From this article you will learn:
- what is tooth pulpitis in dentistry,
- symptoms of the disease, how to treat,
- how to distinguish it from caries and periodontitis.
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the neurovascular bundle (pulp), which is located inside the tooth crown and root canals. The pulp consists of nerve fibers, vascular capillaries and connective tissue cells, and its function is to nourish the tooth tissue from the inside. Nerves and blood vessels penetrate into the tooth through holes in the apex of its roots. The term “pulpitis” arose from a combination of the word “pulp” and the ending “itis,” which denotes the presence of inflammation in the tissues.
Inflammation of the dental pulp most often occurs due to infection entering it - against the background of long-term caries. This can be either caries, which the patient did not notice or ignored for a long time, or caries that occurs secondarily after tooth treatment (for example, under a filling). More often, pulpitis is acute - patients complain of acute throbbing pain. In the absence of timely treatment, it quickly transforms into periodontitis, in which foci of purulent inflammation form in the area of the apex of the tooth roots.
Treatment of pulpitis before and after photos
More details
More details
More details
Dental treatment
| Pulp removal | Make an appointment | 1,000 rub. |
| Ultrasonic expansion of the root canal of a tooth | Make an appointment | 1000 rub. |
| Unsealing the root canal | Make an appointment | from 2000 rub. |
| Instrumental and medicinal root canal treatment | Make an appointment | from 1500 rub. |
| Filling the root canal of a tooth | Make an appointment | from 1000 rub. |
| Closing the perforation of the root canal wall of a tooth | Make an appointment | 3000 rub. |
| Temporary filling of the root canal with a drug | Make an appointment | 1000 rub. |
| Fixation of intracanal pin/inlay | Make an appointment | 2000 rub. |
| Removing the intracanal pin/inlay | Make an appointment | 4000 rub. |
| Restoring a tooth with a filling | Make an appointment | from 3000 rub. |
| Applying a temporary filling | Make an appointment | 500 rub. |
| Removing a temporary filling | Make an appointment | 500 rub. |
| Temporary splinting for periodontal diseases | Make an appointment | 1000 rub. |
| Permanent splinting with solid removable structures for periodontal diseases | Make an appointment | 5000 rub. |
| Ultrasonic treatment of periodontal pocket in the tooth area | Make an appointment | 500 rub. |
| Ultrasonic removal of supragingival and subgingival dental plaque in the tooth area | Make an appointment | 300 rub. |
| Removal of supragingival and subgingival dental plaque in the tooth area using the manual method (CURETAGE) | Make an appointment | 500 rub. |
| Removal of supragingival and subgingival dental plaque | Make an appointment | 5000 rub. |
| Full price list of dentistry |
What is tooth pulpitis
In this article we will tell you more about what pulpitis is and how it manifests itself. The definition of this term implies inflammation of the neurovascular bundle located inside the tooth. The pulp located inside performs many functions, ensuring the normal viability of the masticatory organs. A disruption in its functioning develops when microorganisms begin to enter from the carious cavity along with the decay products of the hard tissues of the tooth. In response to the invasion of the irritant, an inflammatory process occurs, which leads to an increase in pressure inside the pulp chamber. Therefore, a person experiences pain due to compression of the nerve endings.
This disease includes several types that differ from each other in symptoms, clinical manifestations and time of onset:
- Spicy:
- focal;
- diffuse;
- Chronic:
- fibrous;
- gangrenous;
- hypertrophic;
- Chronic in the acute stage.
According to statistics, 20% of people who go to a dental clinic for acute pain come with pulpitis.
Reasons for the development of pulpitis
- Long-term sluggish caries process
- Fracture of the crown of a tooth due to trauma
- Opening the pulp chamber when preparing a carious cavity
- Overheating of the pulp during tooth processing with a drill
- Excessive enamel wear
- Impact on the pulp of toxic components of antiseptic and filling materials during dental treatment
- Penetration of an infectious agent through the blood during influenza and other infections
- Exacerbation of periodontal diseases
Causes
Many patients wonder: what causes pulpitis? All the reasons for its occurrence can be divided into the following types:
- Infectious nature:
- Due to the carious process;
- From other sources of infection;
- Non-infectious nature:
- Physical factors;
- Chemical factors.
In most cases, it develops as a result of an advanced carious process. Dentin has tubes in its structure through which the soft tissues of the tooth deliver nutrients to the hard ones. If the pulp layer is too thin, the pulp becomes more susceptible to infection. Therefore, deep caries at any time can lead to inflammation of the neurovascular bundle.
The reasons for the development of pulpitis may be associated not only with carious lesions of the tooth crown. So, when treating medium or deep caries, there should be an insulating or therapeutic pad between the filling and the bottom of the cavity. Many filling materials, due to their toxic effect, lead to irritation of pulp tissue.
Continuous preparation without water cooling may cause burns. Then, even with healthy dentin and an unopened cavity, inflammation of the neurovascular bundle develops, leading to pulpitis. But for us, such a possible complication has been reduced to zero. Dentistry "Academy Dent" is equipped with only the most modern equipment, and all dental units have a water supply.
Very rarely, an infectious agent can penetrate into the pulp from other sources of the pathological process not related to the carious cavity. This condition is called retrograde pulpitis. The main route of entry of the pathogenic microorganism is through the blood and lymphatic vessels, and also if there is a periodontal pocket.
If a problem arises in a tooth, it will not solve itself. Due to fear of the dentist, people seek help late. Some of them endure pain for several days, hoping that everything will work out.
We figured out what tooth pulpitis is. Now let's move on to how it is identified.
You can't leave it deleted. Pulpitis: what is it and how to treat it?
Inside each tooth there is a small cavity in which the source of its “life” is located - nerve endings and blood vessels that form the so-called pulp. Inflammation of the pulp - pulpitis - is a disease that, according to statistics, affects every fifth person on the planet. Zorigto Mungen-Dorzheevich Oshorov, a dentist at the Expert Clinic, Irkutsk, talks about what it is, how to recognize and cure this disease.
— Zorigto Mungen-Dorzheevich, what is hidden behind the diagnosis of “pulpitis”?
- This is an inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth (pulp) after its eruption. This pathological process from the section of therapeutic dentistry accounts for an average of 28-30% of all visits to the dentist.
— For what reason does pulpitis occur?
— The main reason for the development of pulpitis is infection of the pulp as a result of carious lesions of the tooth.
Inflammation of the pulp can also be of a non-infectious nature. This happens, in particular, as a result of traumatic damage to the tooth (for example, when it is fractured) and due to erroneous manipulations of the dentist - such as overheating of the pulp or opening of the pulp chamber during treatment (pulpitis resulting from medical interventions is called iatrogenic ). Another reason for the development of pulpitis is pathological abrasion of teeth.
Rarely does pulpitis develop due to inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues, and even less often - with general somatic diseases, for example, osteomyelitis, sepsis, acute respiratory viral infections.
— Tell us about the types of pulpitis.
— There are acute and chronic forms of pulpitis. In case of acute pulpitis, patients usually immediately turn to the dentist. The chronic process can be asymptomatic during the period of remission, and in the acute stage it is often confused with other pathological processes.
There are many nosological forms of pulpitis, but for the patient it is important whether the form of pulpitis he has is reversible or irreversible, that is, whether it is possible to cure a tooth without removing the pulp, or whether this is impossible.
— What are the symptoms of pulpitis?
— The insidiousness of pulpitis is that often its symptoms do not correspond to the pathological changes occurring in the tooth.
The initial stage of development of pulpitis is characterized by aching pain with “light” intervals, attacks of which are associated with exposure to temperature stimuli. In the terminal stages, the pain becomes spontaneous, it spreads along the branch of the trigeminal nerve, so patients feel diffuse pain in the temple, jaw, and ear.
The scant symptoms characteristic of chronic pulpitis are one of the reasons why patients seek help from a dentist late. Since the manifestations of pulpitis may be similar to the symptoms of sinusitis, trigeminal or facial neuralgia, otitis, alveolitis, caries, there is a need to differentiate the problem by resorting to various diagnostic techniques.
— How is pulpitis diagnosed?
— Diagnosis of pulpitis consists of patient complaints, questioning, examination, and x-ray examination. An additional research method is electroodontometry, the indicators of which allow one to assess the level of electrical conductivity of the pulp (with pulpitis they decrease).
— What treatment methods for dental pulpitis does modern dentistry offer?
- They depend on the form of pathology. In the initial focal form of pulpitis, therapeutic fillings are used. More advanced forms require removal of inflamed or necrotic (dead) pulp.
In some cases, vital amputation of the pulp is performed in children, that is, only the coronal part is removed.
After complete removal of the inflamed pulp, antiseptic treatment of the cavity and canals of the tooth is carried out, dense obturation (filling) of the canals with filling materials. After this, an x-ray is taken to evaluate the quality of the manipulations performed. Then the damaged crown part of the tooth is restored.
The duration of treatment for a tooth affected by pulpitis can range from one to four visits. This depends on the type of tooth, its location, the complexity of the anatomical structure of its canals, the shape and stage of pulpitis, and the degree of tooth destruction.
If tooth restoration requires the installation of an orthopedic crown, another 2-3 visits may be required.
— Can pulpitis go away without treatment?
- No. The inflammation may go into remission, and the patient may think that the problem has been resolved.
— Are there complications of pulpitis? If so, why might they develop?
- Of course, there are. In acute and chronic pulpitis, inflammation can spread to the periodontal tissues with the development of periodontitis (inflammation of periodontal tissues), up to a purulent form of the inflammatory process. This complication is associated with the patient’s late visit to the dentist.
— What should a patient do if, after treatment of pulpitis, the filled tooth continues to hurt?
— Often, after treatment of pulpitis, the patient may experience pain when biting. This is due to trauma to periodontal tissues during treatment. The pain usually goes away within two to three days. If your tooth continues to hurt a week after treatment, you should consult your doctor.
— What preventative measures will help avoid pulpitis?
— Among the primary prevention measures, I would like to note a balanced diet, daily high-quality oral hygiene, regular dental examinations, and the use of fluoride-containing medications. If the disease has already occurred, to prevent complications of pulpitis and prevent the development of new pathological foci, complete sanitation (improvement) of the oral cavity is required.
More information about dental services in Irkutsk can be found in the “Dentistry” section here
Interviewed by Sevilya Ibraimova
The editors recommend:
The ubiquitous “bone eater”: what does modern medicine know about caries?
For reference:
Oshorov Zorigto Mungen-Dorzheevich
Graduate of Irkutsk State Medical University with a degree in Dentistry in 2010.
In 2011, he completed an internship in dentistry at Irkutsk State Medical University.
In 2011-2012, 2016-2017, he completed cycles of retraining and advanced training in orthopedic and therapeutic dentistry.
He holds the position of dentist-orthopedist-therapist at “Clinic Expert” Irkutsk. Receives at the address: st. Kozhova, 9A.
How is the diagnosis made?
An oral examination alone is not enough to make a diagnosis. The dentist, interviewing the patient, tries to find out as much information as possible about the disease. He pays great attention to such issues as:
- When did the pain start?
- How long does it last?
- Did your tooth hurt before?
- What reasons provoke it?
- At what time does it occur?
- What calms her down?
To complete the diagnosis, the following data from clinical studies can be considered reliable signs of pulpitis:
- Thermometry;
- Electroodontodiagnostics;
- Probing;
- Percussion;
- X-ray.
A thorough history taking and clinical examination allows the dentist to choose a rational treatment method. Clinical manifestations of dental pulpitis may be similar to other inflammatory diseases. And then the doctor will need to differentiate from them.
Diagnosis of pulpitis
Correct diagnosis of pulpitis is a primary task for any dentist, since this disease can be confused with caries, trigeminal neuralgia and exacerbation of chronic periodontitis. Each of these diseases is characterized by pain symptoms, so in order for the diagnosis to be correct, it is necessary:
- identify the causes of pain;
- determine the frequency of pain;
- determine the intensity of attacks;
- conduct a visual inspection;
- carry out x-ray diagnostics.
Acute pulpitis
Acute tooth pulpitis is a disease whose duration does not exceed 14 days. It is divided into focal and diffuse. Their differences consist not only in the time period, but also in clinical manifestations. Acute forms differ from chronic forms by severe and throbbing pain, which is paroxysmal in nature. They are especially pronounced at night.
The focal form of acute pulpitis lasts 1-2 days. Eating cold food or water causes extremely unpleasant sensations that do not go away for a long time. Painful attacks can last from 10 to 20 minutes. This stage of tooth pulpitis is the most favorable, because at this time the purulent melting has not yet had time to develop and the pulp can be preserved. But in practice, this is very rare, since the patient is in no hurry to see a dentist when a toothache occurs.
Most often, patients ignore the pain or mask it by taking painkillers, hoping that the root of the problem is neutralized. But many people don’t even think that a disease such as tooth pulpitis can lead to the loss of this organ.
Acute diffuse pulpitis develops already on the second or third day. The duration of this period is 12-13 days. The attacks turn into constant aching pain, and the “light” intervals become shorter. In contrast to focal pulpitis, symptoms arise from the hot temperature of the irritant. A person cannot tell which tooth is sick, since signals from the source of inflammation are sent along the branch of the trigeminal nerve, affecting the entire jaw. Clinical research methods help determine where the inflamed pulp is located.
In the first days, the symptoms of diffuse pulpitis are of the nature of serous inflammation. And later, as the process progresses, purulent inflammation of the pulp occurs. The transition from the alteration phase to the exudation phase can be determined by thermometry. With a purulent process, pain will always arise from hot things. In order to diagnose it, it is necessary to differentiate it from such types of diseases as:
- Periodontitis;
- Trigeminal neuralgia;
- Sinusitis;
- Retention of a wisdom tooth.
All types of acute pulpitis are characterized by the presence of a deep carious cavity filled with a large amount of softened dentin. But there is no opening leading into the pulp chamber. However, inflammation leading to pulpitis still occurs for some reason. The thing is that with deep caries, the bottom of the dentin passes through the dentinal tubules with an infectious agent. And the toxins released by it stimulate the development of a local immune response from the dental pulp.
Symptoms of pulpitis of baby teeth
The following symptoms are characteristic of childhood pulpitis.
Strong pain. Most often it occurs in the evening and at night, or during chewing and pressure. In addition, the child may refuse to eat hot or cold food or complain of pain outside in the cold.
There is one problem with this symptom - due to the rapid transition of pulpitis into chronic pain, the pain can go away in just a couple of days, so sometimes the child simply does not have time to complain, and the parents do not have time to react.
In addition, if pain bothers a very young child, he often cannot clearly explain what is wrong, so you need to focus on external signs - crying, moodiness, refusal to eat.
A noticeable carious cavity on a tooth . This is not a mandatory sign - sometimes the tooth is externally intact, but the pulp in it is inflamed. However, if a child complains of pain or feels unwell, and one or more teeth are damaged, this is a sign of pulpitis.
Loosening of the tooth. Due to injury or destruction of the pulp, the tooth may begin to become loose, although it is too early for it to fall out.
Increase in temperature and deterioration in general health . It is especially common in young children, as they react particularly acutely to inflammation.
Swelling or swelling of the cheek. It doesn't happen very often, but it is a clear sign that something is wrong with your teeth. This can be a symptom of both pulpitis and periodontitis or periostitis - a doctor will make an accurate diagnosis.
All these symptoms are weak and unexpressed, sometimes even the child himself ignores them. Only a doctor can accurately diagnose pulpitis, and various methods are used for this, from a simple examination to an x-ray. Therefore, it is important, even in childhood, to regularly take your child to the dentist in order to recognize the disease in time.
Chronic pulpitis
Chronic pulpitis is a tooth pathology that can exist from several months to several years. It happens that sometimes at a dental appointment it is discovered completely by accident. The patient may not experience discomfort or complain. However, the dental pulp undergoes structural changes, which can subsequently cause complications in the periapical tissues.
According to statistics, in 30% of cases with chronic forms, an x-ray can identify a center of clearing in the area of the tooth root. If chronic inflammation of this bundle is not treated, bone loss may occur and, as a consequence, periodontitis. Not every doctor will agree to treat such a tooth, and in the end it will be removed.
There are three chronic forms of pulpitis: fibrous, gangrenous and hypertrophic. The first occurs in most cases, the other two are extremely rare. The age category of people with dental disease such as pulpitis varies from 20 to 50 years. A distinctive feature of chronic forms from acute ones is the presence of an opening between the carious cavity and the cavity of the tooth.
Complications and consequences
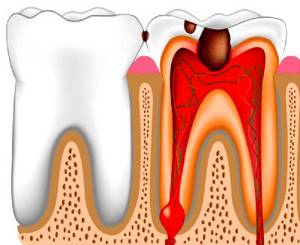
If pulpitis is not treated in time, serious problems may appear. For example, periodontitis may occur. The infection contained in the pulp also spreads to the soft tissues that are around. After this, the jawbone begins to deteriorate. The result is that periodontitis turns into osteomyelitis or purulent periostitis. Also, through the bloodstream, the infection can affect the entire body, and because of this, internal organs can suffer.
Fibrous pulpitis
Chronic fibrous pulpitis can be a consequence of acute forms, or it can occur independently. Characteristic of this disease is the proliferation of fibrous tissue inside the tooth cavity. Symptoms of fibrous pulpitis are a feeling of heaviness and “bloating” in it. The affected organ reacts to all types of irritants, but most of all to sudden changes in temperature. A painful reaction, as with focal pulpitis, occurs to cold food and drinks.
Chronic fibrous pulpitis looks like deep caries, but when probing the bottom, the dentist reveals an opening leading into the pulp chamber. It sometimes happens that defects in hard tissues are localized in an inaccessible place and the pulp does not respond to external influences. Therefore, signs of tooth pulpitis may not be observed.
How to understand that there is pulpitis on a tooth?
A person cannot calmly chew food; pain occurs, which is very sharp. In this case, it occurs if a hot or cold liquid gets on the tooth. If we talk about external signs, then usually the gums swell, bleed, and the enamel may darken.
Pulpitis can be acute or chronic. The first option is marked by sharp, sudden pain. Such pulpitis will affect some part of the tooth or the entire area. As for chronic inflammation, the whole process is slow, but the pain will be less. Unpleasant sensations may fade and then return again.
Gangrenous pulpitis
Necrosis of the soft tissue of the tooth leads to such pulpitis. The neurovascular bundle is no longer viable and must be removed. Upon external examination, the carious cavity is filled with putrefactive decay of hard tissues and has a dirty gray color. The cause of pulpitis is the addition of pyogenic microflora.
Typically, with gangrenous dental pulpitis, the appearance of halitosis is observed. There is no pain syndrome due to mechanical and chemical influences, but the tooth actively reacts to heat. Probing can be painful deep in the root canals if there is still living pulp in them. Its complete death can be judged by electroodontodiagnosis data. With total necrosis, electrical excitability indicators exceed 100 mCa. This form of pulpitis is not subject to conservative treatment.
Hypertrophic pulpitis
This form of pulpitis develops more often in children or adolescents, but it is also rare in them. The patient may notice gum growing out of the tooth cavity, but it is actually pulp. It can increase in size, as its constant injury leads to the growth of granulations. Hypertrophic pulpitis is divided into two forms:
- Granulating,
- Pulp polyp.
The first form looks like an overgrowth of granulation tissue. It has a bright pink, even red color. When subjected to mechanical action, it bleeds and creates unpleasant sensations. The pulp polyp is a transitional form from the first. The cause of this type of pulpitis is the contact of the oral epithelium with granulation tissue. The formation acquires a pale pink color, and upon probing does not create painful sensations.
The patient complains of acute pain that occurs when eating. Bleeding may even occur, since rough food gets into the tooth and injures the soft tissue. Over time, hygiene in this place ceases, because due to pain a person cannot fully clean this area. Bad breath appears because the accumulated food substrate begins to be actively fermented by microorganisms.
This form of the disease cannot be diagnosed with the naked eye. But before doing this, you need to make sure that the grown formation is not a hypertrophied gum or interdental papilla.
Classification of pulpitis
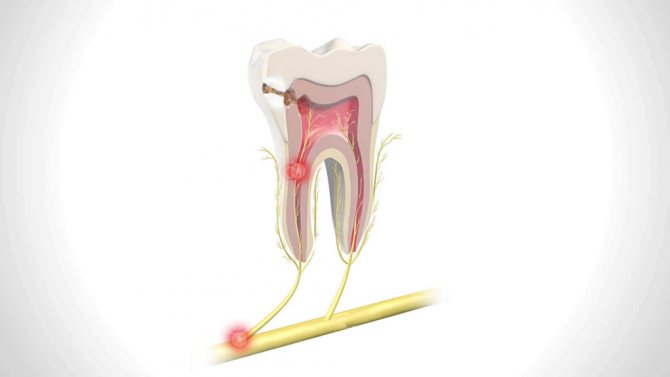
The disease is usually classified according to the main defining characteristic - the type of process. Depending on this factor, pulpitis can be acute or chronic. Acute, in turn, is divided into focal (with a focus in the apical part), diffuse (infection spreads to all parts of the pulp) and purulent (accumulation of pus in the pulp chamber). The chronic form of the disease can be fibrous (initial stage), hypertrophic (tissue growth like a polyp) and gangrenous (decay of pulp tissue and tooth destruction).
Treatment methods for pulpitis
The choice of treatment method will be based on the anatomical features of the tooth and the form of the disease. There are two main treatment options: conservative and surgical. The first option can be used in the first 24 hours, when pulp inflammation is localized only in the coronal part. An applied medical pad can reverse this process. In all other cases, doctors resort to preparation and opening of the tooth cavity in order to remove the inflamed nerve.
Anesthesia is always necessary before starting such an intervention. Therefore, there is no cause for concern for patients. In Moscow, dentists at Academy Dent use only the most effective anesthetics, which allow this procedure to be carried out painlessly.
Removal of the nerve can be complete or incomplete. The choice of method depends on the duration of the disease and how many roots the tooth produces. Molars have 2 to 3 roots, and the front teeth have only one. The cavity of the crown of the front incisor or canine smoothly passes into the root canal, and the border between them is little noticeable. In this case, it is better to remove the pulp with one cord. With multi-rooted teeth, you can choose to remove it only in the crown area or capture the root part.
Tooth pulpitis can be treated with the following options:
- Vital amputation;
- Vital extirpation;
- Devital amputation;
- Devital extirpation.
Based on the symptoms, treatment of tooth pulpitis will be carried out either in one or in several stages.
How will pulpitis be treated in the dentist's office?
Only a doctor can give you an exact answer to this question after examination and diagnostic measures. But in most cases, pulp removal is chosen. How will treatment be carried out using this method? Let us consider in detail all stages of the treatment process:
1. A patient comes to the dentist's office. The doctor carefully examines his oral cavity and the diseased tooth, and takes an image that allows him to assess the stage of development of inflammation. The patient is given an injection of an anesthetic drug.
2. The tooth is drilled with a drill to gain access to the pulp chamber, which contains the dental nerve. The doctor removes the pulp with a special instrument - a pulp extractor.
3. Another photograph of the tooth is taken, which will allow the doctor to see the shape, length and all branches of the dental canals.
4. The dentist carries out thorough cleaning and antiseptic treatment of the cavities of the dental canals. This is necessary to completely eliminate the risk of re-inflammation.
5. The canals are filled and the tooth is restored.
With this treatment regimen, it can be completed in one or two visits to the dentist. In some cases, patients are additionally prescribed antibacterial therapy.
This is how pulpitis is treated in a dental clinic. One of its most important stages is channel processing. If mistakes are made in this process, a relapse of the disease is possible.
In our dental clinic in Moscow - “Aesthetica”, treatment of canals for pulpitis is carried out under a microscope - an optical device that allows the doctor to accurately see all the structural features of the canals and qualitatively remove diseased tissue without affecting healthy tissue. This approach to the treatment of pulpitis guarantees high efficiency and allows you to save the tooth even in the most difficult cases!
Why do we need x-ray diagnostics?
This research method is always carried out during endodontic intervention. During treatment, x-rays are taken several times. Before the dentist begins to treat the tooth, he will send the patient for an x-ray. In the resulting image, the masticatory organ will give a complete picture of the course of the roots and the number of root canals they contain.
Pulpitis in the image does not provide information since the dental pulp cannot absorb rays. Accordingly, pulpitis cannot be diagnosed radiographically. However, performing this action is necessary in order to:
- Recognize the location of caries and its depth;
- Exclude pathology in bone tissue;
- Differentiate pulp inflammation from other diseases.
The photo shows a pathological focus near the root. This is periodontitis:
His symptoms and pulpitis may be the same, but this research method allows a definitive diagnosis.
In addition, the doctor determines from the image the length of the endodontic instrumentation that will be used during the treatment process. After completing all the manipulations, the patient should take another picture, since at this stage the dentist looks at how the root canals are filled.
Do not be afraid of radiation coming from the X-ray machine. Dentistry "Academy Dent" uses modern equipment that has a reduced radiation exposure to the patient's body.
Prevention
Usually, caries leads to the pulp of the tooth. If you do not want to diagnose yourself with pulpitis, then it is worthwhile to prevent this disease. It is important to visit the dentist regularly to treat those teeth that are problematic.
To strengthen the enamel, you can use some products that contain fluoride, calcium, and vitamins. You should not let your sore throat become chronic, as this can also cause dental disease.
If you have an inflammatory process or pain in your teeth, then you should immediately go to a specialist. Until then, to improve the condition, you can rinse the tooth with herbal decoctions and solutions. It could be sage, eucalyptus, chamomile. As for solutions, these are chlorhexidine, miramistin. This will relieve the pain for a while. If there is pus, you can rinse your mouth, but only with liquid at room temperature. This will prevent the spread of the purulent process. And it is important to understand that it is better not to delay treatment, so as not to get more serious problems.
Cost of treating a pulpit tooth
The website of our dentistry presents the price list for the services we provide. Treatment of pulpitis with root canals starts from 6,500 thousand rubles. The cost will depend on several factors. The doctor takes into account the number of channels, because the amount of work directly depends on this. Thus, treatment of pulpitis in the front tooth will be cheaper than in the side tooth. It is no less important what condition the tooth is in, or rather what stage of development of pulpitis the patient came with. The rule here is: the sooner, the better and cheaper.
To summarize, I would like to once again remind patients of the importance of timely treatment. Take care of your teeth and start caring for them as early as possible. A tooth is an organ incapable of self-regeneration. And if any disease has arisen in it, then in the future it will only lead to complications that are more difficult to treat. So, pulpitis can cause the development of periodontitis and saving the tooth will be more difficult.
Diagnostic methods
Correct diagnosis of the disease is a guarantee of successful treatment. The examination protocol contains the following methods:
- patient interview;
- visual inspection;
- probing with a dental probe;
- percussion (tapping);
- electroodontodiagnosis (testing the electrical excitability of the pulp substance);
- radiography.
Please note: our dental network is equipped with modern diagnostic equipment from Germany. This allows you to accurately determine the type of pulpitis in the shortest possible time and carry out its effective treatment.