Photo of the MRI machine Neurological pathology becomes a serious problem not only for the patient himself, but also for the whole family. The lesion may be associated with both the brain and the vessels supplying it. In order to find the cause of the disease in a timely manner, diagnostic methods are needed that will help the doctor reliably determine the essence of the problem and begin treatment. There are various ways to visualize tissue, some of them are magnetic resonance imaging and Doppler ultrasound. Which method is better, ultrasound or MRI of blood vessels, we will discuss below.
With age, many people experience a decrease in memory, concentration, mood swings, and unsteadiness in gait. Cognitive impairment may be a manifestation of brain atrophy. This pathology occurs during the physiological process of aging. However, sometimes the cause of neurological symptoms is a disease that can be cured. At such a moment, the main thing is a reliable diagnostic search, a correct doctor’s conclusion and the fastest elimination of the causes.
The etiological factor for dysfunction of the nervous system can be:
- congenital gene defects;
- toxic effects of various substances;
- disturbance of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics (due to a tumor, cerebral vascular abnormalities);
- neuroinfections;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- stroke;
- vasculitis;
- atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head and neck, etc.
What can be diagnosed using an ultrasound scan of the brain?
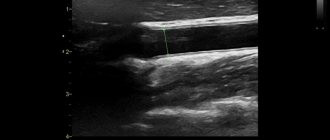
Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive and safe examination, in which the patient is protected from harmful radiation. The technology includes traditional ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound. Interesting fact: the only contraindication to ultrasound scanning is the patient’s condition, which does not allow him to lie down.
When diagnosing intracranial vessels, TCD (transcranial dopplerography of vessels) is used to assess the level of their blood supply.
This type of hardware examination is named after the Austrian scientist Christian Doppler, who was the first to “catch sound,” that is, to find the relationship between the source of movement and the change in the length of sound waves. It was this simplest effect that made it possible to measure speed, which was previously not available for direct measurement. The use of this discovery in Doppler ultrasound of the brain allows:
- determine the intensity of blood flow;
- identify the reasons on which the blood supply to the vessels of the brain and the appearance of diseases such as ischemia and stroke depend;
- establish the degree of abnormal blood pressure, venous insufficiency.
Using ultrasound, the presence of blood clots, stenoses, thinning, plaques, atherosclerosis, as well as deformations and varicose veins is determined.
THEY DO NOT REMOVE THE HEAD HERE or FUNCTIONAL DIAGNOSTICS - WHAT IS THIS?
This text will help you understand why functional diagnostics (FD) is needed and what types of FD exist in neurophysiology, what is the difference between these studies and other (primarily X-ray and tomographic) methods.
Types of diagnostics
Conventionally, we can divide all devices and instruments that allow us to look inside the body into two groups - structural and functional diagnostic tools. The first (this group includes routine magnetic resonance and computed tomography, x-rays, ultrasound) shows “how the organ is structured.” The second (the already mentioned electrophysiological methods, means of visualizing electromagnetic, thermal radiation and many others) is how it works.
Functional methods are characterized by a broader focus - they are used not only and not so much to identify a disease, but to assess how an organ or organ system copes with its responsibilities (as a rule, one or several indicators are determined, so we are talking about “diagnosis of the whole organism” and it cannot be). An essential feature is also the absence of a one-size-fits-all norm - since each organism is unique and works in its own way. All functional diagnostic methods are practically harmless - they can be performed every day and are performed relatively quickly (5...20 minutes). However, no less important than recording the results is their “decoding”. Since there is no single standard, during the examination the doctor has to give the body special loads - functional tests, compare the results of repeated examinations (this is why we always ask you to bring the results of previous studies), and take into account the entire set of factors that can affect the functions being studied.
Methods
Cardiointervalography (CIG) - based on the results of analyzing changes in the speed and rhythm of the heart, it allows one to judge the state of the autonomic nervous system that regulates it.
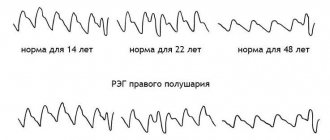
Rheoencephalography (REG) – reflects the state of blood flow and tone of cerebral vessels.
Electroencephalography (EEG) - registration of brain biopotentials. Brain activity is accompanied by electrical activity, which can be recorded in the form of electroencephalograms. EEG reflects the total activity of the brain; It is naive to expect, say, the content of a thought from deciphering such a recording. Echoencephaloscopy (ECHO) – shows the state of intracranial pressure.
The evoked potential (EP) method allows you to test the state of the central nervous system by sending signals to its inputs at constant time intervals.
This way you can check the functioning of the brain systems responsible for vision, hearing, or memory and processing new information. Share
How is ultrasound done?
Ultrasound of cerebral vessels includes examination of the temple area, occipital region of the head, and orbits. To assess the condition of large vessels, a neck examination is performed.
The patient is placed on the couch, having previously placed a hard pillow under his head. The doctor applies a small amount of gel to the areas of the head that will be examined (this is necessary for maximum contact of the ultrasound sensor with the surface of the head). During the scan, the patient may be asked to take several deep breaths and hold their breath (this is done if functional tests are used to maximize the reliability of the ultrasound results).
During the procedure, the obtained data is displayed on the monitor and stored in the computer memory. Then the ultrasound specialist deciphers the data and prepares a conclusion, which contains a list of data on the diameter, level of stenotic changes, wall thickness, intensity of blood flow, etc. All these characteristics are then used to make a diagnosis.
Differences in contraindications
There are some differences in contraindications for ultrasound and MRI. Ultrasound examination is not performed if there is damage to the skin where the sensor touches. MRIs are not performed on patients with implants containing metal components or electronic devices such as pacemakers.
During tomography, a contrast agent is not used if you are allergic to its components. The procedure is not performed for people with acute mental disorders. Another nuance lies in the features of the research devices. For ultrasound, the height and weight of the patient do not matter, and some closed-type tomographs are not designed for patients with significant body weight. In addition, during magnetic resonance imaging, certain problems are created by the fear of closed spaces, because the patient is inside the tomograph tunnel for a certain time.
These studies are characterized by painlessness, absence of harmful effects on the body and accuracy of the results.
When choosing a method, the doctor is guided by a number of conditions, according to which he selects the best option: ultrasound or MRI. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
Doppleography in children
The issue of early and accurate diagnosis continues to be the main problem of pediatric neurology. The choice of diagnostic method depends on many conditions, of which the most important are:
- non-invasive;
- safety.
Since the fragile body of a child is much more susceptible to the influence of radiation than the body of an adult, for diagnosing the condition of cerebral vessels in newborns, preference is given to neurosonography, and in older children, doppleography.
The neurosonography procedure for very young children is carried out online. In this case, the ultrasound waves pass through the fontanel and do not cause the slightest harm to the baby.
Using ultrasound, children are diagnosed with:
- obvious and hidden pathologies;
- insufficient blood supply to the brain;
- various morphological changes;
- cerebral hemodynamics and assessment of genetic abnormalities;
- possibilities of cerebral arteries, etc.
In case of perinatal brain lesions such as asphyxia, various birth injuries, Doppler ultrasound is necessarily prescribed. For older children, a transcrural Dopplerography procedure is indicated, which a neurologist can prescribe for delayed speech development, hyperactivity, excessive fatigue, inability to concentrate, various memory impairments, etc.
Why are ultrasounds and MRIs performed?
Each of these methods is safe for the body, so the examination can be repeated as often as necessary. And this is different from a computed tomography or x-ray, where harmful ionizing radiation is present.
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound or MRI based on the indications:
- When studying the condition of cerebral vessels, MRI is more informative, and medium and large vessels are more often studied using Doppler ultrasound;
- When studying the brain, the choice of method is determined by the suspected disease, but in most situations MRI is considered more informative;
- Examination of the pelvic organs in women is often performed with ultrasound. MRI shows prostate damage well, so the technique is relevant for men;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys allows you to determine the shape and size of the organs, and more detailed information can be obtained using MRI;
- Tomography is more suitable for studying soft tissues located quite deep.
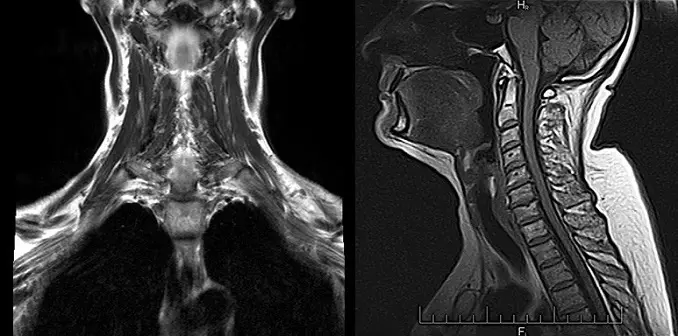
In general, the use of ultrasonic waves makes it possible to diagnose organ dysfunction, disorders in tissue structure, neoplasms, and internal bleeding. MRI is prescribed for detailed examination. It is believed that ultrasound is better suited for obstetrics and for examining pregnant women, but in most situations, tomography is not contraindicated.
MRI allows you to confirm or clarify a preliminary diagnosis, identify diseases of the pituitary gland and thyroid gland, lesions of internal organs and damage to bone tissue, spinal cord, and brain in the early stages. This method is relevant for diagnosing cancer with metastases and diseases of the nervous system. The intestines are poorly visible on an ultrasound, so an MRI is prescribed to examine it.
Which is better: MRI or ultrasound of the brain?
If we make an objective comparison of Doppler ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, then MRI, an advanced high-tech technique that uses nuclear magnetic resonance to diagnose diseases, will take precedence in the volume and accuracy of the information obtained. Only on MR images of layer-by-layer sections are visible the smallest structural changes, deformations, and abnormal neoplasms.
Meanwhile, the ultrasound ultrasound procedure has no equal as a primary diagnostic technology in terms of efficiency and clarity of information. This is especially important in emergency situations, when a few minutes of delay can cost a person his life. In addition, the cost of ultrasound scanning, unlike MRI, is affordable for almost every patient.
One way or another, various situations may arise when the use of a certain diagnostic method becomes vital. And only the attending physician can decide which one is optimal.
Research principle
The first difference between ultrasound and MRI is the different mechanism of its implementation. The first type of research is based on the properties of high-frequency ultrasonic waves reflected from tissues. The organs of the human body have different densities, so they reflect ultrasound differently. After processing the data with special equipment, images similar to photographs are obtained.
Magnetic resonance imaging works differently. The tomograph creates a magnetic field into which the nuclei of hydrogen atoms located in the human body fall. As a result, a resonance arises, which is captured by the device’s sensor, transmitted to a computer, processed and converted into a digital image of the structures under study.
MRI or duplex scanning: contraindications to procedures
When determining whether you will undergo an MRI or duplex scanning, it is important to consider contraindications to the examination. The duplex scanning method is practically devoid of them.
Tomography is contraindicated in a number of situations:
- the presence of pacemakers and metal implants in the patient’s body;
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- heart failure in the stage of decompensation.
Contrast enhancement is excluded at any stage of pregnancy, in case of kidney damage, hematopoietic anemia and individual intolerance to contrast.
What to choose - MRI or duplex scanning - is decided by a specialist, based on anamnestic data and provided medical documentation.
What are the differences
The main difference between MRI of the brain and MRI of blood vessels is the diagnostic results due to differences in the focus of the scan. In the first case, the nervous tissues of the pituitary gland, cerebral cortex and sella turcica are studied.
Areas of necrosis after a stroke and neoplasms are identified, and benign and malignant tumors are clearly identified. During the examination of cerebral vessels, dysfunctions in the circulatory system and disruptions in blood circulation are determined.
Depending on the complexity of the clinical picture (for ischemia or stroke), the doctor prescribes both examinations. Detailed results and a correctly diagnosed disease are obtained.
For example, symptoms such as dizziness, tinnitus and frequent headaches provoke vascular malformations and tumors in the brain.