Determining the size of lymph nodes
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with Doppler sonography is prescribed for enlarged lymph nodes. Their increase may indicate both an inflammatory process and the formation of a tumor. It is important to identify the cause and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Detection of thyroid lesions
Often, Doppler sonography of the thyroid gland is prescribed for lesions of the organ or suspected pathology. Inflammation of the thyroid gland, or thyroiditis, is common.
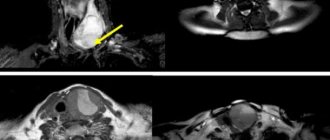
Detection of malignant tumors
Determining the nature of blood flow in the gland, as well as the size and condition of the organ, will allow us to draw a conclusion about the presence of a tumor process. Moreover, diagnostics allows us to determine the location of the tumor and its exact size.
Determining the size of the thyroid gland in the fetus in the womb
Doppler ultrasound of the thyroid gland may be performed to evaluate fetal development during a woman's pregnancy. All results obtained during the diagnostic process are carefully recorded in a report, with which you can go to your doctor.
Performing an aspiration biopsy
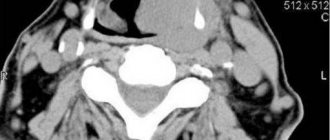
It involves taking thyroid tissue to determine the nature of the neoplasm. No matter how informative an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound is for examining the thyroid gland
, it will not be able to show the nature of the tumor. However, research is indispensable when planning such an intervention.
What does an ultrasound show?
Sonography is used in medicine both for diagnosing various diseases and for visual monitoring of complex surgical interventions.
The scope of application of ultrasound includes the study of:
- abdominal organs;
- thyroid gland;
- heart (echocardiography);
- vessels (carotid arteries or veins of the legs);
- mammary glands;
- uterus, ovaries (including during pregnancy);
- joints, such as the hip.
There are two types of ultrasound: diagnostic and therapeutic. Diagnostic ultrasound creates images using high-frequency sound waves generated by a transducer (probe). But for better visualization, the ultrasound head can also be inserted into the body through the gastrointestinal tract, vagina or blood vessels.
Therapeutic ultrasound also works with sound waves, but does not generate images. It is used to move and apply pressure to tissue, heat it, dissolve blood clots, or administer medications. Standard ultrasound has no harmful effects.
Abdomen
It is used both for diagnosing diseases and for monitoring the course of pathological processes in the body. Used to evaluate the condition of various organs, such as the liver, kidneys and spleen. The doctor determines the structure, size and location of the bladder, gallbladder and pancreas.
Limited assessment of bowel health is possible. It is also possible to detect free fluid in the abdominal cavity, such as inflammatory effusion or blood.
Thyroid
It is possible to determine the structure, size and focal formations. Scanning allows you to identify problems at the initial stages of progression, which makes it possible to begin treatment in a timely manner - before complications develop. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is the most accessible and informative research method that can be performed as many times as necessary without harm to the patient’s health.
Echocardiography
Typically, an echo examination of the heart is performed like any other ultrasound, that is, using a sensor that the doctor moves over the surface of the patient’s body. When diagnosing the heart, transesophageal (TEE - transesophageal) echocardiography can be performed. The doctor pushes a special probe through the esophagus to the entrance to the stomach. The heart is in close proximity and can therefore be examined better.
Doppler ultrasound
A comprehensive study aimed at determining the anatomical structure, nature, speed of blood flow and condition of the vascular walls (tension, elasticity). Allows you to identify damage to vascular structures, congenital anomalies and pathological tortuosity. Visualizes atherosclerotic changes, blood flow disorders, aneurysms and occlusions, as well as inflammatory processes and thrombophlebitis.
Ultrasound of female breast
A painless examination is the “gold standard” for the prevention of breast diseases. Allows you to examine all areas of glandular tissue, much more informative than with radiography and mammography. Using breast sonography, it is possible to identify various pathological changes: cysts and tumors, as well as assess the condition of the lymph nodes.
Gynecological ultrasound
Sonography of the pelvic organs is prescribed to evaluate ongoing therapy in gynecology or to identify pathological changes in the uterus, appendages, etc. Gynecological ultrasound reveals the fact of pregnancy, fetal development abnormalities and pathological disorders in the reproductive health of a woman.
Sonography of joints
Aimed at studying the condition of soft tissues and bone structures to identify pathological foci and prescribe effective therapy. Ultrasound of joints is performed for congenital anomalies, after injuries and to diagnose degenerative or inflammatory diseases. The diagnostic procedure does not replace radiography of the joint, since it does not allow assessing the displacement, the presence of fragments and the nature of the fracture.
Why do thyroid diseases occur?
To prevent thyroid diseases, it is necessary to boost the immune system, as it directly affects the condition of the body as a whole. Thyroid diseases often occur after infectious diseases, viral infections - ARVI, influenza, as well as chronic infectious processes in the ENT organs (ear, throat, nose).
To do this, you need to adhere to a balanced diet, which will include a lot of fresh vegetables and fruits, and also eliminate or minimize the amount of sugar, flour and other fast carbohydrates. It is also important to be physically active, especially now when all work is mostly done while sitting and physical activity is significantly limited. Don't forget to regularly walk in the fresh air and get enough sleep.
Another factor that increases the risk of thyroid disease is stress. If possible, you should reduce nervous tension, extinguish negative emotions, and prevent mental fatigue and sleep disturbances.
To produce thyroid hormones, iodine is necessary, so it is necessary to consume a sufficient amount of food with this element for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland. Disturbances occur not only with iodine deficiency, but also with its excess, but deficiency is typical for our country.
Seafood (sea fish, shellfish, sea kale) and some fruits (persimmon, feijoa, kiwi), as well as walnuts and chokeberry, are high in iodine. If the iodine obtained from foods is not enough, it is recommended to take vitamins.
It is with a lack of vitamins and non-compliance with a healthy lifestyle that thyroid diseases often appear. Some of them are very dangerous for the general condition of a person and require complex treatment. We will talk about some thyroid diseases later in this article.
Indications for ultrasound examination
Ultrasound is prescribed in the presence of symptoms of diseases of internal organs and tissues. Widely used to identify benign and malignant tumors, as well as to detect metastasis of cancer cells. Ultrasound is used for preoperative examination and postoperative monitoring.
Angiology and karyology
Doppler ultrasound measures the direction and speed of blood movement and determines blood pressure. Diagnoses various heart conditions, including heart valve problems and congestive heart failure, and assesses damage after a heart attack. Cardiac ultrasound provides images of the cardiovascular system and helps measure the movement of heart tissue.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows:
- examine the walls of blood vessels;
- determine deep vein thrombosis;
- accumulations of plaques and clots;
- control tumors and congenital vascular injuries.
Sonography is used to monitor decreased, absent, or increased blood flow in various organs. Information obtained from a Doppler ultrasound image can determine whether a patient is a suitable candidate for a procedure such as angioplasty (widening of the arteries).
Emergency conditions
Used to evaluate traumatic wounds, fluid accumulation around the heart, internal bleeding, etc. Gastroenterologists use ultrasound to obtain images of the spleen, kidneys, bile ducts, gallbladder, liver, aorta, inferior vena cava, pancreas and other abdominal organs.
Sonography detects swelling or infection in the appendix area.
Pediatrics and pregnancy
Ultrasound in newborns is performed in the soft spot on the skull (fontanelle) to monitor for brain damage or abnormalities, genetic disorders, cerebrovascular disease, bleeding, hydrocephalus. Sonography is also used to examine the baby's hip and spine.
Ultrasound during pregnancy is a standard component of prenatal follow-up care. Obstetric ultrasound helps monitor the health of the child and mother.
Urology and gynecology
In urology, ultrasound helps examine the amount of urine remaining in the bladder after urination and the health of organs in the pelvic area, including the uterus and testicles. A urological ultrasound is performed to examine the kidneys or bladder for stones.
Orthopedics
Diagnoses problems with soft tissues, muscles, blood vessels, tendons and joints. Muscular skeletal sonography can be used to study connective tissue, bony surfaces, soft tissue masses, nerves, muscles and tendons.
Thyroid goiter
In medicine, goiter refers to all benign neoplasms in the thyroid gland. A goiter is a knot in the thickness of unchanged tissue or an increase in the entire volume of the gland. The most common causative factor in the development of pathology is iodine deficiency, which leads to a decrease in the production of iodolipols by thyroid cells.
Treatment is carried out with goitrogenic drugs that suppress hormone synthesis, or the producing adenoma is removed. Insufficient function, on the contrary, is compensated for by synthetic endocrine drugs. Nodular goiter cannot be treated with any medications; removal of a benign neoplasm is necessary if cancer is suspected or there is compression of surrounding structures.
Principle and safety of the procedure
Depending on which organs are being examined, ultrasound diagnostics are performed while sitting, standing or lying down (on the stomach or side). Gel is applied to the sensor, and often to the skin in a specific area, to establish even contact. The equipment sends waves into the tissue through a sensor. They are reflected by the fabric in different ways depending on its structure, i.e. they are thrown back.
The sensor again picks up the reflected waves and the device detects the image. The result obtained is reflected on the monitor. The doctor often shows and explains to the patient what is shown on the screen. The ultrasound technician can print individual, especially significant images directly on the device itself.
Classical sonography does not pose any health risks. The sound waves are not noticeable to the patient and do not cause injury. Additionally, these are not the beams used in, for example, X-rays or CT scans. Therefore, ultrasound is also safe for pregnant women and children.
Preparing for the study
Although most ultrasound examinations do not require preparation, there are a few exceptions:
- before an ultrasound of the gallbladder, the patient is asked not to eat or drink anything 6 hours before the procedure;
- a full bladder may be required during pelvic ultrasound;
- to improve image clarity, a harmless substance called contrast agent is injected before the examination;
- If necessary, intravenous tranquilizers are used.
Young children may require additional preparation for an ultrasound. We are talking about the use of sedatives to prevent the child from being overly active during the procedure.
Treatment of thyroid diseases
Treatment depends on the type of disease, the form of pathology and the patient’s condition. Most often, drug therapy is prescribed. The drugs can be taken by the patient for some time or for life if necessary.
In some cases, surgical treatment may be prescribed. A thyroidectomy (removal of the thyroid gland) is performed. Sometimes only a lobe of the thyroid gland is removed (hemithyroidectomy). Removal of the thyroid gland is required when malignant neoplasms are detected, a large goiter that impairs breathing and swallowing, and thyrotoxicosis.
Advantages of performing ultrasound at Medscan
You can get an ultrasound done at the Medscan clinic at the best prices in Moscow. The medical center has ample capabilities to conduct comprehensive diagnostics of a wide range of pathologies of various systems and organs. The clinic is equipped with modern expert-class ultrasound machines, which allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and, based on the results obtained, prescribe effective treatment.
The scan is carried out in accordance with the recommendations of European medical imaging societies. The results obtained are accepted both in Russia and abroad.
Sign up for diagnostics by phone or on the website. We also suggest that you read the reviews of our patients, which confirm the high quality of the services provided.
Sign up
Thyroiditis
—
Inflammation of the thyroid gland resulting from an infectious or autoimmune process. Complications of inflammatory diseases of the thyroid gland are most often associated with a decrease in the endocrine function of the organ. For example, chronic autoimmune thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism.
Deficiency of thyroid hormones leads to sudden weight gain, neurological and mental disorders, infertility, anemia and other consequences.