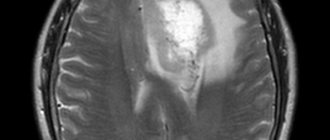
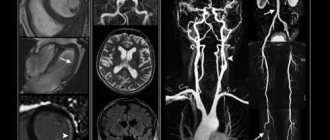
MRI scanner The phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance is actively used in all branches of medicine for diagnosing diseases. This technique is especially informative in relation to soft tissues. How often an MRI of the brain can be done depends on the diagnosis. The procedure is based on the influence of magnetic fields on tissue (similar to those emanating from electronic devices), but there is no objective scientific evidence of its complete safety.
How often can an MRI be done?
Before you figure out how often you can do an MRI, you need to understand what this method is based on and how harmful it is for the patient.
Is MRI safe?
Currently, MRI can be done not only to study bone tissue and joints; it is often prescribed for the diagnosis of blood vessels, the nervous system, soft tissues, inflammation, and tumors. Unlike other methods of examination, it is not only the most informative, but also safe, since the tomograph does not emit radiation.
Impact of MRI on the body
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the principle of electromagnetic waves, which, when reflected from tissues, give a picture of their condition.
Computed tomography is the effect of x-rays. With repeated penetration, they also provide a three-dimensional image. However, it has long been proven that X-ray radiation has a detrimental effect on human cells. Electromagnetic waves do not have such an effect and are absolutely harmless. Therefore, unlike MRI, CT can be done no more than twice a year, not more often. When prescribing a CT scan, doctors are guided by the “risk/benefit” principle, since the harm caused may be higher than the positive effect of the diagnosis.
How often can an MRI be done?
MRIs can be taken as often as needed. It carries no radiation load, which means it is absolutely safe. The method is used both to make a diagnosis and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and further prevent a possible relapse.
Anatomy of the knee joint
The knee joint is the most complex and largest joint, formed by the heads of the tibia and fibula below, and the condyles of the femur above. In the joint cavity there are two cartilaginous menisci, which act as a gasket and shock absorber, softening shock loads. The front of the knee joint is protected by the patella, an irregularly shaped bone located deep within the quadriceps tendon.
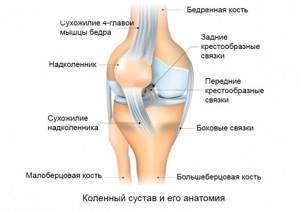
A special feature of the knee joint is its powerful ligamentous apparatus, which strengthens and stabilizes the joint. There are external ligaments of the knee - lateral and posterior, and internal, represented by the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments.
The increased loads and complexity of the knee joint explain why this joint is most susceptible to various injuries, especially sports and everyday ones. Most often, damage to the cruciate ligaments and menisci occurs when exposed to excessive force that occurs during sharp turns in the knee joint, impacts and falls, jumping and squats.
Contraindications for MRI
Sometimes doctors still tend to use alternative examination methods, since MRI has some contraindications:
- Metal prostheses and complex mechanisms built into the patient's body. These can be either pacemakers or implants to improve hearing. Electromagnetic waves can interfere with their operation and thereby cause harm to humans.
- Any other metallic inclusions: from subcutaneous implants and dentures to colored tattoos with a metallic sheen. In this case, MRI can be done if the organ being examined is located far from the metallic inclusion; often the error does not play a decisive role. Contrary to popular legend, metal does not move in the body under the influence of electromagnetic waves. It can distort the results of the study and shade the image.
- Weight more than 120 kg.
- Claustrophobia.
- Individual intolerance, panic attacks, etc.
- If MRI is performed using contrast, then the following contraindications are added to the above: pregnancy and breastfeeding, severe kidney damage, allergic reactions to the contrast agent.
Preparing for an MRI of the knee joint
MRI of the knee is performed without prior preparation. It is important to remember that before the examination, it is necessary to leave all foreign objects in the storage room - jewelry, accessories, electronic devices, credit or other cards, belts - especially those made of magnetic metal. Otherwise, there is a risk of burns or injury.
If you have already had an MRI of the knee joint and come back for a repeat examination, do not forget to bring your old images on disk or film with you. By comparing them with the results of the new examination, doctors will be able to determine whether the disease is progressing and whether there are improvements.
How often can I have an MRI with contrast?
MRI with contrast is often prescribed to examine both tumors and the brain as a whole. It allows you to determine: inflammation, bleeding, changes in blood vessels and nerves, tumors at an early stage. This becomes possible precisely thanks to the contrast agent, which stains the affected cells and makes them more visible. MRI of the brain
with contrast can be done frequently, but at intervals of several days, since the contrast agent must completely leave the body.
What does an MRI of the knee show?
MRI scanning allows you to obtain a series of layer-by-layer images, which consistently show all the anatomical features of the area under study. In the resulting images, one can distinguish the condyles of the femur, the heads of the tibia, the spongy and compact layer of bone tissue, articular cartilage, the joint cavity, intra-articular ligaments and menisci, and the synovial membrane of the joint. MRI allows you to detect the smallest changes - bone marrow edema (a sign of osteomyelitis), sclerotic and trophic changes, inflammation of the synovium, cartilage destruction, ruptures of the cruciate ligaments, menisci, pathological effusion/blood in the joint cavity and many other signs of diseases and injuries of the knee joint.
Getting the result
The scanning duration is from 30 to 40 minutes. During this time, the subject is stationary in the inside of the tomograph. Even minor movements of the limbs can cause severe distortion of images. You need to remember this.
As soon as the device stops working, the table leaves the scanner, the person is freed from the fastenings, and he can immediately leave the office. Meanwhile, the doctor begins to decipher the received images and prepare a report. This usually takes no more than an hour. In rare cases, a specialist will need a little more time.
The patient can wait for the conclusion at the medical center, or he can go home and go about his business. In this case, the results will be sent to him by email shortly. With the obtained images, you must contact the doctor who has written a referral for an MRI. The doctor will evaluate the results and prescribe the correct treatment.
Description of the procedure
Tomography of the knee joint is a new direction in the field of radiology diagnostics. The study allows you to obtain a high-quality image of the examined part of the body or organ. MRI is a relatively new technique, but has already gained a good reputation during this time. Ten years ago, it was possible to undergo examination only in reputable clinics. Now this method is available even to residents of the provinces.
Scanning is used both for examining adults and very young children. The diagnostic principle boils down to the effect of a magnetic field on the human body. This process results in highly accurate images. Now developers of MRI machines have begun to change the flow of radiofrequency pulses. This made it possible to improve the quality of the images. Despite the high cost, diagnostics are in demand.
Does it make sense to examine all parts of the spine?
There is no clear answer to this question. But there are often cases when the doctor needs to diagnose two or more parts of the spine within which the symptoms are localized (for example, MRI of the lumbosacral spine and MRI of the coccyx), or parts of the spinal column and the adjacent area (MRI of the craniovertebral junction, MRI of the sacroiliac joints). A complete examination of the spine (cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx) lasts more than an hour.
Indications for tomography
MRI of the knee is usually prescribed in the following cases:
- to examine the severity of injuries received;
- against the background of progressive degenerative changes in the joint;
- to determine the degree of bone damage when other diagnostic methods do not provide a complete picture;
- for chronic diseases of the knee joint;
- if the patient complains of pain in the knee area, identify the cause of the occurrence, which did not work out;
- due to decreased joint mobility;
- to determine the causes of blood and fluid accumulation in the joint;
- to determine tumor processes and metastases;
- before preparing for surgery;
- to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
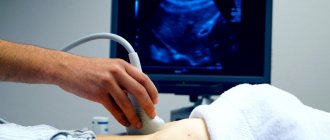
MRI or ultrasound of the knee
In some cases, the doctor refers the patient not to an MRI, but to an ultrasound. Only a specialist can decide which is better in each specific situation - MRI or ultrasound of the knee. However, ultrasound diagnostics of the knee joint has a main drawback - insufficient accuracy. This makes it difficult to establish a correct diagnosis.
Ultrasound is often performed to examine internal organs. MRI is prescribed to detect bone pathology. Ultrasound diagnostics is non-invasive and safe, which cannot be said about MRI: a magnetic field is created during scanning, which is why this diagnostic method has contraindications. MRI of the knee is strictly prohibited for some patients.
The availability of such methods is an important point: everyone can pay for ultrasound, but not everyone can pay for MRI. From the above, a logical conclusion suggests itself: only a doctor can make a decision about undergoing an MRI or ultrasound of the knee, based on their medical history.
High-quality MRI of the spine is not only a modern tomograph
But technical support is only one component of the accuracy of an MRI examination. The second key link is the preparation of a conclusion describing the identified deviations from the normal state of the spinal structures. The qualifications of a doctor, his experience, the possibility of consultation with colleagues - these are the elements that save health and lives. And they are the focus of the entire international network of MIBS diagnostic centers, two of which operate in Moscow. Even in cases where complaints lead the patient to an MRI of the spine earlier than to an initial consultation with a doctor, the identified changes can suggest a diagnosis and save time on sorting through doctors of different specialties, determining whose jurisdiction the problem is.
Features of the study
Not all patients are aware that each tomograph provides for a specific range of examinations. An experienced radiologist always knows the pathological and normal anatomy, because this helps to avoid a number of diagnostic errors.
The examination of the knee joint is carried out under the influence of a powerful magnetic field. This is what allows you to obtain high-quality and most accurate images. It is simply impossible to create such conditions in open tomographs. MRI on such cases does not always pay off. Such devices have low power, which is why they are much inferior to closed devices. Patients are not always informed of such nuances. People often choose open devices because they inspire more confidence and do not cause fear.
How to save on MRI of the spine without losing the information content of the examination?
But, as promised in the title of the page, there are some “secrets”, knowledge of which will allow you to significantly reduce the cost of MRI of the spine and any other parts of the body without reducing the accuracy of the examination.
First of all, these are special price offers with the help of which diagnostic center managers optimize equipment utilization. It should be emphasized that when we mention discounts on MRI, we are not talking about “virtual” discounts, with which less technological examinations are offered on low-field tomographs, and not about discounts from “MRI factories”, where tomography is carried out, although with good equipment, but with an increased step ( distance between slices) and preparing a conclusion within 10-15 minutes, during which it is difficult to even briefly view the entire array of images.
We are talking about discounts on professional studies that allow you to attract patients during a decrease in activity on weekends, holidays and at night. For example, at the MIBS-Moscow MRI Centers there are regularly discounts from 5 to 15%, which subscribers of our account on Instagram and other social networks will find out about (icons at the bottom of the page). In addition, we provide special conditions for certain social groups.
Therefore, if you, like many thousands of patients, are already ready to choose the quality of diagnostics at MIBS centers in Moscow, but prefer to wait for a special price offer, subscribe to our groups. Or simply call us to find out how to undergo a high-quality MRI of the spine with maximum comfort for your own budget.
Sixth - use contrast when not required
“You can often hear the following phrase: “Let’s do a study with contrast, it’s more reliable.” Actually this is not true. Contrast in CT and MRI is a very difficult thing, especially if we are dealing with a patient whose kidney or liver function is impaired. Just in case, contrast cannot be used; in this case, the doctor deliberately exposes the patient to danger. In approximately 10% of cases, patients develop an allergy to contrast during CT, and about 3% of cases develop a fatal allergy to contrast during MRI,” notes Oleg Serebryansky.
Tomography with contrast is a very serious medical procedure. An excellent solution is to locate the diagnostic room next to the intensive care unit, so that emergency measures can be taken if something goes wrong.
Which specialist should I contact?
An oncologist, orthopedist or traumatologist can prescribe a referral for a scan. The doctor conducts a visual examination and inquires about complaints. A specialist may make such a decision for a number of reasons:
- significant knee injuries;
- decreased mobility;
- suspicion of neoplasms;
- degenerative changes.
Based on the referral received, each patient can count on undergoing a tomography free of charge. However, you usually have to wait a long time for your turn. Because of this, patients choose paid clinics. There is no need to provide referrals to private centers. All you need to do is make an appointment and come at the appointed time for the examination.