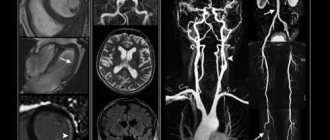
Among treated citizens referred by doctors for tomography, a common question is which scanning option will be better in terms of its diagnostic properties: computer diagnostics or MRI of the brain? According to medical professionals, it cannot be said that any of the tomography options is superior in quality to the other. Each of them is more important for examination in different clinical cases. There is no point in discussing their interchangeability, although in two cases the end results are serial photographic images. Computed tomography, abbreviated CT, and magnetic resonance imaging, MRI, have many significant properties that distinguish them by functional focus. Here are examples of situations when preference is given to searching for pathology, and when it is better to resort to MRI.
MRI of the brain and CT: what is common?
- The results of the examination of patients are a series of layer-by-layer images. They are formed when a computer processor processes data from a tomograph. They are given to the visitor on disk or printed out.
- It involves scanning a person in a supine position. In some cases, when examining certain areas of the body, the person being diagnosed may be asked to turn on their side.
- They last quite a long time (sometimes up to an hour), while urging the patient to remain still.
- The appearance of the installations is the same.
- In both methods, a contrast agent is administered.
Ultrasound Dopplerography (USDG)
Doppler ultrasound is one of the modern and accessible research methods. The principle of ultrasound scanning is based on the reaction of ultrasound to moving red blood cells in the blood, which makes it possible to determine the patency of blood vessels and even diagnose a number of vascular diseases based on indirect signs. Ultrasound ultrasound has no contraindications; it can be done even for pregnant women and children from the first days of life. Doppler ultrasound is often prescribed to infants with unsatisfactory results of ultrasound neurosonography.
How is the ultrasound procedure performed?
Ultrasound scanning
takes up to half an hour and is performed with the patient lying or sitting. During the procedure, the sonologist applies a sensor to the patient’s temples, back of the head and neck; if necessary, the eye area can be examined. During the ultrasound procedure, the patency of blood vessels is examined at points of the body that are usually scanned. However, since the outline of the vessels is not visible, the study is carried out blindly, and the results are interpreted based on indirect signs of pathologies.
Difference between CT and MRI of the brain
- They differ in operating principles. With computer diagnostics, the body is scanned with X-rays, and with magnetic resonance imaging, it is placed under a magnetic field.
- On a CT scan, a specialist monitors the physical parameters of the brain, and on an MRI, he looks at the chemical components of brain tissue.
- During a CT scan of the head, only this part of the patient's body is pushed into the scanner. For MRI, the entire person's brain is placed in the machine.
- On a computed tomography scan, the cranial bones are clearly visible. With MRI, the focus of imaging is on the soft tissue of the brain.
- The head is examined on MRI if there is a suspicion of oncology, genetic diseases of neurons, inflammation processes in the nerves or membranes of the brain.
- A CT scan checks to see if a person is having a stroke.
Don't risk your health by choosing comfort during MRI
This paragraph is about something that is difficult to understand. We are talking about the main characteristic of a tomograph - magnetic field strength. Without going into the technical details of magnetic resonance imaging, we will inform you: the resolution of the image depends on the parameter expressed in units of “Tesla” (or “T”). That is, MRI images taken with 0.5 Tesla and 1.5 Tesla tomographs will be fundamentally different for the doctor who has to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. The “Rubicon” from which the field strength parameter meets modern diagnostic standards is a field strength of 1.5 Tesla.
All tomographs that have a lower magnetic field strength are usually called “low-field”; everything above is “high-field.” The only reason why examination on a low-field tomograph is permissible is the inability to undergo a “high-field” examination.
There are three main restrictions:
- excess weight of the patient exceeding the maximum value, after which the movable “table” of the tomograph may fail;
- the patient's size (the circumference of the body at its widest point) is greater than the diameter of the ring magnet into which the patient is placed during the examination;
- claustrophobia.
These limitations are due to differences in the designs of low-field and high-field tomographs. The weaker magnetic field of the first category of devices is created using a large permanent magnet. This allows the patient to be placed on a “table” with a permanent magnet on top of the area of interest. A more powerful tomograph uses electromagnets that look like a “tunnel” into which a movable table with the patient “drives” to obtain MRI images.
In order to attract more patients, diagnostic centers call their low-field tomographs “open” and their “high-field” tomographs closed, shifting the emphasis from technical parameters to comfort.
Yes, the open design has fewer restrictions on patient weight and volume. A low-field tomograph is also cheaper to operate - it does not require constant maintenance of a magnetic field, which consumes a significant amount of electricity and liquid helium used for cooling. Therefore, the cost of MRI can be low. But such savings are very conditional: the quality of images taken with a low-field tomograph will be low. Keep this in mind before you get excited about the low price.
CT scan of a patient's brain
Maximum depth of detail is the primary criterion for the advantage of computed tomography. It clearly shows manifestations of vascular atherosclerosis, swelling of arterial walls, and changes in the tissues of the skull bones.
- Determines deformation of the facial bone and maxillary sinuses. He will see the presence of injuries to the cerebral cortex.
- Reveals the causes of the disease without resorting to contrast. Does not cause pain to the patient.
- On a CT scan, the doctor looks at the soft tissue structures of the brain, along with the vessels of the circulatory system and the cranial bones. The image of the area being examined is clearer than on an x-ray.
- A CT scan of the brain can be performed in emergency situations, in particular in cases of intracranial hemorrhage.
- If during the procedure the patient accidentally disturbs the immobility of the body, then there will be no interference in the image.
- Implants implanted into the body that contain metal will not be prohibited for diagnosis.
Today, CT, which does not cause any discomfort to a person, is an alternative to laparoscopic examination.
Why is the cost of MRI in Moscow so different?
In the final section, we will consider the factors influencing the cost of magnetic resonance imaging: both those already mentioned in the article earlier and new ones.
What determines the cost of MRI and the effectiveness of the examination?
Magnetic field strength (and, accordingly, tomograph design)
Examination with a high-field tomograph (1.5 Tesla) is always more expensive, but always more informative than with a low-field tomograph (up to 1.5 Tesla). Ultra-high-field tomograph (3 Tesla and higher) - always more expensive services, but justified if specific examinations are necessary
Trust in the referring doctor
If you have no doubts about his professionalism and integrity, feel free to go for a tomography at one of the recommended MRI centers in Moscow. But it wouldn’t hurt to ask why these particular institutions are recommended. But if a patient with a serious illness, the treatment of which requires accurate diagnosis, is sent to an MRI center with a low-field tomograph, we recommend that you think about changing the doctor.
MRI with and without contrast
The introduction of a special substance into the body that increases the differences between tissues of different types in MRI images is an important component of modern examination. But the use of contrast is not always justified, but the cost of an MRI examination always increases. To avoid misunderstandings, always check with your doctor whether it makes sense to undergo an MRI with contrast. And when comparing the cost of services from different MRI centers, be sure to specify the type and cost of the contrast agent to eliminate “hidden fees” during the visit.
Discounts, special programs, bonuses for activity on social networks, etc.
This part is dedicated to the financial side. A priori, any MRI center is interested in more fully utilizing its existing tomographs. This helps to divide the cost of research among a larger number of patients, thereby offering the optimal price. For example, at the MIBS-Moscow Centers there is a special price for more extensive MRI studies (for example, MRI of all parts of the spine), and a special cost for MRI at night. In addition, any commercial institution is required to inform the public about its capabilities and successes in order to attract new patients. That is why MIBS-Moscow is happy to exchange mentions of us for discounts. It’s easy to find out about discounts and get them - just subscribe to our pages ( Facebook , Instagram )
In conclusion. Regardless of which MRI center in Moscow you choose to undergo the examination, the tips given above will help you choose the most optimal option. We are sure that by sharing this material with your friends and acquaintances, you will provide the same chance to others. Why not do it right now?
But if you choose MIBS-Moscow, we guarantee the highest diagnostic accuracy and optimal cost. Call now!
MRI or CT scan of the head: negative aspects
Due to the use of CT, the risk that malignant cells will begin to grow is minimal. This occurs due to X-ray rays that are applied to the patient.
- CT scans will never be performed on pregnant women because there is a high risk of harm to the fetus.
- If contrast is used, especially drugs that contain iodine, the patient may experience an allergic reaction to it.
- Women who are breastfeeding after applying the enhancement are prohibited from breastfeeding for about two days.
- Tomography is contraindicated for children under 12 years of age.
- Repeated CT examinations will also not be used for children.
- An MRI will not show a picture of stroke bleeding or head injury.
- People with pacemakers do not undergo MRI. The ban also applies to the presence of medical items made of metal in the body.
Summing up: advantages and disadvantages of magnetic resonance imaging
The advantages of this method of identifying brain pathologies include the following:
- safety (magnetic waves do not have an adverse effect on the body);
- absence of painful sensations, which is why the procedure can be prescribed even to small children;
- accurate visualization of even small vessels;
- clear localization of tumors, blood clots and other abnormalities.
The only disadvantages of MRI include the high cost of diagnosis, as well as the duration of the examination, during which you will have to maintain a motionless body position.
The difference between MRI and CT and their impact on the choice of procedure
The most important thing about methods is their informative capabilities.
MRI is more preferable for intracranial tumors, multiple sclerosis, and disorders in nerve fibers.
- An MRI makes it easier to see deformed facial bones, manifestations of otitis media, or sinus infections.
- An MRI will be performed if the patient has an allergic reaction to an iodine-containing substance.
- Pregnant women can undergo an MRI in emergency situations. However, they are not at risk of radiation exposure.
- For children, an MRI may also be prescribed and performed under general anesthesia.
- Computed tomography is more considered an emergency diagnostic option.
- For small children and women carrying a child, CT is prohibited.
- An MRI can last approximately an hour. CT scan will be faster in this regard.
- The specificity of MRI is detailed monitoring of soft brain structures. A CT scan shows the bone structures of the skull better.
- CT diagnostics will be somewhat cheaper, although not by much.
What is MSCT?
Multislice computed tomography is based on the ability of body tissues that are not the same in composition and density to retain x-rays differently. Unlike conventional CT devices, multislice devices have wider capabilities. The gantry circle is equipped with several detectors and X-ray tubes. The rotation is faster. The equipment allows you to examine a larger anatomical area in one revolution, monitor physiological processes in real time, and obtain the number of images necessary for detailed diagnostics.
X-ray methods are the most informative regarding bone tissue and organs with a heterogeneous structure (lungs, etc.). If necessary, contrast enhancement with iodine preparations is used. If you have to choose MRI or MSCT, the doctor takes into account the diagnostic goals and potential risks.