acute pyelonephritis), and thinning of the parenchymal tissue indicates long-term degenerative processes: diabetic nephropathy, renal hypertension, chronic pyelonephritis.
Parenchyma changes
When interpreting kidney ultrasound, special attention should be paid to the term “echogenicity”. An increase or decrease in echogenicity indicates a change in the density of parenchymal tissue. The cause of these conditions can usually only be discovered by a urologist, based on the patient’s full range of tests.
Kidney ultrasound can reveal organ cysts, which are usually described in the protocol by the following terms and characteristics: “anechoic formation”, “homogeneous formation without internal echo”. Parenchymal cysts are small bubbles of fluid that are not treated unless they grow abnormally.
A cancerous tumor on ultrasound is described as an “echo-positive formation” with a heterogeneous echostructure and an unclear contour. The shape and size of the neoplasm must also be indicated. Kidney ultrasound is the leading method for detecting malignant tumors of these organs.
Changes in the pelvis
Here you should be wary of such verbal forms as “microcalculosis” or “calculi”, which will indicate the presence of stones or sand in the kidneys. Cancer of the renal pelvis can also be diagnosed, but in the transcript it will be described, like formations in the parenchyma, but indicating the location.
The interpretation of kidney ultrasound should be entrusted to an experienced urologist or nephrologist in order to make the correct diagnosis and develop the correct therapeutic strategy.
How much does a kidney ultrasound cost?
At the Diana Clinic in St. Petersburg, an ultrasound of the kidneys costs 1000 rubles. The cost of this study in other clinics may vary significantly. This is due to the policy of private clinics. We do not inflate prices, so it is profitable to have an ultrasound of the kidneys in our clinic.
Where to do an ultrasound of the kidneys in St. Petersburg
Kidney ultrasound in St. Petersburg should be performed at the Diana clinic, since the highly qualified medical staff will allow you to get a quick and high-quality result. Our patients are also satisfied with our loyal pricing policy.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
The structure and features of the functioning of the adrenal glands in the human body
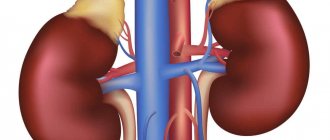
Anatomically, the adrenal glands are located in close proximity to the upper pole of the kidneys. The organs are paired, but not symmetrical: the right gland has the shape of a triangle, and the left one is oblong, and seems to lie along the surface of the kidney, encircling it with a crescent. The right adrenal gland is narrower and located higher than the left. It is directly adjacent to the inferior vena cava, and, except for a small part of the anterior surface, is not covered by the peritoneum. Only the lower region of the anterior plane of the organ comes into contact with the liver, leaving a slight depression on it in this place. The left adrenal gland is located in the area of the upper pole of the left kidney, closer to its medial surface. In front, in its upper section, the left adrenal gland is covered with peritoneum. The left adrenal gland is adjacent to the cardiac part of the stomach, and is located next to the spleen and pancreas.
The structure of the adrenal glands is represented by the anterior and posterior surfaces, as well as the concave renal surface - the part that lies on the kidneys. The anterior and posterior planes have grooves. One or more grooves are visible on the anterior surface of the adrenal glands. The deepest groove is the so-called “gate” (hilus), through which the adrenal vein emerges. The lymphatic vessels of the adrenal glands are also located in the hilum area, and the adrenal arteries can supply blood to the organ from the anterior and posterior surfaces.
The size of the organs is quite small and does not change significantly during a person’s life. The size and weight of the adrenal glands vary from person to person. Their weight in humans at different ages can range from 6 to 20 grams. The length of the right adrenal gland in an adult varies from 1 to 2 centimeters, while the width should not exceed 1.5 cm and the height - 1-2 cm. The width of the left adrenal gland ranges from 0.9 to 1.7 cm, length and height ranging from 1.4 to 2.6 cm.
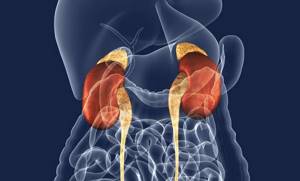
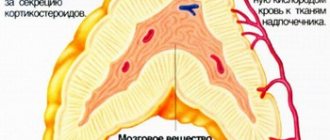
The structure of the organs is:
- fibrous capsule;
- cortex;
- brain matter.
The fibrous capsule is a thin layer of fibrous tissue containing muscle fibers. Processes extend into the thickness of the gland from the outer shell.
The cortex is thicker than the medulla, and is yellowish-brown in color, formed by glandular and connective tissue. It is responsible for the production of corticosteroids - steroid hormones with glucocorticoid or mineralocorticoid activity.
The structure of the adrenal cortex is represented by:
- zona glomerulosa under the adrenal capsule;
- fascicular zone;
- reticular zone surrounding the medulla.
Mineralocorticoids are produced in the zona glomerulosa. These include aldosterone. Thanks to the production of this hormone, calcium ions are secreted into the urine, as well as sodium ions are reabsorbed into the circulatory system in the kidneys.
Glucocorticoids, including cortisol, are produced in the zona fasciculata. With its participation, almost all metabolic processes in the body occur, and the functioning of the cardiovascular system, kidneys, and the functioning of the nervous system is also regulated.
The zona reticularis of the adrenal gland produces sex hormones, including dehydroepiandrosterone and androgens.
They influence the development of secondary sexual characteristics, protein synthesis and the ability of muscles to contract.
The medulla makes up about 10% of the total mass of the adrenal gland. It is located under a thick layer of the cortex, inside the organ. Its cells produce adrenaline and norepinephrine. These hormones help increase blood pressure and activate the heart muscle, and also affect metabolic processes.