Computed tomography (CT) is one of the most informative methods for studying the brain. Its use allows obtaining high-quality images of the brain. CT scanning of a child’s brain simplifies the diagnosis of complex and severe diseases. Sensitivity to radiation in children is several times higher than in adults. However, if indications are present, the use of this diagnostic method makes it possible to identify serious diseases and pathologies at an early stage. Therefore, a study is ordered only if the benefit from the study outweighs the possible harm.
Features of a child's brain CT scan
A CT scan of a child's brain is different from a similar procedure for an adult. Children under three years of age are highly mobile. It is very difficult to force a baby to remain motionless for a long time: it is impossible to hold him for scanning. Newborn babies may also require the procedure. Therefore, in both cases, the study is carried out under general anesthesia.
But general anesthesia and radiation are dangerous for the child. Therefore, testing is recommended only when there are no other ways to obtain a diagnosis. MRI is performed using electromagnetic radiation, so no harmful x-rays are used. However, such a study is not always able to show the pathologies and diseases of the brain that are visible on CT. When a test is ordered, the benefit of diagnosing a disease must be many times greater than the harm from it. But do not forget that late diagnosis of serious diseases is often even more dangerous than X-ray radiation or harm from the necessary general anesthesia.
Contraindications and restrictions in children
If tomography is necessary even before the age of 14, it is worth considering that the procedure has certain limitations. If you do not follow them, you may encounter negative consequences of a brain CT scan for your child.
Kidney failure
In this case, it becomes impossible to use a contrast agent, since it puts a lot of stress on the kidneys. The release of the drug after the examination will be impaired, which will negatively affect the health of the small patient. Therefore, the answer to the question of whether a CT scan of the brain is harmful to a child in this situation is unequivocal - yes - and it will be necessary to find a different research method.
Mental abnormalities in pronounced form
In case of inadequate condition and fear of confined spaces, the harm of a brain CT scan for children will be much more pronounced than the benefit. In such cases, it is better to focus on another type of diagnosis.
At what age is a CT scan allowed?
Computed tomography is prescribed for children of any age. The study can be prescribed even to a newborn with absolute indications for this particular research method. For example, if MRI and other research methods turned out to be uninformative. Up to a year, neurosonography is most often used to diagnose diseases and pathologies of the brain. This is an ultrasound of the brain, performed due to the presence of an open fontanel.
After the fontanel is closed, neurosonography is no longer informative, so CT is necessary.
CT scans are prescribed for children to identify tumors and the consequences of injuries, so the importance of early diagnosis cannot be overestimated. There is no particular difference in conducting research on newborns, as well as children under and after three years of age. However, for young children the procedure is performed under general anesthesia due to the need to remain motionless for a long time.
Indications
A head CT scan is prescribed for young children to identify the following pathologies:
- Birth injuries in newborns. Using this research method, it is possible to diagnose a depressed skull fracture, a skull fracture at the sutures of the bones, or intracranial hemorrhage.
- Injuries received by children over the age of one and a half years from a fall or impact. Using CT, it is possible to diagnose the degree of injury, the presence of a hematoma, as well as skull fractures. Computed tomography is the most informative method for diagnosing the degree of bone damage.
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Causes of mental disorders. Even at an early stage, CT can make an accurate diagnosis.
- Tumors and cysts.
- Vascular anomalies and aneurysms.
- Lesions of the musculoskeletal system.
- Malignant neoplasms in the brain.
- Various anomalies in the development of the respiratory organs.
CT is a more dangerous research method, therefore it is prescribed only if there are contraindications to MRI, or this method is not informative.
What does a head CT scan show?
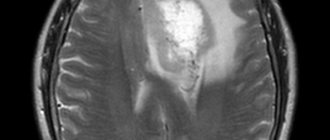
Images obtained during a computed tomography scan allow us to identify the following types of pathological changes:
- acute trauma: damage to bones and soft tissues, wound channel, presence of foreign bodies;
- hematomas of any location;
- displacement of the midline structures of the brain (a sign of the development of space-occupying formations, hematomas and other processes that lead to compression of the brain on one side);
- hemorrhages in brain tissue;
- foci of cerebral ischemia;
- cysts;
- abscesses, pus from meningitis, etc. inflammatory processes;
- vascular changes, congenital and acquired (malformations, aneurysms, atherosclerotic lesions of the arteries);
- space-occupying formations of the brain, skull bones, meninges, soft tissues of the head.
Preparing for the examination
For newborns and young children, the examination is performed under general anesthesia. Therefore, preparation includes a consultation with an anesthesiologist who recommends the previous steps to anesthesia. Older children do not need anesthesia. The main requirement for obtaining high-quality images is the patient's immobility for a long time. Preparation for the study includes:
- Refusal to eat at least 4 hours before the test. If the stomach is full, the risk of choking on vomit increases. Newborns should be given food 3 hours before the procedure. Drinking liquids before a CT scan is also prohibited.
- Moral preparation of the child. If the procedure is performed on an older child who is going to be conscious during the research process, then it is necessary to mentally prepare him. The child needs to be explained that the examination is completely painless. He needs to remain motionless for a long time, and if this rule is broken, he will have to start all over again.
- Using nasal drops. During the examination, the child should have good nasal breathing. If you have a runny nose or swelling of the nasal passages, it is recommended to instill vasoconstrictor drops.
- Analyzes. Before performing a CT scan, you need to undergo tests. Some clinics only require a certificate from a pediatrician, while others require ECG results, general blood tests, urine tests and other studies.
- Allergy analysis. Sometimes a CT scan with contrast is recommended. In this case, allergy tests for a contrast agent are prescribed before the procedure. This analysis is mandatory for children susceptible to allergies.
How is CT scan performed in childhood?
There is no significant difference between how CT scans are performed on children and adults. The general scheme of the study is as follows:
- Preparation. Before entering the diagnostic room, jewelry and accessories with metal elements are removed. Personal items are left in the locker room. The child is placed on the tomograph platform. The conveyor will move, so for safety the baby’s body is secured with soft straps. Protective screens are installed in areas not subject to study. The platform is moved so that the area under study is within the frame of the apparatus.
- Scanning. The radiologist monitors the procedure and controls the equipment from the next room. Gives instructions via two-way speakerphone to remain still or hold your breath. If a contrast CT scan is performed, the scan is repeated after intravenous administration of a special substance.
- The final stage. At the end of the procedure, you can pick up your personal belongings and wait for the results at the clinic, or go away on business and return later.
The main condition for the success of the procedure is the ability of the small patient to follow the doctor’s instructions and remain motionless for 8-10 seconds while the device is operating. The clarity and information content of the images depends on this.
CT machine
In any diagnostic center, children are given a computed tomography scan only as prescribed by a doctor. Patients over 5 years of age who are able to remain calm during the scan can undergo the test. Contrast-enhanced CT is performed for children over 12 years of age.
Before reaching adulthood, patients come for the study with an accompanying person. One of the parents, a guardian or another person (if there is an appropriate power of attorney) can bring the child for diagnosis.
CT scan of an infant
Parents often have a question: “At what age can children have CT scans?” Radiation examination methods are used for medical reasons from birth. Diagnosis of some developmental anomalies, injuries, and serious diseases requires visualization of internal tissues. Computed tomography provides high-quality digital images indicating pathological changes of minimal size. Compared to the diagnostic value of the results, the potential risks are negligible. Untimely detection of pathologies, improper treatment or lack of therapy are more likely to lead to unpleasant consequences.
Due to physiological characteristics, the baby is not able to control his own movements, so CT scans are performed on infants in a state of natural sleep. Doctors recommend purposefully not putting the child to bed for 6 hours and not feeding for 3-4. Upon arrival at the diagnostic center, the little patient is given food (milk or formula) and rocked to sleep. The sleeping child is carefully transferred to the tomograph platform and the examination is carried out.
In preschoolers
For physiological reasons, children 2-4 years old are more difficult to tolerate diagnosis. Difficulties arise due to fear of equipment, unusual surroundings, and the child’s inability to control his activity. Putting a child to sleep during the procedure is extremely difficult, as is explaining the need to remain calm and lie motionless in the tomograph tunnel.
In this case, the research is carried out in a playful way. Parents can be involved in the diagnostic process. The accompanying person is given protective devices, which allows a loved one to be in the office next to the baby, calm the baby or distract him.
Instructing your child in preparation for scanning
If it is difficult to perform a CT scan (contrast is required, the child has a mental or neurological illness), the study is carried out in a hospital setting, under anesthesia.
How the research works
To obtain accurate research results, you must remain stationary throughout the scan. Therefore, newborns and small children are given general anesthesia. To determine the exact dosage of anesthesia, the child is weighed.
If it is necessary to take pictures of the blood vessels of the brain, a contrast agent is first administered. This drug, most often made from iodine, is injected into a vein.
The patient is placed on the table in the correct position, and a stand is placed under the head. The head is secured with straps. After which the patient is pushed onto the table into the device. After this, those present must leave the room, and the scan starts. The patient must remain stationary throughout the procedure. The results of the study will be ready 30–40 minutes after the scan.
What does the equipment look like?
A CT scanner is usually a large, donut-shaped machine with a hole or short tunnel in the center. Rotating around you, the X-ray tube and electronic X-ray detectors are located opposite each other in a ring, performing a CT scan. The computer workstation that processes the information in the images is located in a separate control room where the technologist operates the scanner and monitors your examination with direct visual contact and usually with the ability to hear and talk to you through a speaker and microphone.