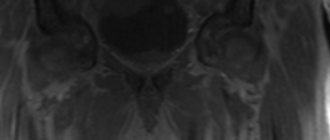
Cholangiography is the study of the bile ducts using X-rays or MRI using a special contrast agent.
We can say that the procedure gives a complete picture of the excretion of bile at a specific moment and identifies for the doctor various obstacles that interfere with the normal functioning of the system. This is about:
- Stones;
- Tumors;
- Cicatricial narrowings.
Indications
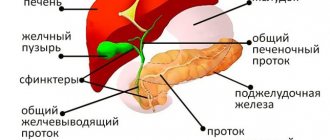
Bile, synthesized by liver cells, accumulates in the gallbladder, so to speak, the closest neighbor of the liver.
After eating, some time later, bile from the bladder enters the duodenum. There it interacts with food that is not completely digested. The task of bile is to break down food components into their component parts.
The bile duct connects the bladder and duodenum. It is where the pancreatic duct enters a little higher.
As we have already noted, the described procedure helps to understand what interferes with the normal functioning of the system. To do this, a contrast agent is used, and on the same x-ray the structure of the ducts, their patency and the interference created by the narrowings become visible. That is, the doctor gets the opportunity to understand what caused the system to malfunction.
Research is requested in the following cases:
- Jaundice of non-infectious nature;
- Pancreatic cancer;
- Inflammatory processes in the pancreas with frequent exacerbations;
- Suspicion of fistulas between the pancreas and duodenum.
When the exact cause of the disease is established, the procedure can develop from diagnostic to therapeutic.
MRI with contrast
If it is necessary to obtain the most accurate image, cholangiography using a contrast agent is prescribed. This is a gadolinium-based composition that is safe for the human body and is eliminated from it within a few hours after the test. The principle of operation of the contrast agent is that it has the ability to accumulate in areas of intense blood supply, the presence of which is an indicator of inflammatory processes and changes in tissue structure. The contrast provides clear visualization of focal liver lesions and allows one to assess their number, size and location. It also provides information on the characteristics and classification of liver lesions, which also has a positive impact on the accuracy of the diagnosis.
Contraindications for the study
There are contraindications to the study. We will present some of them to make it clear that some are absolute and some are relative.
The procedure is absolutely unacceptable for people with:
- Pacemakers;
- Insulin pumps;
- Clips on brain vessels that stop blood;
- Electronic, ferromagnetic middle ear implants;
- Non-ferromagnetic inner ear implants.
Among the relative restrictions:
- Pregnancy in the first trimester;
- Fear of confined spaces;
- Uncontrolled motor activity.
Diseases
The wide diagnostic capabilities of MR cholangiography allow the method to be used for the following diseases:
- cholelithiasis (acute or chronic version of cholecystolithiasis, stones in the bile ducts);
- acalculous inflammation in the biliary tract (cholecystitis, cholangitis);
- benign and malignant tumors of the hepatobiliary system;
- abnormal structure of the bile ducts;
- traumatic damage to the ducts with the formation of stenosis and strictures.
MR cholangiography image in 3D
The maximum diagnostic information can be obtained by using MR cholangiography in the following situations:
- preparation for surgery on the hepatobiliary system;
- control after bile duct surgery;
- diagnosis of the causes of jaundice;
- examination for postoperative complications.
The MR-CPG method is indispensable for oncological pathology. A tomographic image will show the presence of a tumor in the following organs:
- gallbladder;
- bile ducts;
- head of the pancreas;
- liver.
Often, it is during MR-CPG that the doctor, with a high degree of reliability, will be able to timely make the correct diagnosis and refer for surgical treatment.
Kinds
Contrast can enter the bile in two ways:
- When mixed directly with bile in the duct;
- After intravenous administration.
There are several ways to directly mix the contrast agent with bile:
- Retrograde (countercurrent version of the study of RCP, ERCP). This option is considered today the “gold standard” for detecting pathology of the bile excretion process.
- Transhepatic option. A contrast agent is injected into the large bile duct through the peritoneal wall. Typically, this procedure option is chosen before surgical manipulation.
- Transdermal option. It is performed during laparoscopy. Contrast is injected into the gallbladder using a needle.
- Fistulographic option. Usually used in the presence of fistulas.
How does the contrast agent get into the blood? There are several options:
- Intravenous method;
- Magnetic resonance method.
When performing the latter, puncture of the bladder and bile ducts is not necessary. In addition, this option is highly informative in terms of diagnostics. However, there are also disadvantages: in the presence of stones, it is not as effective as ERCP, and it is also expensive.
If we take time as the basis for classification, then the study can be:
- Preoperative (ERCP is often performed);
- Intraoperative (a catheter is inserted into the duct during surgical manipulation);
- Postoperative (more often this option is used to monitor the result of surgical manipulation. The contrast agent is supplied through an installed drainage catheter.
Medical practice gives leadership to ERCP. This is where a high degree of sensitivity and high accuracy of diagnosis are combined.
How is it carried out?
Before the procedure, the patient must provide the diagnostician with information about whether there are implants made of metal or its alloys in his body. Despite the fact that they are not an absolute contraindication, there is a risk of their negative impact on image quality. In addition, they can manifest themselves differently under the conditions of a powerful magnetic field that is formed during the procedure. That is why, before an MRI, our specialist must assess the risk of performing the procedure in the presence of implants and, if necessary, may refuse to perform it.
If the study is approved, the patient is asked to remove all metal objects and is asked to lie down on a mobile medical couch that slides into the scanner. The procedure lasts about 30 minutes, during which the patient cannot move. If necessary, he has the opportunity to contact the radiologist via the public address system. Upon completion of the study, the patient is given a disk and transcript.
Preparation of ERCP
We will talk about preparation for ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography).
In order to conduct this study, the patient must spend some time in a medical facility. This is mainly due to preparation for manipulation and minimizing possible undesirable consequences.
Before the procedure, the patient takes special medications. This is important for its beneficial effects on the nervous system and relaxing muscles of the gastrointestinal tract.
Twelve hours before the study, the patient stops eating, but even earlier (at least a day before) refuses food containing coarse fiber and products that cause gas formation:
- Soda;
- Cabbage;
- Fruits;
- Black bread;
- Kefir, etc.
If gas formation is increased, the patient takes the drug prescribed by the doctor. It could be, for example, “Espumizan”. All other actions related to taking medications are strictly regulated by the doctor.
Symptoms
Indications for MR cholangiography are the following symptoms and external manifestations:
- pressing sensation or nagging pain on the right side and in the hypochondrium;
- severe pain syndrome (biliary colic);
- digestive symptoms (nausea, vomiting, stool instability, flatulence, bitterness in the mouth) associated with eating fatty foods;
- change in color of the skin and mucous membranes (yellowness);
- temperature reaction.
Severe pain in the right side, increased temperature and a yellow tint to the skin is a reason to call emergency medical help. If pressing pain on the right in the hypochondrium occurs every time in response to errors in the diet, then it is advisable to do an MRI diagnosis so as not to waste time. At the first stage, at the clinic, the doctor will prescribe tests and refer you for an ultrasound, where it is not always possible to immediately identify the cause of the pain syndrome.
Methodology
The combination of endoscopic examination and x-ray is very effective. Here the doctor has the opportunity to obtain important information necessary to prescribe subsequent treatment.
The research can be divided into several stages:
- Endoscopic. The esophagus, stomach, and duodenum are examined.
- Insertion of the catheter.
- Filming the localization of the contrast agent and the process of advancing the endoscope.
- Carrying out a biopsy.
- If stones are found, they are destroyed and removed.
- Installation of a stent or drainage catheter if the duct is narrowed.

Fistulography
Complications
ERCP involves intravenous injection, that is, an invasive procedure, plus a contrast agent that is foreign to the body is used. The most common, but in fact very rare complication is inflammatory changes in the delicate tissue of the pancreas - on average three per hundred patients. It manifests itself clinically as pancreatitis - abdominal pain, threefold increase in a specific blood enzyme - amylase. As a rule, the complication develops already on the first day and resolves within a couple of days. Our clinic has developed a method for reducing and preventing this type of ERCP complications.
Bleeding from the site of manipulation is twice as rare when a vessel is damaged during dissection of the duodenal papilla in a patient with blood clotting disorders, which often occurs with prolonged or severe jaundice.
Rupture of the duct is possible in one or two patients out of a hundred, which is due to the looseness of the tissue with reduced extensibility due to scars. The complication can be successfully treated if detected early.
And the most common and common thing is an allergic reaction to a contrast agent. Moreover, repeated examinations using contrast do not guarantee its absence in the future; allergies arise according to the principle: it was not there yesterday, but today it arose.
Cholangiography at Euroonco is performed by experienced medical specialists using modern equipment. Find out more, contact us.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
When should you do MR cholangiography?
“ Is MRI harmful for children? " is one of the frequently asked questions among parents.
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the influence of a strong magnetic field on the human body and does not carry any radiation exposure, unlike fluorography, X-rays and CT. Therefore, MRI can be performed on patients of any age, including newborns and pregnant women, if there are any indications. Unlike MRI, CT scans are prescribed for children, especially younger children, in special cases when the benefits of the examination outweigh the potential risks.
To obtain clear and high-quality images, the main condition for performing MRI on children is to ensure that the child remains completely still throughout the entire scan - from 15-20 minutes or more, depending on the volume and area of study. While children over 3-4 years old can lie quietly for a long time on their own, younger patients will not be able to maintain a motionless position for a long time. Therefore, young children require medicated sleep or anesthesia. MRI under general anesthesia is performed under the strict supervision of an anesthesiologist, and may require necessary tests.
To ensure the child’s comfort during an MRI without anesthesia, the examination can be performed on open tomographs, the design of which does not have a closed tube, and a loved one can be next to the small patient, talking with him or reading a book. It is important to remember that open devices have an important drawback - they have lower resolution and accuracy of images.
MRI of newborns and infants is performed in the presence of intrauterine developmental defects, to identify disorders that were obtained during childbirth, life-threatening diseases of the child, as well as when planning surgical treatment. For children older than this, MRI is performed if there is a suspicion of space-occupying formations, disturbances in the anatomical and functional state of organs and tissues, to study the consequences of injuries, if the child’s development does not correspond to age standards (for example, with delayed speech development, reflex activity), etc.
When answering the question at what age can children undergo MRI , it is worth noting in what mode the study is performed - with or without contrast enhancement. As mentioned above, MRI without contrast is allowed for children without age restrictions. The use of many contrast agents for examination of children under 4 weeks of age is prohibited due to incomplete information about the safety of their use. Also, for children under 1 year of age, contrast enhancement is performed only after assessing the benefits and all possible risks, because At this age, kidney function is not yet fully developed. In this case, contrast agents are administered in a special dosage, and repeated administration of contrast during one screening is not allowed.
MRI plays an important role in modern pediatrics, since it is an informative, fast and safe method of diagnosing a wide range of pathological conditions.