Diagnosing various pathologies of cerebral vessels is a pressing issue, since cases of strokes, which are accompanied by loss of ability to work, disability and death, have become more frequent. Statistics show that only 40% of people after a stroke can return to a full life.
Doppler ultrasound is the leading examination method that can be used to identify various lesions of the brachiocephalic arteries.
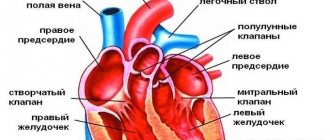
To understand what is meant by the words “brachiocephalic arteries,” you need to trace their path to the brain from the aorta. The blood flow that comes from the aortic arch is distributed into 3 large arteries: the common carotid, the left subclavian artery, and the brasiocephalic trunk. The latter is divided into 3 more arteries, which are located on the right side: subclavian, carotid, vertebral.
All of these vessels, in one way or another, take part in the blood supply to the shoulder girdle and, directly, to the brain. At the same time, they form a complex system in the form of a closed circle, which allows evenly distributing the entire volume of blood in order to ensure adequate blood supply. Impaired blood flow can lead to blood redistribution.
Indications
The vessels located in the brachiocephalic zone can be intracranial and extracranial.
The first ones are called intracranial; they supply blood to the brain itself and the tissues adjacent to it. The latter are responsible for supplying blood to the tissues of the neck, face, and back of the head. During the diagnostic procedure, the functions of these departments are assessed. Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries is performed in the presence of the following indications:
- severe pain in the head area;
- dizziness;
- blurred gait;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
- decreased sensitivity of the lower extremities;
- the appearance of “flies” before the eyes;
- memory problems;
- increased concentration of cholesterol in the body.
Ultrasound scanning of extracranial as well as intracranial sections of the brachiocephalic arteries is performed for vegetative-vascular dystonia, atherosclerotic changes, neck injuries, and vasculitis. Indications for performance may include blood diseases, a previous heart attack or stroke.
Ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic vessels is also performed in patients over forty years of age with diabetes mellitus or elevated concentrations of lipids in the blood. Diagnostics are prescribed before planned surgical intervention on the myocardium.
Indications and contraindications for ultrasonography of brachiocephalic arteries and vessels:
Mostly people suffering from obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, and cervical osteochondrosis suffer. And also if you have previously suffered a stroke, heart attack and people over forty years old. If such diseases are present, then an ultrasound examination must be performed at least once a year.
Also, people suffering from frequent headaches, fainting, sleep disturbances, tinnitus, spots in the eyes, and visual disturbances should also undergo ultrasound examination of the bracheocephalic trunk. And also if there is weakness in the legs and arms and memory becomes worse. There is only one contraindication, and that is the presence of wounds on the neck.
Advantages
It is worth highlighting the main advantages of ultrasound diagnostics:
- great information content;
- no pain;
- possibility of repeating (if there are appropriate indications);
- safety.
This study of the brachiocephalic arteries is more informative than traditional Doppler ultrasound. This method is considered to be the “gold standard” in the field of diagnostics. Timely ultrasound scanning of blood vessels is a powerful obstacle to possible disability.
What happens during the study
The triplex vessel procedure is completely painless and, of course, does not require either local or general anesthesia. Depending on the area being examined, diagnostics are carried out in a lying, sitting or standing position. Having applied a special gel to the patient’s skin, the diagnostician installs an ultrasound sensor in the projection of the examined vessels. The gel is necessary to improve signal transmission inside the patient’s body. During the procedure, the diagnostician may ask the subject to change his body position, hold his breath briefly, and perform other simple actions. The average duration of a duplex scanning procedure lasts about half an hour, sometimes a little longer, and usually does not cause any discomfort or discomfort in the patient.
Progress of the procedure
Before performing ultrasound scanning, it is recommended to exclude from the diet foods that can negatively affect vascular tone. On the day of the procedure you should not drink:
- strong brewed tea;
- coffee;
- alcoholic drinks;
- coca cola.
On the eve of the study, you should not be overly fond of salty and spicy foods. The patient is not recommended to be in a smoky or stuffy room before the diagnosis. This can negatively affect the blood supply to the vessels.
The day before performing ultrasonography, you should refrain from taking nootropics and vitamin and mineral preparations. Patients taking medications that affect heart function should consult their doctor first.
The diagram of the diagnostic procedure is as follows:
- the patient needs to lie down on a couch located near a special apparatus. A cushion is placed under his neck.
- your head needs to be turned in the direction opposite to the device.
- The area of the body being examined is lubricated with gel to facilitate the passage of a special signal.
- By using a sensor, the doctor smoothly moves from one segment in the neck area to another. At the same time, changes in the signal are monitored, which is recorded on the monitor.
The specialist may ask the patient to hold his breath for a short period of time. If any deviations from the norm are detected, a more detailed examination of the vessels is carried out.
If there are appropriate indications, functional tests are also recommended. At the same time, changes in indicators in the horizontal and vertical positions of the body are assessed.
There is no discomfort observed during the procedure. The average duration of ultrasonography is 30 minutes.
Triplex extracranial scanning of the main arteries of the head
What it is?
This is a special method of ultrasound examination of the arteries of the neck and head.
The main arteries are vessels that supply blood to the brain, soft tissues of the head and shoulder girdle.
Extracranial scanning means that the doctor examines those parts of the arteries that are below the level of the head (neck and shoulder girdle).
Triplex scanning is a dynamic ultrasound examination, which is carried out in three modes:
- conventional ultrasound;
- color Doppler mapping;
- spectral Dopplerography.
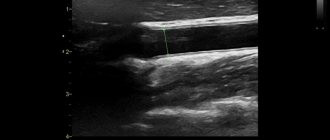
As a result of triplex scanning, the doctor sees the condition of the vessels: their patency, possible narrowings, tortuosities, kinks, atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, occlusions, developmental anomalies; can estimate the blood flow in each examined vessel, and ultimately calculate the total cerebral blood flow.
In what cases is the triplex vascular scanning method used?
- For headaches, dizziness, fainting;
- In case of impaired coordination of movements;
- With decreased visual acuity, “spots” before the eyes;
- For hypertension, atherosclerosis;
- If there are signs of impaired blood supply to the brain;
- With cervical osteochondrosis;
- For anomalies in the development of arteries;
- For aneurysms, vascular malformations, vascular ruptures and anephrisms;
- For acute strokes and post-stroke conditions;
- For diseases leading to cerebral circulation disorders (infectious, allergic, cardiac, as well as any tumors);
- For injuries of the spine, brain; and in other cases.
The triplex scanning method is effective for diagnosing headaches of unknown origin, dizziness, fainting and other conditions.
What are rotation tests?
These are functional tests with which the doctor can assess the disturbance of blood supply to the brain. When turning the head, blood flow in the vertebral arteries may change if there are developmental anomalies or acquired pathologies. Therefore, assessment of blood flow in different arteries is necessary for differential diagnosis of various diseases.
How is the research conducted?
It is not recommended to smoke on the day of the test, as nicotine can affect blood flow in the arteries. The patient lies on his back, the doctor moves the ultrasound sensor over his skin in the area of the vessels being examined, sometimes pressing them. During turning tests, the doctor asks the patient to turn his head, inhale, hold his breath, and exhale. The method is absolutely safe and has no contraindications. It is also suitable for patients at risk of stroke, elderly patients, and pregnant women. The study lasts no more than 20 minutes.
How to sign up for an ultrasound?
- The fastest and most convenient way is to register online, which is available 24 hours a day and takes no more than 5 minutes!
- You can also call the clinic’s 24-hour phone number +7(812) 327 03 01, and we will make an appointment for you at a convenient time.
What does it show
Dr. Khizriev Seyfedin Magomedovich prescribes a diagnostic procedure if the presence of atherosclerotic changes or aneurysms is suspected. Ultrasound scanning is intended for diagnosing structural and functional arteriovenous changes.
When conducting diagnostics, the specialist recognizes the presence of such unfavorable changes:
- plaques;
- blood clot formation;
- thickening of the walls of blood vessels.
When performing an ultrasound scan, the speed of blood flow is detected. The diagnostic procedure also shows dilation of the walls of blood vessels and stenosis.
All readings obtained during diagnostics are entered into the scanning protocol. On average, the process of deciphering the Doppler spectrum and assessing the blood flow cartogram takes ten minutes. After this time, the patient will be able to receive the results.
The optimal indicators that distinguish the branches of the common carotid artery are listed in the corresponding table.
| Relevant Parameters | Acceptable values |
| The diameter of the internal branch | From 3 to 5.5 (mm) |
| Outer branch diameter | From 3 to 6 (mm) |
| Systolic blood flow velocity in the area of the internal branch | 35-100 (cm/sec) |
Different vessels included in the brachiocephalic zone have their own sizes. For the common carotid artery, the optimal vessel resistance index is from 0.6 to 0.9. In this case, the systolic blood flow velocity is 55-105 (measured in cm/sec).
Preparing for the study
The tactics for preparing for triplex scanning are determined by which anatomical zone will be examined. Thus, when scanning the abdominal cavity, it is prescribed to follow a gentle diet for 3-5 days and carry out the procedure on an empty stomach. But the triplex of vessels of the neck, head, arms and legs does not require special preliminary preparation from the patient. It is recommended on the eve of the procedure not to smoke, not to drink alcohol or tonic drinks, and also to refrain from taking drugs that change vascular tone (the latter if possible).
In most cases, the diagnostic test time does not exceed 60 minutes. The diagnostician's report is issued immediately upon completion of the procedure.
Detectable diseases
The price of duplex scanning of brachiocephalic vessels is quite affordable and is presented below in the price list. Thanks to this study, you can diagnose:
- atherosclerosis;
- angiopathy;
- varicose veins;
- vascular damage;
- changes in the tone of the vascular walls, which can occur with VSD.
Khizriev S.M. considers ultrasound an important diagnostic method that is used to study the anatomy of the vessels of the head and neck. During the procedure, the tortuosity of the arteries and the presence of atherosclerotic plaques are revealed.
Causes of vascular system disorders
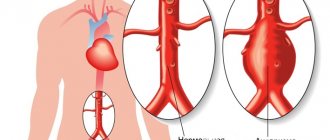
The main cause of pathological changes in the brachiocephalic vascular system is atherosclerotic lesions of the arteries. A study of people in relatively good health showed the presence of atherosclerosis in the initial stage in 3 percent of those examined. Their age ranged from 40 to 50 years. This result may indicate a fairly high probability of stroke in people after 55-60 years of age.
Atherosclerotic changes are considered an indirect cause of structural changes in blood vessels. For example, the appearance of tortuosity.
Treatment
Treatment of BCA diseases is aimed at:
- Normalize blood supply;
- Prevent further progression of atherosclerosis and narrowing of the artery lumen.
- Eliminate unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
Drug therapy is used, which includes taking drugs that reduce cholesterol levels, the excess of which is deposited on the vascular walls. The patient is prescribed medications to normalize blood pressure and strengthen blood vessels. When treating any pathology of the cardiovascular system, secondary prevention is important - it allows you to minimize risk factors.
Severe lesions are eliminated surgically: in the treatment of stenoses of the brachiocephalic vessels, open operations or innovative and painless methods of vascular reconstruction are used. The latter include balloon angioplasty and stenting. These minimally invasive operations help restore the vascular lumen and prevent further stenosis.