Diagnostic laparoscopy is a modern diagnostic method, which is considered one of the most informative and reliable. As a rule, laparoscopy is performed on the abdominal and pelvic organs, which is reflected in the very name of the procedure: the term “laparoscopy” is a derivative of the Greek words “womb” and “to look”. Synonyms for the concept of “laparoscopy” are “peritoneoscopy” and “ventroscopy”. This procedure involves examining internal organs through small holes using a special instrument called a laparoscope.
Laparoscopic diagnosis is carried out if other types of examination turned out to be insufficiently informative.
Historical reference
Before the advent of laparoscopy, the only way to examine the abdominal organs was laparotomy. In other words, the patient’s abdomen was cut open and examinations and operations were performed through this incision. Laparotomy was a difficult and painful procedure for the patient. Scars remained on the anterior abdominal wall, the risk of complications was incredibly high, and the patients recovered very slowly.
Diagnostic laparoscopy was first discussed at the beginning of the 20th century, but the technique remained practically in its infancy until the 1960s.
Content:
- Historical reference
- Indications for the procedure
- Contraindications for diagnosis
- Benefits of diagnostics
- Disadvantages of the procedure
- Diagnostic laparoscopy in gynecology
- Preparing for diagnostics
- Methodology for diagnostic laparoscopy
- Regimen after diagnostic laparoscopy
The pioneer of laparoscopy is the Russian obstetrician-gynecologist Dr. Ott. It was he who, in 1901, first performed an endoscopic examination of a patient's abdominal cavity using a frontal reflector, an electric lamp and a mirror. He called his method ventroscopy. In the same year, in Germany, Professor Kelling conducted the first endoscopic examination of the abdominal organs in animals.
During the 1920-1930s, a large number of publications devoted to endoscopic studies appeared. Their authors were scientists from Switzerland, Denmark, Sweden and the USA. They extol laparoscopy as a highly effective method for diagnosing liver disease. During the same period, the first, still extremely imperfect, laparoscopes appeared. In the 1940s, the design of devices for laparoscopy was improved, and laparoscopes equipped with devices for biopsy appeared. During the same period, laparoscopy began to be used in gynecology.
In the 1960s, laparoscopy began to be actively used for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the abdominal organs.
Application area
Laparoscopy cannot be performed without modern equipment, so such operations are performed exclusively in equipped clinics. The method is used for the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies of the peritoneum and pelvic organs.
Laparoscopy capabilities:
- diagnosis of tumors in the peritoneum and pelvis;
- determination of treatment for various conditions (endometriosis, adnexitis);
- identification and treatment of causes of infertility;
- obtaining tissue for biopsy;
- assessment of the spread of the cancer process;
- damage detection;
- sterilization;
- determining the causes of pelvic pain;
- removal of the uterus, ovaries, gall bladder, appendix, spleen;
- complex resections (removal of the colon).
Laparoscopy is performed according to all surgical rules. It is allowed to carry out both planned operations with additional preparation and examination, and emergency operations necessary to save a person’s life.
Indications for elective laparoscopy:
- Sterilization.
- Endometriosis (overgrowth of the endometrium of the uterus).
- Recurrence of endometrial hyperplasia.
- Myoma and other benign pathologies of the uterus.
- Pathologies causing infertility.
- Tumors and cysts in the ovaries.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Defects in the anatomy of the genital organs (congenital and postoperative).
- Chronic pelvic pain syndrome.
Indications for urgent laparoscopy:
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Cyst rupture.
- Ovarian apoplexy (tissue rupture accompanied by hemorrhage).
- Complications of benign formations in the uterus (hemorrhage, tissue death).
- Torsion of the appendages.
- Bleeding due to adenomyosis (growth of the endometrium into the layers of the uterus).
- Acute lesions of the fallopian tubes, accompanied by inflammation.
- Differential diagnosis in the presence of unclear symptoms of acute pathology.
Thanks to innovative devices, the doctor is able to monitor the process and make cuts with perfect precision. Laparoscopy has significantly reduced the percentage of medical errors, but such an operation can only be trusted by a professional.
Indications for the procedure
Today, diagnostic laparoscopy is in the stage of active development. It is used in various fields of medicine, since this diagnostic method makes it possible to choose the right treatment tactics and subsequently carry out radical surgery without laparotomy.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is indicated for various diseases of the abdominal cavity. So, with ascites, this diagnosis makes it possible to identify the root causes of the appearance of fluid in the abdominal cavity. In case of tumor-like formations of the abdominal cavity, the doctor, during diagnostic laparoscopy, has the opportunity to carefully examine the formation and perform a biopsy. For patients suffering from liver diseases, laparoscopy is one of the safest methods that allows you to obtain a piece of organ tissue for research. In addition, diagnostic laparoscopy is used in gynecology for a more complete diagnosis of patients suffering from infertility, endometriosis, uterine fibroids and cystic formations in the ovaries. Finally, the doctor may recommend diagnostics for pain in the abdomen and pelvic area of unknown etiology.
Contraindications for diagnosis
Since diagnostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure, the list of contraindications for this procedure should be taken extremely seriously.
Thus, there are absolute and relative contraindications for this research method. Laparoscopy is strictly prohibited in case of hemorrhagic shock caused by severe blood loss and in the presence of adhesions in the abdominal cavity. Also reasons for refusing the procedure are liver and kidney failure, acute form of cardiovascular diseases, and lung diseases. Laparoscopy is contraindicated in cases of severe bloating and intestinal colic, as well as in cases of ovarian cancer.

Relative contraindications for diagnostics are allergies to several types of medications, the presence of large fibroids, a gestational age exceeding sixteen weeks, and diffuse peritonitis. The procedure is not recommended if the patient suffered from an acute respiratory viral infection or a cold less than four weeks ago.
Benefits of diagnostics
Compared to laparotomy, laparoscopy has a huge number of advantages:
- First of all, this method is minimally invasive. In other words, the surgical effect is very gentle, the risk of infection is minimal, and blood loss is practically absent. In addition, since the peritoneum is not damaged, adhesions will not form after the procedure. The pain syndrome is also minimal, since during abdominal operations the source of the main discomfort is the sutures placed on the incision. The cosmetic effect is also important - after laparoscopy, unaesthetic scars do not form, which are the result of laparotomy.
- In addition, after laparoscopy the patient recovers faster. Due to the fact that there is no need to adhere to strict bed rest, the risk of blood clots is reduced.
- Finally, diagnostic laparoscopy is a highly informative diagnostic method, which makes it possible to literally “shed light” on the condition of internal organs, find out the etiology of the disease and select the optimal method of therapy. By displaying a multiply magnified image of the internal organs on the screen, the doctor is able to study the tissues in detail from different angles.
Laparoscopic removal of an ovarian cyst: features of the operation
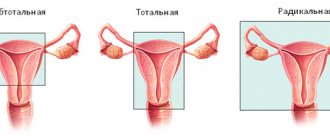
Treatment of ovarian cysts, depending on the type of disease, tumor size and symptoms, can be carried out with medication or surgery. Laparoscopy of an ovarian cyst is one of the types of surgery to remove a tumor. The peculiarity of this method of therapy is minimal intervention and a short rehabilitation period.
Surgery is performed to completely remove the tumor and preserve the woman’s reproductive function. Removal of an ovarian cyst by laparoscopy, the cost of which is higher than laparotomy, has a number of advantages:
- low probability of formation of adhesions;
- small amount of tissue dissection, rapid wound healing and restoration of performance;
- minimal impact on nearby organs;
- absence of cosmetic defects after wound healing.
When choosing treatment methods, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital give preference to gentle and minimally invasive methods. On the territory of the medical institution there is a modern diagnostic center where you can undergo a comprehensive examination, on the basis of which a woman can be prescribed laparoscopy for an ovarian cyst in Moscow.
Disadvantages of the procedure
However, like all medical procedures, diagnostic laparoscopy has not only advantages, but also disadvantages.
First of all, it is necessary to take into account that this diagnosis is carried out under general anesthesia. The effect of this type of anesthesia on each organism is strictly individual, and therefore before carrying out the manipulation it is necessary to carry out all the necessary studies to avoid complications.
In addition, if the doctor performing the diagnosis is insufficiently qualified, there is a risk of injury to organs when inserting instruments. Due to the fact that the doctor operates instruments “remotely,” he sometimes cannot adequately assess the force applied to the tissues. Tactile sensations are reduced, which can complicate diagnosis if the doctor does not yet have enough experience.
Possible complications
The number of unpleasant consequences after laparoscopy is minimal, as is the chance of their development. After traditional operations with large incisions, complications occur much more often. The low invasiveness of the method allows you to reduce the list of possible complications during and after the operation. This became possible with the use of special instruments that almost do not affect tissues and organs that are not subject to surgery.
However, there is always a risk of injury to internal organs and blood vessels from trakars. Sometimes after laparoscopy bleeding occurs, usually minor. When gas is injected, subcutaneous enphysema may form. Complications of laparoscopy include bleeding that occurs when the vessels in the operated area are insufficiently cauterized. Most of the consequences of the operation are mild and reversible.
Undoubtedly, laparoscopy is a tremendous achievement in medicine. This operation greatly simplifies the treatment of many gynecological pathologies, allowing women to quickly return to their normal rhythm of life without complications.
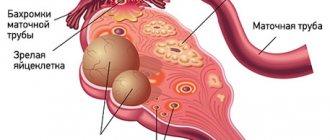
Diagnostic laparoscopy in gynecology
Diagnostic laparoscopy is widely used in gynecology. During the procedure, the doctor may conduct a detailed examination of the woman’s internal genital organs: the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes.
Gynecological laparoscopy is performed either under general anesthesia or local anesthesia in combination with sedation. The method for performing it is almost the same as for conventional laparoscopy. A cannula is inserted into the abdominal cavity, through which gas enters, as a result of which the abdominal wall is raised into a dome. Next, a small incision is made through which the trocar is inserted. The latter is used to insert a tube equipped with a video camera lens and a light bulb into the abdominal cavity. The image of the pelvic organs is displayed on the monitor, and the progress of diagnostic laparoscopy is recorded on an information medium.
In gynecology, diagnostic laparoscopy is indicated when the cause of diseases of the reproductive system cannot be identified using ultrasound and x-ray methods. In particular, diagnostic laparoscopy can be used in gynecology to identify the cause of pain, clarify the nature of tumor formations in the pelvis, and confirm previously diagnosed edometriosis and inflammatory diseases. This procedure also helps to check the fallopian tubes and identify the cause of their obstruction.
Treatment of gynecological pathologies
In addition to visual examination and taking a biopsy for research, laparoscopy is also used to eliminate pathological processes in the reproductive system. For this purpose, new hardware technologies are used: • Laser destruction, laser vaporization - the use of a laser to remove pathological areas of affected organs (the “evaporation” effect); • Electrocoagulation is a method of cauterizing pathological areas with electric current; • Radio wave method is a non-contact method of cutting and coagulating soft tissues using high frequency radio waves • Ultrasound scalpel is a device for cutting and coagulating (cauterizing) tissues using ultrasound, with minimal thermal damage to tissues.
Their use minimizes the risk of complications and accelerates healing, as well as reduces blood loss during and after surgery.
After the procedure, the punctures are sutured or taped if their diameter is less than 5 mm.
Preparing for diagnostics
In order for the diagnostic laparoscopy procedure to be carried out without complications and to be as informative as possible, it is necessary to conduct a number of preliminary examinations and follow the recommendations of doctors.
It is recommended to begin preparations for routine diagnostic laparoscopy approximately one month before the procedure. During this period, the patient must undergo the most thorough examination, including a complete medical history, as well as laboratory diagnostics and consultations with specialists. Doctors must find out what diseases the patient has previously suffered, whether he has had serious injuries, or whether he has undergone surgical interventions. It is imperative to check for any allergic reactions to medications.
To find out whether the patient suffers from diseases that may be considered as contraindications for diagnostics, it is necessary to visit a cardiologist, therapist, gynecologist and other specialists. Ultrasound, fluorography and a standard blood test are also performed, as well as a coagulogram, tests for HIV, hepatitis and syphilis. The blood type and Rh factor are determined in case complications arise.
Despite the fact that this surgical procedure is considered relatively safe, patients must be informed about all the details of the procedure and possible pitfalls.
Two weeks before testing, it is usually recommended to stop taking blood thinning medications. In addition, the diet is adjusted. It is usually recommended to minimize or completely eliminate spicy and fried foods, smoked foods, and dishes that stimulate gas formation from the menu. Two to three days before the laparoscopic examination, it is necessary to reduce the amount of food taken, and the day before, reduce it to a minimum.
Dinner the night before the procedure should be very light. Doctors usually recommend a cleansing enema in the evening.
Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed exclusively on an empty stomach. Immediately before the operation, an anesthesiologist is consulted.
Methodology for diagnostic laparoscopy
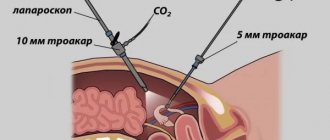
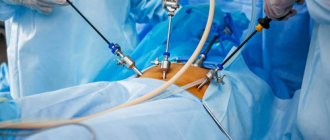
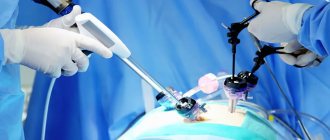
As noted above, laparoscopic diagnosis is most often performed under general anesthesia. It begins with a puncture of the abdominal cavity, after which heated carbon dioxide is injected into it. This is necessary in order to increase the volume of internal space - this way the doctor can more easily manipulate the instruments and examining the organs will not be difficult.
After this, small incisions are made at certain points in the abdomen, into which a laparoscope is inserted - an instrument with which organs are examined and all manipulations are monitored. The laparoscope is equipped with a high-resolution video camera that displays the image on the screen.
If necessary, several more punctures are made on the anterior abdominal wall, through which various manipulators are inserted, allowing, for example, to perform a biopsy or cut adhesions. After inserting the laparoscope, the doctor begins to examine the upper parts of the abdominal cavity and assess the condition of the organs.
Once the operation is complete, the instruments are removed, gas is removed from the abdominal cavity, and the small incisions are treated with antiseptic and stitches.