The procedure for taking a smear for flora is known to every woman who has visited the examination room. Since the analysis makes it possible to determine the microbiological composition, identify hormonal disorders and inflammatory processes, a smear is taken regardless of whether the woman has health complaints or not.
COST OF A FLORA smear IN OUR CLINIC IN ST. PETERSBURG
| Flora smear price | 500 rub. |
| Production time | 3 days |
| Our laboratories | Helix, LabStory |
| Call free: 8-800-707-1560 *The clinic is licensed to provide these services | |
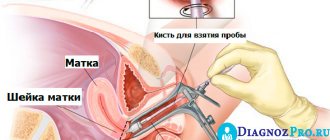
How to take a genital smear
A smear is rarely taken from the labia, unless there are special indications for this, for example, the presence of inflamed areas. In this case, the smear is replaced with a scraping. More often, the gynecologist needs a vaginal smear. It is taken with a spatula from the posterior vaginal fornix, and in case of inflammation - from a visible area.
The resulting material is applied to glass, dried, and a few drops of ethanol are applied on top. The sample is labeled and sent in a closed container to the laboratory.
When an STI is detected, a smear is taken using a swab, which is placed in a sterile tube and submitted for testing.
Many medical institutions practice accepting patients with disposable diagnostic kits. For example, the Juno kit is often used, designed specifically for taking samples of various types (venereological, gynecological). All items are aseptically packaged and have different compositions depending on the nature of the inspection.
- The Juno-0 set consists of examination gloves, a diaper and a Volkmann spoon, which is used to take a sample of the mucous surface of the vagina, urethra or cervix.
- Juno 1 includes a Kuzco mirror instead of a Volkmann spoon. With its help, the examination area is doubled; you can see swelling, tissue coloring, and scars. The doctor's hands are free and he can perform any manipulation.
- “Juno #3” has both a Cusco mirror and a Volkmann spoon. This is necessary so that it is possible to take smears from both the vagina and the cervix or urethra without fear of accidental transfer of microflora.
- Set “Juno” No. 4 additionally has a cytobrush, with which a smear is painlessly taken from the cervical canal.
- “Juno-5” is equipped with an Eyre spatula with micropores at the end; it can be used to take a smear from any surface. Slides are needed to transfer smear material onto them, but usually slides are available in every examination room.
At the Diana Clinic, all disposable consumables are already included in the cost of an appointment or test, so you do not need to carry anything with you.
How to take a smear from the urethra
A smear from the urethra is taken in two ways:
- A Volkmann spoon is inserted into the urethra several centimeters, and epithelial cells are scraped by pressing the applicator against the walls of the urethra and rotating it in different directions. This is a rather painful procedure if there is injury or inflammation of the urethra.
- For heavy discharge, there is no need to place a Volkmann spoon inside the urethra. It is enough to press on the front wall of the vagina so that the contents of the urethra come out. It is then collected by an applicator and placed in a test tube.
Prevention of the appearance of polymorphic rods
To avoid microflora disorder:
- You should not use scented intimate hygiene products or antibacterial soap.
- Try to change pads and tampons as often as possible, and do not leave them in the vagina all day.
- Sex should be protected, reduce the number of casual sexual contacts.
- When purchasing underwear, give preference to cotton products to allow air access to the external genitalia.
- Include fermented milk products, fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet. Limit sweets and sugar, because they do not contribute to the formation of normal vaginal microflora that is resistant to the development of vaginitis.
How to take a smear from the cervix
There are 4 types of cervical smears:
- flora research;
- sterility examination;
- testing for latent infections using polymerase chain reaction;
- Pap test for cytology.
A flora smear from the cervix reveals not only pathogenic bacteria, but also pathogenic epithelial cells.
The procedure is carried out using a Cusco mirror. This mirror is not in the usual sense of the word. It is more like transparent forceps that push apart the walls of the vagina, allowing access to the cervix. Then a scraping is made with a spatula or cytobrush, by which the condition of the epithelial cells is assessed.
Interpretation of the results of gynecological smear tests. Norm
| Index | From the vagina | Their urethra | From the cervix |
| Lactobacilli | Dederlein sticks | No | No |
| Number of rod flora | from + to ++++ | from + to ++++ | from + to ++++ |
| Candida | up to 104 CFU/ml | absent | absent |
| Flat epithelium | 5-10 | 5-10 | 5-10 |
| Leukocytes | 0-10 | 0-5 | 0-30 |
| Red blood cells | 0-2 | 0-2 | 0-2 |
| Slime | moderate amount | absent | moderate amount |
| Gonococcus Gn | absent | absent | absent |
| Trichomonas Trich | absent | absent | absent |
| Key cells | none | none | none |
What do abnormal vaginal smears mean?
Deviations from the norm in a vaginal smear indicate the following:
Low content of Dederlein rods
indicates a poor microbiocenosis with a predominance of pathogenic microflora. Dederlein's rods are elongated lactobacilli that produce lactic acid as a waste product. Thanks to them, an acidic environment in the vagina is maintained, protecting against the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. Lactic acid activates immune cells that fight microbes.
With a decrease in the number of Dederlein bacilli, a woman develops vaginal dysbiosis. This happens during illness, hormonal therapy, taking antibiotics and hormones, severe or prolonged stress, or contracting an STD.
If a small amount of lactobacilli is detected, the woman is additionally prescribed a PAP test for hidden infections. If it does not give a positive answer, then patients are prescribed vaginal suppositories, which suppress pathogenic microflora, helping Dederlein's sticks.
High content of coccal flora
and a decrease in rod flora indicates weakened immunity or activation of opportunistic microflora. The degree of vaginal cleanliness is determined from normocinosis to vaginitis.
- At stage 1 (normocenosis), the acidity of the vagina is pH 3.8 - 4.2, there are many Dederlein rods, no leukocytes, and there are single epithelial cells.
- At level 2 of purity, the number of leukocytes increases to 10, and there are quite a lot of epithelial cells. Acidity increases to pH 4.0 - 4.5.
- At the 3rd degree of purity, the acidic environment is replaced by a slightly alkaline one (pH 5.0 - 5.5), coccal microflora dominates over lactobacilli, leukocytes are within normal limits. 4 degree of purity there are no lactobacilli at all, the environment in the vagina is alkaline (pH 6.0 - 6.5). In addition to various cocci, there are single Trichomonas and key cells.
A normal smear corresponds to the 1st and 2nd degrees of purity. In this case, the “population” of the vaginal mucosa must correspond to the following parameters:
- lactobacilli in the amount of 107-109 CFU/ml (CFU is one microbial cell (colony-forming unit) that actively multiplies in a nutrient medium and forms a colony);
- streptococci up to 105 CFU/ml;
- candida, clostridia, staphylococci, prevotella - up to 104 CFU/ml;
- ureaplasma, mycoplasma – up to 103 CFU/ml;
With grade 3 purity, a woman is diagnosed with bacterial vaginosis - a violation of the natural balance with a decrease in the number of lactobacilli and an increase in the content of gram-negative bacilli.
Also, with grades 3 and 4 of vaginal cleanliness, vaginitis (colpitis) is characteristic - an increase in the amount of opportunistic microflora, accompanied by inflammation of the vaginal surface.
Features of treatment
Features of treatment for polymorphic rod in a smear are as follows:
- Therapy for diseases of this nature is usually prescribed in a comprehensive manner - both for the patient and for his sexual partner. The latter should undergo at least preventive treatment. For example, this is typical when candidiasis is detected.
- It is worth noting that in men, pathogenic changes in the microflora of the genital organs are most often asymptomatic. Thus, a person continues to exist with a hidden pathology, infecting his sexual partner over and over again. Treatment of the second, of course, will be ineffective in this case.
- To restore the normal balance of microflora, the doctor most often prescribes antibiotics. The forms of these medications are varied - tablets, vaginal suppositories, capsules, ointments and topical creams. For therapy to be most effective, a combination of several medications is prescribed.
What pathogens and abnormalities are found in bad smears?
- Candida
is a fungal infection of the vagina, urethra or cervix caused by decreased immunity and vaginal dysbiosis. Every woman has encountered the disease at least once. It is quite easy and quick to treat, but sometimes it indicates a more serious pathology - diabetes mellitus. - An increase in the number of epithelial cells
indicates an inflammatory process, and a complete absence indicates atrophy of the vaginal walls or estrogen deficiency. Flat epithelium is dead, exfoliated mucous cells from the surface of the vaginal walls. They constantly fall off, and new cells are born in their place. Normally, a smear should not contain more than 10 epithelial cells. - Leukocytes
. These are immune cells that fight pathogenic microflora. There are no more than 10 of them in a smear of a non-pregnant woman, and up to 30 of them in a pregnant woman. An increase in leukocytes above normal indicates both nonspecific inflammation (with colpitis, vaginosis) and specific (with STIs). It is imperative to find the source of inflammation. This may be adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages), endometritis (inflammation of the endometrium), vaginal dysbiosis, acute form of candidiasis. - An increase in red blood cells
indicates severe inflammation. Erythrocytes are red blood cells; normally their number should not exceed 2. If there are more of them, this means that small vessels were damaged when the cytobrush came into contact with the vaginal wall. Also, the number of red blood cells increases immediately after menstruation. - A large amount of mucus in the smear
indicates inflammation of the cervix, because mucus is secreted there (the vagina does not have glands). Normally, a woman leaks 4 ml of mucus per day. If it is pinkish in color, and when analyzed, leukocytes are found in it, this indicates inflammation of the cervical canal. Also, the amount of mucus increases in pregnant women. - Gonococci
. These are sexually transmitted microorganisms. This bacterium should not be in the smear. If, in addition, leukocytes and erythrocytes are also high, then the patient needs to take a Pap test and undergo a PRC diagnostic to detect microbial DNA. - Trichomonas
. This is an STI that indicates infection with trichomoniasis. Even one microbe requires urgent treatment. - Key cells
indicate an inflammatory process caused by the entry of STIs into the body, as well as the development of diseases of the reproductive system - cervical erosion, ectopia, endometrial polyps. They appear when the acidic environment of the vagina changes to alkaline. Key cells (this is ordinary squamous epithelium surrounded by pathogenic microorganisms) tend to degenerate, so if at least one of them is detected, a woman should undergo regular examination.
Warning symptoms and signs
Two procedures can determine the polymer rod in the flora of the genital organs - bacteriological culture and the already mentioned smear. But how do you know that you need to go for an emergency examination to the clinic?
Changes in the microflora of the genital organs usually manifest themselves externally in a similar way:
- Large volumes of vaginal discharge with a characteristic grayish, whitish, yellowish tint.
- The smell of the mass is sour, somewhat reminiscent of sour milk or rotten fish.
- There is constant discomfort and itching in the genital area and perineum.
- Sexual intercourse is painful.
- When urinating, discomfort or even pain is experienced.
- Sometimes uncharacteristic discharge comes out of the vagina - with pus, green in color.
- Pain in the perineal area, lower abdomen.
Such symptoms indicate not only changes in the flora, as indicated by a polymorphic rod in a smear. They may also indicate the development of thrush, dysbacteriosis, colpitis, vaginosis, and a number of sexually transmitted infectious diseases.
Normal values of urethral smears
When taking a smear from the urethra, the normal smear is as follows:
| Number of epithelial cells | Leukocytes | Red blood cells | Candida | Slime | Flora composition |
| to 10 | up to 5 | up to 2 | No | No | in small quantities Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria |
- Normally, 95% of the urethral microflora should be lactobacilli. If opportunistic microflora dominates, this indicates a weakened immune system or diseases of the pelvic organs.
- A large amount of squamous epithelium indicates previous inflammatory diseases (cystitis, kidney disease).
- Red blood cells indicate severe swelling caused by the inflammatory process, as well as damage to the urethra.
- White blood cells are higher than normal during inflammation caused by hypothermia, decreased immunity, or infection.
- Yeast, in particular candida, is a consequence of the transfer of infection from the vagina when the disease reaches a serious form. Normally, there should be no yeast in the urethra. As well as mucus, the appearance of which in the urethra indicates infection.
To find out the causative agent of the infection, a bacterial culture is taken from the patient - a laboratory test that allows you to find a competent antibiotic to which there is good sensitivity.
Preparation
Taking a smear for any study requires compliance with a number of requirements and recommendations:
- Refrain from intimate contact at least 2 days before the scheduled examination.
- Do not empty your bladder a couple of hours before taking a smear to ensure more accurate results.
- Perform genital hygiene before going to bed, but you should not do this before visiting a doctor, so as not to wash off the infectious agents.
- A week before sampling, stop taking medications other than those prescribed by your doctor. Notify your urologist about taking medications, especially antibiotics.
Norms of a smear from the cervical canal
A smear from the cervical canal and a scraping from the cervix have different meanings.
Scraping belongs to the field of cytology - identifying pathological proliferation of cells that can degenerate or have already degenerated into cancer. The procedure is performed for girls over 18 years of age.
The smear is carried out from the cervical canal itself. To do this, the walls of the vagina are pulled apart using a speculum, and biomaterial is taken from the canal. The procedure is quite unpleasant, but very informative.
The results of the smear should be as follows:
- Epithelium (dead cells of the mucous membrane) is possible, but not more than 10 units. If there is more of it, this indicates a progressive inflammatory process, not only on the cervix, but also in the fallopian tubes or the uterus itself.
- If in the vagina the number of leukocytes should not exceed 10, then in the cervical canal their number increases to 30. Phagocytosis (increased activity of leukocytes) indicates the active activity of pathogenic bacteria.
- There are no Dederlein rods in the cervical canal.
- Mucus is produced by the glands of the cervix and is therefore found in small quantities in the cervical canal.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment can be represented by the following drugs:
- Pimafucin suppositories and ointments.
- Vaginal tablets and suppositories "Terzhinan". They fight the inflammatory process caused by itching.
- Antibiotics "Cefixin" and "Ceftriaxone". Suppress the metabolism of pathogenic microorganisms, relieve irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Clindamycin and Fluconazole. Medicines that are prescribed by a doctor when a fungal infection is detected.
Please note that only the attending doctor can prescribe medications suitable for the patient, their dosage, time, and frequency of use!
Along with taking medications, you must also adhere to a special diet. It should contain as much fermented milk products as possible, and a minimum amount of sweet and starchy foods.
What to do if the smear results are bad?
The test results are delivered to your hand or sent to the treating gynecologist. If there are deviations from the norm, the doctor prescribes treatment or additional diagnostics.
After completing the course of treatment, you need to take tests again to make sure that the disease has completely gone away. Untreated diseases result in complications and chronic forms. Chronic diseases can only be suppressed, but they cannot be completely eliminated.
SIGN UP ON THE SITE
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter