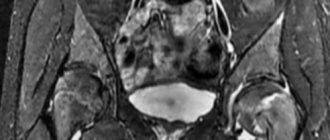
Knee joints regularly experience various impacts. Their condition is negatively affected by physical activity, traumatic injuries, hypothermia, infections, and age-related changes in the body. Pain, crunching, stiffness and other unpleasant symptoms appear, forcing a person to see a doctor. To make a diagnosis, a specialist may prescribe a CT scan of the knee joint. Scanning with a computed tomograph allows you to obtain detailed layer-by-layer images, on the basis of which conclusions are drawn about the presence or absence of pathology.
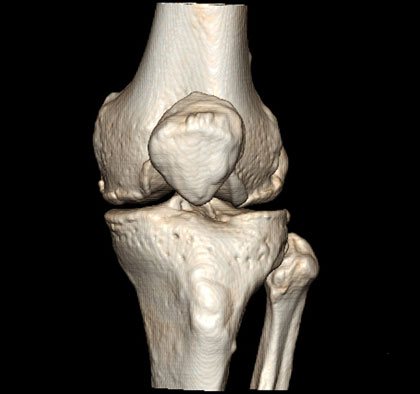
CT scan of the knee joints (3D reconstruction)
What does a CT scan of the knee show?
The study evaluates bone and, to a certain extent, soft tissue. Scan shows:
- developmental anomalies of the knee joints;
- swelling of the periarticular tissue;
- ligament ruptures, joint dislocations, bone cracks, fractures in the area being examined;
- narrowing of the joint space;
- osteophytes (growths of bone tissue in the form of protrusions);
- accumulation of blood, pus, effusion inside the joint cavity;
- tumor neoplasms;
- metastases.
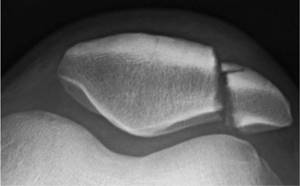
Fracture of the patella (kneecap) on CT
When performing a CT scan of the knee joint, a number of diseases are detected: arthrosis, arthritis, gout, Osgood-Schlatter disease, tendinitis, synovitis, bursitis, etc. The examination is carried out in preparation for surgery, to determine the effectiveness of conservative and surgical treatment methods.
Preparation for CT scan of joints
CT scan of joints is a layer-by-layer scanning in several planes of the examined area and compiling its three-dimensional image using a computer program.
This technique is ideal for examining bones and joints, as it is very sensitive to dense tissue. During the scan, the circumference of the joint and its anatomical features are checked. If necessary, the quality of the vascular system providing blood supply to this area, as well as the condition of the soft tissues, is assessed.
A referral for this examination is usually given by a surgeon or therapist if:
- Limitations in joint movement
- Painful sensations
- Injuries
Typically, the examination is limited to a specific area and the doctor focuses on the knee, hip, elbow or shoulder joint.
Also, examination of the hand, wrist joint, collarbone, etc. A comprehensive examination is also possible, as well as checking other parts of the body.
Indications
The main task of the examination is to establish the cause of the pathology and find out about the condition of the bones in this area. With the help of an examination it is possible to detect:
- Arthritis, osteoarthritis
- Diffuse connective tissue diseases that cause damage to the motor activity of joints: gout, spondylitis, etc.
- Osteomyelitis, tuberculosis
- Myeloma
- Foreign bodies
- Injuries and any consequences
- Results of an incorrect operation
- Tumors of bone or cartilage tissue
Based on the images obtained after the scan, the doctor determines the structural features of these parts of the body. Thanks to this, an accurate diagnosis is made and a decision is made on the necessary treatment, whether surgical intervention is necessary, etc. The examination is also indispensable for assessing the effectiveness of the therapy and the possibilities of its adjustment.
Contraindications
Computed tomography is prohibited for pregnant women, regardless of age. The remaining restrictions apply only to cases where the examination is planned using contrast. It is prohibited for patients with:
- Endocrine diseases
- Allergy to iodine
- Kidney failure
Preparation
Preliminary preparation is only necessary before using contrast. The patient is advised to follow a diet on the eve of the test and come to the clinic on an empty stomach - not to eat for 5-6 hours. You will also need to take blood tests in advance to identify allergens to the components of the drug.
Before the examination, the patient takes off clothes that have metal inserts: belts, bras, jeans, etc. It is also necessary to remove any jewelry, watches, and put gadgets away. It is best to change into loose, comfortable clothes.
How do they do it?
During the examination, the patient lies on his back on a mobile tomograph table. This table moves the human body under the scanning ring in the area
which interests the doctor. If contrast is used, it is administered intravenously at this stage. With it, the procedure takes approximately 20 minutes.
Without it - 5-10. The tomograph ring rotates around the designated area and takes pictures in 1-2 mm slices. This is accompanied by a slight noise.
Otherwise there will be no discomfort.
Test results are usually provided immediately within 15-30 minutes. The patient receives the photographs and their descriptions. If necessary, a computer program builds a three-dimensional model of the organ, and this is all recorded on disk. With the results, the person comes to his attending physician, who makes a decision on appropriate treatment.
Using Contrast
Contrast is used to detect vascular disorders in the joint area. It is administered intravenously a few minutes before the tomograph starts working.
The contrast itself is safe except in cases of contraindications. Sometimes it causes side effects such as mild itching, nausea, and dizziness.
All this goes away without a trace after the examination. If discomfort increases, the patient should inform the doctor about this via two-way communication.
Advantages of the method
- Ability to examine patients with metal implants.
- Minimum radiation exposure.
- The best way to detect tumors in bone structures.
- With contrast, the soft tissues surrounding the joint, as well as the vascular system, are perfectly visualized, which makes the diagnosis more accurate and reliable.
- Speed and accessibility of the examination.
Possible risks
The possibility of an atypical reaction to the components of the contrast agent is approximately 2-4%. As a rule, allergies are found out in advance by conducting appropriate tests. But it can also manifest itself directly during scanning. In this case, the radiology office always has a set of antihistamines.
Another risk is associated with the use of x-rays. However, the dosage for CT is very small and cannot somehow affect human health.
The only thing is that intervals should be taken between such checks to prevent the accumulation of radiation in the patient’s body.
Alternatives
In some cases, examination of bones and joints is carried out using conventional radiography. However, this procedure is characterized by an increased radiation dose compared to CT and is not highly accurate. Among radiological techniques, MSCT is also popular. She uses a minimal amount
radiation while providing high-fidelity images. Traditional ultrasound is also quite suitable for identifying injuries and fractures. However, for more subtle examinations this is not the best option.
When radiation is contraindicated for some reason, MRI is recommended - a non-radiological examination, which is highly informative and fast.
This technique has almost no contraindications. In exceptional cases, it is even suitable for pregnant women and children. If diagnosing diseases is difficult, and the doctor still has doubts, then PET CT is recommended - an invention of nuclear medicine. This technique helps to see changes that are invisible to everyone else. In addition, it allows you to monitor the functioning of organs in real time.
You can sign up for research by calling +7 (495) 109-39-99
Preparing for a knee exam
When signing up for a CT scan of the knee joint, of course, patients are interested in what it is and how to properly prepare for the procedure. If diagnostics are to be made without the use of contrast, there is no need to do anything special. For examination with the use of enhancing drugs, it is advisable to eat something light before leaving home, since adverse reactions in the form of nausea, dizziness, etc. are more pronounced on an empty stomach. Breastfeeding mothers are advised to express and save milk before the contrast procedure: after diagnosis, you will have to skip two consecutive feedings. For contrast studies, blood test results for creatinine are required.
The essence of the computed tomography (CT) method
Just like MRI, SCT (spiral computed tomography) is a cross-sectional tomographic method for examining the human body. In general, computed tomography has a lot in common with MRI. You could even say that everything is common except the basics of methods from the point of view of physics. MRI uses a magnetic field, CT uses x-rays. Hence the differences in abilities: what CT can do well, MRI cannot do. Everything else, even the appearance of the devices and the resulting images, are practically indistinguishable to the average person.
How is a CT scan of the knee done?
Before the scan begins, the patient is asked to remove all items containing metal. If there is an allergy to radiopaque agents or there is an implant in the examined area, you should be warned about this. The doctor briefly talks about computed tomography of the knee joint in the clinic - what it is, how to behave during the examination, what to do if it suddenly becomes bad. Then the patient lies down on the conveyor table of the device, which is pushed into a ring equipped with sensors. To ensure high-quality images, it is important to remain calm during the procedure.
All this time, the patient is alone in the office; specialists monitor what is happening through the glass wall of the adjacent room. A CT scan is absolutely painless, but if discomfort occurs or your health worsens after the administration of contrast, you should inform your doctor about this via a two-way communication device.
Computer tomograph
How is diagnosis carried out?
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Diagnosis is carried out on an outpatient basis. The patient is positioned on the apparatus table. He is tied with belts. As soon as the scanning begins, the table slides into the tomograph. While the scanner moves slowly to take the appropriate pictures, the patient lies motionless.
During the procedure, the radiologist, who monitors the entire process and controls the equipment, is behind the door.
As a rule, such a diagnostic event lasts 40 minutes.
After the diagnosis, the patient should drink as much fluid as possible, which promotes the rapid removal of contrast.
CT scan with contrast of the knee joints
Additional tools during CT or multislice tomography (MSCT) of the knee joints are required to improve the quality of visualization of the studied area. Preparations with iodine are used as image clarity enhancers. After injection into a vein, they spread through the vessels and accumulate in places with the most intense blood supply - in areas of inflammation and tumors. Thus, the presence of pathology becomes more obvious to the specialist.
Contrast agents are harmless to health and are completely eliminated from the body within two days. But before using them, it is necessary to take a creatinine test (to rule out kidney problems) and make sure that there is no allergy to the components of the drug.
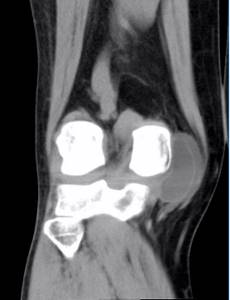
CT scan of the knee joint with contrast
How is the procedure performed?
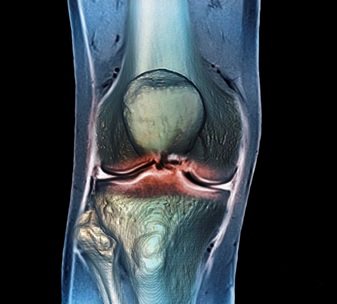
During a CT scan, the patient lies on a narrow table inside the scanner and during the examination, the X-ray emitter moves around the patient.
The computer processes tissue sections obtained using an X-ray beam and transforms them into images that can be viewed on a monitor or printed on film. It is also possible to carry out 3D reconstruction of images of the knee joint structures.
The patient must remain motionless during scanning of the knee joint to avoid the appearance of artifacts in the images.
A CT scan of the knee joint takes no more than 20 minutes.
Indications and contraindications
CT and MSCT are prescribed in the following cases:
- constant pain and crunching in the joint;
- disruption of normal knee mobility;
- meniscus damage;
- suspicion of tumors, dystrophic, inflammatory, degenerative pathologies of bones or cartilage tissue;
- dislocations, subluxations, fractures of articular structures;
- preparation for surgery;
- control after conservative and surgical treatment.
Computed tomography is not performed:
- during pregnancy at any stage;
- young children (not recommended until the age of five);
- with a weight of more than 150 kg and a chest or abdominal circumference of more than 150 cm.
Contraindications for examination of knee joints with contrast:
- iodine intolerance, allergies;
- severe renal or liver failure;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- age up to 12 years.
How to prepare for the procedure?
Some CT scans require the use of a contrast agent, which is administered before the scan. Contrast material allows better detailing of the structures of the study area
- Contrast material may be injected intravenously. And if contrast injection is planned, the patient is advised to avoid food and liquids 4-6 hours before the test.
- You should tell your doctor if you have had a reaction to contrast in the past.
- If the patient has diabetes and is taking metformin, the use of contrast may be risky as it may lead to lactic acidosis.
- Excessive weight may damage the scanner's working parts. If the patient weighs more than 130 kg, then it is necessary to find out what weight is critical for a particular CT scanner.
- The patient is advised to remove jewelry and wear a hospital gown during the CT scan.
Photo tomography of the knee joints
MSCT photos of the knee joint primarily show the bones (femur, tibia, tibia, patella). You can also see in the pictures:
- articular cavity;
- intra-articular cartilages;
- synovial membrane;
- intra- and extra-articular ligaments.
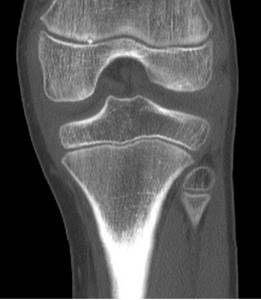
MSCT of the knee joint (coronal projection)
CT scan of the knee ligaments
Various knee ligament injuries are especially common among active young people and athletes. Injuries are common as a result of road accidents, other emergency situations, falls on ice, and jumps from low heights. In this case, the shin is tucked inward, outward, or twisted along the longitudinal axis. The result is a sprain or rupture of the ligamentous fibers, requiring long-term treatment.
Signs of trauma to the ligamentous apparatus are:
- pain when palpating the attachment points of the ligaments to the bone;
- swelling in the area of injury;
- the appearance of a bruise.
When performing a computed tomography scan of the knee, it is problematic to examine the ligamentous apparatus in detail. In the images you can see the cruciate and pterygoid ligaments, but their visualization, even with a minimum slice step, will be much worse than on an MRI. For an accurate diagnosis, it is better to do not a CT scan, but a magnetic resonance examination of the knee joint ligaments.
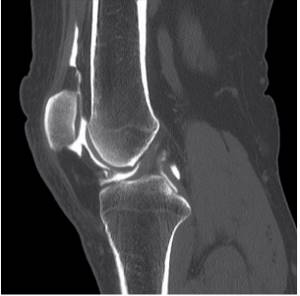
Computer tomogram of the knee joint (sagittal projection)
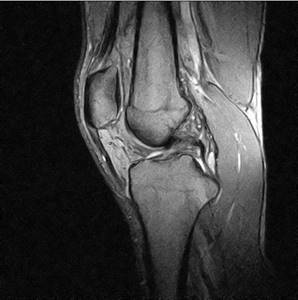
MRI of the knee joint - photo (sagittal projection)
What is hardware diagnostics?
The era of hardware diagnostics began with the discovery of X-rays at the end of the 19th century. This is how an X-ray machine appeared in the arsenal of doctors. A little later, fluorography and mammography appeared on its basis. In the early 30s of the 20th century, the diagnostic capabilities of ultrasound were discovered, and medical centers began to perform ultrasound diagnostics of various internal organs and evaluate fetal development during pregnancy. In the 70s of the 20th century, the first attempts were made to use the power of magnetic resonance for diagnostic purposes. Since the 80s of the last century, medical institutions in Russia began to be equipped with magnetic resonance imaging scanners. Medicine never stands still, and with the development of X-ray technology, an improved version of radiography appeared, which was called computed tomography. It was widely used in clinical practice in the 80s of the 20th century. First-generation computed tomographs have been replaced by spiral and multispiral tomographs - MSCT. Now most medical institutions in St. Petersburg are equipped with them.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
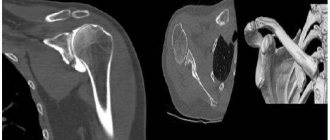
Osteoarthritis of the knee joints on CT
Arthrosis is the name given to dystrophic changes in the joint that begin in the cartilage (chondrosis) and spread to the bone (osteochondrosis). The pathological process develops over years. Articular cartilage gradually loses its elasticity, becomes denser, thinner, becomes rough, lumpy, overgrown with bone formations along the edges, and in some areas is completely destroyed.
In the early stages, degenerative changes are asymptomatic: arthrosis of the knee joint is often detected in advanced stages, when pain, a feeling of stiffness and limited mobility appear.
Computed tomography shows:
- narrowing of the joint space;
- marginal osteophytes;
- increased bone density under the cartilage (subchondral osteosclerosis);
- destruction of cartilage;
- deformation of bones at joints;
- focal cyst-like formations.
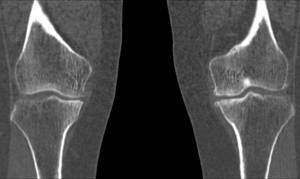
Arthrosis of the knee joint, photo of tomography images