Research using ultrasound waves is absolutely safe for health and is widely used in pediatrics. Parents need to know how ultrasound is performed on children. The information will help to properly prepare the baby for the procedure, which will increase the effectiveness of the diagnosis.
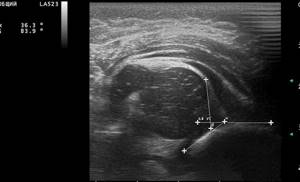
Subluxation of the hip joint on ultrasound
Body tissues reflect high-frequency pulses generated by the device. Sensitive sensors record the response waves, and a computer program converts the signal into a “live” black and white image on the monitor. The advantage of the method is the ability to evaluate the functioning of internal organs and anatomical structures.
How is an ultrasound performed on a child?
Ultrasound scanning (sonography) has no age restrictions. The study is carried out using a device consisting of a sensor, processor, monitor, and control panel. The distance to the anatomical structure being studied is determined by the speed of propagation of the sound wave.
The gaseous medium dampens the impulse, so a special gel is used to ensure a tight fit of the sensor to the skin and smooth sliding. The doctor makes circular movements with the scanner in the area of interest. An image of the internal structures appears on the computer monitor. At the same time, a study protocol is filled out, indicating standard parameters and pathological changes. Depending on the clinical manifestations, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound of one or more areas. The study of each site has a number of features.
Abdomen
The scan allows you to assess the condition of the internal organs located below the diaphragm and above the pelvic region. The study area includes:
- peritoneum;
- esophagus;
- stomach;
- intestines;
- retroperitoneal space;
- liver and gall bladder with ducts;
- pancreas;
- spleen;
- abdominal lymph nodes;
- blood vessels.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in children is performed routinely (for preventive purposes) and according to indications. Reasons for research may include:
- sudden changes in weight;
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain;
- yellowness of the skin;
- repeated bowel movements without obvious reasons;
- skin rashes of unknown etiology;
- abdominal injuries.
The child lies face up on the couch, and the doctor applies heated gel to the skin of the abdomen. To clarify the structural features of the internal structures, the specialist can lightly press on the abdominal wall, pressing the scanner tightly against the body.
The procedure takes 15-20 minutes. The doctor may ask you to turn over on your side, bend your legs slightly, and take a breath.
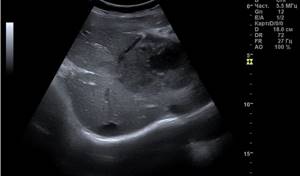
Ultrasound of the child's abdomen
At the end of the procedure, wipe off the remaining gel with a napkin or towel.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity reveals:
- damage to the liver, spleen and other organs due to mononucleosis;
- pancreatitis;
- urolithiasis;
- pyelonephritis;
- abscesses of internal organs;
- benign and malignant neoplasms of the abdominal cavity;
- internal bleeding due to injuries;
- helminthic infestation;
- dropsy, accompanied by accumulation of fluid in the abdominal organs;
- violation of tissue integrity due to injuries;
- ischemic processes;
- pathologies of the vascular system in the abdominal area.
The exact diagnosis is determined by the attending physician based on the results of ultrasound and other research methods.
Small pelvis
An ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition of the child’s genitourinary system. The scan is performed with a moderately full bladder.
Ultrasound of the bladder for a child under one year old
The study protocol reflects information about the condition:
- cervix, ovaries, fallopian tubes (in girls);
- prostate and testicles in boys;
- Bladder.
Pelvic ultrasound in newborns can identify malformations of the pelvic organs. Indications for the study are:
- a sharp increase in body temperature for no apparent reason;
- pain in the lower back, lower abdomen;
- difficulty urinating;
- severe swelling of the face and limbs;
- increased blood pressure of unknown etiology;
- hematuria;
- non-compliance with the norm of clinical tests (CAM).
To scan the pelvic organs, the child lies on his back and gel is applied to the skin in the lower abdomen. The doctor examines the internal structures, noting the structural features of the anatomical formations and the nature of the blood supply to the area being studied.
Using pelvic ultrasound, they diagnose:
- cystitis;
- pelvic neoplasms;
- delayed sexual development of adolescents;
- cysts, ovarian torsion (in girls);
- pelvic organ injuries;
- internal bleeding;
- cryptorchidism, hydrocele (in boys).
Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs in children is carried out transabdominally (through the abdominal wall). Transrectal scanning is done strictly when indicated. The method involves inserting a special sensor into the lumen of the rectum. Examination of the pelvic organs of girls using transvaginal ultrasound is not used.
Heart
Echocardiography is included in the complex of screening examinations. The method allows you to assess the condition of the coronary blood vessels, chambers, valves, and walls of the heart, and shows the functioning of the organ.
Indications for cardiac ultrasound:
- complaints of pain in the left half of the chest;
- cyanosis (blueness) of the nasolabial triangle after minor exercise;
- increased fatigue, shortness of breath, sweating;
- arrhythmia;
- severe course of infectious processes in the anamnesis.
During the examination, the child is asked to lie on his left side; young children are placed on their back. The chest is freed from clothing, and a conductive gel is applied to the skin. The doctor uses a scanner to examine the condition of the heart, noting the changes detected in the ultrasound report.
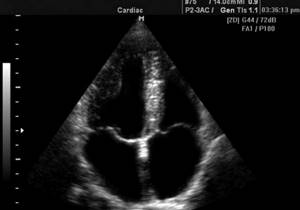
Echocardiography image of a child
The method helps determine:
- congenital and acquired defects;
- inflammatory processes (endocarditis, myocarditis);
- accumulation of fluid in the heart sac;
- presence of blood clots in the chambers.
Ultrasound of the heart is a safe and painless way to visualize the condition of the organ and surrounding tissues.
Brain
Neurosonography allows you to assess the condition of cerebral structures, identify the causes of increased intracranial pressure, and clarify the degree of hypoxia.
Preventive ultrasound of the brain is done with an open fontanel. Starting from the second year of life, the study is carried out according to the following indications:
- hearing impairment, decreased visual acuity;
- problems with memory, coordination, speech;
- delayed psycho-emotional and physical development;
- regular headaches;
- tremors of limbs, convulsions, strabismus;
- history of head trauma.
Scanning reveals:
- hypertensive syndrome;
- brain tumors;
- hematomas;
- hydrocephalus;
- signs of ischemia.
For babies up to one year old, an ultrasound is performed through the fontanel, moving the scanner along the parietal part of the skull. For older children, the sensor is applied to the temporal bone.
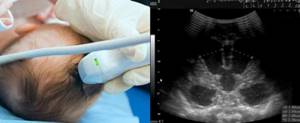
Neurosonography of a child under one year old
Neck and head
Ultrasound of this area is performed to study the condition of soft tissues, assess the patency and functionality of the brachiocephalic blood vessels. In the second case, Doppler ultrasound (USDG) is used.
Ultrasound is used to diagnose diseases of the child’s head and neck:
- tongue and oral cavity;
- salivary glands;
- cervical lymph nodes;
- thyroid gland;
- ear;
- orbital cavity;
- nasal sinuses.
The procedure allows us to identify congenital developmental anomalies, inflammatory, neoplastic, infectious processes, and the consequences of injuries.
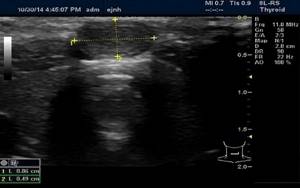
Sonography of the thyroid gland in a child
Ultrasound does not require invasive manipulations and allows you to study the structure of the head and neck in a painless and comfortable way for the baby.
Preparation
No special preparation is required for the procedure. If there is increased gas formation, the research picture may not be accurate enough. In this case, a three-day diet is prescribed, which excludes animal products from the diet. The child can be given cereals, vegetables, potatoes, nuts, fruits, black bread, wholemeal flour products. You can also eat dried fruits and honey in small quantities. For drinks, you can give your baby herbal teas and natural juices. An ultrasound scan of the child's kidneys is performed on an empty stomach. If prescribed by a specialist, you may take a laxative before the procedure. Ultrasound can be performed on infants three hours after feeding without additional special preparation. The ultrasound procedure has no contraindications, but it is better to postpone it if the child was tested for the Wasserman reaction less than a day ago.
Ultrasound measurements in children: normal
In the study protocol, the diagnostician notes the standard parameters of the organ. Changes in the location, shape, boundaries and size of an anatomical formation indicate possible diseases and developmental abnormalities.
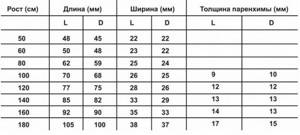
Kidney sizes in children depending on height
The following criteria are considered to be the result indicating the absence of pathology:
- the walls of the blood vessels retain their structure throughout, the lumen is not changed, there are no blood clots;
- parenchymal organs have a homogeneous structure;
- there are no neoplasms, foci of inflammation, cavities or stones;
- the sizes of the studied anatomical formations correspond to the age tabular norms;
- hollow organs without inflammatory exudate, diameter corresponds to age standards;
- no birth defects.
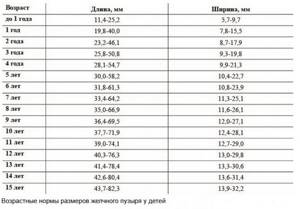
Age norms for the size of the gallbladder in children
The dimensions of the child’s internal structures depend on age and external anthropometric characteristics. There are a number of generally accepted methods for determining ultrasound norms.
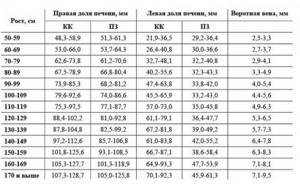
Dimensions of the liver (CC - cranio-caudal, PZ - anterior-posterior) of a child depending on height (according to Pykov)
How to prepare your baby for ultrasound diagnostics?
At the ultrasound, parents should bring an extract from the child’s medical record, a referral from the attending physician, and the results of previous examinations. For your baby, you can take disposable diapers and wet wipes.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs requires preliminary preparation. It is necessary to take measures to reduce gas formation in the intestines. Flatulence affects the scanning results, reducing the information content of the method.
2-3 days before the procedure, exclude from the baby’s diet:
- legumes (peas, beans, soybeans);
- dishes made from whole milk;
- fresh fruits, vegetables;
- cabbage, turnips in any form;
- confectionery.
The child should not drink carbonated sweet drinks and juices; you can drink water, tea, and compotes. If the baby is breastfed, the mother must comply with the listed restrictions. In case of flatulence, your doctor will help you choose medications (sorbents).
Examination of the child's abdominal cavity
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed on an empty stomach, the last meal is possible 3-8 hours before the procedure (depending on age).
A bowel movement is required before pelvic sonography. The study is carried out with a full bladder, for which 30-60 minutes before the scan the child is offered 0.5-1 liter of clean still water.
Before echocardiography, it is recommended to feed and calm the baby.
Scanning the neck, head, and cerebral structures does not require prior preparation; it is enough to tell the child about the ultrasound procedure. Children are examined in the presence of their parents.
At what age do children undergo kidney ultrasound?
About 5% of children in the world are born with various pathologies of the urinary system. As a rule, this is due to failures in the processes of fetal formation during intrauterine development. This is why kidney ultrasound is one of the mandatory procedures included in the newborn screening program. The child's first ultrasound is performed at the age of one month. If necessary, the procedure can be performed at any frequency. Also, an infant may be prescribed an ultrasound for preventive purposes to exclude pathology in one of the following cases:
- close relatives have kidney pathologies;
- the child is at risk due to prematurity, intrauterine infection in the mother, difficult childbirth, etc.;
- Immediately after birth, the child was nursed in intensive care.
What does the procedure reveal?
- Third kidney (does not affect the child’s health, does not function).
- Double kidney (a common congenital anomaly that does not significantly affect the quality of life).
- Urolithiasis (presence of shadows - anechoic inclusions).
- Nephroptosis, or wandering kidney (displacement of the organ downward or to the side by more than three percent of growth).
- Cysts (hypoechoic formations filled with fluid).
- Glomerulonephritis (autoimmune inflammation of the glomeruli, which needs clarification).
- Pyelonephritis (acute bacterial inflammation of the renal tubules).
- Tumors (high-density formations, the benignity of which is additionally diagnosed using a biopsy).
Indications for the procedure
An ultrasound of a child’s kidneys is performed for preventive purposes, to exclude pathologies, and for diagnostic purposes. Indications may include:
- suspicion of kidney disease, adrenal glands;
- ambiguous clinical picture after laboratory tests;
- pain syndrome in a child;
- detection of tumor lesions;
- the presence of previously discovered diseases in order to identify foci of spread, clarify the degree of severity, and possible complications.
Research results
The main criterion for assessing an organ during ultrasound examination is echogenicity, that is, the ability of tissues to absorb an ultrasound signal. You should not try to decipher the results yourself. A pediatrician or nephrologist interprets the results of an ultrasound examination of a child. Standards for organ size and structure vary for each age group. The calculation takes into account the length and thickness of the tissue, the density and width of the organ, etc. Changes indicate the presence of abnormalities or pathological processes in the kidneys. Ultrasound makes it possible to react quickly and begin treatment on time.
Neurosonography (NSG)
An ultrasound of a newborn’s head is performed through the fontanelles - soft tissue “windows” on the vault of the child’s skull that have not yet closed by this time. That is why it is so important not to delay the examination until the fontanel has healed and the doctor has the opportunity to fully evaluate all accessible structures of the brain, the space around it and the ventricles. The method allows you to quickly and safely identify the presence of such unpleasant and often dangerous pathologies as cysts, hemorrhages, vascular problems, an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, and tumors. In the initial stages, many serious diseases may not manifest themselves in any way, so early detection of undesirable changes allows timely treatment to begin and is the key to a speedy recovery for the little patient.
In the future, neurosonography will help track the dynamics of unwanted processes in the brain and judge the effectiveness of the measures taken.
Important!
“On an expert-class device, even the smallest changes up to two millimeters are visible. Compared to MRI, the neurosonography method, having a high level of information content, does not require anesthesia or any special training. In addition, ultrasonic waves are absolutely safe, unlike X-rays,” shares Margarita Topolnik.