Cardiotocography is a parallel recording of uterine contractions and fetal heartbeat. The frequency of a baby's heartbeat in the womb can be influenced by the following factors: gestation period, time of day and the presence of various risk factors. To get a more accurate CTG result, there is no point in performing it earlier than 30 weeks.
The heartbeat can also be heard well during an ultrasound, but CTG provides a more holistic picture of development. Cardiotocography recording is carried out for 30-60 minutes and it is expected that the child will be active during this time and not sleep. Otherwise, erroneous results will be obtained.
To decipher the recording results, a rating system with a 10-point scale is most often used. Each parameter can be scored - “0”, “1” or “2”. When receiving an answer after recording cardiotocography, pregnant women often ask themselves: what does a CTG score of 8 mean? Is this normal? How does the baby feel and how will this affect the upcoming birth?
What do CTG readings mean during pregnancy?
Cardiotocography indicators are necessary for a qualitative assessment of the intrauterine state of the child. How do you know if your baby has enough oxygen? How to decipher CTG during pregnancy - read below.
Baby's basal heart rate
The basal rhythm - abbreviated as BHR - determines the frequency with which the fetal heart contracts over a specific period of time. The printout of the analysis results usually indicates the heart rate range - two numbers characterize the lower and upper limits of normal.
Basal rate variability
The study shows frequency pulses of the amplitude of fetal cardiac activity. Fluctuations are defined as the level of deviation from the base threshold of the basal rhythm in vertical amplitude. Frequency is the range of number of oscillations per minute. Based on variability, CTG analysis provides the following indicators of basal rhythm:
- monotonous - up to 5 vibrations per minute;
- easily undulating - up to 10 amplitudes;
- undulating - range from 10 to 15 vibrations per minute;
- saltatory - varies from 25 to 30 amplitudes.
Dawes-Redman tests
These criteria are used for computer evaluation of cardiotocograms performed on automatic devices. The computer evaluates the recording according to the same parameters specified above. The result of the recording is a special indicator of variability - STV (short-team variation), based on the total assessment of all significant criteria of the cardiotocogram.
- STV 6-9 ms are normal indicators indicating the complete well-being of the fetus.
- STV 5-3 ms are borderline and clearly suspicious indicators that require close attention from doctors.
- STV 2.6-3 ms – a high risk of fetal hypoxia, requiring rapid action by medical workers.
- STV less than 2.6 is a fatal condition of the fetus, which within the next few hours will end in its death in the womb.
- A feature of STV is the absence of its upper limit, that is, indicators of 10 or more, with other recording standards maintained, are completely normal.
The Dawes-Redman system is not used during labor, but is successfully used to monitor pregnant women. On average, CTG is recorded once every 2-3 weeks at 28-32 weeks, once every 2 weeks at 32-37 weeks, and once a week during full-term pregnancy.
Normal, questionable and pathological CTG indicators during pregnancy, including FIGO
Norms and deviations of CTG during pregnancy:
- BHR - in the range from 120 to 160 vibrations per minute. A discrepancy between the parameters according to the lower criterion indicates bradycardia. According to the upper level, there is a risk of developing tachycardia;
- basal rhythm - within 10-25 in 60 seconds. Everything that falls within this norm indicates the normal development of the baby. A low threshold for sleep variability is normal. When awake - pathology. Most often it is a lack of oxygen;
- acceleration - CTG norm - 2 or more. Recall that they are visible as tall spikes on the graph;
- decelerations are absent normally;
- non-stress test values - determine motor activity. Normally, its episodes coincide with acceleration.
Assessment of fetal condition - points
To assess the condition of the fetus, doctors use scoring methods. Women often raise reasonable questions about what 4 or 5-6 points on CTG mean, which can be indicated by 10, 11 or 12 points. The interpretation depends on the calculation method used by the program or how the doctor calculated the result if the assessment was done “manually”.
The most commonly used system is the Fisher grading system.

By Fischer
Fisher scoring table (Krebs modification):
| Indicator determined on CTG | 1 point is awarded if: | 2 points are awarded if: | 3 points are awarded if: |
| Base heart rate | Less than 100 beats/min or more than 100 beats/min | 100-120 beats/min or 160-180 beats/min | 121-159 beats/min |
| Expressiveness of slow oscillations | Less than 3 beats/min | From 3 to 5 beats/min | From 6 to 25 beats/min |
| Number of slow oscillations | Less than 3 during the study period | From 3 to 6 during the study period | More than 6 during the study period |
| Number of accelerations | Not fixed | From 1 to 4 in half an hour | More than 5 in half an hour |
| Decelerations | Late or variable | Variable or late | Early or not fixed |
| Movements | Not fixed at all | 1-2 in half an hour | More than 3 in half an hour |
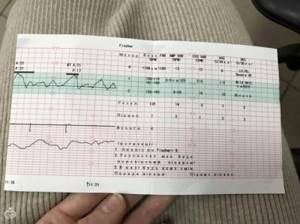
The interpretation of the results looks like this:
9,10, 11, 12 points – the child is healthy and feels quite comfortable, his condition does not cause concern;
- 6, - the baby’s life is not in danger, but his condition is cause for concern, since such an indicator may be a sign of initial pathological changes and adverse external influences. A woman should do CTG more often to monitor the baby’s dynamics;
- 5 points or less – the child’s condition is threatening, there is a high risk of intrauterine death, stillbirth, neonatal death in the early postpartum period. The woman is sent to the hospital, where an urgent diagnosis is carried out and in most cases it ends in an emergency caesarean section to save the baby’s life.

By FIGO
This assessment table was adopted by specialists from the International Association of Gynecologists and Obstetricians. It is used less frequently in Russia than the Fisher assessment, but is more understandable for expectant mothers.
FIGO interpretation table:
| Parameter determined during the study | Meaning – “norm” | Meaning – “doubtful” or “suspicious” | Meaning: “pathology” |
| Basal heart rate | 110-150 beats/min | 100-109 beats/min or 151-170 beats/min | Less than 100 or more than 170 beats/min |
| Variability | 2-25 beats/min | 5-10 beats/min for 40 minutes | Less than 5 bpm over 40 minutes or sinusoidal rhythm |
| Accelerations | 2 or more in 40 minutes | During the 40-minute examination there are no | Absent at all |
| Decelerations | Not registered at all or there are rare variable | Variable | Variable or late |
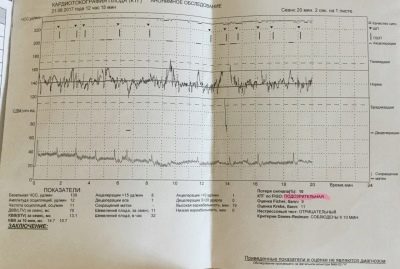
PSP
This is the key value that is derived from all measured and analyzed parameters.
It is very difficult to clearly imagine by what algorithms and mathematical formulas this calculation is carried out if you do not have a mathematician’s diploma on your shelf at home. This is not required. It is enough for the expectant mother to know which PSP indicators are considered normal and what they mean:
- PSP less than 1.0. This result means that the baby is healthy, he is comfortable, his well-being and condition are not impaired. This is a good result, in which the doctor sends the pregnant woman home with a clear conscience after CTG, because nothing bad should happen to the baby.
- PSP from 1.1 to 2.0. This result indicates likely initial changes that differ from normal well-being. Violations with such PSP are not fatal, but they cannot be ignored. Therefore, the woman is asked to come for CTG more often, on average once a week.
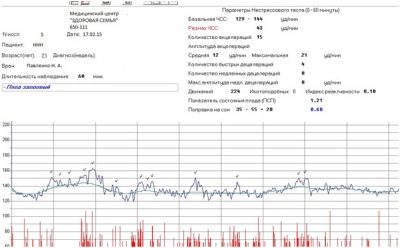
- PSP from 2.1 to 3.0. Such indicators of the fetus' condition are considered very alarming. They may indicate severe discomfort that the child experiences in the womb. The cause of the baby's unwellness may be a Rh conflict, a state of oxygen deficiency, entanglement in the umbilical cord, or intrauterine infection. The pregnant woman is sent to the hospital. She is indicated for a more thorough examination and, possibly, early delivery by cesarean section.
- PSP is above 3.0. Such results may indicate that the child’s condition is critical and he is at risk of intrauterine death, which can occur at any time. The woman is urgently hospitalized and an emergency caesarean section is indicated to save the baby.
What does a “non-stress test” mean with CTG and what are its norms during pregnancy?
A non-stress test is an examination method that determines the baby’s heartbeat over a 20-minute observation period. It is carried out using a non-invasive method. It is considered absolutely safe for mother and child. Indicated from 33 weeks of pregnancy.
In a calm state, the fetal heart makes 110-160 rhythms per minute. If the child is awake and active, the range expands from 130 to 190 oscillations. This is considered the norm.
Additionally, periods of activity are recorded. In this state, the baby's heart beats faster - about 15 beats per minute. Observe this phenomenon for 15 seconds. After 20 minutes, repeat measurements are taken. If the indicators are the same, the test result is normal.
If the number of heart rhythms does not change, the test is negative. The doctor concludes that there are problems with the fetus. An oxytocin test will give a more accurate result - it examines the biophysical profile of the child.
How is cardiotocography done?

In order for this study to be informative, the following rules must be adhered to:
CTG recording is carried out for at least 40 minutes. It is during this time that certain patterns of rhythm changes can be traced.
A pregnant woman should lie on her side during the examination. If a pregnant woman lies on her back during CTG registration, unreliable results may be obtained, which is associated with the development of the so-called inferior vena cava syndrome. This condition develops as a result of pressure from the pregnant uterus on the abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava, which may result in disruption of uteroplacental blood flow. Thus, if signs of hypoxia are obtained on CTG performed with the pregnant woman lying on her back, it is necessary to redo the study.
The sensor that records the fetal heartbeat must be installed in the projection of the fetal back. Thus, the location of the sensor’s fixation depends on the position of the fetus in the womb. For example, with a cephalic presentation of the baby, the sensor must be installed below the navel, with a pelvic presentation - above the navel, with a transverse or oblique presentation - at the level of the umbilical ring.
A special gel must be applied to the sensor to improve the conduction of the ultrasonic wave.
The second sensor (strain gauge) must be installed in the fundus of the uterus
It is important to know that you do not need to apply gel to it.
During the study, the woman must be given a remote control with a button that must be pressed when the fetus moves. This allows the doctor to compare rhythm changes with the baby’s motor activity.
Types of devices
Medical facilities have various options for assessing your baby's heartbeat. Most often, the doctor simply listens to the baby’s heart rhythm using an obstetric stethoscope, but if there is any doubt (or if there is evidence), it is necessary to use a special device. What types of CTG devices are there?
- CTG without automatic analysis
These outdated devices are generally quite rare in modern hospitals, but they can still be found in remote corners of our country. The main inconvenience of these devices is that the doctor must independently evaluate the fetal heartbeat graph. If the doctor has experience and masters this technique, then the effectiveness of these devices is no lower than that of new CTG devices.
- CTG with computer analysis
Modern cardiotocographs not only record the graph, but also independently process the data. The doctor only needs to read the finished result and decide on the need for treatment. This version of CTG is used most often in medicine.
The modern mobile era offers an excellent option for monitoring the baby using a special sensor attached to the skin of the abdomen and a smartphone connected to the Internet. Information about the fetal heartbeat in real time is transmitted to the web portal, processed and provided in the form of a ready-made report to the doctor. Unfortunately, online CTG is still rarely used.
Why is it prescribed?
CTG monitors the rhythm of the fetal heart, the frequency and strength of uterine contractions in a woman. The listed indicators depend on the presence of pathological processes and external factors, so on their basis they make a conclusion about the child’s health. The following factors or symptoms are indications for CTG:
- pathological diagnoses after earlier studies;
- infectious diseases of pregnant women;
- difficulties in bearing first children;
- gene or chromosomal mutations in the parents' families;
- suspicious mobility or passivity of the fetus;
- high or low water levels;
- premature maturation of the placenta;
- threat of early birth during any period of pregnancy;
- conception outside the country, especially in tropical countries;
- vaccination with a drug that disrupts fetal formation;
- symptoms of gestosis;
- drug therapy during pregnancy;
- chronic and autoimmune diseases in pregnant women;
- smoking, drinking and drug addicted mothers.
The presence of these factors increases the risk of developing pathologies; such women should take a particularly responsible approach to the diagnosis of pathologies and undergo a high-precision examination using CTG.
Contractions on a cardiotocogram
In addition to the fetal heart rate and its movements, CTG can record contractile movements of the uterus, that is, contractions. The recording of contractions on CTG is called a tocogram and is also depicted as a graph. Normally, the uterus reacts to the movements of the fetus in it with its contractions (contractions). At the same time, a decrease in the child’s heart rate is recorded on CTG in response to uterine spasms. Contractions are the main sign of impending labor. Based on the tocogram, the doctor can determine the force of contraction of the muscular layer of the uterus and distinguish false contractions from true ones.
Based on all of the above, it is clear that CTG is a very important examination of the condition of the developing fetus in the womb, which allows you to obtain information about the state of the heart rhythm, movements and even evaluate contractions. Any deviations on CTG require a thorough cumulative analysis by a competent specialist in order to take the necessary measures that can save the life of the little man. All these properties make CTG an indispensable type of examination.
Research methodology
Most often, the examination is carried out at 32 - 34 weeks of pregnancy. CTG is performed in the pregnant woman's supine position with a small bolster under her right side (the optimal position is a slight turn to the left side). It is possible to perform CTG in a position lying on your side, or sitting, leaning back in a chair.
- First, the doctor uses a stethoscope to find the point on the abdomen where the baby's heart can best be heard.
- An ultrasound probe is placed on this site, and a probe is placed on the fundus of the uterus to assess muscle tone.
- To notice the baby's movements, the woman is given a special device with a button that she will press when she feels intrauterine movements.
- Recording time is 40-60 minutes.
When CTG is done, the study is carried out using sensors with a frequency of ultrasonic waves of 1.5-2 MHz, which is absolutely safe for the fetus even with prolonged exposure. Any modern device has the ability to assess the vital functions of two fetuses at the same time, which is used in women with twins.
Fisher ten scale
The results of cardiotocography are assessed by specialists on a ten-point Fisher scale, which is based on assigning points from 0 to 2 to each of the above indicators. These scores are summed up, and a general conclusion is made about the information content of CTG and the presence of pathological changes in the fetus. so-called “fetal health indicator” (FSI) is assessed.
- If the total CTG from 1 to 5 , then the baby’s condition in the womb is poor, he is experiencing hypoxia (lack of air).
- What does it mean if the total CTG score is 6-7 ? The child shows initial signs of developing oxygen starvation.
- What does it mean if the sum of CTG points is from 8 to 10 ? This indicates the normal and good condition of the baby.
With a PSP of 1-5 points, immediate delivery is indicated; with a PSP of 6-7 points, repeat CTG is indicated; with a PSP of 8-10 points, continued periodic monitoring of the pregnant woman and fetus using this research method.