One of the most used methods of prosthetics in dentistry today is metal-ceramics; it is installed for many patients. However, in the case when a person, for one reason or another, needs to undergo a magnetic resonance imaging procedure, he will have a logical question: is it possible to do an MRI with metal-ceramic crowns or are they a contraindication for such a diagnosis?
How an MRI scanner works - the essence of the method
Before understanding how MRI machines and dental crowns interact with each other, you need to understand the essence of the analysis itself. So, magnetic resonance imaging is a method of obtaining layer-by-layer images of internal organs, based on nuclear magnetic resonance.
The magnetic field of the tomograph and electromagnetic waves interact with the nuclei of hydrogen atoms - and this element is found in large quantities in tissues (water, that is, hydrogen plus oxygen, makes up about 70% of the human body). The computer records information received from hydrogen nuclei and converts it into layer-by-layer images - these are virtual sections of organs, blood vessels, and nerves. The thickness of one such slice is only 0.2 mm on modern tomographs with a power of 1.5-3 Tesla. And there are a lot of cuts themselves. That is, as a result, you can see very tiny pathologies inside the body without surgery or a microscope.
Only until 30.09 South Korean implant Osstem - 19,900 rubles.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and lock in promotional prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
The MRI technique is used primarily to study soft tissues and organs of the body. Whereas CT (computed tomography using X-rays) better reflects the condition of hard tissues - bones.
How metal products influence research
As a rule, employees of diagnostic centers answer positively the question of whether it is possible to do an MRI with dental crowns. But you need to understand that prostheses with the presence of magnetizable metal can cause distortions in the image. These are the so-called field artifacts. However, for modern tomographs this is not a problem. The patient only needs to notify the center administrator about the metal crown in advance or indicate this information in the questionnaire (it is filled out before the study). And the device will be adjusted in such a way as to minimize distortion or eliminate it altogether.
If the patient forgot to report metal crowns on his teeth, then it is possible that an MRI of the head or brain will have to be taken again - wasting time and money. However, if, for example, a metal prosthesis is in the mouth, and the area below the neck (chest, pelvis, arms or legs) was examined, then the image will not be spoiled in any case.
When and who should not undergo the study
In response to the question: “Is it possible to perform MRI with dental implants?”, doctors answer in the affirmative. But a number of conditions must be observed - they do not relate to the implants themselves, but are of a general nature. First, let's systematize the contraindications to this study. They are divided into 2 groups – relative and absolute. The following are considered absolute contraindications:
- any large ferromagnets in the human body: large metal implants on bones, middle ear prostheses, metal fragments in soft tissues. But dental implants are not included here,
- electronic stimulators: on the heart, middle ear prosthesis.
Ferromagnets are substances and alloys containing nickel, chromium, steel, cobalt, and any compounds with a large percentage of iron. Highly susceptible to magnetism. In a powerful magnetic field, ferromagnets can move if they are located in soft tissues. The consequences of such a movement are almost always unpredictable and can cause harm.
Relative contraindications - this term hides restrictions on MRI that can be circumvented. For example, undergo diagnostics later or on a different device. Let's consider the relative contraindications to MRI:
- inability to lie still during the examination: this may include small children and patients with nervous disorders. They are put into a short medicated sleep,
- early pregnancy: due to the lack of confirmed data on the harmful effects of the magnetic field on the fetus,
- hemostatic clamps in blood vessels,
- tattoos: if metal is present among the components of the pigment, then it will heat up in the device, even causing burns,
- braces, crowns or other prosthetic devices that contain ferromagnetic metals - primarily steel. But there are some peculiarities - if the prosthesis is in the mouth, and you do an MRI of the leg, then there are no risks.
Contraindications mainly relate specifically to MRI, and the closed type - when the patient is completely placed in the machine. There are also open-type tomographs - they have fewer restrictions for diagnosis, but their accuracy is lower.
Interaction of metals with a tomograph
Taking an MRI if you have crowns can, in principle, lead to displacement and/or heating of metal prostheses. But only under a combination of several conditions - a relatively large mass of the metal and the presence of magnetization properties. Here you should refer to the following classification of metals and their alloys:
- ferromagnetic materials (iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, chromium): these substances are highly susceptible to the action of a magnetic field. It is they that can shift or heat up during MRI, but if their concentration is large enough,
- Diamagnets (hydrogen, silver, copper, gold): the ability to magnetize is very weak, i.e. There is no harm to the body during the examination,
- paramagnetic materials (titanium, tantalum, platinum, aluminum): do not interact with the magnetic field, i.e. absolutely safe for research - they will not heat up and will not move. For example, gurneys that can be brought into the room with a tomograph are made of aluminum.
Magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of a dental implant
So why wouldn't a dental implant be an absolute limitation to MRI? Here you need to understand that implants are made from metals endowed with diamagnetic and paramagnetic properties. What it is? The operation of an MRI scanner is based on the magnetizing properties of certain substances. So, para- and diamagnets react weakly to powerful magnets, such as those installed in the tomograph.
Paramagnetic materials are almost not subject to the action of a magnetic field and do not shift in it. These are the following materials:
- titanium: the main metal from which modern implants are made,
- aluminum: medical gurneys made of this metal can be brought into the room where MRI is performed,
- platinum: softer and more expensive than titanium.
Diamagnets - magnetization is not significant, it occurs in the direction of the applied field:
- hydrogen: it was the presence of this element in the human body that made magnetic resonance imaging possible,
- copper: oxidizes quickly, not suitable for implantation into the body,
- gold and silver: very soft metals.
Magnetic resonance imaging can be performed on any part of the body. If the organ being studied is located in the lower half of the body, then the implant will not affect the result in any way. And if the upper part is examined, then there may be some distortions - however, the implant itself will not move, that is, it will not be magnetized and will not break out of the body.
How does the type of prosthesis relate to the quality and possibility of performing MRI?
MRI in the presence of dental crowns is most often performed as a routine procedure; less often, the laboratory assistant has to adjust the equipment, and in exceptional cases the patient is denied examination. Next, we will talk about which crowns and other orthopedic elements can be used for magnetic resonance imaging without fear, and which ones can cause harm.
Plastic and metal-plastic
Synthetic materials, in particular dental plastics and acrylic, are not prone to magnetization. And in metal-plastic ones, the thickness of the metal is very small. Therefore, as a rule, there are no contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging.
Ceramics, composite and metal ceramics
Ceramics and composite materials, as well as ceramic composites, are not attracted to or repelled by a magnet. Therefore, if you have ceramic (porcelain), ceramic-composite, glass-ceramic, zirconium dioxide and aluminum dioxide crowns, bridges or veneers, there is absolutely nothing to fear. Are MRIs done with metal-ceramic crowns or bridges? Yes, there are practically no contraindications here either. But it is optimal if the patient knows what metal the metal base of the prosthesis is made of and will not hide information before diagnosis.
Metal crowns
Is it possible to do an MRI with metal crowns? Here the answer will depend on what metal the prosthesis is made of[1]. Gold or titanium are not magnetized, therefore they are safe during the examination process and do not cause distortion. Cobalt-chromium or nickel alloys contain ferromagnets, but despite this fact, magnetic resonance imaging is also often performed on such patients. For example, with single crowns. But if there is a long bridge made of an inexpensive alloy in your mouth, then you need to consult in advance with a specialist at the clinic where the tomography is planned.
“My mother underwent an MRI of the brain in 1995, and she had 2 gold “Soviet” bridges in her mouth. Nobody asked anything about crowns then. The examination went well, without any problems at all. So there is no need to be afraid. Just don’t forget to take off all rings and earrings, hairpins, and a belt with a buckle before the MRI. They can cause problems."
Autumn_19, review from gidpozubam.ru
Pins, stump inlays
The presence of metal pins and stump inlays also does not become an obstacle to MRI. But again, you need to know what they are made of, whether these metal alloys are magnetized or not. On the other hand, the size of these orthopedic elements is very small, and the pins and inlays themselves are firmly “seated” on dental cement, which should protect them from displacement.
How does a patient with metal ceramics feel during the procedure?
During a diagnostic examination in the presence of metal-ceramic structures, the patient will not experience any discomfort, much less acute pain or other painful sensations. The patient's life is also in perfect order and nothing threatens her.
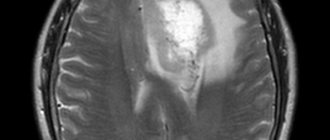
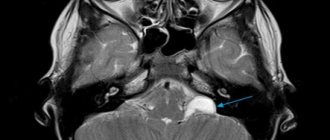
If for one reason or another you are denied an examination, this will be due to the fact that your metal-ceramic crowns will greatly distort the final result. This will happen due to the resonance of the metal elements of the dental structure and the magnetic field of the tomograph. As a result, the doctor will either not be able to see the tissues he needs, or marks will appear on them that will give a false diagnosis.
Attention! Patients with metal-ceramic crowns are often denied examination due to the high cost of MRI. Since it is difficult to predict the final result, some laboratories prefer to refuse treatment to the patient, especially when it is carried out on a budgetary basis, when it is not the patient who pays, but the clinic.
Contraindications to MRI with crowns, bridges, removable dentures
MRI in the presence of metal crowns may be refused if the prostheses are massive and made of ferromagnetic materials - steel, iron, nickel or cobalt-chromium alloy. For example, if it is a fixed extended bridge or a removable clasp prosthesis (but the latter can be removed if necessary). In the case of single orthopedic structures, it is better to clarify in advance whether it is possible to undergo an MRI with metal crowns from a radiologist at the diagnostic center. If a specialist says that there is a danger of the prosthesis shifting or heating, then it is recommended to turn to alternative research methods (more on them below).
How can MRI affect iron crowns?
Prostheses made of iron, steel, cobalt alloys and other ferromagnetic materials are still most often installed. Yes, there is titanium, porcelain and zirconium dioxide - but they are expensive, so not everyone can afford them.
Iron orthopedic structures are durable and cheap. But they become a problem if you need to do an MRI for 4 reasons:
- They distort the picture. The results will not be accurate. This is especially critical when diagnosing oncological pathologies: MRI is the best method for identifying tumors at the initial stage, when recovery success is high.
- They get very hot. This leads to a burn of the mucous membrane.
- They move from their place. After displacement, the crowns will have to be adjusted, re-attached, or new ones made.
- Possible loss. The magnetic field attracts metal crowns - it literally rips them out of your mouth.
Iron crowns get very hot and distort MRI results
Patients with metal prostheses are recommended to remove the structures before MRI or undergo another study - CT, PET. The above applies to closed-type tomographs or when examining the head, cervical or thoracic region. There is no risk when diagnosing other parts of the body.
Do I need to tell my doctor about the presence of metal prostheses and implants?
Definitely necessary! After all, the tomograph needs fine tuning for an informative image. And as for dental implants, you should know that the bulk of them are created from the bioinert paramagnetic titanium. There is a small percentage of dental implants made from tantalum, which is also used to make surgical tantalum staples and “sutures” - tantalum is also paramagnetic, i.e. does not pose a danger. Another option is a combination of zirconium dioxide and titanium (Roxolid alloy), which is also not magnetized. In any case, a patient with dental implants should have a service book on hand, which indicates the model and brand of implants - it is easy to check from them what the structures are made of.
But if the implant was placed a long time ago - more than 20 years ago, or was made individually in a laboratory at the clinic, then most likely it is not made of titanium or tantalum, but from a cheaper alloy that can be magnetized. Here it is better to abandon MRI in favor of alternative diagnostics.
Is it possible to have access to tomography if I have crowns?
Are there any special features in MRI diagnostics for patients with dental crowns? This question also worries many. Some people worry that under the influence of magnets, metal, metal-ceramic crowns and pins can fly out of their places and damage something in the mouth. Experts note that metal crowns and pins have absolutely no effect on MRI results, but only if they are made of pure ceramics, zirconium dioxide or high-quality alloys. If the crown is made of metal-ceramics, then it is worth clarifying the metal content in the base - it is likely that you will not be allowed to conduct research.
Myths about MRI with implants
The worst thing that patients who have dental implants think about before an MRI is that the implant will heat up, move into the bone, or even be torn out of the jaw and stuck in the tongue or cheek. This opinion is wrong. After all, as already noted, almost all implants are made of titanium or other paramagnetic materials that are not magnetized in both weak and strong magnetic fields. The same can be said about other titanium implants - spine, joints, etc. But, for example, some breast implants, metal wires for bone fractures (not titanium), vascular filters can be dangerous during MRI - they can move and overheat. Therefore, before the examination, you need to give the doctor complete information about the presence of any implants in the body, as well as about the pacemaker, if any.
Read on the topic: what is better to choose – implantation or classic prosthetics. We consider in detail the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
User Questions
Question from Victoria: Tell me, if I have a gold crown in my mouth, is it possible to undergo an MRI of the head with it or is it better to remove the crown?
Answer: Hello, Victoria. Gold is very weakly magnetized, so a gold crown cannot become an obstacle to magnetic resonance imaging of the head. But it will be better if you tell the diagnostic center in advance that you have a metal gold crown. Because it may be necessary to adjust the device for a more accurate study and eliminate distortions.
[1] Sergeeva L. Fixed prosthetics, 2021.
MRI of the brain in the presence of braces
At the beginning of the article, we talked about relative contraindications to undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. These include various bracket systems. Such structures rarely contain titanium (the structure is still bulky, and titanium is not a cheap metal), so they are made from inexpensive ferromagnetic materials (mostly medical steel). These materials, in turn, are magnetized in an MRI scanner. Therefore, braces, retainers and clasp dentures are prohibited from MRI scanning of the head and neck.
But you can undergo diagnostics of the lower part of the body or in an open-type apparatus.
But if the clasp prosthesis is easy to remove and undergo diagnostics without problems, then difficulties may arise with braces. There are 3 ways here:
- Braces and retainers can be removed: if urgent examination is required,
- undergo PET or computed tomography: there are no contraindications for them,
- undergo an examination after the end of the period of wearing braces or retainers: if the diagnosis is not urgent.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS WITH 4 OSSTEM IMPLANTS FOR 1 JAW - RUB 130,000.
Implantation even with bone tissue atrophy. Work guarantee! Save RUR 20,000.
on promotion >> Free consultation with an implantologist +7 (495) 215-52-31 or write to us