1 Historical background
2 General description of ECG
3 Preparatory stage
4 How to install electrodes?
5 ECG recording in children and pregnant women
6 Recommendations for patients
It is not for nothing that the heart muscle is called the engine of the human body, since it constantly pumps huge amounts of blood. Any disturbances in the functioning of the heart immediately have a negative impact on a person, and therefore the diagnosis of pathologies of the cardiovascular system should always remain at a high level.
An electrocardiogram is one of the most accessible and highly informative methods for assessing the functioning of the heart muscle. In most cases, its implementation allows you to immediately make a diagnosis and determine the tactics for managing the patient.
Historical reference
The study of biocurrents created by the heart muscle was actively carried out back in the 19th century. At the same time, the first device was created that made it possible to record these impulses and use them to evaluate the work of the heart. Thus, the world's first electrocardiograph was created, thanks to which it is possible to record data on the contraction of the heart muscle and the conduction of an electrical impulse along special paths. Since then, the medical field has continued to improve and every year the accuracy of reading biocurrents when recording an electrocardiogram increases.
Introduction
Dear Colleagues!
The manual has a purely practical orientation, so you will not find here extensive discussions about the nature of the electrical axis of the heart and other phenomena. I invite those who want to gnaw on the theory to the pages of numerous books about ECG; there are plenty of them freely available on the Internet.
The manual is illustrative. The main thing in the presentation of each item in the table of contents is the corresponding picture, to which is attached the minimum possible description. On this site, small pictures are enlarged and moved using the left mouse button! Give it a try. (By the way, this picture shows an ECG machine. Would you like to work on one?)
In the conditions of market medicine, the ECG is forced to take its place among other, more informative methods, so here you will not find “shamanism” like “ECG for alcoholic heart disease.” I will describe only those facts about the ECG that I am 100% sure of.
The mass of electrocardiographic signs is “probabilistic” in nature and is not 100% proof of pathology (including elementary hypertrophy of the LV myocardium). Therefore, a cardiologist who has an ultrasound scanner with a cardiac sensor in his office will not “shamanize” the ECG regarding the P-mitral, but will simply look at the mitral valve with his eye and measure the blood flow on it using EchoCG.
Very often, ECG pathology is not detected during a 20-second recording of a standard resting ECG, but manifests itself only during a 24-hour recording (Holter ECG monitoring). Therefore, in this manual, most of the illustrations are taken from Holter recordings.
I was lucky enough to work with 12-channel Holter monitors, which are essentially a full-fledged ECG device with the ability to record 24 hours, so the concepts of “ECG” and “HM (Holter monitoring)” are very close to me, hence the name of the course.
General description of ECG
The procedure for recording an electrocardiogram currently remains the most accessible and informative diagnostic procedure, which does not cause any discomfort to the patient and does not require specific preparation. You can record an ECG at any medical institution in your locality. The general registration algorithm is as follows:
- Preparing the patient for recording: placing him on the couch, exposing the necessary parts of the body, putting aside any objects that may interfere with the recording;
- Installation of electrodes in strict sequence;
- Connecting an electrocardiograph in compliance with safety precautions and rules for using the device;
- Recording specific leads;
- Removing paper with an already recorded electrocardiogram;
- Deciphering and (or) issuing the result to the patient or attending physician.
In the operation of an electrocardiograph, every detail matters. You can purchase components for the device (cables, electrodes, terminals, etc.) in various online stores. Reasonable prices are offered by the Avicena-med website, which works directly with the manufacturer and guarantees high quality and a wide range of products.
Preparing for an ECG
An ECG is an electrocardiogram of the heart. This is a very informative examination to assess the condition of the heart.
Electrodes are attached to certain areas of the body, the ECG is recorded on a special tape, on which electrical impulses are recorded in the form of curves, straight and jagged lines. A cardiologist, functionalist, therapist, or emergency physician is required to see any abnormalities on the electrocardiogram and evaluate acute cardiac pathology.
Often the patient asks the doctor questions: isn’t an ECG and an ultrasound of the heart (EchoCS) the same thing, when to do an ECG and when to do an EchoCS, what does an ECG show and what does an EchoCS? ECG, unlike EchoCS, does not show morphological and structural changes.
WHAT DOES THE ECG SHOW?
- rhythm and heart rate;
- hypertrophy of the walls of the left ventricle;
- enlargement of the cavities of the heart;
- electrolyte changes in the myocardium;
- circulatory disorders in the heart;
- regularity of the pacemaker (electrocardiostimulator).
Thus, many heart diseases, such as arrhythmias, tachycardias, blockades, ischemia, myocardial infarction, myocarditis, hypertension and many other cardiac pathologies, can be recognized by ECG recordings.
HOW TO PREPARE FOR ECG?
Although an ECG is a simple procedure, preparation for the study is necessary so that the doctor does not receive a false result and send the patient for additional examinations. To obtain the most reliable result, preparation is necessary the day before and on the day of the study.
PREPARATION FOR ECG BEFORE THE EXAMINATION:
MEDICINES. If the patient does not take medications on a regular basis, they must be discontinued 2 days before the procedure. If it is not possible to discontinue the drugs, you must inform the ECG specialist.
ALCOHOL. The day before, it is recommended to stop drinking alcohol, since alcohol affects the composition of the blood and the functioning of the heart, and the ECG readings may be distorted and the film may reveal arrhythmia, tachycardia, electrolyte disturbances in the myocardium, and, often, ischemia.
DREAM. If the body is tired, various abnormalities may be detected on the electrocardiogram. Therefore, 5-7 days before the examination, it is recommended to get enough sleep - at least 7-8 hours per night.
NUTRITION. It is undesirable to eat fatty, spicy foods on the eve of an ECG, and it is advisable to make breakfast as light as possible.
SPORT. It is advisable to refrain from physical exercise 2 days before the examination.
EMOTIONAL CALM. 2-3 days before the ECG is taken, it is advisable to find peace of mind - not to be nervous. Stress, psycho-emotional instability, depression, and anxiety can distort the ECG results.
THERMAL PROCEDURES. It is advisable to avoid visiting a solarium, bathhouse, or sauna for several days, as this can also affect the distortion of ECG results.
PREPARATION FOR ECG ON THE DAY OF EXAMINATION:
LIGHT BREAKFAST
ENERGY. It is necessary to exclude tea and coffee.
CLOTH. To avoid problems with connecting sensors, it is recommended to wear light clothing that is easy to remove, roll up the sleeves or the bottom of the trousers.
SMOKING. It is advisable not to smoke 3 hours before the examination, since nicotine leads to vasospasm, and this, in turn, affects the functioning of the heart, activating the work of the myocardium muscle.
CREAMS AND LOTIONS. On the day of the examination, you should not apply greasy products, because creams and lotions interfere with the attachment of sensors to the body for recording ECG.
IN WHAT CASES IS ECG PRESCRIBED?
- fainting;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the chest, neck, back;
- swelling of the legs;
- pregnancy;
- preparation for surgery;
- body check;
- trip to a sanatorium;
- sport competitions;
- as a preventive measure once a year.
SYMPTOMS FOR MANDATORY CONSULTATION TO A CARDIOLOGIST:
Proper functioning of the heart is the key to health!
Any disturbance in the functioning of the heart causes failure in all systems of our body. Nausea, tachycardia, weakness, dizziness, and neuroses appear. Preventing heart disease requires a more careful attitude to your health.
The heart is a very reliable organ; it takes a long time to warn a person about problems. The sooner we see a cardiologist due to heart problems, the better.
- A sharp decrease or increase in blood pressure.
Suddenly there is a headache, malaise, nausea, weakness, lightheadedness, and lightheadedness.
- Lip cyanosis (bluish color).
This is a sign of improper functioning of the lungs, there is not enough oxygen saturation of the blood, or improper functioning of the heart. It pumps blood weakly. Oxygenated blood, which has a bright color, does not enter the capillaries of the lips, and dark blood, saturated with carbon dioxide, does not drain well.
- Swelling of the legs. There are many reasons for swelling of the legs. One of the main reasons is heart problems. Edema often appears with cardiomyopathy, heart failure, aortic aneurysm, various heart defects, and after a myocardial infarction.
- Incorrect pulse. Normally, a person’s pulse is considered no higher than 90 and no lower than 60 beats per minute. With a low pulse, there can be fainting, even cardiac arrest. Due to insufficient oxygen supply to the brain, oxygen starvation occurs. Due to an excessively rapid pulse, there may be cerebral hemorrhage, arrhythmic shock, and much more.
- Interruptions in the heart. If the heart rhythm is abnormal, weakness, ripples in the eyes, and dizziness appear. This indicates direct heart problems.
- Fainting. Presyncope. They can be a consequence of a stuffy room, diabetes mellitus, or accompany a stroke, myocardial infarction, cardiac arrhythmia until it stops completely.
- Chest pain. This is a signal about the destruction of the body. Malaise after physical activity, aching chest pain may indicate a pre-infarction condition. The pain radiates to the back, neck, and left arm.
For all of the above symptoms and complaints, it is necessary to do an ECG and, if possible, seek qualified help from a specialist, as well as perform all procedures for treatment.
Try to get rid of bad habits, adjust your diet, reduce your excess weight, increase your physical activity, try to avoid stressful situations in life, manage your attitude towards these situations.
Be healthy!
Sign up for functional diagnostics
Functional diagnostics doctor - Andrienko Olga Leonidovna
You can make an appointment by calling (391) 205−00−48 or through your personal account
Preparatory stage
The ECG is performed in a separate room, where satisfactory sanitary and hygienic conditions are established to ensure complete patient comfort. This room may contain additional structures intended for stress tests or bicycle ergometry.
Patient preparation consists of the following manipulations:
- The person is calmed down and completely relaxed;
- The forearms, shins and upper body are exposed;
- The areas where the electrodes are installed are degreased and moistened with a special gel to improve electrical conductivity;
- The essence of the study is explained to the patient.
Enhanced ECG leads from limbs
Enhanced limb leads record the potential difference between one of the limbs on which the active positive electrode of this lead is installed and the average potential of the other two limbs (see figure below).
The so-called combined Goldberger electrode, which is formed by connecting two limbs through additional resistance, is used as a negative electrode in these leads. Three enhanced unipolar limb leads are designated as follows: aVR - enhanced right arm lead; aVL—increased abduction from the left arm; aVF - increased abduction from the left leg. As can be seen in the figure below, the axes of reinforced unipolar limb leads are obtained by connecting the electrical center of the heart to the site of application of the active electrode of a given lead, i.e. in fact, from one of the vertices of the Einthoven triangle. Formation of three reinforced unipolar limb leads. Below - Einthoven's triangle and the location of the axes of three reinforced unipolar limb leads
The electrical center of the heart, as it were, divides the axes of these leads into two equal parts: positive, facing the active electrode, and negative, facing the combined Goldberger electrode
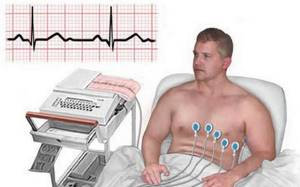
How to install electrodes?
The reliability of the results obtained depends on the correct installation of the electrodes. Medical personnel working in the ECG room undergo special training, so they do not have the right to confuse the algorithm for applying branches.
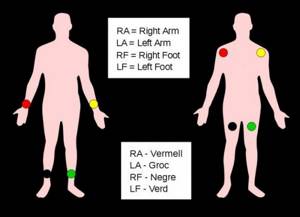
There are a total of 12 leads (standard, amplifying and chest leads), which are recorded by applying 10 electrodes (with a small-channel cable, 4 electrodes are installed on the limb, and the chest leads are recorded alternately with the fifth. The order of installing the electrodes is as follows:
- A green electrode is attached to the right hand;
- A yellow electrode is installed on the left hand;
- A green electrode is attached to the left leg;
- A black grounding electrode is installed on the right leg;
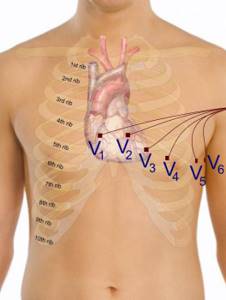
- A green chest electrode is placed in the 5th intercostal space to the right of the sternum;
- At the same level, but to the left of the sternum, a yellow chest electrode is attached;
- A green chest electrode is attached along the left parasternal line, at the level of the 5th rib;
- A brown electrode is attached at the apex of the heart or in the 5th intercostal space along the midclavicular line;
- A black chest electrode is installed along the anterior axillary line at the same level;
- A purple chest electrode is attached along the midaxillary line in the 5th intercostal space.
All electrodes can have different sizes and configurations, which depends on the type of study (one-time recording, daily monitoring or stress test) and the features of the device. In addition, there are disposable and reusable electrodes. You can choose the appropriate option in the online store, but keep in mind that disposable electrodes are designed for modern models of electrocardiographs.
Recording a cardiogram
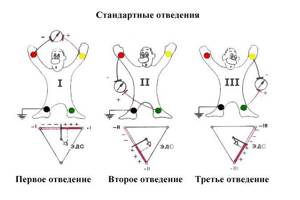
3 standard leads
After applying the electrodes and connecting them to the device, the leads are fixed and recorded on the paper recording tape of the cardiograph. In the case of an ECG, the patient’s arms and legs will be “conductors” of the electrical activity of the heart, and an imaginary, conditional line between the arms and legs will be leads. Thus, 3 standard leads are distinguished: I forms the left and right arms, II forms the left leg and right arm, III forms the left leg and left arm.
First, using limb electrodes, an ECG is recorded in standard leads, then in amplified ones (aVR, aVL, aVF) from the limbs, and then in chest leads (V1-V6) using chest electrodes. The electrocardiograph has a scale and a lead switch, and there are also buttons for voltage and tape feed speed (25 and 50 mm/s).
Recording devices use a special registration tape (for example, OKPD code 21.12.14.190), in appearance it resembles graph paper, has divisions, where each small cell is 1 mm, and one large cell is 5 mm. At a speed of movement of such a tape of 50 mm/sec, one small cell is equal to 0.02 seconds, and one large cell is equal to 0.1 seconds. If the patient is recording an ECG at rest, he should be explained that at the time of direct recording one cannot talk, strain, or move so that the recording results are not distorted.
Recording an ECG in children and pregnant women
Electrocardiography is performed on pregnant women and even newborn children. There are no contraindications to the study, but certain difficulties will arise with people with serious mental disorders. The difference in recording an ECG in an adult and a child is only in the size of the electrodes, which can also be purchased on the Avicena-med medical consumables resource.
Some nuances arise when taking an ECG in people with dextracardia. In such patients, the heart is on the right side, so the results of the study will be exactly the opposite of normal. If the patient is aware of his peculiarity, he is obliged to warn the medical professional.
Algorithm of actions

Cardiograph
The technique of taking an ECG is one of the practical skills that every student of a medical college and university has. And if a student has not mastered this technique, he will not be familiar with medicine. It is not for nothing that medical staff are carefully trained in this manipulation, because in emergency situations, recording an ECG and the ability to decipher a cardiogram can save the patient’s life. The ECG registration algorithm is extremely simple at first glance, but it has its own nuances, without knowledge of which the manipulation will not succeed.
The ECG registration scheme is as follows:
- Preparation for the procedure,
- Application of electrodes,
- Recording on tape.
Let's look at these three points in more detail.
Recommendations for patients
Before undergoing an ECG, patients are advised to:
- Remove foods that affect the cardiovascular system from your diet;
- Stop taking certain medications (only with your doctor's approval);
- Avoid strenuous physical activity;
- Do not apply creams or lotions to your arms, legs, or chest.
If there is severe shortness of breath in a patient in a supine position, it is allowed to record an electrocardiogram while sitting. But in this case, the nurse must more carefully monitor the electrode attachments so that they do not slip.
Electrical axis of the heart.
In numerous textbooks on ECG, enormous attention is paid to the description of the concept of the electrical axis of the heart. In short, it is the resulting vector of impulse motion, or the predominant direction of electrical flow, measured in degrees of deviation from the horizontal in the frontal plane.
Unfortunately for students who have broken their foreheads into rubble while mastering this concept in detail, at the beginning of practical activity it turns out that, regardless of its location, this axis is “strictly parallel to the clinic,” that is, it does not intersect with it in any way.
A slight deviation of the axis to the left, the horizontal, normal and vertical position of the axis do not carry any reliable information, only assumptions from the field of “shamanism”, the role of which is especially small if there is an ultrasound scanner with a cardiac sensor in the office.
The only fact with reliable clinical significance is a sharp deviation of the axis to the left in combination with a moderately widened QRS complex. This condition is called “blockade of the anterosuperior branch of the left bundle branch” (see also the page on conduction disorders).
A picture of a sharp deviation of the axis to the left is characterized by a “negative” (downward) direction of the QRS complex in lead AVF (look at it first), as well as a “fall” in the direction of the QRS complex from top to bottom from the first lead through the second to the third.
In most modern ECG devices and computer programs, the position of the axis is calculated automatically, but just in case, I provide a picture of assessing the position of the axis based on the ratio of the heights of the complexes in different leads.
The thin black triangle with colored vertices is the leads.
The options for the axis position are indicated in green.
The red rectangles show the ratio of the heights of the complexes.