What is bilirubin?
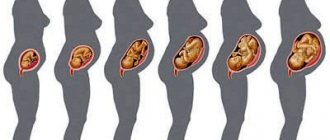
Just over half of newborns become noticeably icteric in the first week of life. This infantile jaundice usually goes away in 2-4 weeks. What causes jaundice in children? Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes caused by hyperbilirubinemia - that is, an increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood serum.
Bilirubin is a yellow-orange natural pigment that is released during the natural breakdown of red blood cells - erythrocytes: as a result of the breakdown of hemoglobin into unconjugated bilirubin. The liver clears the blood of excess bilirubin by filtering it out and converting it from the free form (unconjugated) to the bound form (conjugated with glucuronic acid), which enters the bile and digestive tract, exiting along with the stool, giving it its characteristic color.
Is jaundice in newborns dangerous?
Neonatal jaundice is common among healthy newborns, and most cases are physiological. In adults and a small proportion of newborns, jaundice is pathological, that is, it means the presence of a disorder that causes it. Some of the most common causes of newborn jaundice include:
Physiological:
- Physiological hyperbilirubinemia.
- Breastfeeding jaundice.
- Breast milk jaundice.
Pathological:
- Hyperbilirubinemia due to hemolytic disease.
- Liver dysfunction (eg, caused by parenteral nutrition causing cholestasis, neonatal sepsis, neonatal hepatitis).
Physiological hyperbilirubinemia occurs in almost all newborns. The shorter lifespan of red blood cells in newborns increases bilirubin production, and low levels of bacterial flora in the intestines (which convert bilirubin into an insoluble form)
in combination with increased hydrolysis of conjugated bilirubin, they increase enterohepatic circulation, as a result of which the liver will not be able to cope with excess incoming bilirubin. As a result, bilirubin levels may rise to 308 µmol/L by 3–4 days of life (by 7 days in Asian infants) and then decline.
Breastfeeding jaundice develops in one sixth of infants during the first week of life. Breastfeeding increases the circulation of bilirubin from the intestines to the liver in some infants who do not consume enough milk and who are dehydrated and calorically deficient.
Jaundice from breast milk is different from jaundice from breastfeeding. It develops after the first 5-7 days of life and reaches a peak after about 2 weeks. It is thought to be caused by increased concentrations of beta-glucuronidase in human breast milk, which causes an increase in the conversion of insoluble bilirubin back to the soluble (unconjugated) form and its reabsorption in the colon.
Still have questions?
Get an online consultation from leading pediatricians in St. Petersburg!
A professional and experienced pediatrician will answer your questions.
Medical care for a child without leaving home at a convenient time.
sign up for a consultation
A Skype consultation lasts 45 minutes.
When should you contact a pediatrician for newborn jaundice?
If jaundice in a newborn lasts longer than usual, you should contact your pediatrician as soon as possible, since indirect bilirubin in high concentrations has a toxic effect on the child’s brain cells and causes so-called bilirubin encephalopathy.
Bilirubin encephalopathy is manifested by the child's lethargy, apathy, the baby begins to suck worse, burps more, and his gaze becomes “wandering.”
If treatment is not started in time, damage to the nervous system can lead to irreversible consequences such as cerebral palsy, paralysis, paresis, deafness, mental retardation, etc. For severe hyperbilirubinemia, treatment is a total blood transfusion.
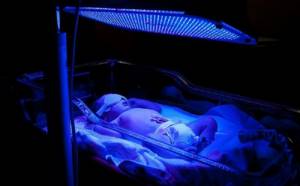
Phototherapy - treatment of jaundice at home.
For phototherapy of newborns, special blue light lamps (photoirradiators) are used. Treatment takes several days, the duration of therapy is determined by a pediatrician. Photoisomerization of bilirubin occurs in the skin, therefore, the larger the body area used for phototherapy, the more effective the treatment process. The lamp is a bath made of harmless plastic, in the base of which blue light lamps are mounted.
We have prepared an article about phototherapy, as well as information on where to rent a device in St. Petersburg: Phototherapy at home - treatment of jaundice
Bilirubin in the blood of a newborn
What is bilirubin
Bilirubin is a bile pigment. It gives color to bile.
Where is it formed and how is it excreted from the body?
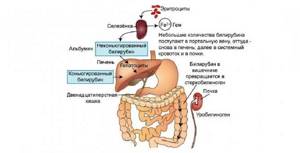
Bilirubin is a product into which iron-containing proteins in our body, such as hemoglobin and cytochromes, are broken down. If we consider the path of hemoglobin breakdown, the following substances are formed: verdoglobin, then biliverdin, then bilirubin. This occurs as a result of the action of a system of phagocytic mononuclear cells, for example, in the spleen.
The breakdown of 1 g of hemoglobin produces 34 milligrams of bilirubin.
Bilirubin circulates in the blood plasma along with albumin. In this form it is called free (indirect) . It is then carried by the bloodstream to the liver. The process of conjugation (binding) with glucuronic acid occurs in the liver. This form with acid is called conjugated (bound, direct) bilirubin . It then enters the bile duct and bile.
Thus, bilirubin enters the intestine, where, under the influence of intestinal microflora, it is converted into mesobilirubin . It can then be converted into urobilinogen and excreted in the urine. Another way is the formation of stercobilinogen , which is excreted in the feces. All these substances impart color to the biological material with which they are excreted from the body.
Do not confuse bilirubin with stercobilinogen and urobilinogen. The presence of bilirubin in the urine is a clear sign of a pathological condition.
How to distinguish physiological jaundice from pathological?
Jaundice that develops in the first 24-48 hours of life or persists longer than 2 weeks is most likely pathological.
Jaundice that does not appear until 2–3 days of life is most likely physiological.
An exception is pathological jaundice due to Crigler-Najjar syndrome, hypothyroidism or drug exposure, which also manifests itself after 2-3 days. In this case, the bilirubin concentration peaks in the first week, increasing at a rate of up to 86 µmol/L per day, and may persist for a long period.
What else is important to know about newborn jaundice?
If jaundice appears in a newborn baby, you should contact your pediatrician and find out the reasons for its appearance in order to correctly determine treatment tactics. It is important to know that constipation and insufficient fluid in the child’s body delay the natural excretion of bilirubin. It is important that a newborn baby has bowel movements every day and that the baby receives enough fluids. During this period, it is recommended to breastfeed the baby 8-12 times a day, without a night break.
Diagnosis of jaundice in children
The diagnosis of hyperbilirubinemia is suspected by the color of the infant's skin and whites of the eyes and confirmed by measuring serum bilirubin.
The level of serum bilirubin required to cause jaundice varies depending on skin tone and body area, but jaundice usually becomes visible on the whites of the eyes when higher than normal and concentrations range from 34 to 51 µmol/L, and on the face from approximately 68 to 86 µmol/l. As bilirubin levels increase, jaundice progresses from the head to the feet, appearing in the umbilicus at approximately 258 µmol/L and in the legs at 340 µmol/L.
Bilirubin concentration > 170 µmol/L in preterm infants or > 308 µmol/L in full-term infants requires additional tests: hematocrit, blood smear, reticulocyte count assessment, direct Coombs test, total serum bilirubin and serum direct bilirubin concentration, blood group and Rh comparison -baby and mother factors.
Recommendations for parents after discharge
If your child has high bilirubin levels, you should not switch to feeding formulas in the first six months.
Doctors also advise walking with your child in the fresh air. Ultraviolet light will fulfill its function of reducing bilirubin in the blood. If necessary, they prescribe drugs that activate the liver and eliminate bilirubin.
If, when you donate blood again for bilirubin, its value does not reach normal by 2 months, this indicates a clear pathology. Therefore, you should consult a doctor for a full examination.
Is physiological jaundice dangerous in infants?
Although the increase in bilirubin concentration in physiological jaundice is not caused by disease and goes away over time, hyperbilirubinemia is neurotoxic, that is, it causes damage to nerve cells in the child. For example, high concentrations of bilirubin in the blood can cause acute encephalopathy, accompanied by a variety of neurological disorders, including cerebral palsy and sensorimotor impairment. An even more severe consequence of the neurotoxicity of elevated bilirubin concentrations may be kernicterus, caused by the deposition of free (unconjugated) bilirubin in the basal ganglia and nuclei of the brain stem. Typically, bilirubin bound to serum albumin remains in the intravascular space, but sometimes it can cross the blood-brain barrier:
- With a high concentration of bilirubin in the serum (acute or chronic).
- When the concentration of serum albumin decreases (for example, in premature infants).
- When bilirubin is displaced from albumin by competitive binders (drugs:
- sulfisoxazole, ceftriaxone, aspirin) or free fatty acids and hydrogen ions (for example, in malnourished and starving children).
For neonates born at less than 35 weeks' gestation, the threshold bilirubin levels for treatment are lower because preterm infants are at greater risk of neurotoxicity.
What methods in a hospital reduce the level of bilirubin in the blood of newborns?
Bilirubin has this peculiarity: in sunlight, its content in the body decreases. This is used to speed up the reduction of bilirubin in children. They are placed under a lamp with ultraviolet rays.
Medicines may be prescribed that bind and remove bilirubin and activate the liver.
In particularly severe cases, if bilirubin continues to rise and there is a risk of brain damage (hemolytic disease), significant blood transfusions are resorted to.
Recommendations before taking blood from a vein
To avoid excessive anxiety of the baby during blood sampling from a vein, it is advisable to carry it out in a trusted medical institution with experienced staff.
Please be understanding if you are asked to leave during the procedure. There is no need for unnecessary nervousness, because nothing terrible can happen in a few minutes of your absence. If a clinic practices taking blood from a baby without the presence of his parents, this means that this method is productive, and also that it has been tested by long-term practice. So don't doubt that everything will be fine.
In order to distract the child, you should take with you his favorite rattle or a new toy that will interest the baby and help him quickly forget such an unpleasant process.
After the procedure, give your child positive good emotions - kiss and hug him and be sure to do his favorite thing - watch an interesting cartoon, assemble a pyramid, read a book so that he cannot remain negative.
Taking blood from a vein is an alarming process not only for babies, but also for their parents. Due to the painful sensations, the child will experience slight discomfort, but it will disappear without a trace after a few minutes. Be sure that what is happening is necessary, try not to create panic, and then your example will help the child behave more calmly. Be always healthy!
What to do if your baby has neonatal jaundice?
- Consult with a pediatrician at one of our medical centers, or call a pediatrician at your child's home.
- If there are indications for phototherapy, the pediatrician will tell you what kind of lamp is needed for treatment, what course of phototherapy is needed, and how to conduct phototherapy sessions at home.
- At any children's medical center you can rent a lamp for phototherapy of newborn jaundice for the required period
- After finishing therapy, be sure to show your child to the pediatrician again. A repeated consultation with the pediatrician is necessary to make sure that the treatment was successful and the child is healthy.
How to reduce high bilirubin in a 1 month old baby
You can reduce high bilirubin in a child at 1 month by the following measures:
- phototherapy sessions - for this purpose special lamps are used, which can be compact for home use or voluminous for use in hospitals;
- frequent feeding of the child - applies only to breastfeeding, when mother's milk will “work” as a cleanser: bowel cleansing will improve, urination will become more frequent.

Such therapy is appropriate only if physiological jaundice is diagnosed; sometimes doctors prescribe an intravenous infusion of glucose solution, but the injections do not have any therapeutic effect.
If a child is diagnosed with pathological jaundice, then treatment is carried out with medications and is aimed, first of all, at stopping the progression of the underlying disease. For example, if an infectious liver lesion is diagnosed, then it is advisable to carry out therapy with antiviral, antibacterial drugs and hepatoprotectors.
Symptoms of changes in total bilirubin in a one-month-old baby
The first symptom of a change in the level of total bilirubin in a one-month-old baby is considered to be yellowing of the skin: first the dermis becomes slightly lighter, then acquires a yellowish color, which over time becomes brown and orange. Particularly worrying signs are:
- weakening of the sucking reflex;
- sleep disturbance – it becomes short-term and restless;
- the eye sclera becomes yellow;
- limb spasms;
- lack of appetite;
- general lethargy, decreased response to sounds and light.
When examining a child with similar symptoms, a pediatrician can diagnose an enlarged liver and spleen, as well as low blood pressure - this also applies to characteristic signs of increased total bilirubin.
What is important for making a diagnosis?
To make a diagnosis, it is important to take into account not only the indicators of total and direct bilirubin; doctors must analyze data on ALT and AST indicators - this refers to a biochemical blood test. This abbreviation refers to enzymes that are responsible for metabolic processes at the cellular level. A comparison of the data obtained will give the doctor a complete clinical picture of how impaired the functioning of organs and systems is.
Parents can see for themselves the results of a child’s blood test at 1 month for bilirubin; next to the results obtained, the norms for this age are written. But drawing any conclusions, making diagnoses, and even more so taking therapeutic actions on your own is strictly prohibited.
Indications for phototherapy
Indirect hyperbilirubinemia of newborns (including immaturity of liver enzymes, conjugative hyperbilirubinemia, hemolytic disease of newborns, Rh conflicts).
Contraindications for phototherapy:
- presence of a diagnosis of “Porphyria” in the family history or in the child
- with a significant increase in the concentration of direct bilirubin
- use of photosensitizing medications.
Recommended phototherapy regimen:
In recent years, continuous and intermittent phototherapy regimens have been proven to be equally effective, with:
- the maximum break between phototherapy sessions is no more than 2–4 hours;
- phototherapy sessions should be repeated regularly;
- the optimal phototherapy regimen for most newborns with conjugative hyperbilirubinemia is sequential alternation of phototherapy sessions with breaks for feeding;