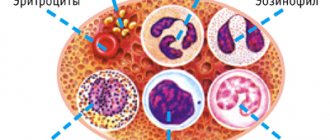
Read more about blood tests in our article
“Hematological tests: norms and interpretation of results.” First of all, a serious decrease in lymphocytes in the blood occurs during AIDS. It is at the deep stage of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome that lymphopenia occurs.
For tumors of lymphoid tissues. They can cause significant lymphopenia.
Bone marrow diseases. Moreover, any disease can lead, as a rule, to lymphopenia. Sometimes there are oncological lesions in which we see, on the contrary, an uncontrolled growth of young lymphocytes, but now we are talking about “singing”, a decrease in the number of lymphocytes, and this mainly happens with bone marrow disease.
Severe heart failure and severe types of renal failure. They, as a rule, in extreme stages begin to lead to serious depletion of the immune system and a drop in the number of lymphocytes.
Taking certain medications, such as cytostatics. If a person takes them for cancer or an autoimmune disease, they can lead to lymphopenia. Glucocorticosteroid drugs also lead to it. Almost all corticosteroids suppress the immune system and therefore reduce the production of lymphocytes. Some antipsychotics reduce the number of lymphocytes.
Any radiation exposure. Radiation can either directly cause the death of lymphocytes, or indirectly through bone marrow suppression.
If we talk about immunodeficiency conditions, there are a huge number of them. There are also immunodeficiency conditions that a child receives from birth, some of which can be expressed by a sharp drop in the number of lymphocytes.
Transient or transient immunodeficiency states can occur after severe illnesses, and the so-called transient lymphopenia can last for several months.
During a normal pregnancy, we will always see a decrease in lymphocytes in the blood. Lymphopenia during pregnancy will be moderate, and, as a rule, should not exceed the reference values of norms. The range can be large - in an adult, from 19% to 37%; in a pregnant woman, this value will be closer to the lower limit, so as not to provoke immunological pregnancy loss, or the formation of fetal rejection, because 50% of fetal cells do not correspond to the female genome. Therefore, nature provides for moderate lymphopenia.
Question answer
An adult has low lymphocytes in the blood. Which doctor should I contact?
A decrease in the level of lymphocytes can be caused by a number of reasons, both physiological and pathogenic in nature. If there are no external manifestations of a specific disease, and repeated blood sampling and analysis shows an identical value below normal, then you should contact a hematologist - a specialist in the etiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases directly or indirectly related to the blood system.
Segmented lymphocytes are greatly reduced. What to do?
You cannot have low segmented lymphocytes, since such cellular elements do not exist in nature.
Most likely, we are talking about segmented neutrophils - a mature subtype of granulocytic leukocytes present in the peripheral blood and, accordingly, the basic leukocyte formula, induced in the red bone marrow and migrating into the blood after reaching the band state. They are responsible for protecting the body from bacterial and fungal infections through NETosis. A decrease from the level is called neutropenia and occurs against the background of the development of chronic forms of bacterial and acute forms of viral/fungal infections, radiation therapy, aplastic anemia, as well as severe post-infectious conditions.
I can recommend contacting a hematologist for a comprehensive diagnosis and prescribing appropriate therapy.
What does a low level of lymphocytes in the blood mean during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, at certain stages, a low level of lymphocytes is normal. The mechanism of this process is associated with the physiological characteristics of the immune mechanism. It is well known that the above-mentioned cellular elements are divided into several types - the functionality of the B and T components is aimed at searching for and destroying foreign antigens, including the basis of the biological material of the father. With the onset of conception and hormonal changes, the body of the fair sex produces T-suppressors in large quantities, suppressing the work of the H/T components of the immune system, which allows the embryo to develop unhindered, while its protection against infections and other diseases is formed due to an increase in the concentration of phagocytes and neutrophils.
The overall relative and absolute level of lymphocytes begins to decrease from the fourth to fifth week of pregnancy and begins to gradually increase at the end of the second trimester. Accordingly, a reduced concentration of the described cellular elements is the norm from the beginning of the second month after conception until the 26th week.
Questions answered by: Evgeniy Pogolosov
Diagnostics
The level of lymphocytes is measured by calculating the leukocyte formula in a clinical blood test. Since the range of diseases that can cause lymphopenia is quite wide, if it is detected, you should consult a doctor for a detailed examination. Based on clinical and anamnestic data, the specialist draws up a program of diagnostic studies, which includes:
- Lab tests.
Both the total number and percentage of different types of leukocytes are studied. The level of inflammatory markers - ESR, CRP - is determined. The presence of autoantibodies (ACCP, antibodies to DNA, to the cytoplasm of neutrophils) is checked. If sepsis is suspected, procalcitonin and presepsin are measured. In inflammatory bowel pathologies, the content of fecal calprotectin in the stool increases. The concentration of serum immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM, IgA) is examined. - Microbiological research.
To confirm tuberculosis, bacteriological culture and microscopy of sputum, tuberculin diagnostics (Mantoux test, Diaskin test) are performed. The enzyme immunoassay method identifies antibodies to pathogens (viruses, bacteria). A verification test for HIV infection is the detection of viral envelope proteins (gp120, gp41) by immunoblotting. - Instrumental research.
With tuberculosis, radiographs of the lungs show an increase in lymph nodes (hilar, mediastinal), and infiltration of the upper lobes of the lungs. Images of joints in rheumatoid arthritis reveal narrowing of the joint space, marginal erosions, and osteoporosis. During fibrocolonoscopy in patients with IBD, hyperemia of the mucous membrane and areas of ulceration are found. MRI of the brain in multiple sclerosis shows oval-shaped foci of demyelination measuring 1-2 mm. - Histological studies.
When examining material obtained by biopsy of a lymph node, diffuse proliferation of lymphoid cells with blast morphology, Berezovsky-Sternberg cells, is noted in patients with lymphoproliferative diseases. In case of systemic vasculitis, perivascular infiltration with plasma cells and histiocytes is detected in the biopsy specimen.
Complete blood count - a method for detecting lymphopenia
The norm of lymphocytes in the blood. Which level is reduced?
Below are the standard absolute and relative norms for the content of lymphocytes in the blood. If the tests show lower values, this condition is called lymphopenia and requires at least additional diagnostics, and in most cases, the prescription of specific therapy.
In adults
The absolute value of the lymphocyte level is from one to 4.5 X 10⁹ units/liter.
- Lymphocytes: increased and decreased levels, functions, how to bring them back to normal
The relative value of the level of lymphocytes is from twenty to 34 percent.
In children
In children, there are much more lymphocytes in the blood than in adults, and specific norms depend on the age of the child:
Age—relative/absolute value of lymphocyte level:
- Children under one year - from 55 to 75 percent / 4–10.5 X 10⁹ units/l.
- Children under four years of age - from 45 to 65 percent / 2-8 X 10⁹ units/l.
- Children under six years of age - from 35 to 55 percent / 1.5–7 X 10⁹ units/l.
- Adolescents up to ten years - from 30 to 50 percent / 1.5-6.5 X 10⁹ units/l.
- Young people under 21 years of age - from 30 to 45 percent / 1–4.8 X 10⁹ units/l.
Based on the data presented above, the normal level of lymphocytes in the blood decreases with age - their highest concentration occurs in children under 12 months.
What does it mean?
A low lymphocyte count indicates that the patient has developed lymphopenia. This condition is usually associated with the migration of the above-described cellular structures from the lymphatic localized fluid into the tissues - thus, the analysis reveals a lack of the latter in the blood.
The above condition cannot be considered a disease - it is a symptom caused by a number of reasons, among which there may be both physiological and pathogenic factors, most often infectious-toxic fast processes.
This diagnosis is made after an initial and repeated blood test and determination of the patient’s exact immune status. Symptoms of lymphopenia are often very mild or absent altogether. The problem may be indicated by constant changes in the size of the tonsils and lymph nodes, the appearance of associated diseases such as eczema, pyoderma, alopecia, and frequent repeated infectious lesions over a short period of time.
Forecast
Lymphocytopenia is quite often a predictor of an unfavorable prognosis and is associated with an increased risk of infectious diseases and activation of opportunistic microflora. The outcome and life expectancy of patients are determined by the underlying pathology against which the lymphopenia occurred. The most benign is lymphocytopenia, which develops after prolonged stress or protein starvation. Hereditary immunodeficiency conditions and oncohematological diseases are characterized by a high probability of death in the early stages.
The role of lymphocytes in the body
Scientists have isolated several types of lymphocytes. Each of them differs in the way they act on pathogenic microorganisms.
- T lymphocytes. This group is the most numerous. It is divided into 3 more subspecies. Each of them plays a role. Killer T cells kill infectious agents, as well as altered (tumor) cells. Helper T cells improve immunity, while suppressor T cells suppress the immune response.
- B lymphocytes. Their number is 10-15% of the total concentration. The functions of B-lymphocytes are among the most important. They consist of resisting viruses, bacteria and developing cellular immunity. It is these substances that make vaccination effective.
- NK lymphocytes. This prefix is translated from English as “natural killers.” The proportion of these leukocytes is estimated at 5-10% of the total mass. The main function of agents is to kill elements of their own body if they are infected.
Lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow. From the blood, most of the lymphocytes pass to the thymus (thymus gland), where they are converted into T-lymphocytes, which protect the human body from foreign agents. The rest become B lymphocytes, which complete their formation in the lymphoid tissues of the spleen, tonsils and lymph nodes.
B lymphocytes synthesize antibodies upon contact with infectious agents. There is a third type of lymphocyte. These are the so-called natural killers. They also provide protection to the body from cancer cells and viruses.
- How to reduce lymphocytes in the blood?
ethnoscience
To increase immune strength, you can use the following alternative medicine recipes:
- 5 tbsp. pour a tablespoon of fresh pine needles into a liter of hot water, simmer over low heat for 15 minutes, leave for a couple of hours, filter. Add 2 tbsp. spoons of honey, take a glass twice a day;
- Drink ½ cup of fresh pomegranate, beetroot, blackberry, cranberry or apple-carrot juice 3 times a day;
- Mix flower pollen and bee honey in a 2:1 ratio, eat a teaspoon of the mixture on an empty stomach, with ½ glass of whole milk.
Different roles of lymphocytes
h27,0,0,0,0—>
May protect against cancer
h317,0,0,0,0—>
A higher level of CD8+ T-type lymphocytes (directly in the tumor) indicates an increase in the overall survival of cancer patients. (20)
p, blockquote53,0,0,0,0—>
Specialized tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte therapy can treat liver cancer and may help stop the cancer from coming back. (21)
p, blockquote54,0,0,0,0—>
Supports Gut Health
h318,0,0,0,0—>
- The norm of leukocytes in the blood of children in the table, low and increased values in a child
Lymphocytes in the intestine play an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of this organ. They are also critical for early response to intestinal infections. (22)
p, blockquote55,0,0,0,0—>
Protects against damage due to arthritis
h319,0,0,0,0—>
Patients with arthritis and high levels of lymphocytes in their joints had less cartilage and bone damage than people with low levels of lymphocytes. (23)
p, blockquote56,0,0,0,0—>
Correction
There are no ways to independently relieve lymphocytopenia. To normalize the level of lymphocytes, it is necessary to eliminate the cause, namely, treat the underlying pathology. If lymphocytopenia occurs due to stress or protein deficiency in the diet, treatment is not required, it is enough to adjust the diet. For persistent, long-term lymphopenia, medical intervention is necessary. Depending on the reason, the following measures are applied:
- Fighting infection.
To treat HIV infection, antiretroviral therapy is prescribed - nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, protease inhibitors (saquinavir). Oseltamivir is indicated for influenza. For the treatment of other viral infections, there are no etiotropic medications; symptomatic methods are used (antipyretics, detoxification therapy). For nonspecific bacterial infections, antibiotics are recommended; for tuberculosis, combinations of antituberculosis drugs (isoniazid, rifampicin). - Anti-inflammatory therapy.
To achieve remission of autoimmune diseases, medications are used that suppress the inflammation process - glucocorticosteroids, synthetic derivatives of aminoquinoline and 5-aminosalicylic acid, immunosuppressants (methotrexate, cyclophosphamide). - Treatment of lymphoproliferative diseases.
For lymphogranulomatosis and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, polychemotherapy (vincristine, dacarbazine, etoposide) is indicated. Irradiation of tumor-affected lymph nodes is effective.
Preparing for analysis
The analysis for lymphocytes is included in the general blood test, the rules for their conduct are the same. That is, such an examination does not require special preparation. There are only two conditions that must be met:
- Blood is taken in the morning.
- 8-12 hours before blood sampling you need to abstain from food.
You should also not smoke 2-3 hours before the procedure. Components of tobacco smoke can cause serious temporary changes in white blood cell levels. You should avoid drinking alcohol 2-3 days before taking the test, as alcohol can also affect the reliability of the results obtained.
If these requirements are not met, the accuracy of the examination may deteriorate, which will lead to the doctor receiving unreliable information and possible errors in diagnosis or re-prescribing the examination.