- What does a CT scan of the cervical spine show?
- CT with contrast
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Preparing for the examination
- How is the procedure performed?
- Decoding the results
- How often can you do it
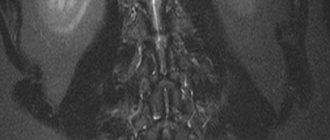
CT scan of the cervical spine is a modern, informative, non-invasive method for examining the vertebrae, intervertebral discs, spinal canal and spinal cord located at the level of the neck.
Typically, the examination is performed covering the area of the base of the skull above and the first thoracic vertebrae below in order not to miss pathological changes that may be located in these transitional areas.
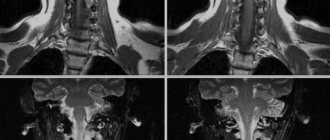
Computed tomography of the cervical spine allows you to obtain images of layer-by-layer sections of the human body. Dark and light areas of the images are a reflection of various organs and tissues, which differ from each other in their ability to retain X-rays. For example, bone tissue appears light, almost white in photographs due to its high ability to absorb X-rays.
The thickness of the sections ranges from 1 to 3 mm. Large slice thickness significantly speeds up the procedure, but will reduce the information content of the examination. Modern models of tomographs allow, in addition to images, to obtain three-dimensional models of the organs and anatomical structures being studied. The doctor can examine such a model from all sides, rotate it, enlarge it, and zoom it in. All this makes it possible to obtain more information about the structure of tissues and organs of the area under study, as well as with a greater degree of probability to identify violations in the structure of individual elements and their relative position relative to each other. This is especially useful in cases of cervical injuries.
What does a CT scan of the cervical spine show?
The following types of disorders can be identified in the images obtained during the examination::
- congenital features of the development of the spine;
- cervical injuries: fractures and displacement of the vertebrae, hematomas;
- narrowing of the spinal canal;
- tumors;
- osteochondrosis, disc herniation;
- changes in vertebral bodies, their deformations;
- inflammatory processes localized in the vertebrae, spinal cord, soft tissues surrounding the spine;
- changes in the spine, characteristic of a number of diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis;
- consequences of injuries and surgical operations.
Alternative Methods
As an alternative method, if it is not possible to perform a CT scan, the patient can undergo traditional radiography. This technique makes it possible to diagnose osteophytes (overgrowth of the vertebrae) and changes in the structure of the intervertebral discs that appear with osteochondrosis. X-rays can also be used to detect osteoporosis, which is a condition in which bone density decreases. This diagnostic procedure allows you to detect large and medium-sized tumors. However, in subtleties she is powerless.
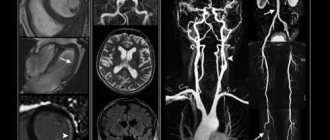
The next alternative method is MRI. However, this technique is primarily used for soft tissue imaging. The information content of MRI for diagnosing vertebral pathology is lower than that of CT.
Myelography is considered an informative method for studying the pathology of the cervical segment of the spinal cord. This technique involves injecting contrast into the spinal canal followed by a series of x-rays. Myelography can be used to diagnose narrowing of the lumen of the spinal canal, tumor formations of the spinal cord, and so on. Today, this study is carried out only if the patient cannot undergo a CT or MRI. This is due to the fact that myelography is accompanied by the need for a puncture (puncture) to administer contrast, which can cause a number of complications.
CT scan of the cervical spine with contrast
The examination can be performed either with or without the use of a contrast agent. Bone tissue is clearly visible in images without contrast enhancement. But vessels, benign and malignant formations, foci of inflammation can be practically indistinguishable on native images.
The decision about the need to administer a contrast agent is made by the radiology doctor who conducts the examination. The need to administer contrast may arise during an examination in cases where the doctor sees changes in the images, but cannot identify them due to the lack of details important for diagnosis.
Examination of the cervical spine is carried out using an iodine-based contrast agent intended for intravenous administration..
Most often, the drug is administered once before or during the procedure. Bolus (long-term, dosed) administration of contrast is indicated in cases where it is necessary to obtain information about the condition of the vessels of the neck and the characteristics of the blood supply to the tissues.
The following symptoms may occur in response to the administration of a contrast agent::
- sour or metallic taste in the mouth;
- pain at the injection site;
- flushes of heat in the body;
These reactions are not harmful to the patient's health.
Contrast drug intolerance is manifested by the following symptoms::
- swelling of the face, ears;
- difficulty breathing due to swelling of the larynx;
- sore throat;
- nausea and vomiting;
- itchy skin;
- hives
- bronchospasm;
- drop in blood pressure.
The appearance of these symptoms requires special treatment, so you should not wait until the end of the procedure; you must immediately report your discomfort to the medical staff using voice communication.
The risk of developing an allergic reaction is increased in individuals with intolerance to drugs containing iodine, seafood, as well as in patients suffering from bronchial asthma.
Contrast enhancement
To improve tissue visualization, detect tumors and vascular changes, CT with the introduction of a contrast agent is recommended. For this purpose, modern centers use iodine-containing drugs such as Omnipaque and Yopamiro. Scanning begins after contrast has been administered to allow it to accumulate in the tissue. Directly during the injection, a feeling of warmth in the arms and legs or other subjective sensations may be noted. These symptoms are considered common when contrast agents are administered.
Indications for examination
Computed tomography of the cervical spine is performed in the following cases:
- acute and chronic spinal injuries;
- the presence of chronic neck pain, headaches, dizziness;
- abnormalities of the spine;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
- hemorrhage in the spinal cord;
- tuberculous spondylitis (inflammation of the vertebrae);
- tumors of the spine and surrounding soft tissues, metastases of tumors to the spine from other organs;
- malformations (vascular anomalies), circulatory disorders in the spinal cord;
- osteomyelitis;
- preparation for surgery on the spine or spinal cord;
- monitoring the condition of the spine and spinal cord after surgical treatment, chemotherapy or radiation therapy during the period of remission.
Price
The price of MSCT of the cervical spine depends on several factors: the need to administer a contrast agent, the chosen clinic, and the need to create a 3D model of the examined area. Some centers offer an independent opinion (as a “second opinion” from outside experts) as an additional service.
In general, the cost of MSCT of the cervical spine starts from 3,000 rubles and above. The price for MRI lies within similar limits. An X-ray examination will cost about a thousand rubles, and a CT scan will cost about 2-2.5 thousand.
Contraindications for examination
CT scan of the cervical spine is not performed in the following cases::
- pregnancy at any stage;
- patient weight that exceeds the maximum permissible load on the tomograph table (about 120 kg).
A CT scan of the cervical spine is performed with caution and only if there are serious indications.:
- children under 12 years old;
- nursing women (milk becomes unsuitable for feeding the baby for some time);
- patients with renal failure;
- with multiple myeloma.
Contraindications for the administration of iodine-containing drugs:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- renal and liver failure;
- diabetes;
- intolerance to iodine-containing contrast agents.
Advantages
The latest generation computed tomograph ensures high speed of examination and reduces radiation exposure to the patient. You will feel comfortable throughout the entire procedure thanks to the comfortable tomograph table. The Aquilion Lightning TSX-035A tomograph has other advantages:
- support for reconstruction algorithms for bones, small structures, soft tissues;
- software packages for suppressing artifacts from metal objects (the image is even higher quality, which increases diagnostic accuracy);
- recording the results onto DVD media.
How is a cervical CT scan performed?
It is necessary to ensure that there are no metal fasteners (zipper sliders, buttons, metal buttons, etc.) or trim elements on the clothing in the neck area. You will also have to remove jewelry such as a chain, pendant, beads, brooch, hair clips, hearing aids, and removable dentures. Metal parts leave shadows on images, which significantly reduces the information content of the examination.
The patient may be asked to change into a special robe with clasps or a shirt. Any voluntary or involuntary movements can spoil the images, so the patient may be secured on the tomograph table with straps.
The table moves into the tomograph together with the patient. The medical staff leaves the room in which the tomograph is located to avoid exposure to radiation, but continues to monitor the patient’s condition through a special window that is impenetrable to X-ray radiation. You can contact the nurse using two-way voice communication or a call button for medical staff, if this model of tomograph is equipped with one.
The examination takes about 5 minutes. If a cervical CT scan is performed with contrast, the patient will have to spend about 30 minutes in the CT scan room.
Advantages of performing CT scans at the CELT clinic
In the multidisciplinary CELT clinic, examinations are carried out using a modern 64-slice tomograph from General Electric. Thanks to the high quality of the equipment, all patients receive accurate examination results.
CT is an absolutely safe and simple examination, so it is often prescribed to clarify the diagnosis for any complaints of pain in the spine. The information obtained from tomography is often sufficient to make a diagnosis and begin treatment. At the CELT clinic, after the examination, the patient can receive advice from an experienced specialist - a neurologist, neurosurgeon, pulmonologist and others.
Native computed tomography does not require any special preparation - all you need to do is arrive on time and follow the doctor’s instructions. If a contrast study is planned, biochemical blood tests may be prescribed. This is required to ensure that the kidneys are functioning normally - the body will have to remove the contrast agent. Such a study is also safe if the patient is not allergic to the components of the compound used.
Decoding the results obtained
A radiologist or radiation diagnostics doctor is engaged in decoding. The description of pathological changes and the formulation of the conclusion take time, so the patient can receive the document either an hour after the end of the examination, or the next day. After decoding, the patient receives photographs on digital media or printed on film, as well as a doctor’s report certified by signature and seal.
It should be understood that the conclusion of a radiology doctor is not a diagnosis. The diagnosis is made by the attending physician taking into account the clinical picture of the disease, patient complaints, data from instrumental and laboratory tests.
How often can a CT scan of the cervical spine be done?
Due to the fact that some of the X-ray radiation is absorbed by tissues during the examination, restrictions have been introduced for computed tomography on the volume of one and the frequency of procedures. Small doses of radiation do not harm human health, so one procedure performed according to indications will not cause disturbances in the patient’s body. It’s another matter if examinations are carried out one after another. In this case, radiation doses accumulate, which can lead to the development of radiation sickness or the appearance of tumors.
The optimal interval between CT examinations is 12 months, regardless of whether the same area of the patient’s body will be examined or some other area. If there are serious indications, a re-examination can be performed no earlier than 6 months after the first.
Risks
CT scanners are being improved every year in order to reduce the patient's radiation dose. Currently, the total radiation dose received during scanning is negligible. But with repeated studies, the risk of negative effects of ionizing radiation increases.
However, in some cases a CT scan may be performed if the diagnostic value of the scan outweighs the risks, for example if a malignancy is suspected.
The contrast that is most often used in CT scans contains iodine and therefore the possibility of an allergic reaction must be taken into account.
If the patient is extremely interested in the administration of contrast and there is a certain allergic mood, then it is possible to use antihistamines or steroids.
The iodine contained in the contrast is excreted by the kidneys. Therefore, if you have kidney disease or diabetes, you must coordinate the procedure with your doctor.
If the patient is taking a diabetes drug, then additional precautions are necessary
All CT scanners have feedback from the radiologist, and if symptoms of an anaphylactic reaction appear, the patient must immediately inform the doctor so that anti-shock measures can be taken, which are necessary for the development of anaphylactic shock.