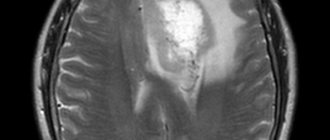
Among neuroimaging diagnostic methods, electromagnetic screening has the highest level of information content and reliability. MRI of the brain is a medical method that helps doctors carefully examine all the structures of the organ, the ventricular section, the substance present, the cavities where there is cerebrospinal fluid. You can find a clinic where you can undergo an MRI of the brain with a contrast reagent or in the usual mode at mrt-v-spb.ru. Call the hotline for a free consultation and get a discount on examination up to 1,000 rubles.
Brief information about the central nervous system
The central nervous system is responsible for the stable functioning of the entire body. When any disorder develops in it, a person experiences painful symptoms, leading to harmful consequences. Factors indicating the progression of abnormalities affecting the performance of the brain are considered: painful sensations, neurological signs (visual, motor, auditory disturbances), fainting, etc.
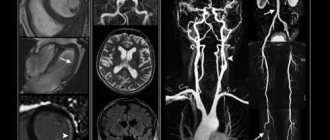
Non-invasive techniques are used to diagnose lesions in this organ. MRI of the brain produces clear, three-dimensional images that can be zoomed in and out to closely examine the structure of the region. The screening programs installed in the device allow you to visualize cerebral vessels. The results of tomography allow the doctor to determine the cause of the disease, its location, as well as establish a diagnosis and create an acceptable treatment regimen.
Which device is better
To perform MRI, open and closed types of devices are used:
- In the first case, the patient simply lies down on the couch, and the coils located on top create a magnetic field. Such devices are ideal for patients suffering from claustrophobia and small children who may be afraid of closed spaces. However, they are not suitable for some types of magnetic resonance imaging;
- The closed tomograph is ideal for most studies. The pictures obtained with its help are clear, and even the smallest details are visible in them.
Both of these devices perform their function perfectly, but the closed design is used more often as it is more versatile. However, without human experience and knowledge, these modern devices are powerless, so when choosing a clinic, the most important thing is that it employs good specialists.
What is an MRI of the brain?
During tomographic screening, doctors can install different diagnostic programs. This helps in targeted testing of different areas of the brain. The main protocols are:
- MRI of the brain - the purpose of the procedure is to evaluate the white and gray matter, as well as the ventricles along with the membranes.
- MR angiography - visualizes the vessels of the organ.
- MRI of the nasal sinuses - the procedure shows the anatomical structure and pathologies in the nose.
- MRI of the eye - the method is aimed at studying the condition of the eyeball along with the optic nerve and orbit.
- MRI of the pituitary gland - diagnosis of the sella turcica area.
The choice of protocol depends on the symptoms, objectives of the study and the goals of the doctor.
What is shown on the results of an MRI of the brain?
The head diagnostic program includes monitoring of the following departments:
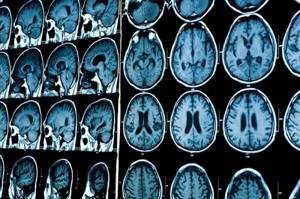
- ventricles of the brain;
- white matter of the subcortical plan, located in the frontal lobe;
- chiasmal area;
- middle sections;
- cerebellar tonsils.
Additionally, during the procedure, the radiologist evaluates the pituitary gland along with the paranasal sinuses.
What does an MRI of the brain show?
A study using electromagnetic equipment makes it possible to visualize the following abnormal conditions in a patient:
- infectious diseases;
- lesions of the nervous system such as multiple sclerosis;
- failures in the structure of the pituitary gland;
- malformations of the brain;
- bleeding from traumatic head injuries;
- malfunctions of the vascular system;
- dementia of a senile nature;
- sources of malfunction of the visual and auditory organs.
Indications for MRI
MRI is used to examine:
- Vessels and structures of the brain
- Cervical, thoracic, lumbosacral spine
- Joints
- Abdominal organs
- Retroperitoneal organs
- Pelvic organs
- Soft tissue
MRI diagnostics can reveal:
- tumors of various etiologies and localizations
- aneurysms
- developmental pathologies
- stroke
- multiple sclerosis
- progressive dementia
- osteochondrosis
- intervertebral hernia
- spondylosis
- spinal stenosis
- arthritis
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system
- injuries
- diseases of the abdominal organs
- bone infection, etc.
When should you get an MRI of the brain?
The main symptoms that become the reason for undergoing research are called:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- double vision;
- epilepsy attacks;
- memory problems;
- high pressure readings.
Other manifestations of unknown origin for which MRI of the brain is prescribed include:

- feeling of weakness in the limbs;
- problems with coordination;
- chaotic thinking;
- neoplasms of various origins;
- pathologies of vascular development;
- vascular lesions such as stroke and their consequences;
- demyelinating disorders; degenerative abnormalities; inflammatory lesions;
- encephalitis, including in patients with HIV status, abscess; congenital developmental anomalies;
- arachnoid type cysts; hydrocephalus; Arnold-Chiari pathology;
- defective development of the corpus callosum; neurocutaneous syndrome; Acute TBI; hematomas.
The doctor recommends undergoing an electromagnetic brain procedure to monitor the radicality of the removal of the tumor body and to exclude its further growth in patients after surgery.
When is research needed?
An MRI of the brain is indicated if the following symptoms are present:
- gradual increase in intracranial pressure;
- disorders in the central nervous system;
- dull, growing pain in the head;
- the presence of constant pain caused by displacement of healthy areas of the organ;
- dizziness and lightheadedness;
- frequent cases of nausea and vomiting after waking up;
- manifestations of seizures;
- decreased or complete loss of hearing;
- disorientation in space;
- decreased vision or a feeling of “clutter” in front of the eyes;
- speech disorders;
- constant drowsiness and weakness;
- bouts of causeless irritability;
- behavioral disorders;
- mental disorders;
- numbness of individual parts of the body;
- weakness felt in the facial muscles or limbs.
Clinical manifestations of pathologies vary depending on the size, location and type of tumor. They are differentiated using data collected through laboratory and instrumental examinations and histological analysis. In particular, brain tumors can be successfully detected on MRI.
Note!
Based on the appearance of the tumor on MRI, one can assume its nature, but verification of formations is carried out only through histological analysis.
When is it prohibited to do an MRI of the brain?
Despite the high level of information content of the procedure, the method is not suitable for everyone. The main contraindications apply to people who suffer from asthma and chronic kidney disease. Pregnant women should be treated with special caution when considering MRI of the brain. Despite the long-term use of tomographic equipment in practice and the absence of adverse effects in pregnant women or newborn children after the examination, patients need to inform the attending physician and radiologist about the current situation.
Relative restriction is called claustrophobia. If the patient is afraid of a closed space (where he will be during the diagnosis), you should choose a clinic with open-type tomographs. Typically, the procedure occurs without consequences for patients with titanium implants.
However, people who have structures made of other types of metal and electronic devices (insulin pump or defibrillator) in their bodies should not undergo MRI of the brain. The presence of such objects in the body can distort the results of the study, disable the device, as well as the devices themselves implanted into the body.
Yak undergoes examination on an MRI machine
Before diagnostics, all metal and electronic objects (jewelry, keys, phones, hearing aids, etc.) will need to be left outside the range of the device's magnetic field.
The MRI procedure takes 10-15 minutes and is absolutely painless.
Features of MRI
During an MRI, it is very important to maintain real estate to obtain clear images. The patient is placed on a special moving table. It moves inside the device until the part of the body needed for research is in the center of the magnet.
Devices for communication with medical personnel are located next to the patient. You can always ask for help in case of anxiety or discomfort. In particularly alarming conditions or with older patients, one of the relatives may be nearby.
During the work process, the tomograph produces noise when changing examination programs - so no need to worry.
How is MRI performed at St. Catherine's Clinic?
MRI diagnostics at St. Catherine's Hospital are carried out by radiologists with many years of experience - the best specialists in their field.
The study is performed on weekdays and weekends from 8:00 to 20:00. The patient receives images with a detailed transcript and description of the study results (if necessary, MRI data is recorded on disk).
Do you need to prepare for an MRI of the brain?
No special preparatory actions are required from the patient. There is no need to stop taking previously prescribed medications or change your lifestyle. To undergo an MRI of the brain, you will need to request an appointment in advance. You can do this quickly and without problems at mrt-v-spb.ru, where dozens of medical centers in the city are presented with a brief description, current prices and technical criteria for equipment.
If the person being examined has built-in metal implants in the body, you will need to notify the doctors of the clinic where you are going to be examined in advance. The patient will need to take with him a document for the design or electronic device, which contains a column about compatibility with research equipment.
When planning to undergo an MRI of the brain with contrast, you should have a light snack 40 minutes before the session. This will help reduce or completely eliminate the patient from vegetative processes when the dye is administered. It is better to come to the procedure in loose and loose clothing without metal fittings, in which you will be comfortable lying.
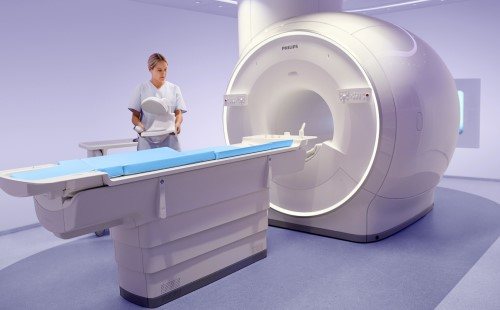
On the day of the MRI, it is best to leave jewelry at home. Women are not recommended to wear makeup as some cosmetics contain traces of metals. Before the diagnosis, the patient will need to leave electronic devices in a safe. It will not be possible to enter the office with a smartphone, watch, player, hearing aid or other devices. If you are concerned about the safety of things, it is better to leave them at home.
Examination of pathologies using MRI involves checking the head. Problems appear in people with metal structures located in the mouth. Braces or dental implants can create artifacts that can distort the image and make it difficult to interpret the data.
Having studied the properties of the material from which the structure was created, the radiologist can change the tomograph settings or recommend an alternative diagnostic method to the patient. If there is an urgent need for an MRI, you will probably need to remove the orthodontic device for a while.
Contraindications to MRI: absolute and relative
The presence of electronic devices in the body may be a limitation for performing an MRI examination.
Such devices include:
- some models of pacemakers
- artificial heart valves
- middle ear implants
The possibility of MRI examination in this case is determined individually. Metal prostheses, stents, surgical clips and other metal objects located in the body react to the influence of a changing magnetic field and can vibrate and heat up. Therefore, an MRI is not performed if there is metal in the body. However, such delays are quite rare because most implantable devices today are made of non-magnetic materials such as titanium. They are also provided with instructions that clearly indicate whether MRI can be performed.
Relative contraindications
MRI does not involve radiation, however, during pregnancy in the early stages (first trimester), MRI studies are carried out strictly according to the indications of a gynecologist.
The St. Catherine's Clinic has a modern MRI machine with advanced capabilities, so excess weight is not a contraindication. The Diagnostic Center of the Clinic conducts tests for patients weighing up to 250 kg.
For patients with fear of confined spaces and small children who find it difficult to remain still inside the machine, an MRI examination can be performed under general anesthesia.
Brain MRI technology
The electromagnetic scanning method is carried out as follows:
- The patient fills out documents at the reception desk at the clinic, where you can make an appointment through. You will need to provide results of past examinations and tests related to your current medical condition, as well as a referral from a doctor (if you have one).
- The subject goes to the diagnostician’s office for consultation, clarification of the absence of restrictions and instructions on the norms of behavior inside the scanner;
- The patient goes into the diagnostic room, lies down on a mobile table, taking a comfortable position.
- The technician may secure the limbs and heads with fasteners to prevent accidental uncontrolled movements during the session.
- During the screening, the entire medical staff leaves the diagnostic room and monitors the process through a glass barrier in the next room.
- When an MRI with contrast is prescribed, an additional enhancer is administered intravenously to the patient before starting the device.
- After completing the examination, the doctor will help the patient get up, take him to the locker room and hand over personal belongings.
Test results can be waited in the break room for 15 to 60 minutes or collected the next day. The patient can also ask the doctor to send the answers by email.
What is MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of internal organs using a magnetic field. This method is used to detect various changes in body tissues and diagnose a wide range of diseases, including cancer.
- What is MRI?
- Benefits of MRI
- MRI diagnostics safely and quickly!
- Indications for MRI
- Contraindications to MRI: absolute and relative
- Preparation before MRI
- How is an MRI examination performed?
- Cost of MRI at St. Catherine's Clinic
- Research is carried out
- Reviews about MRI at St. Catherine's Clinic
At the St. Catherine's Clinic, you can do an MRI examination with or without contrast, using a unique high-field MRI machine Magnetom Aera from Siemens (Germany) - this is the first and only MRI in Odessa of this class, which has:
- increased tunnel size (70 cm) and table load capacity (250 kg), modern noise reduction technology
- Provides full body coverage (Tim 4G technology)
Magnetom Aera from Siemens (Germany) is the first and only expert-class MRI in the south of Ukraine, model year 2021.
The powerful magnetic field of the device (tension 1.5 Tesla) provides:
Fast procedure Patient comfort (it is necessary to remain motionless for a short time, convenient for overweight people and people prone to claustrophobia) High accuracy of examination results
It is possible to perform an MRI with intravenous administration of a contrast agent. For this purpose, a unique Ulrich injector (Germany) is used, with which dynamic contrast is performed. MRI with contrast significantly expands the diagnostic capabilities of magnetic resonance imaging.
Interpretation of brain MRI results
A radiologist is responsible for compiling a description of the diagnostic procedure performed. After an MRI, a series of informative images are obtained, which helps the physician to carefully examine the anatomical structure of the intracranial areas. During the study, the main criteria and detected signs of anomalies are noted. The radiologist deciphers in detail all existing foci of a pathological nature and indicates their volume. At the conclusion of the diagnosis, a conclusion is drawn up about the structure of the organ.
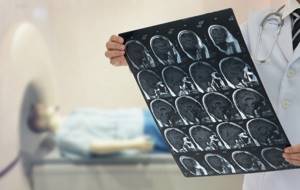
If necessary, the doctor makes recommendations regarding additional procedures or a follow-up examination after some time. The diagnostician may advise the patient to consult with specialized doctors. MRI information is used to make a correct diagnosis, draw up an adequate treatment regimen, and also when planning surgery.
Is it safe to have an MRI of the brain?
An examination based on the electromagnetic method does not harm the patient’s health in any way. It does not involve an ionizing load on the body, which means that the safety of MRI can be compared with ultrasound screening. But the accuracy and information content of tomographic testing is many times higher than that of ultrasound. You are allowed to undergo MRI an unlimited number of times without a long recovery period. The examination can be combined with any other types of hardware or instrumental screening on the same day.
Which is better: CT or MRI of the brain?
The computer monitoring method is based on exposure to radiological radiation. The advantages of the study are the speed of implementation, high levels of information content regarding bones and blood vessels (with contrast). The disadvantages of diagnostics are related only to the radiation exposure to the patient’s body, so there are restrictions on the number of permissible sessions. CT scanning is not performed during pregnancy or children.
It is impossible to determine whether it is better to do an electromagnetic or computer test. CT and MRI of the brain are complementary studies, each of which can be more relevant in a certain clinical situation. Computer scanning is prescribed for:
- damage;
- likelihood of parasitic infection;
- bleeding;
- signs of complications of acute cerebrovascular accidents;
- detection of areas of calcification.
MRI of the head is recommended by doctors to identify ischemic processes, neoplastic lesions and inflammation. The method helps in visualizing vascular diseases that do not cause ruptures in the walls of arteries and veins. For in-depth research, angiographic diagnostic mode or contrast is used.
In some cases, the results of MRI alone are sometimes not enough to make a diagnosis. Therefore, doctors prescribe directions to the patient for two procedures at once in order to collect as much information as possible about the lesion and reduce the chance of an erroneous medical conclusion to a minimum.
Where can I get an MRI of the brain?
Using our search service you can select top-rated and reliable clinics in the city. You will find verified information about each organization: a brief description, current prices, promotions, information about the medical team and technical indicators of tomographs, work schedule, as well as reviews from visitors.

Users are provided with a clear search system for medical institutions for MRI, which can be found near the metro or in a specific area. Additionally, there is an online map with verified addresses and a panel for sorting clinics by price and rating. Registration for diagnostics is carried out remotely.
To make an application to see a doctor at a convenient time and date, call the hotline. Operators provide free consultations and record daily from 8 am to 12 midnight. Call now to get a discount of up to 1,000 rubles on an MRI of the brain.
List of sources used:
- Kornienko V.N., Pronin I.N., Golanov A.V. and others. Diffusion-weighted images in the diagnosis of brain gliomas // Medical visualization. - 2000. - No. 1.
- Konovalov A.N., Kornienko V.N., Pronin I.N. Magnetic resonance imaging in neurosurgery. - M.: Vidar, 1997.
- Antonova O.G. Brain stem strokes as an object of magnetic resonance imaging / Materials of the All-Russian Scientific Forum “Achievements and Prospects of Modern Radiation Diagnostics” M. 2004.
- Warach S, Gaa J, Siewert B. et al, Acute human stroke studied by whole brain echo planar diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging // Ann Neurol, - 1995 - Vol 37.
- Bigler ED, Kerr B, Victoroff J. el al. White matter lesions, quantitative magnetic resonance imaging, and dementia H Alzheimer, Dis, Assoc. Disord, 2002, No. 3 (16).
- Dolgushin, M.B. 3D diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the whole body in patients with metastatic brain lesions / M.B. Dolgushin, L.M. Fadeeva, A.Yu. Zaitseva // Neurovisualization: selected articles / ed. V.N. Kornienko, I.N. Pronina. - M.: TM Andreeva, 2008.
- Belichenko O.I., Dadvani S.A., Abramova N.N., Ternovoy S.K. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases. M.: Vidar, 1998.
- Barber PA Identification of Major Ischemic Change: Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Versus Computed Tomography. // Stroke 1999; 30:2059–2065.
- Kornienko V.N. Magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of intracranial hematomas: Abstract. report All-Union Symposium on Computational Tomography / V.N. Kornienko, A.M. Turkin. Tashkent, 1989.
- Clinical application of new MRI techniques / Yu.N. Belenkov, O.I. Belichenko, V.E. Sinitsyn and others. Medical radiology. - 1990. - No. 3.
Is contrast needed?
In this case, everything will depend on what magnetic resonance imaging is being performed for. Contrast is not needed in all cases, but if there is even the slightest risk of “missing” a tumor, you cannot do without it.
There are several paramagnetic drugs based on gadolinium compounds used for MRI diagnostics, all of them are absolutely harmless, do not accumulate in the body and do not cause side effects. Like any substance, they can cause intolerance. In case of allergic reactions to these substances, only non-contrast MRI can be performed. It is undesirable to use them when examining pregnant women, since the effect of gadolinium chelate complexes on the fetus has not been fully studied.
Abroad, most MRIs performed are done with contrast; this makes it possible to detect the smallest tumor foci and distinguish neoplasms from ischemic areas, inflammatory foci and glial tissue. In Russia, this type of research is less in demand. The reason for this phenomenon is rather economic, because the substances used are quite expensive, and their use almost doubles the cost of the procedure.
You should not try to save on your health if your doctor strongly advises you to do an MRI with contrast. In this case, stinginess can lead to big problems. The decision on the method of conducting magnetic resonance imaging should be made together with a specialist.