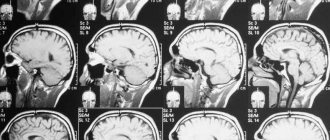
Computed tomography of the spine is a modern method of layer-by-layer scanning of segments of the spinal column with subsequent reconstruction of the image in three projections. The technique of the procedure is based on X-ray radiation, namely, on the principle that tissues of different density and morphology are visualized differently on scans.
On tomograms in three projections, you can examine the vertebrae, see if the processes are damaged, or if there is compression (compression of the spinal canal).
X-rays have high resolution, and CT data is recorded and processed on a computer in high quality. This makes computed tomography the most accurate and preferred method for assessing bones and joints after injuries or before spinal surgery. Standard radiography is a planar two-dimensional image, inferior to scanning data from a modern multispiral tomograph. CT will be most informative in the case of diagnosing infectious and inflammatory processes (osteomyelitis), tumors and bone destructive processes.
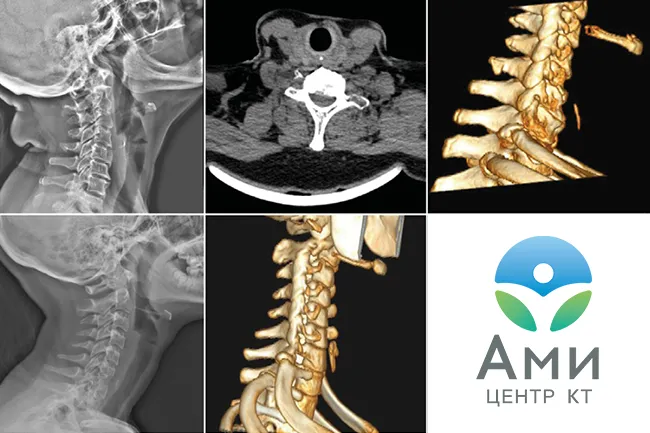
Computed tomography of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral spine allows high-quality visualization of not only bones and joints. The technique has proven itself to be excellent in diagnosing neurological disorders associated with post-traumatic changes. This usually occurs after a spinal injury, and sometimes even after an awkward movement. If the pain becomes chronic and reduces the patient's quality of life, the treating neurologist may recommend a CT scan of the spine to determine the cause. Based on the location of pain, the attending physician will determine which part of the spine needs tomography in this case.
For numbness in the hands and headaches, it is recommended to do a CT scan of the cervical spine. For problems with legs and dysfunction of the pelvic organs - CT scan of the lumbosacral spine. CT scan of the thoracic spine allows us to evaluate not only the condition of the vertebrae in this segment. On tomograms of the thoracic spine, the radiologist will also see rib fractures, foreign objects in the lungs, neoplasms of the pleura, mediastinum, and respiratory organs.
What does a CT scan show?
Computed tomography clearly visualizes fractures and cracks of the coccyx, deformation and displacement of the vertebrae, degenerative changes, and abnormal development of bone structures. A CT scan can also show the presence of foreign bodies and bone fragments in soft tissues. The procedure helps to detect tumors and exclude the presence of metastases in soft tissues.
Using computed tomography, you can determine the severity of the injury: the doctor will see cracks, displacements, etc. The study is prescribed to diagnose various structural changes in the area of the coccyx and sacrum.
Spinal fractures on CT
In matters of diagnosis and assessment of vertebral bone trauma, the “golden branch” of primacy belongs to computed tomography. According to PubMed, the detection rate of spinal fractures using CT (or MSCT) reaches 97-100%. This is the best indicator to date.
Spinal fractures are:
- open;
- closed;
- compression;
- compression splintered;
- isolated (only 1 vertebra is broken);
- multiple, etc.
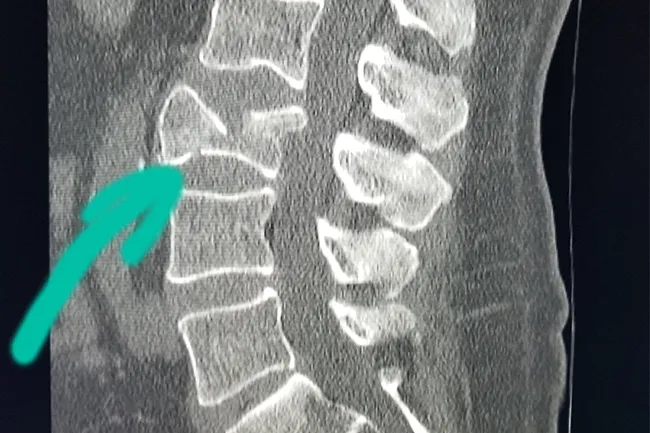
A compression fracture of the spine is a consequence of an injury that occurs during simultaneous compression and flexion, and the fracture site is wedge-shaped with the apex directed forward. These fractures cause severe pain.
Compression fractures occur due to the impact of great force on the spine - as a result of an accident, a fall from a great height and other emergency situations. It is important to check whether the spinal cord is damaged and whether the spine is actually broken in only one place.
According to WHO statistics, most spinal fractures are caused by osteoporosis. About 50% of all fractures occur in the lumbosacral spine, 40% in the thoracic spine, and 10% in the cervical spine. When falling from a great height onto the heel bone and injuring it, in 10% of cases a fracture of the thoracic spine occurs due to axial load.
When assessing post-traumatic changes in the spine on a CT scan, the radiologist looks for dislocations, kyphosis, and bone fragments in the spinal canal.
Preparation
If the study is performed with contrast, a blood test for creatinine is required.
No special preparation is required for the procedure (no different from standard preparation). Before performing the procedure, study the contraindications. The main contraindication may be the patient’s heavy weight, since tomographs have limitations. Please check with a center employee for more details when registering.
Curvature of the spine (kyphosis) on CT
Externally, kyphosis manifests itself in poor posture and changes in the curvature of the spinal column. But this is not only an aesthetic defect. Stooping (increased bending towards the back) indicates an incorrect position of the vertebrae in relation to each other.
Most often, kyphosis affects the thoracic spine. Over time, this leads to displacement of other organs (for example, the diaphragm), wedge-shaped deformities of the vertebrae occur, and intervertebral discs become thinner.
There are 3 stages of kyphosis. And if at the first stage the curvature of the spine manifests itself in stooping, increased fatigue of the spine with muscle weakness, then at the third stage there are malfunctions in the functioning of the internal organs (atrophy of the intercostal muscles, disturbances in the functioning of the lungs).
Spinal curvature is detected by visual examination, but hardware-based radiological diagnostics is necessary to determine the degree of displacement and associated deformities. If surgical treatment is indicated for a patient with kyphosis, it is recommended to do a CT scan of the spine before surgery, since this is the most precise examination method. On tomograms, the neurosurgeon will see not only the osteochondral components, but also the vessels, since in order not to damage them during surgery, it is important to know their location.
Get a CT scan of the coccyx in St. Petersburg
A computed tomography scan of the coccyx can be done at Medical in St. Petersburg. The procedure helps in identifying pathologies and prevents the development of serious diseases. The price of a CT scan of the coccyx and sacrum includes:
- Examination using an expert-class computed tomograph Aquilion Lightning TSX-035A (Canon Japan).
- A detailed, comprehensive conclusion made based on the images by a highly qualified radiologist. The description of the study is checked by the chief physician.
- 24/7 access to your personal account to view all your research and conclusions
- Internal research quality control
- 100% guarantee of photo quality
- Detailed information about prices can be found in the “Prices” section.
- You can find out about the benefits and ongoing promotions in the “Promotions” section.
Sign up for a CT scan of the tailbone in St. Petersburg at the medical office. We work from 9:00 to 21:00 seven days a week - the center administrator will select a convenient appointment time for you.
Degenerative diseases of the spine
Common causes of chronic back pain include a large group of degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Those detected on CT include:
- Osteochondrosis;
- Osteophytes;
- Osteomyleitis;
- Spondyloarthrosis;
- Osteoporosis;
- Degenerative spondylolisthesis.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is the collective name for degenerative diseases that lead to the destruction of intervertebral discs and chronic back pain. Presumably, osteochondrosis occurs due to infections, inflammation, heredity, hormonal disorders, a sedentary lifestyle, and improper physical activity. Osteochondrosis can lead to intervertebral disc herniation, sequestration, and even disability of the patient. On CT scans of the spine, the doctor will see which intervertebral discs are damaged. They can be located at any level: from C1 to L5 , where:
C is the cervical spine;
Th— thoracic spine;
L - lumbosacral spine.
It is important to understand exactly which segment is damaged or causing pain. To restore damaged vertebrae, injection techniques are used, for example, therapeutic blockades and plasma lifting. The attending physician must determine the exact site of administration of the drug.
Osteoporosis
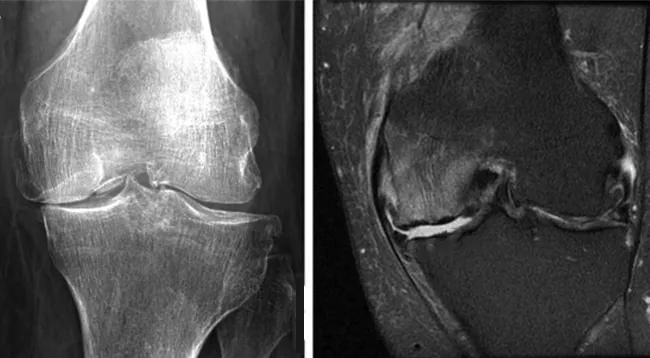
Osteoporosis is a disease associated with bone decalcification. As a result, the vertebrae become very fragile, and CT scans can determine that their structure has become porous. A diagnosis of osteoporosis is associated with a poor prognosis—an increased risk of fractures and injuries. Osteoporosis is most often diagnosed in older people and women after menopause due to hormonal changes.
Osteophytes and spondylosis
Osteophytes are pathological growths of bone tissue that cause painful compression of nerve fibers, blood vessels, and soft tissues. Osteophytes cause discomfort and impede movement, and they arise due to a disturbance in calcium metabolism in the marginal area of the bone, thereby deforming the skeleton.
Osteophytes may not cause severe discomfort, but medical practice shows that the detection rate of this pathology in men and women over the age of 50 with concomitant spinal diseases (intervertebral hernia, osteomyelitis, spondylosis) is approximately 80% and 60%, respectively. Before spine surgery, neurosurgeons often refer patients for a CT scan to check the vertebral bodies for osteophytes and their location, since this will determine surgical tactics.
Facet syndrome
Spondyloarthrosis (facet syndrome) is an inflammation of the intervertebral joints of the spine, which is preceded by disc degeneration. The detection rate of pathology in patients with pain in the lower back, neck and thoracic spine is up to 40%. The pain syndrome also spreads to other parts of the body: face, ribs, hips - depending on the location of the inflammation.
Spondylolisthesis (spinal segment instability)
Degenerative spondylolisthesis is a pathological displacement or slipping of the upper vertebra onto the underlying one. Using computed tomography, the angle of displacement is determined and the degree of trauma is assessed (described in detail in the conclusion). Facet syndrome occurs due to injuries, bone defects, unsuccessful operations, and congenital structural features of the skeleton. Displacement of the vertebrae is best visualized on CT, but the attending physician may recommend that the patient undergo an MRI of the spine.
What can be seen during this diagnosis?
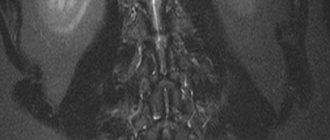
The coccyx is a process consisting of fused vertebrae. It is considered a vestige of a tail. The main purpose of the coccyx is to attach ligaments and muscles that ensure the full functioning of the intestines and reproductive system. This section distributes the load and promotes flexion and extension of the hip.
Many people are interested in the safety of MRI of the coccyx.
, as the study shows. Magnetic resonance imaging shows the general condition and shape of the coccyx, allows you to identify the number of fused vertebrae, study the condition of the sacrococcygeal joint, and evaluate the location and absence of displacement. Using the method, the necessary information is obtained and the following problems are identified in this area:
- consequences of injuries;
- congenital and acquired anomalies;
- development of degenerative and destructive anomalies;
- cysts, tumors, abscesses and fistulas;
- osteochondrosis, hernias, protrusions, arthrosis and spondylosis;
- vascular diseases;
- Bekhterev's disease.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that MRI does not involve violating the integrity of the skin, does not expose the body to radiation, and can be performed repeatedly, the procedure has several limitations. MRI is not prescribed or is prescribed with caution at the discretion of the doctor if:
- Pregnancy (especially in the first trimester)
- The presence of permanent metal particles in the body: pins, metal fragments.
- Installed electromagnetic devices that are sensitive to the magnetic field: pacemakers, insulin pumps and other devices.
- Fear of confined spaces and other mental disorders that may prevent the patient from remaining motionless throughout the procedure.
- Up to 3 years of age.
- Obesity and significant body volume.
The possibility of conducting an examination if there are any contraindications is assessed by the doctor. In some cases, he may prescribe mild sedatives or an MRI while in a state of medicated sleep.
How is the examination carried out?
Before diagnosis, you need to remove piercings from the abdominal area and lower body, otherwise metal products will distort the results.
The patient lies face up on the tomograph table. After this, the table passes through the wide part of the device, made in the form of a large wide ring with installed X-ray sources and receiving sensors.
When passing through the device, the patient’s body in the area of the sacrum and coccyx is scanned with x-rays, and the data obtained is transmitted to the monitor.
Although the technology produces only a black and white image, it is quite informative. Modern technology can reproduce more than 1000 shades of gray, which allows you to examine the spine in detail. When contrast is used, a substance is injected intravenously to make images brighter and more detailed.
The procedure does not affect your health, so after it you can return to normal activities. The results are issued in the form of printouts or copied onto magnetic media.
Indications and contraindications for MRI of the coccyx
Typically, an MRI of the coccyx is prescribed when other diagnostic methods (X-ray, ultrasound) are not informative. Tomography is used for the initial diagnostic search. The main indications for performing an MRI of the coccyx are:
- pain syndrome in the pelvic area (coccydynia), especially of a chronic nature;
- disturbance of the dynamics of the spine in the lumbosacral region;
- irradiation of pain to the lower limbs or perineum;
- pain from the pelvic organs, especially in the absence of any organic pathology in them;
- neurological disorders in the perineal area: numbness, increased sensitivity, dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Also, MRI of the coccyx is extremely necessary in case of planned surgery. The images obtained during scanning allow you to get an idea of the area under study in three planes at once. This helps the surgeon or traumatologist plan their actions and reduces the risk of complications.
MRI of the tailbone and spine is contraindicated for women in the first trimester of pregnancy. At a later date, the examination can be carried out, but permission from the gynecologist will be required.
Also, magnetic resonance imaging is not performed in the following categories of patients:
- having a body weight over 130 kg;
- with ferromagnetic implants and electronic devices installed in the body;
- suffering from claustrophobia and mental disorders.
Is it dangerous to perform a computed tomography scan of the lumbosacral spine?
Computed tomography involves exposing the patient’s body to x-rays, but their dosage is so small that this method does not pose any harm, much less a threat to life. This is a completely safe diagnostic test, which, under certain indications, can be performed even on children. Thanks to modern equipment and hardware and software systems, radiation exposure is biologically determined. Computed tomography can be performed even several times a year, and is not dangerous for the patient’s body.
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors are worried about the health of their patients. And therefore, during absolutely all studies there is an anesthesiologist who carefully monitors the tomography, especially if it is carried out with a contract substance.
Contraindications for the study
Contraindications to CT of the lumbosacral spine
are the following factors:
- pregnancy;
- insufficient age of the patient (up to 14 years);
- diabetes;
- renal failure;
- state of coma or shock;
- excessive weight (more than 150 kg).
You should consult your doctor about the possibility of performing tomography with metal elements or electronic devices, since each case is individual.
CT scan of the pelvic bones: when contrast is needed
In some cases, after a simple (native) CT diagnosis of the pelvic bones, a scan is made using contrast agents, which depict regional vessels in detail. Typically, additional examination is carried out if thrombosis, embolism, traumatic damage to the bloodstream, tumors, or inflammatory processes are suspected.
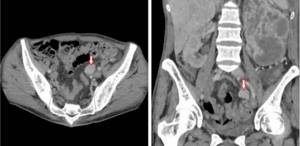
CT scan of the pelvic bones with contrast, the arrow indicates the lymph node affected by the tumor
CT scan (MSCT) with contrast shows:
- atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots in blood vessels;
- deformation of the walls of arteries and veins;
- ruptures of blood vessels with the formation of hematomas;
- inflammation;
- tumors (anatomical features and prevalence of the tumor).
How is an MRI of the coccyx performed?
The procedure is carried out in a diagnostic center using modern equipment. Before the examination, it is necessary to remove all metal items, including removable dentures, watches, jewelry, and piercings. The patient lies down on a special table, which is pushed inside the tomograph. A magnet inside the device rotates around the area being examined. A person must remain completely still in order to get high-quality photographs.
Stages of the procedure
- You need to prepare: remove metal objects and lie on your stomach on a special platform that is pushed into the tomograph.
- The ring in the device begins to rotate around the patient and take pictures of the area being examined.
- The procedure lasts 20-30 minutes, after completion of the diagnosis the table is pulled out. Results are provided within one hour or the next day.
In what cases can a special substance be administered?
A contrast agent for MRI of the lumbar spine and coccyx is administered if cancer is present or suspected. With cancerous tumors, there is a better blood supply in the affected areas, so more particles of the contrast agent accumulate. The price for a procedure with contrast is higher and it lasts longer.