Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an artificial process during which certain sections of DNA (RNA) are copied repeatedly. The method was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Carey B. Mullis. In 1993, he was awarded the Nobel Prize for this discovery.
The areas of application of PCR are extremely wide. PCR occupies a special place in medical practice. And the reason for this is simple: polymerase chain reaction makes the impossible possible.
PCR diagnostics have been figuratively described as a method by which you can find a needle in a haystack and then build a haystack from these needles. The "needle" is a tiny piece of a cell's genetic material (DNA or RNA).
The discovery of this method is an outstanding event in the field of molecular biology in recent decades. The development of the PCR method has allowed medical diagnostics to rise to a qualitatively new level.
Why is timely testing for hidden infections important?
Unprotected sexual contact with an untested partner can cause the transmission of a latent disease pathogen - infectious, viral, fungal. The danger of infection is that the disease can remain latent for a long time without showing its symptoms. Due to its asymptomatic course, the infection is usually discovered accidentally, and quite often in a chronic form. In addition to localization in the organs of the reproductive system, the pathogen can spread to other organs, causing inflammation of the bladder, kidneys, etc. Some hidden infections are dangerous due to the possible development of benign and malignant neoplasms.
To avoid an unfavorable prognosis and detect a possible disease in time, it is recommended to regularly get tested for hidden sexually transmitted infections. If a woman has had unprotected sex with a man whose health she is not sure about, it is advisable to undergo examination as early as possible. The time for testing for latent sexually transmitted infections depends on the disease: for example, to identify the causative agent of syphilis (Syphilis), it is recommended to be diagnosed 21 days after the suspected infection, for trichomoniasis - after 2-21 days, and for chlamydia - after 10 days.
If you have a permanent partner and use barrier methods of contraception, the frequency of examination is less - a smear and blood test for hidden infections are recommended for preventive purposes approximately once a year or when planning pregnancy.
PCR Basics
The basis of the method is repeated selective copying (amplification) of a certain section of DNA in order to obtain such an amount of genetic material that will be sufficient for visual detection. In this case, only a given section of DNA is copied repeatedly, provided that it is present in the biomaterial under study.
In addition, the research allows for other manipulations with genetic material. Therefore, the method is widely used in scientific research, biological and medical practice: in the diagnosis of infectious and hereditary diseases, in identifying mutations, genotyping, establishing paternity, personal identification, etc.
Analysis for hidden infections in women: what diseases can be detected with its help?
Below you will find a list of diseases that the analysis for hidden infections shows and allows to detect. However, it must be taken into account that each laboratory offers its own package of services, differing in cost and range of tests, so the diagnostic methods included in it may vary. For example, in addition to the main infections, the list of which is given below, some laboratories also offer tests for hepatitis B and Hepatitis C viruses, HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), and syphilis.
Genital herpes
The herpes virus can be present in the human body for years without manifesting itself. If the symptoms of genital herpes do appear, then small blisters filled with a cloudy liquid form on the vaginal mucosa, on the surface of the labia, perineum and around the anus. Their appearance is preceded by itching and burning, and sometimes chills and malaise.
HPV (human papillomavirus)
The peculiarity of HPV (HPV - Human Papillomavirus) is that some of its types are highly oncogenic and can cause the development of cervical cancer, while others are relatively safe. Therefore, if you suspect you are a carrier of HPV, it is necessary to undergo an examination to differentiate the type of pathogen. The infection manifests itself in the form of warts - genital warts - on the cervix, vaginal walls, labia minora and around the anus.
CMV (cytomegalovirus)
This is one of the types of herpes virus. CMV (Cytomegalovirus) has many “masks” of its course. The risk of acute infection with this infection increases if a woman is in the early stages of pregnancy, since CMV has a detrimental effect on the developing fetus and can cause pathologies in the development of the nervous system - the spinal cord or brain.
Candidiasis
In most cases, candidiasis (thrush) is manifested by the appearance of a white, cheesy coating on the walls of the vagina, accompanied by itching and burning. However, sometimes this disease can be present in the body in a latent form - in this case we are talking about candidiasis.
Chlamydia
The most common STD. The asymptomatic course of chlamydia makes it difficult to diagnose. Therefore, in order to find out whether you have this disease, you need to be tested for hidden infections. With symptomatic chlamydia, mucous or mucopurulent discharge with an unpleasant odor, vaginal burning and pain when urinating appear.
Gardnerellosis
The presence of Gardnerella in small quantities in the vagina of a healthy woman is absolutely normal. However, if, due to an imbalance in the microflora, this microorganism begins to actively multiply, gardnerellosis develops. The disease can be either asymptomatic or manifest itself in the form of vaginal itching and burning, an increase in the volume of discharge with the smell of “rotten fish”.
Mycoplasmosis
This disease is caused by mycoplasmas - microscopic organisms that occupy an intermediate position between viruses and bacteria. Characterized by hidden symptoms; in rare cases, clear or yellowish-white vaginal discharge, pain during urination, and discomfort after intercourse may occur.
Ureaplasmosis
The cause of the disease is microscopic ureaplasma bacteria that populate the vaginal mucosa. It occurs asymptomatically or in the form of unusual vaginal discharge that differs from normal in consistency or quantity. Causes ascending diseases of the urinary system: urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis; reproductive system: salpingoophoritis, endometritis.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea (Gonorrhoea) is caused by Neisseriagonorrhoeae gonococci, gram-negative microorganisms that are sexually transmitted from an infected person. The probability of a woman becoming infected during unprotected sex with a carrier of the infection is quite high and is about 50%. In isolated cases, there is a household route of infection. However, this is rare, since gonococci are unstable in relation to environmental conditions and quickly die outside the human body. A vertical route of infection is also possible - the infection spreads during pregnancy, from mother to fetus. In this case, the child experiences gonococcal conjunctivitis. The infection is manifested by swelling of the eyelids, redness of the conjunctiva and yellowish-white purulent discharge from the eyes.
Expert opinion
Women often have an asymptomatic course of the disease. If symptoms do exist, they are represented by yellowish-white or greenish purulent discharge from the vagina, itching and burning, intermenstrual bleeding, increased urge to urinate, pain during bladder emptying. In especially severe cases, fever, chills and general malaise may occur. Possible complications of gonorrhea in women include inflammation of the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes, and pelvioperitonitis.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
Tests for hidden infections in women: list of research methods
What tests need to be taken for hidden infections, how are they taken and where do they come from? Below you will find a list of the main laboratory tests used to identify the causative agent of the disease. The price for them depends on the location: in private laboratories it is usually higher than in public laboratories.
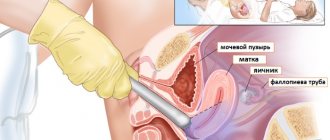
- Examination of urogenital smear for microflora. To carry it out, the doctor takes a small amount of biomaterial from the mucous membranes using a disposable spatula, and then applies the resulting samples to a glass slide. The essence of this research method comes down to the effect on biomaterial of special substances that color different microorganisms in certain colors. Carrying out this study allows us to identify a number of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms, as well as assess the general composition of the microflora of the vagina, urethra and cervix.
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction). This method of testing for infections, considered the “gold standard” in modern diagnostics, is highly accurate. To carry it out, the doctor uses a disposable gynecological spatula to take a smear of secretions from the vagina, urethra and cervix. The collection of biomaterial is painless and should not cause discomfort to the patient. The smear is placed in a special device (reactor) and the concentration of nucleic acid is gradually increased. The analysis includes three cycles (denaturation, annealing and elongation). During the study, a laboratory worker works with DNA or RNA molecules of the pathogen found in the biomaterial. PCR helps determine whether a woman has chlamydia, candidiasis, gardnerellosis, mycoplasmosis, trichomoniasis, human papillomavirus, herpes virus, cytomegalovirus.
- Bakposev (bacterial inoculation). This method involves growing microorganisms obtained as a result of taking biomaterial in a suitable nutrient medium. It makes it possible to detect the presence of infectious microorganisms in the biomaterial and determine their quantity, as well as establish the sensitivity of the infection to antibiotics. Using a gynecological spatula or brush, the doctor takes a smear from the patient’s cervical canal, urethra and vagina. The resulting biomaterial is placed on sterile glass, after which it is transferred to a suitable biological environment. How long does the analysis take? Depending on the type of microorganism, its cultivation may require different times - from 3 days to 3 weeks. After the required period, the nature of the resulting colonies of microorganisms is assessed and a diagnosis is made based on these results. Bacterial culture is recommended in the presence of any inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs of unknown etiology, if the presence of infections causing candidiasis, trichomoniasis, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis is suspected, as well as if a large number of leukocytes are detected in the urogenital smear.
- ELISA (the so-called enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). A smear taken from the cervical canal or venous blood is used as research material. Thanks to ELISA, it is possible to detect the presence not of the pathogenic agents themselves, but of antibodies to them - immunoglobulins G and M. The method has a fairly high accuracy. It allows you to assess the severity of the process, and the avidity index - the duration of the disease.
- RIF (immunofluorescence reaction). During the study, biomaterial (a smear of mucus from the cervical canal and vagina) is treated with special fluorescent substances, after which the result is assessed using a fluorescent microscope.
Expert opinion
The choice of the optimal research method should always remain with the doctor. An unprepared patient is not able to independently choose the type of analysis by contacting the laboratory directly.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
PCR diagnostics of hepatitis
At least 5 viruses are known that can cause liver damage - hepatitis A, B, C, D, E. In rare cases, hepatitis can be caused by Epstein-Barr and herpes simplex viruses. All these viruses belong to different families, have different biological properties and, accordingly, treatment tactics will also differ significantly.
Quickly and accurately identifying the pathogen is the doctor’s primary task. This is impossible without the use of modern molecular biological methods. Therefore, diagnosing hepatitis using the polymerase chain reaction method is an important step in establishing the cause of the disease and determining further treatment tactics.
- Hepatitis A virus, qualitative determination
- Hepatitis B virus, DNA quantification
- Hepatitis B virus, qualitative determination of genotype
- Hepatitis C virus, qualitative determination of RNA
- Hepatitis C virus, RNA quantification
- Hepatitis D virus, qualitative determination of RNA
Analysis for hidden infections in pregnant women
The presence of hidden infections in the body can negatively affect a woman’s ability to become pregnant and safely give birth to a child. The presence of an inflammatory process in the ovaries caused by a pathogenic agent has a detrimental effect on the formation of follicles and ovulation, due to which anovulatory infertility becomes possible. In the case of the presence of some latent infections, conception is carried out, but the death of the embryo may occur in the early stages. Another danger is that hidden infections can cause congenital malformations and abnormalities of the baby’s organs and systems.
There is also a danger that the child may become infected with certain infections while passing through the birth canal. For example, infection with the herpes virus or candidiasis is possible. Therefore, if at the time of birth a woman was diagnosed with genital herpes in the active phase, a cesarean section is recommended.
Therefore, testing for hidden infections is recommended for all couples (not only women, but also their partners) planning to have a child. Of course, it makes more sense to do this at the planning stage. before pregnancy. It is mandatory to test for hidden infections in the early stages of pregnancy when registering at a dispensary.
What tests for hidden infections are taken during pregnancy? Typically, in addition to the above tests for sexually transmitted infections, the test package for pregnant women also includes the diagnosis of hepatitis, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, toxoplasmosis and rubella. These diseases are included in the TORCH panel of studies, which are recommended when registering with an antenatal clinic. Control examinations for hepatitis B and C, HIV, and syphilis are repeated in the third trimester.
How to prepare for tests for hidden infections?
To obtain reliable research results, proper preparation for tests for hidden infections is important. It includes the following:
- Refusal to take antibiotics 10-14 days before the study.
- Abstain from intimacy for 2 days before taking the test.
- Use for washing with clean water without adding intimate gels or soap a day before collecting biomaterial.
- Refusal of vaginal douching, installation of vaginal suppositories and use of gels 1-2 days before the examination.
- To obtain the most accurate results, it is recommended to take the test on days 5-6 of the menstrual cycle, but not in the first days of menstruation.
Usually, the collection of biomaterial for analysis for hidden infections is painless. However, in some cases, a woman may experience slight discomfort caused by contact of a medical spatula with the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix. To reduce discomfort, after the examination you can use the Gynocomfort restorative gel. This product has all the necessary documentation and quality certificates. It not only allows you to cope with possible discomfort, itching and burning, but also provides rapid restoration and protection of the mucous membrane, restores and maintains the pH level at a physiological level, and has anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and antiseptic effects. According to clinical studies conducted at the Department of Dermatology with the clinic of St. Petersburg State Medical University under the leadership of Ignatovsky A.V. and Sokolovsky E.V., the gel is well tolerated and provides excellent results due to the tea tree oil included in its composition.
Sources:
- MODERN METHODS OF DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS. Borovkova L.V., Chelnokova E.V. // Medical almanac. – 2010. – No. 2 (11). – pp. 150-156.
- SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS: FEATURES OF THE EPIDEMIC PROCESS, CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSIS. Batyrshina S.V., Batyrshin R.F. // Practical medicine. – 2011. – No. 1 (49). – pp. 12-16.
- Sexually transmitted infections. Sokolovsky E.V., Savicheva A.M., Domeika M., Ailamazyan E.K., Belyaeva T.V. // Guide for doctors. M.: MEDpress-inform. - 2006. - P. 20-243.
- Urogenital infections during pregnancy (diagnosis, prevention, treatment). Sidorova I.S., Makarov I.O., Matvienko N.A., Borovkova E.I., Oveshnikova T.Z., Leonova I.P. // M.: LLC Publishing Partnership "Adamant". 006. - P. 3-15.
- Guide to outpatient care in obstetrics and gynecology. Kulakov V.I., Prilepskaya V.N., Radzinsky V.E. // M.: GEOTAR-Media. - 2007. - P. 134-156.
- https://express-med-service.ru/ginekologiya/obsledovanie-na-ippp/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/47509879_Latent_Class_Analysis_Is_Useful_to_Classify_Pregna…
- https://bmcpregnancychildbirth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12884-017-1300-1
- https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0193589
- https://www.bmj.com/content/321/7254/142
How is diagnostics carried out?
For a diagnostic test for COVID-19, a health care worker will take a sample of mucus from your nose, throat, or saliva. The sample needed for diagnostic testing can be collected at a doctor's office, health care facility, testing center, or at home (and in some situations, a laboratory technician can come to your home). A long nasal swab (nasopharyngeal swab) is recommended, although a throat swab is acceptable. A doctor or other health care professional inserts a thin, flexible, cotton-tipped stick into the patient's nose or swabs the back of the throat to collect a sample of mucus. This can be somewhat unpleasant. For a nasal sample, a swab may be performed in both nostrils to collect enough mucus for testing. The tampon is left in place briefly before being gently turned as it is removed. The sample is sealed in a tube and sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Popular questions
Hello.
I was tested for infections. Found: chlamydia trachomatis, biovar u.urealyticum T960, biovar ureaplasma parvum, gardnerella vaginalis, HPV 16 genotype. I paid 3,500 rubles for the first appointment. In order to prescribe treatment, you need to pay again for the appointment, about 2000. There is no way to go to the appointment again. Please advise some treatment. You need to see a doctor again to prescribe treatment, because when drawing up a regimen and stages of therapy, not only test results are taken into account, but also examination data assessing complaints, prevalence and duration of the disease.
Please tell me for all infections it says: not detected, but ureaplasma: 10*2.7 Is this normal?
Ureaplasma is a sexually transmitted infection. The microbial number can change with a decrease in immunity, as well as infect a partner. An identified infection requires treatment.
Hello, what is the likelihood of reliable information from an hCG analysis (detection of pregnancy at an early stage), if the day before the test I took a gynepristone tablet? Can a yellow cyst and pregnancy be confused during an ultrasound examination? Hello! The analysis for determining the level of hCG is the most reliable in terms of diagnosing early pregnancy. Taking the drug will not affect the indicator, since emergency contraception is used to prevent the attachment of a fertilized egg and no later than 72 hours after unprotected sexual intercourse. A corpus luteum cyst forms in the ovary after ovulation and ensures the production of the required amount of progesterone in the 2nd phase of the menstrual cycle. Based on ultrasound signs, it cannot be confused with a possible ectopic ovarian pregnancy.
Hello. My diagnosis: chronic active HPV associated cervicitis. Subacute vaginitis. HPV 6.53 type. HSV type 2. Cervical dysplasia, unspecified. While I am preparing for treatment, I am taking: Unidox, Ornidozol, Maxilac, fluconazole, Vagiferog suppositories and Viferon. Start of taking the drugs on the 14th - end of the 23rd. Since the drugs are antibiotics, the question is: is it possible to drink low alcohol at the event on the last day of administration (23)? Wouldn't this be fatal? Or maybe you shouldn’t take your pills on the 23rd, but the next?
Hello!
You should complete the course without interruption. Taking a weak alcoholic drink in very small quantities will not play a big role before the planned further treatment. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
What is included in the complex
- Herpes virus type 1, DNA (HHV-1, PCR) scraping, count.
- Herpes virus type 2, DNA (HHV-2, PCR) scraping, count.
- Chlamydia, DNA (Chlamydia trachomatis, PCR) scraping, count.
- Ureaplasma, DNA (Ureaplasma species, PCR) scraping, count.
- Mycoplasma, DNA (Mycoplasma genitalium, PCR) scraping, count.
- Mycoplasma, DNA (Mycoplasma hominis, PCR) scraping, count.
- Gardnerella, DNA (Gardnerella vaginalis, PCR) scraping, count.
- Trichomonas, DNA (Trichomonas vaginalis, PCR) scraping, count.
- Gonorrhea, pathogen DNA (Neisseria gonorrhoeae, PCR) scraping, count.
- Candida, DNA (Candida albicans, PCR) scraping, count.
- Cytomegalovirus, DNA (Cytomegalovirus, PCR) scraping, count.
- HPV type 16, DNA (HPV, PCR) scraping, count.
- Lactobacilli, DNA (Lactobacillus spp., PCR) scraping, count.
- HPV type 18, DNA (HPV, PCR) scraping, count.