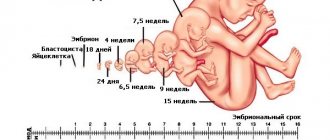
11 weeks of pregnancy is an important date. It corresponds to 13 obstetric weeks and marks the end of the first trimester. The three months following the 11th week are a real respite for you morally and physically, since the period is considered the safest for the development and gestation of the fetus.
If in the early stages there is a high risk of miscarriage (during the periods of embryo implantation and organogenesis, placenta formation and hormonal surges), then in the later stages the woman has an increased risk of gestational diabetes and preeclampsia, as well as premature birth. Of course, even in the middle of pregnancy there are critical weeks (for example, the development of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, leading to premature dilatation of the cervix and the loss of the child). However, the percentage of such cases is significantly lower than in other periods.
Most likely, you have already visited an antenatal clinic or gynecologist, registered and completed all the research required at this time. If not, you still have a few more days to do your first screening. It consists of an ultrasound (in which you can ask for a photo of your tummy to be printed) and a biochemical blood test for hCG and PAPP-A (which we discussed in detail in a previous article).
The first screening is aimed at assessing the dynamics of the pregnancy process and the health of the expectant mother and child. It allows you to determine what happens to the baby at 11 weeks of pregnancy, identify possible chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus (especially Down and Edwards syndrome), as well as factors that can subsequently lead to various pathologies. To do this, the results of both studies (ultrasound and biochemical) are analyzed and compared with generally accepted standards in order to determine in percentage terms how high the risks of having a sick baby are. To avoid excessive excitement, we remind you: the accuracy of the first prenatal screening is about 70%! Its results cannot be considered separately from the planned study of the second trimester and it is premature to draw conclusions.
How does a pregnant woman's appearance change at 11 weeks?
The first trimester continues.
At the 11th week of pregnancy, the expectant mother’s belly continues to slowly grow, the uterus increases in size, the mammary glands become engorged, and the nipples become even more sensitive. Metabolism increases in the woman’s body, associated with the increasing need of the fetus for nutrients. Some pregnant women note the appearance of sweating during this period, as well as a constant feeling of thirst. Right now, most mothers’ nails become brittle and their hair becomes dull and prone to falling out. The skin also undergoes changes during pregnancy: the work of the sebaceous glands increases, thereby causing the appearance of unwanted oily sheen, acne and enlarged pores. Some pregnant women at 11 weeks experience the exact opposite picture: hormones have a beneficial effect on the condition of hair, skin and nails. This difference is explained by the individual characteristics of the body; the nutrition of the pregnant woman during this period is also of considerable importance. Correctly selected vitamins for pregnant women, as well as various cosmetic procedures that are not prohibited by your doctor, will help solve the problem.
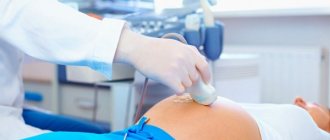
Ultrasound during pregnancy
Ultrasound during pregnancy
Ultrasound is an absolutely harmless diagnostic method based on echolocation of the ultrasound signal. That is why it is prescribed even to pregnant women.
Pregnant women are recommended to have ultrasound scans three times during pregnancy:
- 9 – 11 weeks of pregnancy (first trimester of pregnancy);
- 16 – 28 weeks of pregnancy (second trimester of pregnancy);
- 32 – 36 weeks of pregnancy (third trimester of pregnancy).
If there are indications, the doctor can refer the pregnant woman for an ultrasound scan much earlier than the required period or prescribe an unscheduled ultrasound scan for her.
The main tasks of fetal ultrasound in different trimesters of pregnancy
Ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy is necessary to ascertain the normal development of the pregnancy process, determine the presence of polyhydramnios or ectopic pregnancy, the threat of miscarriage, as well as: to determine the duration of pregnancy, the nature and heart rate of the fetus, to identify the presence or absence of diseases or anomalies in a pregnant woman pelvic organs, identifying problems associated with impaired formation of the placenta. In the first trimester of pregnancy, it is possible to determine the presence of possible defects in the fetus (by the size characteristics of the collar area).
Ultrasound in the second and third trimester of pregnancy is necessary to confirm the normal development of the fetus, determine the age, position of the fetus, its gender, identify developmental defects in it, and detect previously unidentified anomalies and defects in the pelvic organs, uterus, and placenta in a pregnant woman. In addition, in the third trimester, the structure of the lungs of the unborn child is mandatory. If there is a suspicion that the fetus has any defects, additional research methods are prescribed to accurately diagnose them.
Fetal ultrasound indicators and weekly development of pregnancy
Ultrasound at 5–8 weeks of pregnancy allows you to identify and confirm the presence of pregnancy, as well as accurately indicate the site of implantation of the fertilized egg. Starting from 5–7 weeks of pregnancy, the viability of the embryo is ascertained; during this period, ultrasound reveals distinct fetal heart contractions and its motor activity (8–9 weeks of pregnancy). During this period, it is too early to measure fetal parameters. As a rule, only the coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus and the diameter of the amniotic sac are subject to measurement; during this period, ultrasound pays attention to the condition of the future placenta and its waters.
At 10–11 weeks, an ultrasound confirms the developing pregnancy and again clarifies its duration. Thanks to ultrasound during this period, it is possible to determine the expected date of birth with an accuracy of 2 to 3 days. Then the doctor measures the thickness of the soft tissue in the neck of the fetus (thickness of the collar zone) in order to exclude chromosomal diseases, after which the quality and quantity of water, as well as the place of placenta attachment are determined, and associated complications are additionally identified (placental abruption, uterine hypertonicity, isthmic-cervical failure).
An ultrasound scan prescribed at week 22 (range: 20–24 weeks) is a screening period, during which all the specialist’s attention is directed to identifying or excluding fetal malformations, additionally determining the correspondence of the fetal size to the gestational age, and examining the condition of the placenta and amniotic fluid.
At 30–32 weeks of pregnancy, the motor activity of the fetus is assessed, a Doppler study is performed, assessing the intensity of fetoplacental and uteroplacental blood flow.
An ultrasound before birth is usually performed to determine the baby’s weight, position, condition, and the presence or absence of the umbilical cord entwining the baby’s neck.
Ultrasound indicators of a pregnant woman
Ultrasound in a pregnant woman allows you to determine: the condition of the cervix, its myometrium, placenta, the amount and structure of amniotic fluid.
- Condition of the cervix The length of the cervix is measured in proportion to the duration of pregnancy and is 3 cm. The cervix should not be shortened. The outer and inner pharynx must be closed. The closer to childbirth, the more smooth the cervix becomes. If any pharynx opens prematurely, isthmic-cervical insufficiency occurs (it is necessary to apply tightening sutures to the uterine cervix).
- Condition of the myometrium If the uterus is in a state of hypertonicity, on ultrasound it appears as a thickening of some part of its body, which is a sign of spasm of the smooth muscles of the muscles. Hypertonicity of the uterus is a variant of the norm in the third trimester of pregnancy, when the uterus is preparing for childbirth, or it may mean a possible threat of termination of pregnancy (progressive “stone belly”).
- Condition of the placenta The main function of the placenta is to supply the fetus with oxygen and nutrients and protect it from negative, harmful influences. Ultrasound allows you to identify the location of the placenta (in the area of the anterior, posterior walls of the uterus, in the fundus, on the right, on the left). It is also possible to identify placenta previa (the lower edge of the placenta overlaps the internal uterine os). Placenta previa is dangerous due to its premature detachment during childbirth. The distance from the lower edge of the placenta to the os of the uterus should be more than 5 cm; if it is less, a cesarean section is indicated for the woman in labor. Using ultrasound, the degree of maturity and structure of the placenta is also determined (27 weeks - zero degree of maturity, 27 - 32 - first, 32 - 36 - second, 36 - third).
- The amount and structure of amniotic fluid The distance from the fetal body to the uterine wall should be from 2 to 8 cm in the deepest pocket (a pocket is an area located between the fetus and the uterine wall, containing free fluid). Oligohydramnios (small amount of amniotic fluid) can be caused by infection or post-term pregnancy. Polyhydramnios (a large amount of amniotic fluid) can be physiological and be an individual characteristic of a woman or, on the contrary, indicate anomalies of fetal development, infections, Rh conflict, a large fetus, or multiple pregnancy. Turbid amniotic fluid may be associated with the presence of floating epithelium (from 30 weeks) or meconium (from 35 weeks). Sometimes suspensions in amniotic fluid can cause an infectious process.
- Structural changes Structural changes may manifest as calcifications, lobulation of the placenta, or devitalized areas. Calcifications are salt deposits in the placenta (possible in the third trimester of pregnancy). A healthy, mature placenta has the appearance of an orange with the peel removed - lobulation of the placenta (this is the norm for the second degree of placental maturity). Dead areas of the placenta (infarction) are areas where there is no blood circulation. If the area of the dead area is large, this condition can cause placental insufficiency and subsequent intrauterine growth retardation.
Baby activity at 11 weeks of pregnancy
At 11 obstetric weeks, the little man growing inside you develops a sense of smell: he can already smell the food you eat. The baby responds to his mother’s sudden movements and covers his face with his hands, stretches and becomes active. At the 11th week of pregnancy, the fetus can turn over 360 degrees and push off from the walls of the uterus, but the expectant mother does not yet feel its movements - this will happen later.
The 11th week of pregnancy is the time when your doctor can prescribe your first screening. This is necessary to assess fetal development, identify pathologies (such as Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, fetal neural tube defect, etc.) and the course of your pregnancy in general. Ultrasound at the 11th week of pregnancy is not a mandatory procedure; some pregnant women refuse to undergo it, however, obstetricians-gynecologists, geneticists and neonatologists strongly recommend not to avoid this study.
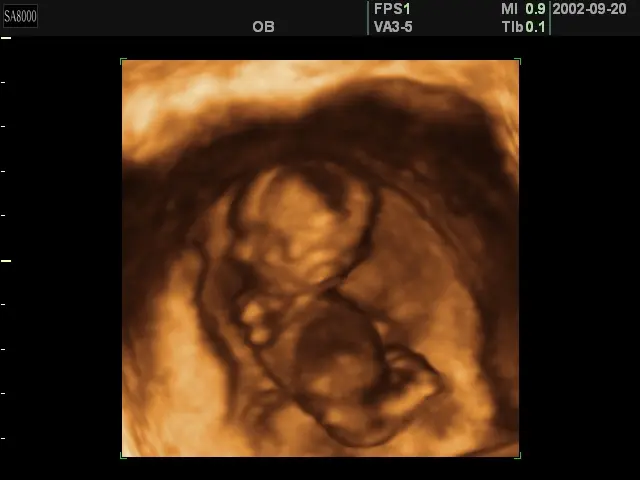
3D ultrasound at 11 weeks of pregnancy Weight gain at 11 weeks of pregnancy ranges from 0.8 kg (with a BMI of more than 26) to 1.9 kg (with a BMI of less than 19.8). To calculate your individual weight gain at 11 weeks, use the pregnancy weight gain calculator.
Decoding the results
The radiologist examines the results and evaluates the fetal parameters. During the study, the coccygeal-parietal size, head and abdominal circumference, limb length, condition of the stomach, bladder and heart are measured. These data allow us to exclude severe developmental anomalies. To detect chromosomal abnormalities, changes in the nuchal zone are used.
Based on the results of the examination, a conclusion is drawn up, which indicates the parameters of the fetus and the woman’s reproductive organs.
How pregnancy develops at 11 weeks
At 9 weeks the baby is about the size of a plum.
By the beginning of the third lunar month of life, the child’s length is about 50 millimeters. All the main organs of the child are already formed, but they continue to improve both in their structure and in their functioning:
- red blood cells are formed in the spinal cord;
- the liver, which makes up a tenth of the Baby’s body, is functioning. This important organ produces proteins that go into building the body;
- the gallbladder produces bile;
- the pituitary gland produces hormones;
- the connections between bones and muscles are strengthened, and the Baby’s movements become more and more energetic;
- fingers and toes appear;
- the cartilaginous auricle is formed;
- all major areas of the brain are formed;
- The nervous system develops very intensively: several thousand nerve cells are added every second!
- the number of connections between nerve cells and muscles increases many times - the nervous system begins to coordinate the work of muscles;
- the sense of touch improves, almost the entire surface of the body becomes sensitive to touch;
- the rudiments of baby teeth appear;
- eyebrows and eyelashes are noticeable on the face;
- the developing placental-umbilical cord merges with the Baby’s circulatory system.
How much amniotic fluid should there be?
The quality of amniotic fluid (amniotic, from the Greek amnion - fetal membrane) fluid is an important component of the successful development of the Baby. It contains many components: proteins, carbohydrates, sugar, fats and hormones that nourish the child until birth. What does “nourish” mean? Here are just a few facts:
- A certain amount of amniotic fluid is absorbed through the baby's skin before 24 weeks of pregnancy (later the skin becomes impermeable to amniotic fluid as it becomes keratinized).
- Already from 9 weeks, taste buds appear on the Baby’s tongue, and he begins to swallow amniotic fluid. In the last months of pregnancy, the fetus swallows about 20 ml of amniotic fluid in 1 hour.
Both in quantity and quality, amniotic fluid changes throughout pregnancy. So, if at 10 weeks the Baby needs 30 ml of amniotic fluid, which is similar in quality to plasma (the liquid part of the mother’s blood without cells), then by 18 weeks it already requires 400 ml, and two weeks before birth its volume is about 1500 ml . In addition to the components listed above, the amniotic fluid also contains exfoliating epithelial cells of the baby’s skin, vellus hair - lanugo, which covers the baby’s entire body until the last months before birth, secretions of his sebaceous glands, etc. The concentration of one or another component of amniotic fluid depends on the duration of pregnancy.
In order for the Baby to be comfortable in this “nutrient medium”, it must not only be saturated with useful substances, but also “renewed”, including because during the day in the last months before birth, the Baby secretes from 600 to 800 ml into the amniotic fluid urine. This means you should:
- drink at least 2-2.5 liters of liquid per day;
- It is better to completely exclude carbonated drinks from the diet - at least until the end of pregnancy and breastfeeding, since they are not beneficial for either the Baby or you;
- Doctors readily recommend drinking vitamin teas during pregnancy - the simplest and most effective way to extract useful and palatable substances from plants. Plant helpers contain many valuable substances necessary for a growing person;
- It is better to dilute fruit juices with water - this way they are better absorbed by the body, while reducing the load on the organs that secrete enzymes for digesting the juice, for example, on the pancreas.
Tests and studies during pregnancy
Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) - 5 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation, according to indications.
Diagnosis of pregnancy, exclusion of ectopic pregnancy. Blood test for AIDS (HIV), syphilis (RW), hepatitis B - when registering for pregnancy (antenatal clinic, specialized medical center, advisory clinic at a maternity hospital, etc.). These diseases can complicate the course of pregnancy and require a special approach to patient management.
Analysis for blood group and Rh factor - when registering for pregnancy. If there is a risk of Rh conflict (if the woman has a negative Rh factor and the husband has a positive one), pregnancy requires special monitoring.
General and biochemical blood test, blood sugar test - when registering for pregnancy. They give an idea of the general health of the pregnant woman and possible chronic diseases.
General urine test - when registering for pregnancy, then before each visit to the doctor. Indicates the quality of kidney function.
Vaginal smear - when registering for pregnancy. Assessment of microbial flora, exclusion of urogenital infections.
Tests for urogenital infections - according to indications .
Hormone analysis - according to indications .
What to fear and what to do?
Despite the good results of the first screening, absolutely all expectant mothers need to remember about their well-being and the health of the child. If for some reason you still do not receive vitamin complexes, consult a gynecologist and start taking them immediately. Calcium, iodine, iron, and folic acid supplements are especially important at this stage of gestation; If there is a lack of progesterone, appropriate medications can be prescribed - orally or vaginally.
Do not forget about the need for adequate nutrition and providing yourself and the baby with oxygen in order to prevent fetal hypoxia. To enrich your blood with oxygen, try to drink ionized water or water from pure natural sources; take oxygen cocktails; take long walks to avoid stagnation in the pelvis; Do simple breathing exercises every day.
Use all possible methods to relieve anxiety: listen to melodic compositions and birdsong, contemplate artistic paintings, read positive literature, watch humorous programs and comedy films. Do some crafts, drawing or sculpting. If you don't have allergies, visit zoos more often and have contact with pets.
An alarming signal and a reason for an urgent visit to the gynecologist may be: increased toxicosis and swelling, rash on the body and face, the appearance of bloody or unpleasant-smelling discharge from the vagina, itching in the groin area, acute pain in the lower abdomen, sudden excessive hair loss, fever body, high or low blood pressure, exacerbation of chronic diseases. With a competent approach and timely consultation with a doctor, many conditions can be improved without leading to serious complications.
Good to know
Expectant mother in front of the mirror: appearance during pregnancy
I believe - I don't believe. Pregnancy and superstitions
Is it possible for pregnant women to dye their hair and get nails extended?
Safe hair removal during pregnancy
Can pregnant women use household chemicals?
How to care for your hair during pregnancy
Is it possible for a pregnant woman to paint her nails?
Is it possible to get artificial nails while pregnant?
Neither more nor less... How much amniotic fluid is needed?
All texts for pages about mother and baby were kindly provided by RAMA Publishing - these are chapters from the book by Svetlana Klaas “Your Favorite Little Man from Conception to Birth”, reviewer Irina Nikolaevna Kononova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Ural State Medical Academy (Ekaterinburg).