Diagnostics using a magnetic tomograph allows you to study the structure of internal organs without the use of invasive manipulations.
MRI of the pelvic region reflects the slightest changes in the shape, size, and structure of the anatomical formations of this area. The method is based on the use of the phenomenon of magnetic resonance when a force field acts on water molecules in cells. Hydrogen atoms perform vibrational movements, which are recorded by a special device.
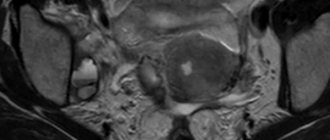
MRI of the pelvis in men, sagittal section
The peculiarity of scanning the abdominal organs is that the gas-filled intestine does not give a response signal, preventing the study of neighboring structures. The presence of feces in the lower sections leads to the appearance of artifacts in the images.
Preparation for MRI of the pelvis in men, as in women, is aimed at reducing flatulence and cleansing the intestines for better visualization of nearby organs.
MRI of the pelvis, which organs are checked in men?
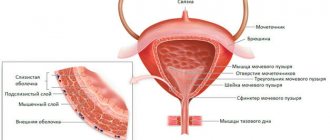
Magnetic resonance imaging is highly informative when studying loose structures containing large amounts of fluid. The area of pelvic examination in men includes:
- bladder;
- prostate;
- seminal vesicles;
- ureters;
- urethra;
- rectum;
- vas deferens;
- fatty tissue;
- The lymph nodes;
- blood vessels.
MRI reflects the condition of the peritoneum located in the pelvic region. If necessary, the doctor can examine the condition of the testicles and scrotum.
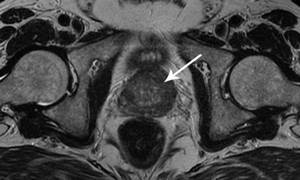
Prostate cancer (indicated by an arrow) on an image taken in axial projection
The lumbosacral and coccygeal spine are also included in the scanning area, but it is more advisable to study bone structures using X-ray methods (CT, MSCT, etc.)
What does an MRI of the abdomen and pelvis show?
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the use of a high-frequency magnetic field, which affects water dipoles in the cells of a living organism. By lining up in a special way, these molecules provide a response from the scanned structures; the intensity of the reaction directly depends on the saturation of the tissues with liquid.
Indications for prescribing MRI of the abdominal region and pelvis are the following symptoms:
- intense pain in the abdominal area;
- yellowness of the sclera and skin;
- dyspepsia (nausea, vomiting, bitterness in the mouth, etc.);
- ascites of unknown etiology;
- signs of internal bleeding;
- weakness, increased body temperature in the absence of obvious reasons;
- pathological impurities in physiological wastes;
- menstrual cycle disorders in women;
- erectile dysfunction and impotence in men;
- infertility.
During the scanning process, tomograms show changes in the anatomical structures of the abdominal cavity and pelvis, which help diagnose various diseases:
- consequences of abdominal injuries;
- inflammatory processes and infectious lesions of the abdominal cavity and genitourinary system (hepatitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, pyelonephritis, etc.);
- cholelithiasis and urolithiasis;
- erosive and ulcerative processes of the gastrointestinal mucosa;
- anomalies in the location and development of organs of the abdominal region and pelvis;
- pathologies of the circulatory system and ischemic lesions in the area of interest;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- disorders of large nerve trunks;
- dystrophic and degenerative changes in internal organs (for example, steatosis);
- adhesive process.
An MRI of the abdominal cavity shows the condition of the organs of the digestive system (stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, gallbladder), fiber, lymphatic vessels and the circulatory network of the area. The scanning area includes the spleen, kidneys, and lumbar spine.
Photo MRI of the intestines, three-dimensional image
MRI of the pelvis determines the condition of the lower part of the large intestine and genitourinary system (uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes in women, prostate gland, seminal vesicles and vas deferens in men).
How can a man prepare for an MRI of the pelvis?
Before a magnetic resonance imaging session, the patient warns the doctor about concomitant diseases and possible contraindications.
MRI of the pelvis is not prescribed for men if they have:
- implanted electromagnetic devices;
- tattoos made with metal-containing inks;
- fixed prostheses made of ferromagnetic metals.
Restrictions on scanning are related to the nature and physical properties of the induction field. Some metals become magnetized during examination, which can lead to heating and displacement of the structure.
Pacemakers, hearing implants, insulin pumps and other medical devices fail when exposed to a directed impulse.
Preparation for MRI of the pelvis in men begins 2-3 days before the procedure. The patient is recommended to follow a diet that prevents the development of flatulence and stool disorders (constipation). Removed from the diet:
- peas, beans and other legumes;
- milk;
- black bread;
- cabbage;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- confectionery;
- nuts, seeds;
- canned foods.
The patient limits the consumption of sweet, sour, spicy, fatty, fried foods. A few days before the scan, it is advisable to give up alcohol and smoking. Carbonated drinks are prohibited; it is better to quench your thirst with clean (bottled) water, weak tea, and compotes.
The patient's diet may include lean meat, poultry, fish, boiled or steamed. Fermented milk products with low fat content, stewed vegetables, and cereals are allowed.
Before an MRI of the pelvis, the lower intestine should be cleansed. If the patient is prone to constipation and bowel movements do not occur naturally, the doctor may prescribe laxatives or a cleansing enema. Self-administration of medications is prohibited. Most laxatives have an irritating effect on the rectal mucosa, which makes it difficult to decipher the results.
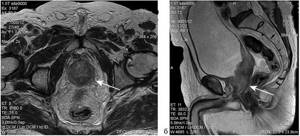
MRI of the male pelvic organs (a - axial and b - sagittal sections), arrows indicate a malignant neoplasm of the prostate with irradiation to the orifices of the seminal vesicles
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach, 4-6 hours after eating. An exception is magnetic resonance imaging with contrast - in this case, an hour before the scan, it is advisable to have a light snack to prevent dizziness and nausea after an intravenous injection.
MRI of the pelvic organs in men is done both with a full and empty bladder. Preparation for the procedure depends on the purpose of the study. To assess the condition of the bladder itself, you need to drink 0.5-1 liter of water before the session.
To avoid the appearance of defects and distortions in layer-by-layer images, the examinee needs to remove metal accessories and change into a comfortable suit (pajamas) that does not restrict movement.
Patients suffering from claustrophobia, increased nervousness and severe pain can, on the recommendation of a doctor, take analgesics and sedatives.
Preparation for MR imaging of the pelvis
- For female patients of fertile age, MRI is best performed on days 7-12 of the menstrual cycle. The study can also be carried out in the 2nd phase of the cycle. MRI during menstruation is not recommended due to the impossibility of assessing the endometrium.
- Recommendations for MRI of the pelvis correspond to points 1-3 (examination of the abdominal cavity, see above.) You can eat a light meal 3 hours before.
- Bowel preparation: on the day of the examination, the large intestine should be free of contents - laxative tea for constipation in the evening before the examination, or natural emptying of the rectum in the morning on the day of the examination.
- Do not urinate 1 hour before the start of the test (no additional fluid intake is needed), the bladder should be moderately full
- In half an hour to 40 minutes you should take 2-3 tablets. “No-shpy” (not the “forte” form!). We perform MRIs on emergency patients without preparation.
MRI of the pelvis in men, how is it done?
Scanning takes place in sagittal, frontal and axial projections. A force field generator located in the tomograph tunnel and additional coils installed above the pelvic region provide a directed electromagnetic pulse. The tissue response is converted using a complex computer program into a series of layer-by-layer black and white images, which are transmitted to the monitor.
To perform an MRI of the pelvis, a man lies down on a table face up, the body and limbs are fixed with special bolsters and fasteners. Remaining still throughout the session ensures that the resulting images are clear and reliable.
The table with the patient is rolled into the tomograph tube. The operating device makes quite a loud noise; headphones are used for protection. Medical personnel are located behind a partition; communication with the patient is maintained using a microphone.
A man undergoes an MRI of the pelvis on a closed tomograph
A native scan takes on average 15 minutes. When using contrast, the duration of the procedure increases by a quarter of an hour. After a series of native images, a pause is made, the patient is given an intravenous gadolinium solution, after which the study is resumed.
The results of an MRI of the pelvis are given to the patient in 15-20 minutes. A series of layer-by-layer images are recorded on a CD or other electronic media; a transcript of the images and a radiologist’s report are attached to the study protocol.
When can you undergo an MRI of the pelvis after classical diagnosis?
The category of abnormal reactions is accompanied by a persistent pain syndrome, which is localized in the lower abdomen and perineum.
The initial method for studying patient complaints in gynecology/urology is called ultrasound. An MRI of the pelvis, where the organs of the reproductive system are examined, should be performed in the following cases:
- unsatisfactory data from ultrasound sonography, x-rays, computer studies;
- differential diagnosis of neoplasms of various origins, cancer staging;
- preparation for surgery;
- monitoring the patient’s condition and the effectiveness of the previously prescribed course of therapy;
- dynamic assessment of disease development/early detection of relapses of tumor lesions in organs;
- determination of biological sex for atypical genitalia.
MRI of the pelvis in men with contrast
Bolus amplification is used in the diagnosis of neoplasms, vascular pathologies, intestinal and bladder diseases. Preparations based on gadolinium chelates (soluble salts), which are characterized by low toxicity and hypoallergenicity, are used as a “coloring” substance.
The solution is administered intravenously using a pre-installed catheter. To ensure a constant delivery rate of the drug, an automatic injector is used. Gadolinium fills the vascular bed in the area of interest and penetrates into the intercellular space. In this case, the solution “illuminates” the bloodstream and provides visualization of neoplasms with a diameter of 3 mm or more.
Based on the results of contrast MRI, the doctor assesses the fullness, patency and condition of the vessel walls. The procedure helps to determine the characteristics of the blood supply to the pelvis, identify areas of ischemia and hemorrhage of organs.
If a tumor is present, experts note the nature of contrast accumulation. Neoplasms have their own vascular network; during malignancy, the capillaries are located chaotically, and a large number of anastomoses occur.
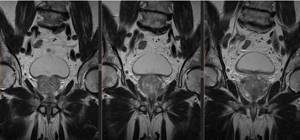
Magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate, photo in frontal projection
Contrast MRI of the pelvis is not performed on men suffering from severe pathologies of the liver and kidneys. The gadolinium solution is excreted naturally in urine and feces. The cleansing process is accompanied by an increased load on the filtration organs, which can lead to decompensation of the existing disease.
Where to get scanned?
MR diagnostics are carried out in any medical institution that has the necessary technical base (equipment for tomography). You can find the nearest diagnostic center on the unified appointment service mrt-v-spb. Open the main page of the site, select the name of the procedure and study the list of medical organizations accepting in this area. Compare clinic ratings and prices for services, read comments and mark the best offers. Reserve time for a tomography through the portal and receive 1000 rubles as a gift for the selected type of diagnosis.
Contraindications
Magnetic or electrical stimulators in the body
The insulin pump, pacemaker, and other electronic and magnetic devices in the body can malfunction as a result of exposure to the magnetic field.
The presence of metal in the area that will be examined on the tomograph
It is contraindicated to undergo the examination if there are implants or other objects made of magnetic metals in the area of the body that needs to be examined. If the metal is amagnetic, then you can undergo an MRI.
Inability to remain still during a CT scan
Other limitations are related to the fact that during an MRI, the subject is placed in a machine in which he must remain motionless for a certain time. Therefore, a contraindication is the inability to remain still during the tomography.
Claustrophobia
During the procedure, you need to be in a tomograph, which is a rather narrow tunnel. Claustrophobia is an absolute contraindication to MRI for this reason.
Indications for the procedure
The need to conduct MRI of the testicles in men is very high, and this should be done regularly. This is dictated by the fact that the procedure allows one to detect illnesses at an early stage, when the chances of a complete cure are greatest and the risks of complications are not so high. There are a number of symptoms that indicate that you need an MRI immediately:
- swelling and redness of the scrotum;
- pain or itching;
- prolapse of the scrotum;
- the appearance of compactions;
- blood in sperm.
What can you see on a pelvic MRI?
Examination using an electromagnetic installation can visualize the following lesions:
- cysts, their origin;
- endometritis;
- abscesses;
- urgent conditions such as cyst rupture, ectopic pregnancy;
- endometriosis;
- progression of abnormal reactions;
- fibroids;
- large polyps, etc.

If the patient has previously been diagnosed with infertility, an MRI of the pelvic organs will show:
- pathologies with genital malformations;
- absence of the uterus or underdevelopment;
- double set of organs;
- abnormal forms of the uterus;
- the presence of septa, which is called Asherman's syndrome;
- adhesive disorders and more.
In case of infertility, doctors designate an MRI, where internal organs are checked, as part of a comprehensive examination. However, screening will not replace endoscopic diagnostic methods.
A urologist may refer a man for an MRI of the pelvis if the following abnormalities in the organs occur:
- neoplasms of unknown origin;
- the need to clarify the obstruction of the urethra;
- inflammatory lesions such as prostatitis, cystitis, vesiculitis;
- cysts;
- abnormal location of the testicle in the groin due to tumors;
- formation of stones;
- hernias;
- diverticula and other pathologies.