During the period of bearing a child, a woman undergoes various examinations. Some of them relate to the growth and development of the fetus, others to the health of the expectant mother. The prescribed studies cannot be neglected. The health of the woman and baby depends on the timely detection of pathology.
Urine culture during pregnancy is one of the important tests. It is surrendered upon registration and at 35-37 weeks. The analysis shows the presence of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system and determines the type of pathogen. How to prepare for bacteriological culture of urine, collect material and decipher the data obtained? What to do if the result is bad?
Types of bacteriological cultures during pregnancy
The analysis is necessary to identify the pathogen that caused the inflammatory process and to quantify the degree of bacteriuria. Infectious diseases of the mother are very dangerous for the fetus, so it is important to identify the pathogen and establish the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotic treatment. A culture tank during pregnancy allows you to examine not only urine; biomaterial for research can be taken from the vagina, cervical canal, nasal sinus and rectum.
During pregnancy, sexually transmitted diseases are very dangerous. They can cause a miscarriage. A culture smear from the cervical canal can reveal the presence of bacteria such as GBS (group B streptococcus), chlamydia, trichomonas, Candida fungus, and mycoplasma. Staphylococcus aureus can be detected by culture from the sinus. There is no need to prepare specially for the test. The biomaterial is collected from the mucous membrane in the laboratory.
What can you see in this study?
A general urine test does not always reveal signs of infection. It is to establish the nature of the pathogen that bacteriological culture of urine is necessary. According to statistics, during prophylactic treatment, asymptomatic bacteriuria is detected in 7% of pregnant women. The most commonly identified pathogens are:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- coli;
- enterococcus
Early detection of the inflammatory process allows timely initiation of treatment measures. Otherwise, the formation of such serious complications of genitourinary infection as glomerulonephritis or pyelonephritis is possible.
Indications for urine culture
Every tenth pregnant woman suffers from a latent infectious disease that is asymptomatic. This could be E. coli, staphylococcus, enterococcus, or fungal infections. In the absence or late treatment, pyelonephritis develops. In the advanced stage, the child becomes infected.
Every woman must take a urine culture tank during pregnancy. The analysis shows the condition of the genitourinary system and helps to identify latent and chronic forms of diseases. It is mandatory to take cultures for GBS twice during the entire gestation period - in the early stages and before birth.
Additional research is prescribed in the following cases:
- the general analysis revealed bacteria, an increased number of leukocytes, protein, sugar;
- after treatment with antibiotics to confirm the effectiveness of therapy;
- harmful working conditions for pregnant women;
- miscarriages in previous pregnancies;
- urolithiasis disease;
- chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- diabetes;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- burning when urinating;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.

How is the material collected?
To collect urine for tank culture during pregnancy, an average portion of urine collected in the morning is required. You need 5 ml of the test material, which is collected in a sterile container. It's better to buy it at a pharmacy. Before collecting the analysis, it is necessary to toilet the external genitalia. If you forget about this point, microorganisms will be detected in the urine, even if they are absent in the urinary tract. After collecting the analysis, it must be delivered to the laboratory as quickly as possible. It is advisable to do this in the first two hours after collection.
Thus, urine culture is a routine test performed during pregnancy for the purpose of early detection of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
Conducting research
Opportunistic bacteria and microorganisms maintain the acid-base balance of the genital mucosa. When elements of pathogenic microflora begin to multiply rapidly, an inflammatory process occurs. Bacteriological culture is a research method effective for diagnosing infectious and inflammatory diseases caused by bacteria.
Examination of urine begins with primary microscopy. The material is divided into several parts for study in different environments; bacteria multiply in different conditions. A pure culture of streptococci is obtained in sugar water, staphylococci - in blood agar, pathogenic fungi - in Sabouraud's medium.
The isolated bacteria are tested for antibiotic resistance to prescribe treatment. The total time required to study the material is 4-7 days. If there is a suspicion of kidney tuberculosis in pregnant women, urine must be taken daily for three days.
How to prepare?
The result of tank culture during pregnancy is distorted if the preparation rules have not been followed. The collection container must be clean and dry. It is advisable to buy a special container with a tight-fitting lid at the pharmacy in advance. When using a glass jar, you should wash it with laundry soap and dry it. Do not wipe off excess moisture with napkins or cloth. There may be lint left on the glass.
A week before the test, you need to exclude salty and fatty foods from your diet. For two days you should not eat foods that stain urine (for example, carrots, beet). The test result is affected by diuretics and antibiotics taken even a week before the test. Two days before, you need to stop therapy with vaginal suppositories.
The day before the examination, physical activity should be avoided. This leads to increased protein in the urine. Immediately before filling the container for the inoculation tank, you need to wash the external genitalia without using special hygiene products; you can use ordinary laundry or baby soap.

How to collect material correctly?
It would be correct to collect biomaterial after waking up. Urine should be collected immediately into a container intended for the laboratory. When pouring from urine bags or other containers, foreign bacteria enter the material. It is advisable to cover the vagina with a sterile cotton swab during filling to prevent bacteria from the genital tract from entering the urine. During pregnancy, the amount of vaginal discharge usually increases. The labia should not touch the edges of the container.
The amount of collected material must be at least 70 ml. To test for SGB, you need an average portion of morning urine. The container with the material should be tightly closed with a lid and delivered to the laboratory within one and a half to two hours.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Sowing of biomaterial begins immediately after the container arrives at the laboratory. If you miss time, third-party microflora will begin to multiply in the urine. The laboratory assistant divides the material into several tubes with a special medium (sweet liquid, agar, Sabouraud).
Each type of bacteria requires specific climatic conditions to reproduce. They are created artificially using a thermostat. In an incubator, the number of bacteria present increases rapidly.
After two days the container is opened. The number of microorganisms is assessed under a microscope. If no bacterial colonies were detected, the result is negative. With a positive culture, obvious growth of microorganisms is visible. They are assessed using a special indicator - colony-forming units (CFU).
Decoding the analysis results
A bacteriologist deciphers the results of bacterial culture. The following bacterial indicators are assessed:
- appearance;
- properties;
- reaction to antibiotics;
- area of colony growth.

A small number of microorganisms is considered normal. A significant excess of the indicator is a sign of a pathological process. What results are considered normal? This depends on the number of colony-forming bacteria detected per milliliter of liquid (CFU/ml). Possible values:
- up to 1000 - negative;
- from 1000 to 10,000 - doubtful;
- more than 10,000 - positive, an inflammatory process is occurring in the body.
If an infection is detected, the form is accompanied by a transcript of the bacteria found in the urine. These can be Trichomonas, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, mushrooms, gonococcus, gardnerella, streptococcus, staphylococcus (we recommend reading: staphylococcus in urine during pregnancy). Depending on the resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics, they are labeled R (absolutely resistant), I (moderately resistant), S (sensitive). For treatment during pregnancy, drugs of groups I and S are used.
What you need to know about bacterial cultures
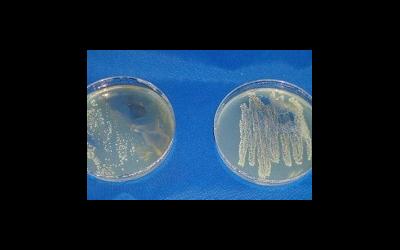
In this article we will touch upon the issues of culture culture: where to take it, how long it takes to do it, deciphering culture culture, the importance of culture culture during pregnancy.
With bacteriological seeding, microorganisms are sown from any biological material. You can examine cerebrospinal fluid, bile, discharge from the eyes, genitals and wounds. You can make a blood culture tank, a stool culture tank, a urine culture tank and a sputum culture tank, as well as a sperm (ejaculate) culture tank.
Normally, human blood does not contain pathogens. It is impossible to confirm or rule out the presence of bacteria in the blood by viewing it under a microscope. The blood culture tank makes it possible to multiply bacteria (if present) first in a liquid nutrient medium. The culture medium with the blood sample is kept at a temperature of +37° C until visible bacterial growth.
This process usually takes 6-18 hours, and in the case of species that grow slowly, it can last several days. The culture is then examined under a microscope - this is the first step in identifying the type of microorganisms that may be present in the blood (cocci, rods and others). When the liquid culture is subsequently inoculated onto a solid medium, colonies are more accurately identified - chemical tests are carried out and the type of microorganism is finally determined. Blood cultures should be done before starting antibiotic treatment because they may delay or suppress bacterial growth and give a false negative result. Blood sampling is carried out at the peak of temperature - at this time the number of bacteria in the blood is maximum. Laboratories recommend taking a second blood sample 1 hour after the first to increase the chances of detecting bacteria.
A stool culture tank for the typhoparatyphoid group is prescribed to identify various intestinal infections to identify the pathogen. The intestines normally contain opportunistic microorganisms - Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Candida, Proteus, Staphylococcus, Clostridia, Pseudomonas. Changes in the normal intestinal microflora (its quantitative or qualitative characteristics) create conditions for the development of opportunistic bacteria, which is accompanied by complaints of abdominal pain, flatulence, rumbling, and unstable stools.
Stool culture for dysbacteriosis is carried out in case of gastrointestinal diseases, which are accompanied by vomiting and stool upset.
Normal composition of intestinal flora
Explanation of the stool culture tank:
I degree – there are unexpressed changes in the aerobic part of the microbiocenosis, while foreign microflora is absent;
II degree - changes in the amount of lacto- and bifid flora are characteristic; in parallel, quantitative changes in Escherichia are manifested;
III degree is characterized by a sharp decrease and even absence of bifidoflora, lactoflora and hemolytic staphylococci and yeast-like fungi predominate;
IV degree – deep changes in microbiocenosis are characteristic: an increase in opportunistic microorganisms, the appearance of Proteus.
When submitting stool for this analysis, it is necessary to remember that taking antimicrobial drugs and probiotics greatly influences the reliability of the result. Therefore, the examination is recommended to be carried out 3 weeks after discontinuation of the drugs.
Urine culture tank allows you to identify, identify microorganisms and determine their concentration. If the number of microorganisms is detected in a concentration at which there is a likelihood of developing an infection, then the culture result is considered positive. If you receive a “bad culture,” then to effectively combat the pathogen, an antibacterial drug to which it is most sensitive is prescribed.
Biomaterial for research is taken before the start of antibacterial therapy, but if this is a control test after treatment, then it must be taken no earlier than two weeks after the end of the course of antibiotics. An average portion of morning urine is collected for analysis in a sterile disposable container. For examination, 3-5 ml of urine is sufficient. Urine collection is carried out after toileting the external genitalia. Urine must be delivered for examination within 1-2 hours, if the temperature is +18+20°C, it can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 5-6 hours.
Explanation of the urine culture tank:
The concentration of microorganisms in the urine is 104 - 105 CFU/ml. However, there are cases when a general urine test is normal, the patient has no complaints, but pathogenic microorganisms are detected in the urine, for example, E. coli, which could appear due to unsterile conditions of the study and irregularities during delivery. In this case, the urine culture tank should be repeated.
In the presence of chronic bronchitis or frequently recurring acute protracted bronchitis, it is advisable to do a sputum culture tank. The sputum culture tank, like any other discharge, is placed in a sterile container and delivered to the laboratory where the culture tank is carried out. A tank culture of sputum and simultaneous determination of sensitivity to antibiotics will make it possible to rationally prescribe treatment, reduce its duration with maximum effectiveness.
In what cases is a sperm culture tank prescribed?
For men with inflammatory diseases of the urogenital area, or infertility, a spermogram and a sperm (ejaculate) culture tank are required. A tank seeding of ejaculate (sperm) allows you to identify the presence of a pathogenic agent and begin treatment on time.
There are rules for donating a sperm culture tank:
- exclude sexual intercourse for 3-7 days;
- alcohol intake is prohibited for 3-4 days;
- tank seeding of sperm (ejaculate) is prescribed 2 weeks after taking antibiotics;
- the ejaculate for tank inoculation is collected in a sterile container with a nutrient medium, which must be obtained in the laboratory;
- in the morning you need to urinate, wash your hands thoroughly with soap, and toilet the external opening of the urethra, also with soap. After this, dry the head of the penis and foreskin with a sterile cloth. The collection of sperm for seeding is done by masturbation; you cannot touch the walls of the container;
- sperm must be delivered to the laboratory within 3 hours after collection. If sperm for seeding tank cannot be delivered during this time, then until delivery it should be stored in the refrigerator, but no more than 24 hours;
- if a tank is inoculated with ejaculate for the purpose of testing for urea and mycoplasmas, the material is placed in a bottle with a special transport medium for mycoplasmas. There is also a medium for culturing Trichomonas. You need to be aware of this and warn the laboratory when you take a sterile container for a sperm culture tank.
Usually after 7 days the ejaculate seeding tank will be ready.
Tank seeding during pregnancy
In any branch of medicine - pulmonology, dermatology, urology, andrology, venereology, gynecology, a culture tank is used during examination.
This examination method is most often used by gynecology. Bacterial culture is mandatory for pregnant women if they did not do this test when planning their pregnancy. With the onset of pregnancy, due to the fact that the woman’s body becomes vulnerable, there is a need to regularly see a doctor. During pregnancy, a woman must undergo tests several times, which is necessary to identify various diseases that can negatively affect the course of pregnancy and affect the health of the baby. The list of mandatory tests also includes bacterial culture during pregnancy - during this period, material from the vagina, nose, pharynx and urine are examined.
Vaginal culture during pregnancy is a necessary and important examination. The collection of material for bacterial culture during pregnancy is carried out very carefully; you should not be afraid of this procedure. Pathogenic vaginal flora (staphylococcus, chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, trichomonas) can cause disturbances in the formation and development of the fetus and cause life-threatening diseases. A tank culture during pregnancy allows you to identify a fungus of the genus Candida in the vagina, which maintains chronic inflammation of tissues that will be most susceptible to rupture during childbirth. Thus, tank culture during pregnancy makes it possible to identify latent diseases that are potentially dangerous for both the mother and the child. If necessary, treatment is carried out, and a control tank culture of a smear after treatment is prescribed no earlier than 2 weeks after the end of taking antibacterial drugs.
A mandatory examination is bacterial culture from the throat and nose during pregnancy. This analysis is done immediately upon registration at the antenatal clinic. The material is collected by medical staff at the clinic or directly in the laboratory. Sowing from the throat and identifying the carriage of Staphylococcus aureus helps to take timely measures: sanitize the pregnant woman and prevent infection of the child. There is another reason why it is important and necessary to do a culture test for Staphylococcus aureus during pregnancy - it is the main cause of purulent mastitis and postpartum sepsis, so its carriage requires treatment before childbirth.
Particular importance is given to urine culture during pregnancy. It is known that during pregnancy, the passage of urine through the urinary tract is disrupted and conditions are created for the proliferation of pathogenic flora, and urine culture during pregnancy and deciphering the culture allows the doctor to detect pathology in time, take the necessary measures and not miss the development of pyelonephritis, which is often found in pregnant women. Urine culture during pregnancy is given twice: during registration and at 36 weeks of pregnancy. In some cases, you have to donate more if there are indications for this: kidney disease, the appearance of protein and leukocytes in a clinical urine test. For the analysis to be reliable, the urine collection procedure must be followed. It is necessary to wash yourself thoroughly, to prevent vaginal discharge from entering, insert a piece of cotton wool into it, release the first portion of morning urine into the toilet and collect the middle portion of urine in a sterile jar and deliver it to the laboratory. For any tank culture, the examination is carried out before taking antibiotics or after finishing them after 3 weeks. A frequently asked question is tank seeding, how many times is it done? After treatment, a single control analysis is performed at intervals of 2-3 weeks.
Bacterial sowing Where to submit?
Many people will have this question. Usually, all necessary examinations are prescribed by a doctor. In this case, all examinations will be scheduled correctly and competently and you will be informed in which laboratory this can be done. But you can go to the laboratory yourself and take a culture test. The laboratory that deals with bacterial cultures has sterile medical glassware for collecting material, trained medical personnel who can take smears from women and men and tell you how to properly prepare for the study and submit the material for research.
As an option, you can offer to take the seed tank to INVITRO, an independent laboratory. This is a network of four high-tech laboratories in the cities of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Chelyabinsk and Novosibirsk. The independent INVITRO laboratory uses the latest modern equipment and uses test systems from the world's leading manufacturers. It offers a wide range of studies: blood and urine tests (clinical and biochemical), cytological studies, determination of allergens and tumor markers, PCR, tank culture. INVITRO – conducts a wide range of laboratory tests.
Everyone is interested in the question of tank sowing, how long does it take to do it? After 5-8 days (depending on the material being tested), you will receive the results of the culture tank. During this time, microorganisms are identified and an antibiogram is performed. Usually, the results of tank culture are handed out and the form indicates the results of tank culture and its norm. The results of the study can also be received by email, fax, or telephone.
The bacterial culture is deciphered by a microbiologist in the laboratory, and a conclusion is issued to the doctor; if the tank culture is bad, treatment is prescribed.
What does bad tank seeding mean? There are certain acceptable standards for the presence of certain microorganisms that do not cause subjective sensations and diseases. For example, ureaplasma and mycoplasma can be part of the normal human microflora, and treatment is required only when there is a large concentration of microbes and signs of inflammation.
There is the concept of colony-forming units (CFU) - this is one microbial cell from which a colony subsequently grows. The results of the inoculation tank are indicated in this unit. For each culture method, there are standards that indicate clinically significant concentrations of microorganisms that can cause disease. If colony-forming units are exceeded, the laboratory immediately performs bacterial culture and antibiotic sensitivity. Such bacterial culture with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics is necessary for the rational conduct of antibiotic therapy.
culture, diagnosis, pregnancy
What to do if the result is bad?
If colonies of bacteria in a smear from the cervical canal or urine culture grow, this indicates problems in the functioning of the kidneys and genitourinary tract, and cystitis is possible. Often the analysis is ordered again. A poor result may occur due to violation of hygiene rules and material collection.
To clarify the diagnosis during pregnancy, additional diagnostics may be required. As prescribed by your doctor, you will need to take a vaginal smear and an ultrasound of your kidneys. Identified inflammation is treated with antibiotics. After the end of therapy, a repeat study is carried out to check the effectiveness of the treatment.
How to take a urine test for tank culture
Often, patients have to re-take a culture test because the results are distorted; as a rule, this is due to improper urine collection. You should prepare a sterile container in advance; you can buy a container for collecting urine at the pharmacy.
Two days before the delivery of the culture tank, you should stop using diuretics and other pharmacological drugs. In addition, the patient should exclude carrots, beets and other foods that can change the color of urine from the menu. Before collecting urine, perform genital hygiene. For culture analysis, the middle part of the urine is collected.
The effectiveness of diagnostics depends on how quickly the test material is delivered to the laboratory. After 3 or more hours, the information content decreases significantly. In summer, urine should not be stored for more than 1-2 hours. The laboratory will conduct tests and observe the growth of bacteria in the urine; this is a long procedure, so the result is usually ready no earlier than in 5-10 days.
To take a urine test for culture, please contact the President-Med medical centers