directions
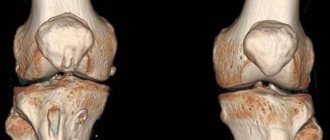
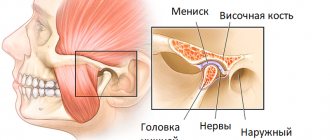
In the structure of the musculoskeletal system, the knee joint is the largest and most complex joint. The knee joint includes menisci - cartilaginous layers that perform the function of shock absorption in the knee and uniform distribution of loads on the knee. It is the knee menisci that are considered the most vulnerable areas subject to injury and mechanical damage. Tears, degeneration, excessive mobility - this is an incomplete list of meniscus diseases. The knee itself, while withstanding daily stress in the form of physical activity and strenuous work, is also subject to wear and tear. X-ray examination of the knee joint helps to identify the cause of the disease, see pathological changes, and diagnose injury. In traumatology, knee radiography is the most common non-invasive diagnostic method.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Structural subdivision of Polikarpov Alley Polikarpov 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Structural subdivision of Zhukov Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Structural subdivision Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
We draw your attention to the schedule of technological breaks in the CT and X-ray rooms.
You can get high-quality and quick x-rays of the knee joint at a multidisciplinary medical clinic in St. Petersburg. In the trauma department of the Medicenter clinic network, you will have an X-ray examination of the knee joint using a safe, modern high-tech digital Clinomat device. The Medicenter’s equipment allows for complete effective diagnosis of the patient, analysis of X-ray images in various processing modes, and quickly and accurately prescribing treatment based on the results obtained.
What is x-ray diagnostics
X-ray diagnostics is based on special X-rays that the device emits. Soft tissues allow them to pass through, while hard tissues absorb them, which is why in the picture the former are painted dark, and the latter light. Bone tissue is most clearly visible in the photographs, so the method is used to examine the condition of bones and joints. The results are provided on paper or digital media and saved on the computer’s hard drive.
Today you can get an X-ray image on digital media
The most common injuries and diseases of the knee joint
Ailments of the musculoskeletal system are a whole group of diseases that affect and damage joints, cartilage, muscles, and periarticular tissues. These diseases are varied, can appear at any age and have different symptoms and signs. Ailments of the knee joint are very painful, affect a person’s motor activity, limit his movements, complicate life and sometimes lead to a complete loss of the ability to walk and disability. Diseases of the knee joint most often develop as a result of injuries, inflammation, infections, and degenerative changes. The knee joint is most often susceptible to fractures, dislocations, sprains and other injuries. The most common knee diseases are arthritis, arthrosis, osteoporosis, osteophyte, meniscopathy, cysts and tumors.
Interpretation of the radiograph
Despite the fact that the average person is unlikely to be able to independently understand the features of the resulting black-and-white “photo,” he can recognize the symptoms of the most common ailments. Signs of their development are indicated by a radiologist, who makes a conclusion transmitted to the treating doctor.
So, if a patient is suspected of arthrosis, then in the official conclusion its confirmation can be found by reading the following theses:
- unevenly narrowed gap;
- deformation of the gap according to the degree of neglect of the process;
- bone growth along the articular edge;
- osteophytes of different sizes;
- compaction of bone tissue at the border with cartilage;
- limestone deposits on ligaments.
But it is much easier to recognize fractures even without proper medical skills. They can be seen upon detailed examination of the photographs, where the damage is clearly visible. It is more difficult with fresh cracks and depressions, which are better visible several days after the injury.
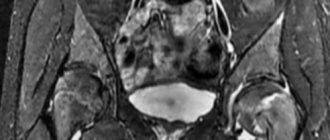
Arthritis, unlike arthrosis, causes widening of the joint space. Anatomically, the phenomenon is explained by the presence of an inflammatory effusion in the joint cavity. In some cases, to establish the exact extent of the lesion, a magnetic resonance imaging scanner is still necessary.
It is relatively easy to recognize a dislocation. It is characterized by bone displacement, where one part does not match the surface of the second. The main victim of dislocations is the kneecap.
With sprains or destabilization of the functioning of ligaments, it is a little more difficult due to the structure of tissues classified as soft. But even such anomalies can be found if you pay attention to the possible increase in the distance between the surfaces of the tibia and femur bones.
A somewhat similar principle is used to look for a violation of the integrity of the patellar tendon. The image will demonstrate the kneecap displacement. When the tendon has additionally undergone a process of sclerosis, its outline can be seen more clearly. To create an image of increased accuracy, you can use an artificial technique by adjusting the hardness of the radiation.
Since people usually seek advice from a surgeon or traumatologist at the “I can’t stand it anymore” stage, they develop a pronounced degenerative-dystrophic process. An X-ray examination will reveal it due to the proliferation of bone tissue formed on the sides of the articular surfaces. Growths in the form of osteophytes gradually lead to irreversible deformations, significantly worsening the quality of life of the victim.
Another common reason for visits to the radiography office is referrals from oncology clinics. Tumors of a benign or malignant nature are located not only in the joint, but also in the periarticular soft tissues of the knee. You can find them by marks without a clear shape with destroyed cells around them. The more affected the area around the pathological focus, the higher the chances that metastases have formed nearby.
The final common disease is osteoporosis. This is where only an experienced doctor can figure it out, who will pay attention to the lack of calcium in the bones. The image will confirm the fears if transparent inserts become visible there when the borders are sealed.
Causes of knee diseases
Most often, athletes (hockey players, figure skaters, light and heavy athletes, gymnasts) are susceptible to injuries and diseases of the knee joint. Falls, impacts with the knee joint on hard objects, unsuccessful jumps and incorrect foot positioning while running can cause ailments. Diseases and injuries of the knee joint can also occur due to metabolic disorders and age-related changes. In these cases, wear of the cartilage tissue occurs.
Thus, radiography helps to identify the cause of the disease or clarify the diagnosis. A referral for an X-ray of the knee joint is given by an orthopedist, surgeon, rheumatologist, and even an oncologist.
Principles of treatment
At the moment when the articular surfaces have not yet undergone fatal changes, but only minor degenerations, conservative treatment is applied. It is based on the following principles:
- physical therapy exercises without absolute vertical load - the doctor will prescribe the correct (!) set of trainings, which will improve metabolic processes in the joint and make it possible to stop pathological progression;
- losing weight through diet - losing weight is very important for overweight and obese people, because extra pounds put pressure on the joint, making it difficult to function normally;
- exclusion of physical activity , in which the bone joint functions in an enhanced impact mode (running, team sports, jumping, etc.);
- the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve pain and swelling (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Voltaren, Indomethacin, etc.);
- the use of drugs to stimulate the production of synovial fluid and replenish osteochondral components with useful substances (chondroprotectors, hyaluronic acid);
- wearing special orthotic devices, orthopedic shoes;
- prescription of physiotherapeutic procedures (cryotherapy, ozokerite and paraffin applications, UHF, ultrasound, phonophoresis, etc.).

There are no statistics confirming that overweight people have more joint problems. But common sense has not been canceled, there is a big difference when you have 65 kg on your knees. or 110...
If the disease is characterized by a severe course or the conservative approach does not give positive dynamics, there is a need for surgery. Today, orthopedic surgeons carry out unique interventions (stage 2-4), in which the diseased knee joint or a separate part of it is replaced with an endoprosthesis, a biocompatible artificial analogue of a biological joint. We invite you to familiarize yourself with our videos and photos, which perfectly demonstrate the features of the procedure and its benefits.
Attention! It is impossible to cure this disease conservatively. Serious destruction cannot be corrected either by popular intra-articular injections or even by stem cell transplantation. Therefore, do not hope that newfangled minimally invasive and non-invasive techniques will magically help restore damaged hyaline cartilage, which, due to physiological characteristics, is not capable of regeneration. Alternative and official conservative medicine can only slow down unfavorable pathogenesis, and even then mainly only in the early phase of its development.
Endoprosthetics is the only orthopedic method that can relieve the patient from hellish pain and disability caused by gonarthrosis. There is currently no alternative to it! Replacement of the knee joint with a durable implant is carried out in the surgical department of orthopedics at a specialized clinic. Let us draw your attention: in order to achieve the most complete recovery after knee replacement, you should definitely undergo a special course of a rehabilitation treatment program.
With correctly performed implantation surgery and impeccable rehabilitation (it lasts on average 3-4 months), a person returns to a full life. Of course, he will need to follow simple rules so that the new knee joint can function without problems for at least 15 years. What is most remarkable is that 15 years is not the limit. Modern endoprosthetic knee designs, as shown by clinical observations of patients who have undergone this operation, in most cases last 20-25 years.
Knee replacement in the Czech Republic: guarantees, prices, rehabilitation, reviews and statistics.
Find out more
Indications for radiography of the knee joint
The following diseases and injuries may be indications for X-ray examination of the knee joint:
- dislocations, displacements;
- sprains, ligament tears;
- fractures, cracks;
- tendon damage;
- patellar tendon damage;
- osteosclerosis, osteoporosis;
- osteophyte;
- cysts;
- arthritis, arthrosis;
- tumor processes;
- gout;
- bursitis;
Pain when bending the knee, when walking, a characteristic crunch, swelling of the knee and other signs may also be a reason for an X-ray of the knee joint.
Restrictions
X-rays are not performed on children under three months of age, who are prescribed an ultrasound if necessary. Doctors also do not recommend excessively irradiating infants in the pelvic area, as this can lead to infertility, blood disease, and a tumor process in the future. Children are examined strictly according to indications and in a standardized manner, no more than once every six months.
X-rays are not performed on pregnant women to avoid negative effects on the fetus. It is also contraindicated in people with metal prosthetics or implants in the area being examined and in people with schizophrenia (and other mental disorders) who are unable to remain still. Other people, including older people, can undergo the examination.
The procedure for performing an X-ray of the knee joint
In case of severe pain, injury, or fracture, the specialist helps the patient lie down, because The photograph is taken in a supine position. X-rays of the knee joint are usually done in two projections - frontal and lateral. The patient is accordingly placed in a position either lying on his back with his leg extended, or on his side with the leg also fully extended.
If necessary, after conducting the examination in standard settings, the traumatologist or radiologist recommends additional x-rays using special settings. The Schuss position involves an x-ray of the knee joint with the leg bent at an angle of 30 degrees, and the Fick position involves an x-ray of the knee with the leg bent at an angle of 45 degrees.
In general, the procedure is painless and takes about 20 minutes.
Features of x-ray of the upper extremities
X-rays of the elbow are also prescribed after injuries - severe bruises, dislocations, fractures - or if various pathologies are suspected. It allows you to obtain information about the joint space and its narrowing, about the condition of the ends of the bones of the humerus and forearm. The specialist also receives data about the areas adjacent to the elbow joint, which facilitates diagnosis. After all, the cause of pain is not always arthrosis of the elbow, arthritis or bursitis: it often has a spreading nature and a completely different source.
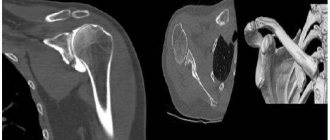
Shoulder pain often occurs against the background of neurological and vascular diseases, but the cause may also be shoulder arthrosis, as well as systemic inflammatory diseases of the shoulder joint. X-rays are mainly prescribed if a dislocation or fracture is suspected. The image also shows adjacent formations - the collarbones and shoulder blades. It is also informative for arthrosis and arthritis, necrosis of the humeral heads, tendonitis and other diseases.
Osteoarthritis of the upper extremities is often discovered by chance on an X-ray
X-ray is a simple, quick, painless diagnostic method that provides information about the condition of bones and joints. When arthrosis is detected, additional instrumental methods are often prescribed to examine the deep structures of soft tissues and study the condition of the cartilage. However, MRI and CT scans are expensive and not always necessary. Therefore, if the orthopedist insists on an x-ray, you should not refuse.