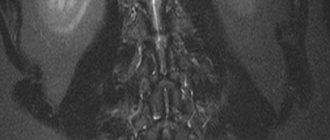
The lower back is the most overloaded part of the spinal column. As a result of the influence of certain provoking factors, intervertebral hernias often form in this area. These formations tend to increase. Their formation is accompanied by severe symptoms. As the disease progresses, the intensity of symptoms increases. Getting rid of this disease completely is quite problematic, especially if it is in the later stages of development. Treatment of intervertebral hernia of the lumbar spine is carried out using conservative or radical methods.
What is an intervertebral hernia?
Intervertebral hernia is a complex pathology of the human musculoskeletal system, in which the anatomy of the spine is noticeably disrupted due to protrusion of the core of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal as a result of a violation of the integrity of the fibrous ring. The danger of this condition lies in the pressure of the hernia on the membrane of the spinal cord, which can lead to paralysis. Prolapse sometimes affects the nerve roots, and the patient begins to feel severe pain. The process of disc destruction that accompanies intervertebral hernia slowly but inevitably leads to disruptions in the functioning of the entire musculoskeletal system. Therefore, to preserve the quality of life and health, one must strive to diagnose hernial formations at the initial stage of their formation (protrusion stage) and, if possible, stop further degradation of the vertebral discs with the help of preventive treatment.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
Operation
Radical intervention is used when it is necessary to free the spinal cord and nerves from the pressure of protruding tissues. The most popular methods are:
- Endoscopy is an operation through an incision in the spine using a probe. A camera and instruments are inserted through a small hole, and displaced tissue is removed.
- Disc endoprosthetics. Damaged elements are removed. A prosthetic structure is installed in their place.
- Percutaneous discectomy. Access is made through a puncture, the deformed core is removed and replaced with a special compound.
- Laser reconstruction – the hernia is removed by evaporating moisture from the tissue.
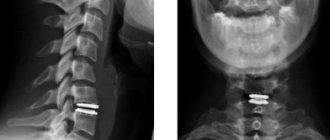
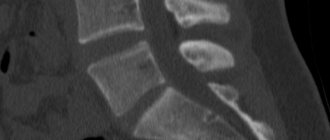
Diagnosis of hernia using MRI
A spinal hernia is detected on MRI even in cases where obvious external symptoms are not observed. The fact is that with an MRI of the spine, the research step is very small. It is only 2-3 mm. This level of detail allows the doctor to see the most minor deviations and anomalies of the spinal column. Using tomography, it is possible not only to understand in which part of the spine ruptures and prolapses of the nucleus pulposus occurred, but also to determine exactly what negative changes the patient has that increase the risk of developing a hernia. Negative factors include:
- signs of osteochondrosis;
- protrusion - the disc protrudes into the spinal canal, the integrity of the fibrous ring is not impaired, but there is a possibility of worsening the patient’s condition;
- violation of the correct position of the nucleus pulposus - it is displaced into the spinal canal and damage to the fibrous ring.
Treatment prognosis
The effectiveness of treatment, both conservative and surgical, directly depends on how accurately the patient follows medical recommendations. Also, the likelihood of relapse depends on the nature of the operation performed. With complete removal of the disc in one way or another, there is no risk of recurrence of the hernia in the same place, but it can form in adjacent spinal motion segments.
On average, the relapse rate after surgical treatment of hernias is 11.5%. But most often they are formed in other PDS.
What does a hernia look like on an MRI of the spine?
On MRI images, a hernial protrusion appears as a protrusion of the nucleus pulposus, a structure between the vertebrae. On tomograms, the radiologist sees a “blurred” nucleus pulposus and a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae. Depending on where the hernial protrusion is directed, the tomography evaluates nearby structures: whether there are signs of spinal cord canal stenosis or compression of the nerve roots. The hernia can be local or sequestered. Sequestered hernia is the most severe form of intervertebral disc damage. With this pathology, a large fragment of the disc core substance falls out and is completely separated from it. On MRI images it looks like a piece of the hernia itself lagging behind.
| Service | Price according to Price | Discount Price at Night | Discount Price During the Day |
| from 23.00 to 8.00 | from 8.00 to 23.00 | ||
| MRI of the cervical spine | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the thoracic spine | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the lumbosacral spine | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the craniovertebral junction | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the sacroiliac joints | 4000 rub. | 3190 rub. | 3690 rub. |
| MRI of the coccyx (MRI of the sacrococcygeal region) | 3300 rub. | 2690 rub. | 2990 rub. |
| MRI of the cervicothoracic spine | 6600 rub. | 5380 rub. | 5980 rub. |
| MRI of three parts of the spine (MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral regions) | 9900 rub. | 6900 rub. | 7900 rub. |
| MRI of the entire spine / MRI of the back | 9900 rub. | 6900 rub. | 7900 rub. |
| MRI of the central nervous system (MRI of the brain, MRI of the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral regions) | 13200 rub. | 9590 rub. | 10890 rub. |
| Appointment with a neurologist | 1800 rub. | free after MRI | free after MRI |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
Features of anatomy
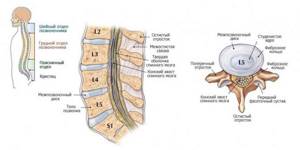
The entire spine is formed by more than 30 vertebrae of different sizes and is divided into 5 sections:
- cervical - formed by 7 vertebrae (C1–C2), which are the smallest and most mobile in the body;
- thoracic - formed by 12 vertebrae (Th1–Th12), least likely to be susceptible to degenerative-dystrophic changes;
- lumbar – consists of the 5 largest vertebrae (L1–L5), which bear the greatest load during physical work;
- sacral – has 3 vertebrae (S1–S3);
- coccyx – formed by 1–3 fused vertebrae.
Between all the vertebrae there are cartilaginous structures that provide shock absorption when walking and the natural flexibility of the spine. They are called intervertebral discs. Each disc has a pulpous nucleus pulposus and a tough outer shell called fibrous. It is protected on the sides by end plates.
Why does a hernia form?
Every day a person loads his spine. Sometimes this load turns out to be excessively high, and the spinal column begins to lose a sufficient level of strength and flexibility. There are many reasons why a herniated disc occurs. For example:
- traumatic impact;
- being overweight;
- infections that affect the spinal column;
- lack of movement, sedentary lifestyle;
- degenerative processes that have arisen in the vertebrae and discs;
- congenital spinal abnormalities;
- changes associated with spinal curvature.
What program should I use to open MRI images?
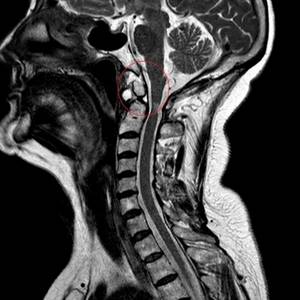
To open MRI images, you will need a special program (DICOM Viewer, RadiAnt, etc.), which can be downloaded on the Internet. Sometimes there is a file on the electronic media to install the application: run it following the instructions.
You must insert the CD into the drive or memory card into the appropriate slot on the computer. With the latter, a problem may arise due to the lack of a suitable connector; in such a situation, additional components will be required - a card reader and a USB cable.
After connecting the electronic media, you need to wait a while - the operating system must detect the disk or card and install the driver. An autorun program will appear on the screen in which you should open the folder to view files. If this does not happen, go to the “Start” menu, select “My Computer”, after the window appears, find “Devices with removable storage” and left-click on it.
You can view photos of an MR procedure as individual images or as a series of frames.
Hernias of the cervical and lumbar spine on MRI
Hernias can form in any part of the spine, but the lumbosacral region (150 cases per 100,000 people per year) and the cervical spine are most often affected by this pathology. Its sizes vary, which allows us to classify intervertebral hernias into the following types:
- median;
- lateral;
- posterolateral;
- anterolateral;
- combined (combined).
Regardless of the location, type and cause that caused the hernia, all patients ultimately get the same result - an inflammatory process and swelling of the tissues. The hernia grows gradually and at the initial stage of its formation does not cause pain. Further, these pathological changes are accompanied by mild discomfort, and later constant pain occurs. Clinical manifestations of an intervertebral hernia will be: pain in the lower back (if a hernia appears in this section), sometimes radiating to the buttocks, weakness and numbness of the legs, and there may be difficulty urinating. If the hernia is localized in the cervical or thoracic regions, its symptoms will be pain radiating to the shoulder, frequent dizziness in combination with high blood pressure.
If you observe the appearance of any of the above symptoms, you should contact a neurologist who will conduct an initial examination. Based on its results, the specialist can recommend clarifying diagnostic studies. An MRI is usually the recommended way to detect a herniated disc.

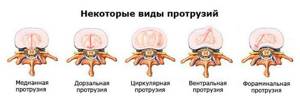
Kinds
All hernias can be divided into anterior and posterior (dorsal). The former are rare and have a very favorable prognosis, while the latter pose a danger to a person’s physical capabilities because they fall into the lumen of the spinal canal. Depending on their location they are divided into:
- central (median) – located in the central part of the spinal canal, so they can provoke the appearance of pain, both on the right side of the body and on the left;
- paramedian - formed on the left or right side relative to the central axis of the spine, therefore causing the appearance of characteristic symptoms on the corresponding side of the body;
- circular - the entire posterior surface of the disc protrudes, which leads to filling of the entire spinal canal and the development of severe neurological symptoms, as well as severe pain;
- foraminal - a hernia forms in the area of very narrow openings of the spine formed by the vertebral body and articular processes, and causes burning, excruciating pain.
Depending on the size of the hernia they are divided into:
- small – the size of the protrusion does not exceed 5 mm;
- medium – the hernia reaches 5–7 mm;
- large - the formation increases to 8 mm or more.
But, unlike popular belief, the size of the intervertebral hernia is not strictly related to the severity of the observed symptoms. Even very large hernias can exist for a long time completely asymptomatically and are discovered by chance, while small ones can so infringe on the spinal root that not only severe pain syndrome occurs, but also serious disruptions in the organ innervated by it. Therefore, treatment tactics for each patient are chosen to a greater extent in accordance with the severity of complaints, rather than the size of the formation.
Schmorl's hernia
This is the name for an anomaly in which the cartilaginous tissue of the end plates ends up in the spongy bone of the vertebrae. Pathology can manifest itself in a child during a period of increased bone growth. Soft tissue develops faster than bone, which leads to the formation of voids in the vertebrae. This problem in a child is detected exclusively during an MRI. This pathology in itself is not dangerous, but the Schmorl node indicates a risk of developing a hernia in the future and a high probability of compression fractures of the spine. This warning should not be ignored - if this anomaly is detected in your children, you should definitely listen to the doctors’ recommendations for preventive treatment.
What doctors will see
The two main projections of the procedure allow you to see the vertebral arch and spinous processes. Regardless of the degree of development of the hernial tumor, the image will definitely show the following nuances:
- Distance between disks.
- distinct contouring of each of the vertebrae: the slightest irregularities in the outlines can become a signal. For example, with a Schmorl's hernia, a peculiar concavity of the vertebra is present, and if additional processes are detected, osteochondrosis is diagnosed.
- Bone density level. Bones fixed in one place are particularly brightly colored in the image.
At first glance, all this is quite enough to make the correct diagnosis. In reality, it turns out completely differently. All these are indirect signs of a vertebral hernia; in fact, it will not be possible to consider a serious pathology. But at the same time, one should not underestimate the effectiveness of X-ray examination as part of the general identification of back problems.
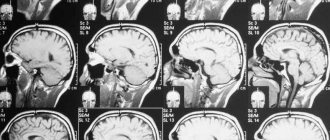
MRI or CT scan of the spine for a hernia - which is better?
CT and MRI of the spine are diagnostic procedures with certain differences between them.
In appearance, a computer tomograph and a magnetic resonance imaging scanner are very similar, but the scanning principles in them are different. MRI is based on the effect of nuclear magnetic resonance. A computed tomograph is an advanced X-ray machine whose operating principle is based on the ability of X-rays to pass through human tissue. Both types of diagnostics are very informative, but each has its own strengths. Thus, during an MRI of the spine, soft and cartilage tissues are more clearly displayed in the images. The same can be said for lymph nodes and blood vessels. A CT scan is indispensable if necessary to determine the location of bleeding and diagnose neoplasms in bone tissue, as well as identify salt deposits. Because magnetic resonance imaging is a better image of soft tissue, MRI is better suited for diagnosing the herniated disc itself and its impact on the nerve roots and spinal cord. It will be possible to evaluate the hernia on CT images only by secondary signs, for example, by changes in the distance between the vertebrae. When choosing a method for diagnosing the spine, the safety aspect of the examination also plays a role. The magnetic field of the tomograph is completely harmless to humans, therefore magnetic resonance imaging can be performed more often than CT, in which there is a certain danger in the form of radiation, and it should be done no more than 1-2 times a year. For the same reason, computed tomography is not prescribed to certain categories of patients - children, women carrying a child, and people who have recently undergone fluoroscopy or radiography.
Initial appointment with a NEUROLOGIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
Which doctor should I contact?
Spinal diseases are treated by vertebrologists and neurologists, who often also work as chiropractors. They should be contacted if the slightest of the above-described deviations occurs. They are also the ones who interpret MRI, CT and X-ray images.

But due to their own workload, and often laziness, when symptoms of hernias and, in particular, back pain occur, people delay seeing a doctor. Painkillers in the form of tablets or ointments are often used on their own. But they only temporarily eliminate the symptom that is key to the disease.
This allows you to continue to lead your usual lifestyle, but has a negative impact on the prognosis, as the protrusion continues to increase. Therefore, over time, the pain syndrome intensifies, then neurological disorders in the form of numbness of the limbs or even paralysis join it, and internal organs corresponding to the level of damage also suffer.
Often in such situations people say that they are “falling apart.” And the reason lies in the intervertebral hernia. Therefore, in order to prevent this from happening, you should consult a doctor if the slightest manifestations of the disease appear. This specialist will be able to choose the right treatment tactics and assess the prospects for conservative therapy. Indeed, in advanced cases, the situation can only be corrected through surgery.
Prolonged ignoring of the problem can lead to the development of severe complications, including:
- spinal canal stenosis;
- disorders of the pelvic organs, up to loss of control over urination and defecation, as well as persistent erectile dysfunction;
- complete paralysis of the limbs.
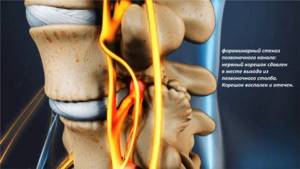
Therefore, we recommend not to delay and contact a vertebrologist, chiropractor or neurologist as early as possible. Otherwise, conservative therapy will not bring results and the patient will have to muster the courage, as well as material resources, to perform a neurosurgical operation. Moreover, no neurosurgeon can give a 100% guarantee that it will be effective.
The specialist will prescribe the necessary studies, based on the results of which he will select the correct treatment tactics, taking into account the nature of the existing changes, the size of the hernia, its location and the clinical picture.
MRI and Hernia: Frequently Asked Questions
How to determine a spinal hernia without an MRI?
First of all, it is worth noting that such an opportunity does not always exist. If the doctor can determine the diagnosis even before a tomographic examination, then the situation is already advanced. A large intervertebral hernia makes itself felt by severe back pain, a feeling of numbness in the limbs, pain when moving, migraines and dizziness. In any case, you cannot do without an examination, because it is during an MRI scan that the following is determined: the width of the spinal canal, the degree of damage, the size and location of the hernia. Without tomography, the diagnosis may be incorrect.
Is it possible to diagnose a herniated disc on an MRI?
When the doctor evaluates the MRI image of the spine, the hernia is visible very clearly. A specialist can accurately identify the existing problem. On tomographic scans, all structures of the spine will be clearly visible: the soft tissues with which it is surrounded, spinal nerve trunks, intervertebral discs.
Is it common to find a spinal hernia on MRI?
According to statistics, a herniated disc is found in 220 people out of 100,000 people. In almost half of all cases, the formation is localized at the level of L5-S1 or L4-L5 of the lumbosacral region. If you regularly undergo examinations and monitor the condition of your spine, your risk of developing this disease to a condition requiring surgical intervention is low. The most important thing here is early diagnosis.
How often should an MRI be done for a herniated disc?
The doctor decides this issue. But, as mentioned above, due to its painlessness and safety, the number of tomographic procedures is not limited. MRI can be performed at any time interval.
Author: Kasimov Evgeniy Tulkunovich
Neurologist with 8 years of experience
Conservative treatment
In the absence of severe neurological symptoms (weakness in the limbs, dysfunction of the pelvic organs) and not pronounced compression of the nerve endings, non-surgical treatment of the hernia is possible. Its effectiveness largely depends on the correct selection of each component of conservative therapy, which are:
Drug treatment
It is developed individually and always includes drugs from the NSAID group in oral (tablets), injection form or in the form of ointments for pain relief, B vitamins (Milgamma) to improve nerve trophism. Taking muscle relaxants is also indicated. Additionally, patients may be prescribed chondroprotectors (their cost is quite high, and their effectiveness has not been officially confirmed, but many patients notice positive dynamics).
Blockades
Indicated in cases requiring pain relief. There are several types of blockades depending on the site of drug administration. They can be performed with solutions of corticosteroids or analgesics.
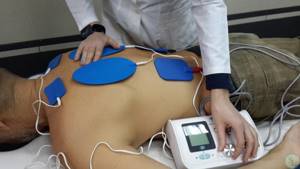
Physiotherapy
A course of magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, phonophoresis and ultrasound therapy procedures increases the effectiveness of treatment and helps accelerate pain relief. In mild cases, physiotherapeutic procedures can be performed at home by purchasing a special device.
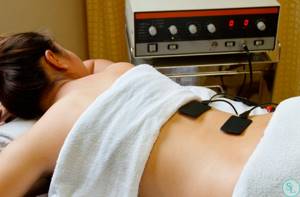
Exercise therapy
An obligatory component of conservative therapy. Aimed at improving blood supply in the area of the compressed nerve, due to the flow of blood, regeneration of nerve cells occurs. A set of individually selected exercises should be performed daily, monitoring sensations and avoiding sudden movements. If pain appears or intensifies, you should consult a doctor to understand what caused the discomfort and, if necessary, adjust the set of exercises.
Spinal traction
Traction therapy is an effective method for treating hernias, especially in the cervical region. The essence of the method is to temporarily relieve the pressure on the nerve by the hernia, which allows you to supply the affected area with nutrients, minerals and vitamins. The procedures are carried out using a special apparatus (sometimes in water), which gives a positive result within the first month.
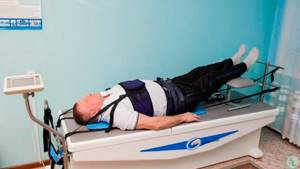
Kinesitherapy
One of the areas of exercise therapy, which involves performing certain passive and active movements. By triggering active muscle contractions, the muscle corset is strengthened, which subsequently takes on the load and relieves the joints of the spine and improves their blood supply. Which helps reduce swelling and eliminate muscle spasms.

Acupuncture
The impact of special needles on specific bioactive points increases the effectiveness of the treatment and helps to quickly eliminate pain.
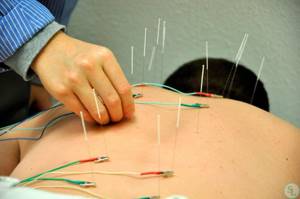
Reflexology
This involves using, for example, the Kuznetsov applicator, which helps relax spasmodic muscles and eliminate back pain. Its design allows you to simultaneously influence acupuncture points and perform a massage, but the use of the Kuznetsov applicator is possible only as prescribed by a doctor. To treat different areas, different types of applicators have been developed: belt, mat, neck roll.
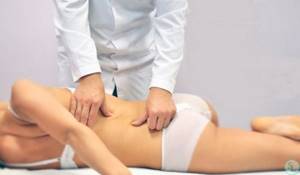
Osteopathy
It involves the influence of the doctor’s fingers on certain areas in order to return joints and muscles to the physiologically correct position and improve their mobility.
Conclusion about conservative treatment:
If you strictly follow medical recommendations, after completing a course of conservative treatment, pain may disappear. In such cases, they speak of remission of the disease. Its duration depends on how closely the patient adheres to the advice of doctors and the amount of physical activity.
At home, you need to avoid static and physiologically incorrect loads on the spine. To reduce the load, on the recommendation of a doctor, you can wear an orthopedic bandage (corset). It is recommended not to sit in one position for a long time, periodically warm up and do exercises, thereby ensuring the necessary blood flow to all muscles and joints.
Classification of hernias depending on size
The larger the size of the protrusion, the worse the state of health. The smallest formation appears in the neck area, the largest in the lower back. The classification of intervertebral hernias by size is as follows:
- Small (from 1 to 5 mm).
- Medium (from 6 to 8mm).
- Large (from 9 to 12 mm).
- Huge (from 12 mm).
Small, medium, and large formations are treated using traditional methods. Huge protrusions require surgery if they severely compress a spinal nerve, causing urinary and fecal incontinence, paralysis, and in men - impotence.
What types of intervertebral hernias are most difficult to treat?
4 stages of treatment for intervertebral hernia