Contrast computed tomography angiography is a very informative method for diagnosing vascular pathology. CT scans use a combination of a high-tech X-ray scanner and powerful computer processing to provide detailed, 3D images of the blood vessels in the brain and neck. CT angiography provides the doctor with comprehensive information about the structure of blood vessels, the presence of narrowings or aneurysms, and the characteristics of blood circulation in the brain.
Since the Innovative Vascular Center deals with high-tech treatment of diseases of the carotid and vertebral arteries, we need an accurate diagnosis of vascular pathology of the cerebral arteries.
We conduct studies of the main arteries of the neck and head at the stationary base of our clinic in Klin, or at a partner organization in Moscow. Vascular surgeons at our clinic perfectly interpret MSCT angiography data and, based on these data, plan surgical intervention. In the hospital, we use a modern 64-slice computed tomography scanner with excellent image characteristics.
Why CT angiography of the brain is the best diagnostic method
The main advantage of this method is its safety. Radiation exposure during the examination is minimal. Unlike classical angiography, CT is a more gentle diagnostic method. Long-term preparation with a hospital stay is not required. In addition, during the procedure, patients do not experience discomfort or negative emotions.
At the same time, the significance of CT angiography of the brain and neck is very high. Using this examination, the specialist examines the walls of the blood vessels of the neck, brain and adjacent tissues layer by layer. For more convenient decryption, all data is recorded on removable media. The patient can additionally show the images to any doctor to get a second opinion.
Decoding the received data
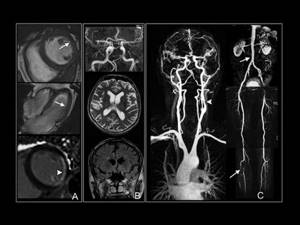
As soon as the examination is completed, the patient will be able to leave the office to await the conclusion. Based on the images obtained, the radiologist will make a diagnosis and write a report. It can be issued both in paper and electronic form on any digital medium. The patient must show the obtained images and the report to the doctor who has been prescribed a referral for magnetic resonance imaging.
In the event that the tomography was carried out on your own initiative, you need to contact the specialist who is involved in the treatment of the identified pathology. It is important to remember that the earlier the correct treatment is started, the higher the likelihood that it will be successful and will not take long.
When is it necessary to do angiography of the vessels of the brain and neck?
Before scheduling a procedure, you must consult with your doctor. Based on the data received, the specialist will decide on the need to prescribe a CT scan of the vessels of the brain and neck.
The main symptoms of developing diseases are:
- pain and pressing feeling in the head;
- dizziness;
- loss and clouding of consciousness;
- tremor (shaking) of hands.
- change in the vessel wall as an accidental finding
Thanks to angiography of the vessels of the brain and neck, it is possible to diagnose many dangerous diseases and select adequate treatment that allows the patient to return to normal life.
The diagnostic procedure has the following goals:
- identify vascular ruptures;
- determine the presence of an aneurysm or neoplasm;
- diagnose thrombosis and embolism;
- find inflammatory processes;
- confirm or refute atherosclerosis and Takayasu’s disease;
- detect abnormalities in the development of the vascular system.
What does it show
A computed tomography scan of the head can be prescribed in any condition of the patient, even if he is unconscious. This technology is used if there is a current suspicion of:
- stroke;
- internal hemorrhage;
- oncology of the head area, of any nature, both malignant and benign;
- hidden fracture at the base of the skull;
- hematoma;
- internal vascular injuries;
- internal inflammatory processes, for example, meningitis;
- foreign bodies
How to prepare for a CT scan of the head and neck vessels
When examining the arteries, CT of the neck with contrast is used to obtain the most complete data. Without a contrast agent, the information content of the examination is extremely low.
Before undergoing diagnostics, there are several preparatory stages:
- do a blood biochemistry test to determine the level of urea and creatinine;
- inform your doctor in advance about the presence of allergic reactions to medications;
- do not eat 3 hours before undergoing a CT scan with contrast;
- provide the doctor with previous results of ultrasound, CT and MRI for review;
- remove all metal jewelry.
pros
CT scan of the brain in Krasnogorsk or in any other city is in considerable demand because tomography has many advantages relative to other methods of studying this human organ.
- No pain. Some discomfort is possible only after the use of a contrast agent. It is worth informing your doctor about this, since this may be how an allergic reaction manifests itself.
- High accuracy rate. Tomography of the brain is a layer-by-layer study of its structure and condition. Contrasting increases information content.
- Efficiency of implementation. On average, 40-50 minutes are enough to complete a session. Results are provided within half an hour.
- Even people with problems such as claustrophobia can undergo the examination.
Price for CT scan of brain and neck vessels in Moscow
The procedure is not cheap. Often the price range between different clinics is quite significant. At the hospital on Yauza you can undergo CT angiography of the neck and brain at an affordable price and in high quality. In this case, the procedure is carried out using high-precision equipment, which allows you to obtain the most valuable results with subsequent 3D reconstruction.
The cost of CT angiography of the vessels of the brain and neck can be found in the clinic’s price list. It is recommended to first consult a specialized doctor. You can make an appointment online directly on the website. You can choose your own appointment time and specialist.
When is an MRI of the head and neck prescribed?
Magnetic resonance scanning is used as an additional examination when the information content of other diagnostic procedures is low and as the main method when initially visiting a doctor.
Indications for prescribing an MRI of the head and neck are the following symptoms:
- repeated fainting;
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- pain in the head and neck area;
- epileptic seizures;
- paralysis of facial muscles;
- restriction of neck movements;
- lack of coordination;
- memory problems;
- inappropriate behavioral reactions;
- speech disorders;
- noise in ears;
- decreased visual acuity.
The listed clinical signs indicate possible damage to the central nervous system, upper spine and soft tissues of the neck. MRI allows you to identify pathological changes, clarify the location and size of the lesion, and determine the cause and nature of the disease.
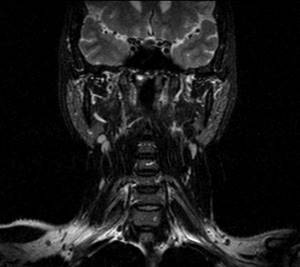
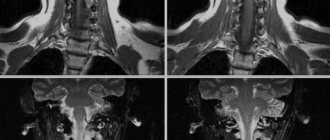
Lymph nodes and soft tissues of the neck, frontal projection
The method is used in neurology, neurosurgery, oncology, orthopedics, and traumatology.
MRI of the head and neck is performed to diagnose:
- benign neoplasms (adenomas, cysts, etc.);
- traumatic injuries;
- inflammatory processes (osteomyelitis, arthritis, meningitis, encephalitis, etc.);
- malignant tumors of the head and neck;
- vascular pathologies (aneurysms, thrombosis, embolism, etc.);
- ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes;
- osteochondrosis;
- hydrocephalus;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- multiple sclerosis;
- intervertebral hernias, protrusions of the cervical spine;
- thyroid diseases;
- pathologies of the pituitary gland, etc.
In the case of traumatic injuries to cerebral structures, MRI will help assess long-term effects on the central nervous system. In preparation for surgery, scanning is prescribed to clarify the scope and nature of the operation. During rehabilitation, a diagnostic procedure allows you to monitor the process of restoration of damaged tissues.
When the functionality of cerebral structures is impaired, magnetic resonance imaging of the head and neck makes it possible to determine the etiology and pathogenesis of the disease. The photographs show:
- spinal canal stenosis;
- compression of nerve roots;
- destruction of the myelin sheath of neurons, etc.
By visualizing the morphological structures of the area in question, the study helps to differentiate degenerative, inflammatory and neoplastic processes in the head and neck area. Thanks to tomography, it is possible to diagnose the disease in the early stages, which facilitates the choice of an effective treatment method.
Description of the procedure
- The procedure takes 10–20 minutes
- it is possible to perform a CT scan using a contrast agent, which increases the information content of the study;
- at the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, CT is performed on a Philips Ingenuity Elite spiral computed tomograph, which reduces radiation exposure to the body, and in the case of CT using contrast, reduces the volume of injected contrast agent
- After the procedure is completed, the doctor decrypts the data, the images are recorded on a disk or flash card
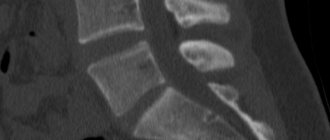
A CT scan of the head clearly shows the condition of the skull bones, including the orbits and sinuses.
In case of injury, you can accurately determine the degree of injury, the presence or absence of displacement. Fluid accumulations are also clearly visible on the tomogram. When performing a CT scan of the head with a contrast agent, the condition of the blood vessels can be assessed, as well as neoplasms can be identified. Indications for a head CT scan are the following patient complaints and doctors’ assumptions:
- head injury
- headache
- dizziness, fainting
- visual or hearing impairment
- seizures
- impaired motor coordination
- sudden mental changes
- suspected stroke
- cerebrovascular accidents
- neoplasms (tumors, cysts)
- preparation for surgery (including maxillofacial), as well as postoperative observation
- assessment of the condition of the eye sockets and sinuses
Since during computed tomography the body is exposed to x-rays, this method has a number of contraindications:
- pregnancy
- younger children (done only in cases where examination is vital)
- the presence of an allergy to the contrast agent is a contraindication to performing CT with contrast
- large body weight. Typically, the tables on which patients lie are designed to hold up to 200 kg.
- renal failure
- diabetes
- multiple myeloma
- thyroid diseases
- during lactation, it is necessary to take a 24-hour break in feeding if contrast was administered during CT scanning
If the patient is in an excited state, then a tomogram is not recommended, since it is necessary to remain still during the examination.
Indications
Head CT scans provide more detailed information than regular X-rays. A head CT scan helps diagnose a number of conditions, including:
- bleeding (eg, subdural hematoma or bleeding into brain tissue)
- bone infection
- brain abscess or infection
- brain damage due to trauma
- swelling of brain tissue
- brain tumor or other mass formations
- cerebral atrophy
- abnormalities of the skull bones
- arteriovenous malformations or pathological changes in blood vessels
- congenital brain abnormalities
- brain aneurysm
- hydrocephalus or intracranial hypertension
- infections or swelling
- injuries to the head, face or skull
- stroke
- tumors
The attending physician may order a CT scan of the head if the patient has had a head injury or has acute symptoms such as:
- loss of consciousness
- Strong headache
- seizures, especially if they have occurred recently
- changes in behavior or thinking over a short period of time
- severe hearing loss
- sharp decrease in vision
- muscle weakness or numbness and tingling
- speech disorder
- difficulty swallowing
A CT scan of the head can also be used to guide biopsy or surgery.
Using the CT procedure
In order to determine the condition of a person’s lungs as accurately as possible, doctors use exclusively computed tomography data. The results of a CT examination allow timely detection and prevention of complications in diseases such as pneumonia. Through chest screening, specialists can determine the presence of calcifications in the coronary arteries and warn the patient against the development of heart disease.
The use of computed tomography provides a unique opportunity to diagnose the progression of cancer.
In addition, the widespread use of this type of diagnostics turns out to be indispensable when examining many organs:
- computed tomography of the abdomen
- CT chest
- CT bowel
- CT lungs
- CT scan of the sinuses
- Kidney CT
- CT joints
With the help of a CT examination, extremely useful information will be obtained in case of kidney diseases, pancreatitis and pancreatic necrosis.
How much does a head magnetic tomography cost?
One of the most important questions of interest to patients considering undergoing a head MRI is the price. In Moscow, you can do the procedure from 3,000 rubles, the upper limit can reach 13,000 rubles.
The amount depends on the area of study (skull, blood vessels, individual brain structures) in combination with manipulations and requests that accompany an MRI of the head. The price is increased by additional consultation with a doctor, the introduction of a contrast agent, recording the result on a disk, special preparation and implementation measures, and the characteristics of the equipment on which MRI of the head and blood vessels is performed.
The price in Moscow also fluctuates depending on the promotions of a particular clinic. When wondering where to get an MRI of the head, you should pay attention to what time of day the procedure is performed, bonuses and discounts. At night, as a rule, the cost of MRI of the head decreases. The clinic address can be chosen in any area
Risks
Risks of CT scans include:
- patient exposed to radiation
- allergic reaction to contrast
- kidney damage from contrast agent
A CT scan uses more radiation to examine than a regular x-ray. Having a large number of repeat CT scans over time significantly increases the risk of developing cancer. However, the risk of any CT scan is small.
- The most common type of contrast used for CT scans contains iodine. If a person is allergic to iodine, CT contrast may cause nausea, vomiting, sneezing, itching, or hives.
- If the patient absolutely requires contrast, antihistamines or steroids may be prescribed before the scan.
- The kidneys actively remove iodine from the body. Therefore, patients with kidney disease or diabetes are advised to take additional fluids after the scan to quickly remove iodine from the body.
- in rare cases, contrast can lead to the development of a severe allergic reaction - anaphylactic shock.
Magnetic resonance diagnostics with contrast
Despite the high information content of the method, there is a way to further detail the resulting images. To do this, a contrast agent is injected into the patient's vein and a scan is performed immediately.
The images acquire greater contrast and resolution, allowing one to determine small tumors, their appearance, quality, assess the degree of aggressiveness of the tumor, its blood supply, and the exact localization of metastases.
Tomography with contrast is successfully used in assessing the dynamics and making an accurate diagnosis of inflammatory, vascular and organic brain damage.
How much a head MRI will cost directly depends on the use of contrast. Contrast agents are gadolinium compounds. Despite the low toxicity, sometimes adverse reactions occur, so contrast agents are used with caution in people with insufficient renal function and allergic reactions, and are prohibited during pregnancy.
Advantages of magnetic tomography
The key advantages of examination using a magnetic tomograph are:
- The magnetic field under which a person is exposed during the procedure is safe and does not have any long-term consequences or side effects.
- Due to the natural high information content and clear visualization in any plane, it is possible to obtain the thinnest sections up to 1 mm, which allows you to make the correct diagnosis in 97% of cases.
- The method is simple, does not require preparation, and the absence of radiation exposure allows it to be used in children, as well as repeated.
The magnetic resonance examination method has helped bring the diagnosis of diseases to a new level, making it possible to detect diseases at the initial stage, clarify the details of the course, prescribe precise treatment and monitor it.
How is the procedure performed?
- A head CT scan is performed in a hospital or clinic x-ray room.
- The patient lies on a narrow table that slides into the center of the CT scanner.
- While inside the scanner, the X-ray tube rotates around the patient and X-rays pass through the tissue.
- A computer converts slice scans of the head and creates images that can be stored on film, viewed on a computer monitor, or burned to disk. In addition, if necessary, images of this area can be converted into 3D models.
- The patient must remain still during the scan, as any movement will blur the images. For this purpose, the patient may be asked to hold his breath for a few seconds.
- The direct scanning process takes from 30 seconds to several minutes.
Computed tomography - what is it?
The most advanced and accurate way to study and research human organs today is the use of computed tomography (CT). Carrying out this procedure makes it possible to reproduce a fairly clear image thanks to the use of x-rays. Since the advent of CT, doctors have been able to study changes in the human pulmonary system, skeletal system and sinuses.
For successful diagnosis of human diseases, the use of computed tomography is justified in the following cases:
- identifying various viral infections;
- diseases of the body's mucous membrane;
- determining the presence of polyps;
- oncological diseases;