Share information with your Facebook friends
VK
Preparing for a colonoscopy is the most important stage in the effectiveness of the procedure itself. Since adequate preparation for colonoscopy makes it possible to examine the entire surface of the intestine for the smallest changes (up to 1 mm). What is hidden from view by the liquid contents can be evacuated through the endoscope channel. If solid components remain in the intestine, then there is a high risk of missing any lesions under these solid components of the intestinal contents. Today, the recommendation of all European and American endoscopic communities is a two-stage (two-day) split preparation.
Preparation for a colonoscopy can be either excellent (there is free or a small amount of clear yellowish fluid in the intestinal lumen) or good (in the intestinal lumen there is a small amount of turbid yellowish fluid).
Preparing for a colonoscopy.
What you can eat before the examination:
- For two days, exclude the intake of foods rich in fiber - vegetables, fruits with skin, berries with small seeds and grains, bread, mushrooms, cartilage, etc.
- The day before the examination, take only liquid food (transparent meat and vegetable broths, jelly and juice without pulp (except beetroot and black currant), black and green tea (except hibiscus and fruit)
- The day before the study at 16-00 the last meal of liquid food
Fortrans or Lavacol
Before the examination, any person has a choice of medication. But it is difficult to decide which one to use, especially when the course of the procedure depends on the effectiveness of the product.
Each patient is informed that if the intestine is perfectly clean, then the examination is faster, allows the doctor to carefully examine the internal walls, take pieces of tissue for analysis, and therefore does not have to repeat this unpleasant procedure to clarify the diagnosis.
Usually choose from two drugs: Fortrans and Lavacol. They have a lot in common:
- macrogoal in the composition;
- Available in powder form;
- have a laxative effect;
- are not absorbed into the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
There are also differences:
- price (Russian medicine is three times cheaper than French medicine);
- taste.
Lavacol is easier to drink due to its milder and less unpleasant taste, and is less likely to cause vomiting and bloating.
The scheme for using this remedy is simple:
- one sachet of powder is designed for 4 kg of weight, and it is diluted in 200 ml of water;
- They begin to drink the resulting liquid in the afternoon on the eve of the morning examination, so that 20 hours pass between taking the first portion and before the start of the colonoscopy.
In total, it will take five hours to use the product, and another three to completely empty it. You should drink the liquid in small sips, taking a fifteen-minute break after taking 200 ml.
For preparation, we recommend two drugs to choose from:
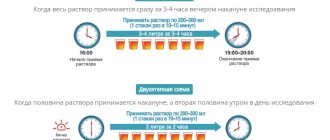
MOVIPREP
- The evening before the study from 18 to 20 pm: 1 large bag + 1 small bag + 1 liter of water
- 1 liter of water
- 1 large bag + 1 small bag + 1 liter of water
FORTRANS
(if the stool is regular or pasty, daily)
- The day before the study, from 18-00 to 20-00, dilute and gradually drink (200.0 ml at intervals of 5-10 minutes) the solution: 2 packets of Fortrans per 2 liters of drinking water. There will be a loosening of the intestines
- On the day of the study, 5 hours before the test, dilute 2 packets of Fortrans in 2 liters of drinking water and gradually drink (200.0 ml at intervals of 5-10 minutes) over the next two hours. There will be a loosening of the intestines, which will disappear over the next 3 hours until the wash water becomes light yellow. Must be located near a sanitary area.
Side effects and overdose
Sometimes, immediately after consumption, patients begin vomiting and nausea. Then this effect stops. Side effects can be identified such as:
- Disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. Accompanied by pain and bloating, vomiting.
- Immune system disorder. Characteristic for people with a high level of sensitivity. Symptoms: itching, rash, urticaria. Anaphylactic shock or angioedema may occur.
Drug overdose is rare. Signs of overdose: diarrhea, electrolyte imbalance in the body, nausea, vomiting. Treatment involves symptomatic treatment (internal fluid intake). More severe cases are rare; if this problem occurs, intravenous infusions are necessary. If these signs occur, you should contact the clinic.
Interaction of Fortrans with other drugs
The diarrhea effect may interfere with the absorption of other agents. The effectiveness of drugs characterized by a short half-life decreases. The doctor must be informed about the medications the patient is taking.
Specific instructions when taking the drug
It is not recommended to consume solid and dairy products two hours before starting the solution. It is better not to do this until the end of the session.
It is also better that there is a gap of at least an hour between taking other medications and Fortrans.
The drug does not affect the ability to drive a car or operate electrical units and mechanisms. The body’s reaction to drinking liquid can provoke a negative effect.
Little tricks (for Fortrans):
- To improve the taste of the solution, you can cool it by placing it in the refrigerator the evening before the test.
- To improve the taste of the solution, you can dilute 1 packet with 900 ml of water + 100 ml of freshly squeezed orange or lemon juice without pulp and zest.
- It is recommended to drink clean water, which should be stopped three hours before the procedure. After this, any drinking before the procedure is not recommended.
- Drink one glass every 15-20 minutes until you have drunk the entire recommended 3-liter volume. You can take a break every hour during this process. And it is advisable to distract yourself with some household chores.
Pharmacokinetics
The drug is dissolved - one packet per liter of water, an isotonic, isosmotic solution appears. Laboratory analysis indicates the absence of sorbate absorption (absorption) of Macrogol 4000 in the body. Biotransformation is also not observed.
When should it be taken?
The indication for use of the solution is bowel cleansing before colonoscopy. This could be an endoscopy, x-ray, surgery, or any procedure that requires colon cleansing.
NOTE!
The drug of choice for preparation for colonoscopy is FORTRANS if:
- the patient is taking drugs from the group of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (Ace Inhibitor, Akf-Inhibitor), such as Convertin, Captopril, Capoten;
- drugs of the angiotensin receptor blocker group, such as Atacand, Oksaar;
- there is renal failure;
- heart failure;
- have diabetes mellitus;
- symptoms that suggest nonspecific diseases of the large intestine (Crohn's disease, UC).
Contraindications and particulars for use
Before using the drug, you should consult your doctor. Contraindications:
- patient sensitivity to Fortrans components;
- chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, stomach ulcers, gastrointestinal obstruction (obstruction) and others;
- colon oncology;
- perforation (or risk thereof) of the gastrointestinal tract;
- problems with gastric emptying;
- colitis, megacolon (with toxic manifestations);
- age up to eighteen years.
It is also necessary to use the drug carefully or under the supervision of a doctor for people with: kidney problems (altered function), inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, heart failure, using diuretic therapy, anyone predisposed to electrolyte imbalance (water), nervous disorders. This category should include people with impaired coordination of movement or bedridden patients, anyone prone to aspiration, etc.
During pregnancy or lactation, the drug is used after consultation with a doctor. Elderly people do not need to reduce the dosage, but should be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
NOTE!
- If the patient is taking anti-clotting drugs such as Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl, Plavix or NSAIDs, they are at risk of bleeding, although small. Therefore, the possibility of interrupting this treatment should be discussed. However, if taking these drugs is necessary (for example, if the patient has had a stroke or if a cardiac stent has been inserted within the last 6 months), it is recommended to consult a cardiologist or neurologist or blood clotting clinic regarding the risk associated with interruption in treatment.
If these medications are used only as a preventive measure, you are advised to stop taking them about a week before the procedure.
- Patients taking Coumadin are at high risk of increased bleeding if a biopsy is performed and a polyp is removed during the procedure. Therefore, it is recommended to interrupt treatment with this drug approximately a week before the procedure and consider the possibility of replacing it with Clexane. In this case, a blood test (clotting study) should be done the day before the procedure. You should also stop taking Clexane approximately 12-24 hours before your procedure.
- Patients taking orally (orally) iron supplements (Venofer | Maltofer fol | Totema | Ferlatum | Fenyuls | Ferinject | Ferroceron | Ferroplex | Ferronal | Ferrocal | Conferon | Tardiferon | Sorbifer) to compensate for anemia, should discontinue these medications 3 days before before the procedure.
print version
TagsColonoscopy Endoscopy
Fortrans: pros and cons
It is made in France
pharmaceutical company Beaufour Ipsen Industrie. The package contains 4 sachets of white powder for preparing a solution. In addition to macrogol 4000, it contains sodium and potassium chloride, sodium bicarbonate, sodium sulfate and saccharinate. The product has a number of positive and negative features.
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Excellent laxative effect: all parts of the colon are cleansed, not just the lower ones. | Bad taste |
| Does not cause dehydration | Causes nausea and vomiting |
| It is not absorbed into the bloodstream, therefore it cannot be overdosed | Bloating |
| Acts quickly (emptying begins within an hour after drinking the first portion) | May cause allergic reactions |
| Many contraindications |
Positive properties prevail
. The drug performs its function perfectly, turning the colon into a clean tube, the walls of which can be easily examined through a colonoscope. The use of the product eliminates interference in the form of fecal residues and guarantees an accurate examination result and the correct diagnosis.
If your feet sweat a lot, it always causes a lot of trouble. Excessive sweating of the feet causes a painful odor, so it is better to get rid of the problem at an early stage. Read more in the article: “sweating feet: cause and treatment.”
No medicine will have its full effect if you do not adjust your diet according to the recommendations of the doctor who prescribed the examination. Although the remedy does not require changes in diet, it is better to adhere to a waste-free diet for three days before the colonoscopy. It is necessary to exclude foods that cause bloating and fermentation. These products include:
- all vegetables except potatoes;
- sorrel and spinach;
- oatmeal, pearl barley, millet in any form;
- legumes;
- fruits;
- nuts;
- Rye bread;
- raspberries and gooseberries;
- carbonated drinks and kvass;
- milk.

Can be eaten in small quantities:
- broths;
- boiled and steamed chicken, fish, beef;
- kefir, fermented baked milk, Varenets, cheese;
- wholemeal white flour bread;
- boiled eggs.
On the day of the procedure, you can drink meat broth, still water or tea.
What is the essence of colonoscopy?
Fibercolonoscopy is an examination of the surface of the mucous membrane of all parts of the large intestine using an endoscope camera. The device used in this case is called a colonoscope; its working part is carefully inserted into the intestinal lumen through the anus. Modern models look like a flexible thin tube; if the doctor is sufficiently qualified, their advancement is not accompanied by severe pain and does not lead to tissue damage.
The image received by the camera is processed and transmitted to the monitor screen. The level of detail depends on the hardware class, screen resolution and the presence of additional software.
If suspicious (modified) areas of the mucous membrane or space-occupying formations are identified, the doctor performs a biopsy - using manipulators, he separates a piece of tissue for subsequent analysis. It is also possible to simultaneously remove small tumors (for example, polyps).
A comfortable option for FCS is to carry out the procedure under anesthesia, when the patient is immersed in a controlled medicated sleep. In this case, the team of doctors includes an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. After completing the procedure, the patient stays in the clinic for some time and returns to everyday life within a few hours.
Why is anesthesia needed for FCS?
Colonoscopy under anesthesia relieves the patient of the physical and psychological discomfort associated with the insertion and advancement of the colonoscope tube. He will not experience pain during a biopsy, if there is a need to take tissue samples for histological examination.
Anesthesia makes it possible to avoid the formation of fear of repeated FCS, so that the patient in the future will not avoid the recommended scheduled regular examinations. According to reviews, after a colonoscopy in a state of medicated sleep, there is no pain in the anus and in the abdomen.
The use of anesthesia also improves the quality of the examination. Moderate muscle relaxation in a sleeping patient and the absence of involuntary resistance on his part give the doctor the opportunity to carefully examine the folds of the mucosa in all parts of the large intestine.
How often should you have a colonoscopy?
According to modern clinical guidelines, indications for FCS include:
- Previously diagnosed chronic bowel diseases.
- The patient has a history of a polyp or other benign neoplasm in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Identification of indirect signs of a tumor according to other research methods (ultrasound, radiography, irrigoscopy, etc.).
- The patient develops symptoms suspicious of tumor growth. These include unstable stools, recurrent or chronic abdominal pain, persistent low-grade fever, detection of blood or mucus in the stool (outside the phase of acute diarrheal infectious syndrome), chronic treatment-resistant anemia (iron deficiency or B12 deficiency), persistent increase in ESR and a number of other signs.
- The patient has cancer risk factors, a hereditary history of gastrointestinal cancer. Currently, permanent residence in large cities and in areas of increased industrial pollution is considered as a predisposition to cancer, including colorectal localization.
Persons with chronic gastrointestinal pathology, previously diagnosed diverticulitis and intestinal polyposis are recommended to undergo fibrocolonoscopy at least once a year. The frequency of visits is determined by the doctor individually; in some cases, diagnostics are carried out every 6–8 months. People from the high-risk group aged 40–45 years are recommended to undergo FCS once every 2 years, and after 45 years – annually.