Prostate function in men
The prostate is a gland of the male genital organs, its main function is to secrete sperm fluid that nourishes, dilutes and protects sperm. The prostate muscles help push semen into the urethra during ejaculation. The fluid produced by the prostate, together with sperm (sperm cells from the testicles) and secretions of other glands, forms sperm.
The functional state of the prostate gland can be determined by its size
The size of the prostate is closely related to the health of the male body. But without special studies, taking into account only the amount of ejaculate, it is not possible to calculate the volume of the prostate. Only by finding out the size of the organ itself can you calculate the volume of the prostate gland to determine its health.
Treatment of large prostate adenoma
If the adenoma volume is more than 150 cm3, it is advisable to perform minimally invasive operations: laparoscopic or robot-assisted adenomectomy. Open surgeries are a thing of the past. First of all, this is due to the fact that robotic and laparoscopic surgery allows you to remove adenoma tissue in one block through a puncture in the anterior abdominal wall, without creating a large incision as in open surgery. Unlike laser enucleation, modern minimally invasive methods require less time to remove a bulky prostate due to the use of optical trocars.
It is very important for men to be regularly examined and monitor their health in order to prevent the progression of pathology in the early stages of development.
Where is the prostate located?
The prostate is located between the bladder and the root of the penis. This gland is located in front of the rectum. The urethra (urethra) runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, this “tube” serves to remove urine from the body.
To get the actual volume of the prostate gland, the formula is taken from a school mathematics course: the length is multiplied by the height and width of the organ. The resulting product is multiplied by the corresponding coefficient, which allows you to calculate the volume of ellipsoidal bodies.
Before determining deviations, you should know the standard indicators. So, the average weight of a normal prostate in adult men is about 11 grams, with deviations ranging from 7 to 16 grams. The round shape and size of the iron resembles a walnut among the sizes.
Structural and functional features of the prostate gland
At different periods of a man’s life, the prostate gland undergoes metamorphosis. Before the onset of puberty, its structure is dominated by predominantly muscle tissue and small volume. At the peak of sexual activity, this is developed glandular tissue. In old age, normal involution leads to a decrease in the volume of the gland, and hypertrophic involution leads to its increase.
Anatomically, the prostate is an unpaired androgen-dependent (male) organ with approximate dimensions of 3 * 2.5 * 2.5 cm and a total weight of up to 20-25 g. The shape of the gland has the appearance of a chestnut or a rounded pyramid, pointing downwards. The initial part of the urethra or urethra passes through the thickness of the gland. The gland itself is located with its wide part or base upward and is adjacent to the bladder. The seminal vesicles are adjacent to the gland at the back, and the prostate itself is separated from the wall of the rectum by a very thin layer - Denonvilliers' fascia. Due to such close proximity of important organs, prostate pathology can be detected during digital examination and palpation.
The gland is covered on top with a fairly dense connective tissue capsule with strands or fibers extending into the thickness of the prostate. Feeding capillaries and nerve endings penetrate deeper through them. Blood circulation has common origins with the plexus of vessels of the final sections of the rectum and the vascular network of the penis. It is for this reason that sexual arousal leads to increased blood flow and metabolic processes in the prostate.
Normally, in the absence of physiological or anatomical and structural changes, the prostate does not manifest itself in any way, and its functioning does not cause discomfort, pain or deterioration in a man’s well-being.
Normal prostate size
The normal prostate gland measures approximately 3 × 3 × 5 cm or a volume of 25 ml. We see that the formula of simply multiplying the length, width and height will not yield a 25-ml prostate volume, because the shape of the prostate is far from a geometrically regular rectangle. For an accurate calculation, a coefficient is used, which we will discuss later.
Various prostate measurements (mean ± standard deviation)
| Age | Group 1 (40–49 years old) | Group 3 (60–70 years old) |
| Length (mm) | 37,55 ± 4,27 | 41,13 ± 6,18 |
| TZW (Transitional Zone Width), mm | 30,25 ± 4,84 | 34,21 ± 7,08 |
| Height, mm | 21,64 ± 3,73 | 25,02 ± 6,07 |
Using age ranges when diagnosing prostate cancer helps avoid unnecessary testing in older men with naturally larger glands (about the size of a large walnut).
Laboratory diagnostics: PSA level analysis
If there are symptoms of prostate adenoma, a man is referred for a blood test to check PSA levels. Prostate-specific antigen is produced by prostate tissue. It is partially found in blood serum and iron.
Enlargement of the prostate gland by 1 cubic cm. leads to an increase in antigen concentration by 0.3 ng/ml.
For each age group, the norm of PSA indicators is determined:
- 30-50 years – up to 2.5 ng/ml.
- 50-60 years – up to 3.5 ng/ml.
- 60-70 years – up to 4.5 ng/ml.
- 70 and older - up to 6.5 ng/ml.
Elevated levels indicate organ pathology.
If the analysis determines an increased antigen value, a biopsy is prescribed. The procedure for taking biopsy samples for further laboratory testing is necessary to exclude oncology. Not only the level, but also the ratio of free PSA in relation to total PSA is assessed. If it is less than 15%, there is a possibility of a malignant process.
Before taking a PSA test, it is important to follow the rules in order to get a reliable result:
- It is necessary to donate blood 4 weeks after any manipulation of the prostate (massage, biopsy, palpation, colonoscopy, etc.).
- For 7 days you cannot drink alcoholic beverages or go for massages.
- For 3-4 days, you should give up spices in your food, avoid masturbation and sexual intercourse, and avoid heavy physical activity.
Why does the prostate enlarge?
There are benign (noncancerous) enlargements of the prostate that block the normal flow of urine through the urethra. Inside the prostate, cells gradually grow and begin to increase the parenchyma of the organ. They put pressure on the urethra, through which urine and semen are released. When the parenchyma begins to enlarge, it gradually compresses the urethra and can lead to a complete blockage of the urethra.
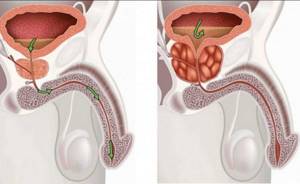
Diagnostic ultrasound shows an increase in the volume of the prostate gland very well. Modern devices allow you to obtain high-resolution three-dimensional images. Next, the volume of the prostate gland is calculated using ultrasound and it is decided whether it is worth starting treatment, whether it makes sense to buy the same Smartprost physiotherapeutic device and take other measures.
The role of estrogen
Estrogen has also been linked to prostate enlargement. As men age, less testosterone is produced in the blood, which leads to an increase in the relative proportion of estrogen. This female hormone provokes a change in the appearance of men, many feminine characteristics appear.
Main risk factors for prostate pathology
In each case, the patient has not one, but several causes that cause a pathological process in this organ. They also significantly influence the dynamics of the development of the disease, the formation of the clinical picture, susceptibility to successful treatment and the overall prognosis. Of this variety, the greatest negative degree has been proven for the following reasons:
- age characteristics;
- hereditary predisposition;
- long breaks in sexual activity;
- local hypothermia;
- low level of physical activity and a predominantly sedentary lifestyle;
- infection of the genitourinary system;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- unfavorable living or working conditions;
- side effects of certain groups of long-term medications.
At what age should you have your prostate checked?
After forty years, men are advised to pay attention to the condition of their prostate gland. Beginning around age 50 (or earlier if family history warrants), all men should consider regular prostate cancer screening. The first step is to donate blood to test the level of PSA - prostate specific antigen.
How often should you have your prostate checked?
If a blood test shows that the PSA level is below 1 nanogram per milliliter of blood and the doctor does not find any bad changes in the prostate, then you can not undergo a rectal examination for another 10 years. However, if the PSA is between one and two nanograms per milliliter of blood, then it is recommended to get tested every two years. The volume of the prostate is calculated using ultrasound, the formula of which reliably shows changes without additional examinations.
Basic options for diagnosing prostate conditions
In order to establish an accurate diagnosis if pathology is suspected, the following diagnostic methods are used in modern urology:
- general detailed and biochemical blood tests;
- general urine test (three-glass sample);
- physical data during a digital examination of the prostate;
- microscopic examination of prostate secretion;
- bacteriological examination of the obtained biological fluids;
- antibacterial sensitivity of sown pathogens;
- immunological test (PSA) – prostate-specific antigen;
- Prostate Health Index (PHI);
- transrectal ultrasound;
- MRI, CT of the pelvic organs – if necessary.
The decision on the need for certain examination options is made by a urologist, based on symptoms.
Symptoms of prostate enlargement
Symptoms of prostate adenoma include:
ORDER
- Weak or slow urine flow.
- Feeling of insufficient emptying of the bladder.
- Difficulty starting to urinate.
- Frequent urination.
- Frequently getting up at night to urinate.
- Intermittent stream of urine that starts and stops.
- Strained urination.
When does the pain occur?
Both prostatitis and benign prostatic hyperplasia (growth) of the prostate gland (BPH) can cause pain. However, if BPH (formerly called an adenoma) causes pain, it usually only occurs during urination. With prostatitis, pain may appear during urination, ejaculation, or manifest itself as generalized pain in the abdomen and/or groin area.
Early signs of prostate cancer
- Burning or pain when urinating.
- Difficulty starting and stopping urination.
- Numerous urge to urinate at night.
- Loss of bladder control.
- Decreased urine volume or flow rate.
- Bloody urine (hematuria).
- Blood in semen.
And to differentiate different lesions, it is not enough to find out the volume of the prostate gland; you need to know how to calculate this indicator to determine the optimal treatment method.
All about prostatitis

How to avoid “aging” of the prostate In most cases, prostatitis and prostate adenoma occur in connection with age-related changes in the prostate tissue, which would seem inevitable. Prostatitis and the ability to conceive Inflammatory diseases of the prostate are one of the most common and potentially correctable causes of a man’s inability to conceive. With chronic prostatitis, the number of healthy sperm in the ejaculate decreases, and their motility is also impaired. Prostatitis and STIs Today, there has been a significant increase in the number of men with prostatitis caused by sexually transmitted infections. In most cases, this disease becomes a complication of urethritis - acute inflammation of the urinary tract.
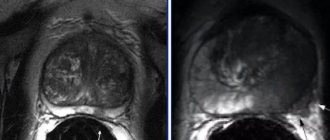
How is prostate size determined?
For transrectal ultrasound, patients are asked to lie on their side with their knees bent. A disposable protective cap is placed on the sensor, lubricated, and inserted into the rectum through the anus. Images are taken from different angles to get the best view of the prostate gland for accurate measurements and diagnosis.
Video: how a prostate ultrasound is performed.
An ultrasound examination of the prostate uses a finger-sized probe that is inserted a short distance into the rectum. This probe creates harmless sound waves. A person cannot hear them, but they bounce off the surface of the organ being examined. An ultrasound machine records sound waves and turns them into videos or photographs. Pictures are flat (2D) or three-dimensional, three-dimensional (3D), black and white or color. They look at the structure of the organ and the presence of nodes. The specialist looks for changes in contours and echogenicity in each zone. At the same time, a small tissue sample may be taken for biopsy.
Ultrasound of the prostate gland is more accurate than x-rays. This is because the technician can see images in real time as the probe moves across the rectum, rather than taking a photo and then examining static images. Ultrasound examinations are also safer than x-rays because the ultrasound machine does not generate dangerous radiation.
Ultrasound of the prostate gland. Risk factors for prostate cancer
Department of Ultrasound Diagnostics Ultrasound diagnostics doctor Gletsevich O.E.
The prostate gland (prostate) is the male reproductive gland. The organ is located in the pelvis, directly under the bladder. Its shape somewhat resembles a large chestnut. The secretion of the prostate gland is responsible for the consistency of seminal fluid, and also contains immunoglobulin, various enzymes and vitamins
The prostate is formed by three types of tissue:
- glandular;
- smooth muscle;
- fibrous.
Glandular tissue is responsible for the production of hormonally active secretions. The smooth muscle forms the basis of the bladder sphincter.
The fibrous forms the capsule of the gland.
The size of the prostate gland depends on the individual characteristics of each individual man: his age, weight, and state of health.
Normal prostate sizes:
anterior-posterior 16-23mm,
transverse 27-43mm,
top-bottom 24-41mm
The normal volume of the prostate is no more than 26 cm3, but it varies depending on age.
The volume of the simple can be calculated using the formula (A.I. Gromov):
A= 0.16 B+ 16.4
in this formula A is the volume of the gland, B is the age of the patient
Ultrasound examination has found wide application in the diagnosis of prostate diseases (ultrasound of the prostate). To perform an ultrasound of the prostate gland, 2 approaches can be used:
Transabdominal ultrasound - performed through the anterior abdominal wall in the supine position. A prerequisite is the filling of the bladder, which serves as an “acoustic window” for visualizing the prostate gland. To do this, it is recommended to drink 1-1.5 liters 1 hour before the test. liquids Both underfilling and overfilling of the bladder make visualization of the prostate gland difficult.
Transabdominal examination is the most accessible and least burdensome for the patient. There are no contraindications to such a study, but there may be limitations, such as the presence of a postoperative wound, a drainage tube (cystostomy) in the area under study, or the inability to sufficiently fill the bladder. Transabdominal ultrasound is performed in standard transverse and longitudinal planes, and, if necessary, for better visualization of certain parts of the prostate - in oblique and in any arbitrarily selected planes. At the same time, the bladder and seminal vesicles are examined. The disadvantage of external scanning is its low resolution. Its capabilities in studying the prostate gland are limited to assessing its shape, size, symmetry, and relationships with surrounding organs. Additionally, the amount of residual urine in the bladder is determined, which is important both for prostate adenoma and prostatitis. Due to the low sensitivity of external scanning, which does not allow detecting minor initial changes in the structure of the prostate gland, it is considered advisable to conduct TRUS of the prostate - transrectal (through the rectum) ultrasound examination of the prostate gland.
Transrectal ultrasound - performed with a special ultrasound sensor through the rectum, lying on your back or left side with your knees bent.
Before transrectal ultrasound of the prostate, it is necessary to do an enema 2-4 hours before the procedure to clean the rectum and adhere to a slag-free diet throughout the day.
The advantage of this approach is the ability to examine the prostate gland with an unfilled bladder. TRUS of the prostate allows you to evaluate the gland by lobes, identify its zonal differentiation, as well as determine the state of the paraprostatic venous plexus and periprostatic tissue? Conduct a pediatric study of the seminal vesicles. In men over 40 years of age, even in the absence of indications of past infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract, pathological changes are often detected in the prostate gland: stones, calcifications, retention cysts, as well as signs of prostate adenoma. The condition for a full-fledged ultrasound of the prostate is currently a Doppler assessment of its vessels, which is preferably carried out from a transrectal approach. The development of inflammation in the prostate gland is associated with characteristic changes in its structure and microvasculature. All phases of the course of prostatitis are accompanied by changes in the structure and are reflected during TRUS of the prostate. In acute prostatitis, TRUS reveals a diffuse or focal decrease in the echogenicity of the prostate gland, usually an increase in its size and volume; when the seminal vesicles are involved in the inflammatory process, their expansion and heterogeneity of contents. Using power Doppler ultrasound in acute prostatitis, a local or diffuse increase in the vascular pattern is determined, and in the case of concomitant vesiculitis, an increase in the vascular pattern around the seminal vesicles is determined. TRUS is very informative in the diagnosis of destructive forms of acute prostatitis. In this case, against the background of enlargement and swelling of the prostate gland, zones of reduced echogenicity are determined, often irregularly shaped, with unclear uneven contours and local enhancement of the vascular pattern along the periphery of the inflammatory focus. The formed prostate abscess looks like a hypoechoic, heterogeneous avascular formation, close in echogenicity to liquid. Chronic prostatitis has a variety of changes in the prostate. Diffuse and focal changes in the structure are observed in the form of calcifications and areas of fibrosis with depletion of the vascular pattern. With congestive (congestive) prostatitis and the presence of venous stagnation in the small pelvis, dilation of the veins surrounding the prostate gland is determined. Ultrasound of the prostate in combination with Doppler sonography can be of great importance in inflammatory diseases of the prostate gland and seminal vesicles as monitoring the course of the disease and monitoring the treatment. Thus, prostate ultrasound and its variant TRUS are an important objective method for diagnosing and monitoring the results of treatment of various phases of the inflammatory process in the prostate gland and seminal vesicles.
Ultrasound is an important method for diagnosing prostate tumors. Of the malignant neoplasms, the most common is adenocarcinoma, which develops from the epithelial cells of the prostatic glands and accounts for 95% of all cases. Transitional cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are quite rare. Even more rare are malignant nonepithelial tumors of the prostate gland, information about which is not discussed in this material. The term “prostate cancer” usually refers to adenocarcinoma.
It is not always possible to answer the question of why one person gets prostate cancer and another does not. However, it is known that prostate cancer is more common in people with certain risk factors.
Research has identified risk factors for prostate cancer.
Age is the main risk factor. Most patients with prostate cancer are over 65 years of age. This disease rarely occurs in men under 45 years of age.
Heredity. If one of your immediate relatives (father, brother) has prostate cancer, the risk of the disease doubles. If prostate cancer is detected in two relatives, the risk increases more than 5 times.
Ethnicity. It has been proven that prostate cancer is more common among blacks.
Some morphological changes of the prostate gland. These changes at the cellular level are only detected by prostate biopsy: men with prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) may have an increased risk of developing cancer.
Genetic predisposition. Certain sections of DNA with genes have been identified, violations of which increase the risk of developing prostate cancer. If a person has genetic changes in one or more of these areas, the likelihood of developing prostate cancer increases. Additionally, other studies have shown an increased risk of cancer in men with changes in specific genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2.
Prostate cancer may not manifest itself for a long time. Symptoms usually begin to appear as the tumor grows and becomes larger. The most common symptoms of prostate cancer include: difficulty urinating (at first it is difficult to start urinating or stopping the flow of urine, later the entire act of urination occurs with great effort), pain or burning when urinating, frequent urge to urinate, especially at night, weak urine flow, erectile dysfunction, blood in the urine or semen, frequent pain in the lower back, pelvis or thigh. These symptoms are not always associated with the presence of cancer. BPH, urinary tract infections, and other conditions can cause similar symptoms. If you have any of the problems listed above, you should consult a doctor for examination.
Prostate cancer may be suspected if the above symptoms are present in a patient with risk factors after performing a digital examination of the prostate through the rectum (digital rectal examination). The study allows you to determine the size and density of the prostate gland, as well as the presence of tumor formations in it. However, the absence of any changes in a rectal examination does not exclude the possibility of prostate cancer. Determining the level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) in the blood can help determine the likelihood of cancer. PSA is a specific protein that is formed in the epithelial cells of the prostate gland and secreted into the lumen of the prostate glands. Some PSA enters the bloodstream and can be detected in serum. In the presence of prostate cancer, the level of PSA in the blood may increase significantly. The upper limit of normal is considered to be PSA = 4.0 ng/ml, however, in recent years there has been a tendency for the PSA level to decrease to 2.5 ng/ml. In most of Europe and the USA, a PSA level greater than 4 ng/ml is considered an indication for pancreatic biopsy. An increase in PSA levels is not always associated with a tumor process and can be observed in the following cases: BPH, inflammatory diseases of the prostate gland (prostatitis), after cycling, after sexual intercourse, after urological manipulations (digital rectal examination), cystoscopy, transrectal ultrasound, biopsy prostate gland. Therefore, to obtain the most “correct” PSA level, it is necessary to exclude possible effects on the prostate gland and sexual intercourse in the week before the test. If there are symptoms of prostatitis, you should first undergo a course of anti-inflammatory treatment. Given the difficulty in interpreting PSA data, the test should be evaluated by a specialist experienced in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer.
Formula for calculating prostate volume
The probe is moved at an angle from one side to the other. Every urologist who conducts such an examination knows how to calculate the volume of the prostate in cm3 based on the measurement results. After measuring the height and length in the sagittal plane and the width in the axial plane, the volume is calculated: the product of the three measured values is multiplied by the index 0.52.
That is, with transrectal ultrasound (TRUS), the volume is estimated using a traditional mathematical calculation of the volume of the ellipsoid based on the resulting height (H), width (W) and length (L) of the prostate.
Calculation of prostate volume formula:
H × W × L × 0.523.
Where the exact index value for calculating the volume of the prostate gland is 0.523.
Instrumental diagnostics
To assess the condition of the prostate gland, the urologist performs TRUS of the prostate and refers it to uroflowmetry.
- TRUS – transrectal ultrasound examination
.
The gold standard for determining an adenoma is examination of the organ using an ultrasound probe placed in the man’s rectum. The method is safe for the patient and is highly informative. With TRUS, the doctor determines the size of the prostate gland and the presence of lumps. The normal size of the prostate is 20-25 cubic meters. see. With hyperplasia, the indicators increase.
Transrectal ultrasound gives objective results if the patient is properly prepared for it: within 30-60 minutes, you need to drink a liter of clean water to fill the bladder.
- Uroflowmetry.
Uroflowmetry is a non-invasive instrumental study that is used to determine urine flow parameters. A man empties his bladder into a special electronic toilet. Data about urination are transmitted to a computer for processing information and building dynamics. In a healthy person, urination occurs at a rate of 15 ml/s or more. Hyperplasia is confirmed if the rate is less than 12 ml/s.
How can you reduce the size of your prostate?
Only a doctor can correctly determine the size and calculate the volume of the prostate gland, conduct the correct examination and diagnose the disease, and then develop an effective treatment regimen. But patients can help doctors control the symptoms of an enlarged prostate. To maintain health, patients must independently:
- Limit drinks in the evening.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol.
- Limit your intake of decongestants and antihistamines.
- Go to the toilet at the first urge to urinate.
- Take a bath regularly.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Stay physically and sexually active.
- Urination should be done in two steps, after a few seconds, this is an important nuance.
Principles of preparation
Transrectal ultrasound implies that the study will be carried out through the rectal canal - the sensor is inserted carefully, slowly, without pressing or jerking. To obtain maximum information, several preparation conditions must be met:
- adjust your diet - exclude those foods that will cause gas formation and constipation, it is better to steam vegetables, bake fruits, eat cereals and purees;
- maintain a water regime - drink at least 1.5–2 liters of clean water, green tea, fruit drinks;
- if you are prone to flatulence, take a short course of carminative drugs, for example, Smecta, Espumisan;
- immediately before visiting the functional diagnostics office, take care of bowel movements, as well as on the morning of the test day - give a cleansing enema or take a laxative.
Sometimes, in order to obtain a high-quality image on the monitor screen, doctors ask a man to come with a full bladder - to assess its functioning and improve visualization of the prostate gland. To do this, it is enough to drink 1.5–2 glasses of water half an hour before coming to the hospital.
Surgical treatment of the prostate
Standard surgical procedures
- TURP: transurethral (through the urethra) resection (truncation) of the prostate gland through the urethra. This procedure is the "gold standard for effective treatment of BPH."
- Open prostatectomy (complete removal of the gland for cancer).
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
This surgery is used to treat problems with urination due to an enlarged prostate gland. This is the most common surgery to treat BPH. The doctor removes only the parts of the prostate gland that are obstructing the flow of urine. A combined visual and surgical instrument (resectoscope) is inserted through the tip of the penis and into the urethra.
Every male urologist must master diagnostic techniques and know how to calculate the volume of the prostate by size. The urologist’s tasks also include determining the most optimal treatment method, incl. determining the need for surgical intervention. It is important for men to consult a doctor on time and carefully monitor their condition.
Prostate massage: misconceptions and reality
If the term prostate massage is taken to mean any indirect mechanical effect on the prostate gland, then the following variants can be distinguished:
- Simple intimate stimulation. Used by sexual partners as an additional source of sexual arousal, obtaining more vivid erotic emotions and impressions. It is carried out using the fingers - manually or with the help of special devices. Can be considered a sign of a high level of intimate trust. Technically it consists of a mechanical effect on the posterior surface of the gland and stimulation of the anal ring and rectal ampulla. The main risk is that, due to the lack of skills and knowledge, there is a risk of injury to the organ and infection, as well as causing pain. At its core, it is not a massage.
- Diagnostic prostate massage. It is one of the main and mandatory methods of a full urological examination. Always carried out by a specialist in compliance with standard generally accepted techniques. .The goal is to obtain prostatic secretion for instrumental and laboratory analyzes and other tests. But it is not carried out in acute forms of pathology or other contraindications.
- Therapeutic prostate massage. It is a therapeutic procedure performed by a specialist. It has a certain generally accepted implementation algorithm. As a method of treatment, it is prescribed according to indications, outside the acute phase of the disease. Duration and number of procedures. For chronic prostatitis, this procedure is preventive in nature: it improves the functioning of the organ and reduces the frequency of relapses.
Any mechanical effect on prostate tissue is potentially extremely dangerous, risky and impossible in the following conditions, regardless of who carries out the effect - a doctor, a partner or the man himself:
- low-grade fever or any temperature reaction if its exact cause is unknown;
- acute bacterial prostatitis, or clinical exacerbation of the chronic form;
- urolithiasis with a condition after “passing of stones or sand”;
- hemorrhoids, especially with significant volumes of nodes, an indication of hemorrhoidal bleeding that has taken place;
- rectal fissures, inflammatory local reactions, bleeding from existing fissures;
- cysts and stones in prostate tissue of any location and origin;
- genitourinary infections in the acute phase, with unstable remission, with remission during antibiotic therapy;
- malignant neoplasms or suspicions of them, established benign tumors due to the risk of malignancy.
The problem of the prostate condition is very significant. This is an important factor for men's health, comfortable intimate life and the ability to fertilize. At the first suspicion, consult a doctor. Maintaining health is easier, faster and cheaper than restoring it. And only a specialist can quickly and completely solve problems.
Sources:
- Lokshin KL PROSTATITIS: WHAT'S NEW IN BASIC SCIENCE AND CLINICAL STUDIES? Vestnik Urologii. 2017;5(4):69-78. (In Russ.) https://doi.org/10.21886/2308-6424-2017-5-4-69-78
- Conservative treatment of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia with 5-α-reductase inhibitors. A.I. Neimark, B.A. Neymark, N.A. Nozdrachev. Department of Urology and Andrology with courses of specialized surgery, Altai State Medical University of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Barnaul, Russia. Newspaper "Moscow Urologist" No. 1-2020
- Brizhatyuk E.V., Shevchenko S.Yu. The influence of the lifestyle of a patient with chronic prostatitis on its quality. Journal of Urology. 2020;8(3):13-17. https://doi.org/10.21886/2308-6424-2020-8-3-13-17
- Ultrasound diagnosis of the prostate gland in modern urological practice / G.I. Nazarenko, A.N. Khitrova. – Moscow: Vidar-M Publishing House, 2012. – 288 p.: ill. ISBN 978-5-88429-171-3
- Frequency of acute urinary retention in patients with prostate adenoma during 8-year treatment with tamsulosin M.I. Davidov, K.L. Lokshin, I.S. Gorbunova 1 State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Perm State Medical Academy named after. acad. E. A. Wagner" of the Ministry of Health of Russia; 2 Research Institute of Uronephrology and Human Reproductive Health State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenov” - “Urology”, 2015, No. 12.
- Features of the clinical course and morphometric parameters of benign prostatic hyperplasia in men with metabolic syndrome and androgen deficiency I.A. Tyuzikov, E.A. Grekov, S.Yu. Kalinchenko 1 Clinic of Professor Kalinchenko; 2nd Department of Endocrinology, Faculty of Advanced Training of the Ministry of Medicine, RUDN University, Moscow - “Urology”, 2015, No. 5.
- Silodosin in the treatment of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia – results of a Russian multicenter observational study D.Yu. Pushkar, A.N. Bernikov, A.V. Sadchenko Department of Urology, Moscow State Medical and Dental University. A. I. Evdokimova, Moscow - “Urology”, 2015, No. 5.
- Chernogubova E.A. MARKERS OF INFLAMMATION IN DIFFERENT FORMS OF CHRONIC ABACTERIAL PROSTATITIS. Journal of Urology. 2018;6(2):44-53. https://doi.org/10.21886/2308-6424-2018-6-2-44-53
Last revision date: 08/19/2021
Treatment of the prostate gland: how does it happen?
The form of prostate treatment depends on the extent of the disease. There is no universal way. There are three classical treatment methods:
- Surgical
- Medication
- People's
Drug treatment is prescribed both at the initial stage of treatment and in parallel with the surgical method. The most common forms of drug treatment are:
- Antibiotics
- Antispasmodic drugs
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
The folk method is treatment at home, using natural methods at hand.
- After consulting with your doctor, you can determine the most convenient method for yourself.
- The most common treatment is pumpkin seeds.
- By including them in your diet on a regular basis, you can saturate your body with the necessary zinc, which helps the body cope with disorders in the prostate gland.
Remember: Before choosing a drug from traditional medicine methods, be sure to consult your doctor. Self-medication is dangerous to health and life!
In what cases is complete removal of the organ performed or when surgical treatment is used, read below.
When is surgery to remove the prostate gland performed in men?
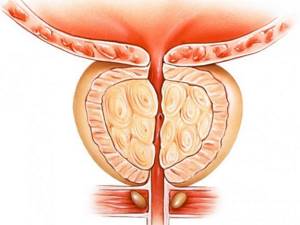
The surgical method is the treatment of the prostate gland through surgery. When is surgery to remove the prostate gland performed in men? Here is the answer:
- It is prescribed in case of neglect and exacerbation, for example, with the formation of a cyst, cancerous tumors, bleeding, purulent wounds, pathological narrowing of the ureter, stones, and so on.
Surgical treatment should only be prescribed by a specialist. The most popular surgical method is transurethral resectoscopy and laparoscopy:
- Transurethral surgery involves partial or complete removal of the prostate gland by inserting a resectoscope (special tube).
- In this case, the patient’s consent is required before performing this operation.
- the laparoscopy method was chosen to remove prostate pathologies , then the operation will be carried out using modern methods, using microscopic incisions.
It is worth noting that laparoscopy is the least traumatic method of surgical intervention.
Prostate massage for husband by woman: video
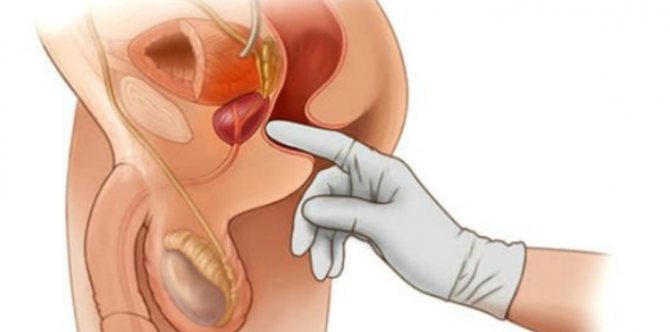
The effectiveness of massage for prostate disease has long been proven. This is an unpleasant procedure that no man likes to undergo. Typically, such manipulations are performed by a urologist directly at the appointment. However, men often feel awkward and embarrassed. What to do? Health is more important and therefore, if a doctor prescribes such a procedure, then you must undergo it.
Before the procedure you need to prepare:
- Give your husband a cleansing enema . Lubricate its tip with Vaseline, pour 200 ml of cool water and insert it into the intestines.
- He should drink 1 liter of clean water 30 minutes before the massage . The bladder should be full before the session.
- Wear sterile latex gloves to avoid introducing infection into the anus.
The technique and tips on how to massage the prostate are described above in the text. It is not recommended to perform this session if you have the following pathologies:
- Urolithiasis of the kidneys
- Tumor or cysts in the prostate gland
- Haemorrhoids
- Anal fissure
Advice: Before the procedure, be sure to consult your doctor. He will tell you whether it is possible to do such a massage and how to perform it correctly.
If a man still refuses to see a urologist and get a massage in the hospital, there is an alternative - massage of the prostate gland for the husband by a woman, his wife. In fact, it is not as difficult as it might seem at first glance. You just need to understand how to do it right. In many couples, the woman massages her man's prostate for pleasure. Watch a video on this topic: