Procedure
The examination itself is carried out as follows. The person exposes his stomach and lies on the couch in a supine position. The doctor applies a special gel to the study area and to the sensor to improve gliding. First, the scan takes place in the middle of the abdominal line, and then shifts to the left by 10 cm. In this way, the doctor gradually changes direction and consistently moves the sensor across the scanning area. Detailed images of the spleen and adjacent tissues appear on the device’s screen. If the patient has an abnormal development of the spleen, it may be difficult to perform an ultrasound scan. In this case, the doctor changes the patient's position. The solution to the problem is to lie on your right side. The patient raises his left hand behind his head, inhales deeply, and while holding his breath, the doctor scans the spleen through the intercostal space.
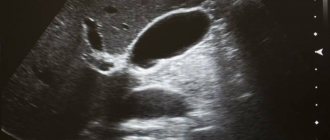
What does the spleen look like on an ultrasound?
Preparation
Ultrasound of the spleen is performed in the morning, on an empty stomach. The most accurate result of the study is possible subject to high-quality preparation for the procedure:
- The last meal should be at least 7-8 hours before the examination. An exception is for patients with diabetes: they are allowed to have a light snack in the morning (ideally tea with crackers).
- 2 days before the procedure, it is necessary to adjust the diet - exclude foods that contribute to gas formation (beans, raw vegetables, black bread, carbonated drinks, dairy products, etc.). This is necessary to prevent fermentation in the intestines: air prevents inspection of the spleen and distorts the result.
- It is recommended to take sorbents and enzyme preparations that stimulate digestion (smecta, festal, mezim, etc.).
- If a person has increased gas formation, then he is additionally advised to take activated charcoal on the eve of the procedure. The dosage is calculated individually at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol are prohibited at least 24 hours before the procedure, as this can cause stomach spasms, which in turn will distort the results.
Preparing for an ultrasound of a child is somewhat more complicated, since he needs to be prepared not only physically, but psychologically. Although this procedure is completely painless and safe, the child may experience overwhelming anxiety and fear. It is possible to reduce the examination procedure to a kind of game.
There are also difficulties in the area of nutrition. Children do not always tolerate hunger well, especially for infants and children under 3 years of age. A pause in feeding a baby must be made 3 hours before the ultrasound, in children 2-3 years old - 4 hours, over 3 years old - at least 6 hours. Do not drink for 1 hour.
Ultrasound of the spleen: normal
Normally, ultrasound examination of the spleen:
- echogenicity should be average;
- the vein size is no more than 5 mm, a vascular network is allowed in the area of the organ’s hilum;
- crescent shape;
- the organ is located in the abdominal cavity on the upper left side;
- with an oblique cut, the size of the organ is 12 cm;
- in a transverse section, the size of the organ is up to 8 cm;
- organ thickness is about 4 cm;
- spleen weight 150-250 grams.
In a healthy person, the stomach should be located at the center of the spleen or slightly lower, the tail of the pancreas should be at the middle of the organ’s gate. The left kidney is located slightly lower in the middle of the spleen. Normally, the structure of the spleen should be homogeneous and the contour continuous.
Description
The largest internal organ in the human body is the liver.
Its weight varies from 1.2 to 1.5 kg. The location of the liver is the right corner of the abdominal cavity. The liver plays a vital role in maintaining a constant internal environment and ensuring protein synthesis. In addition, this organ synthesizes biologically active compounds, regulates fat, carbohydrate, and protein processes. The liver secretes bile, which breaks down fats. Another organ of the digestive system is the gallbladder. It acts as a kind of reservoir where bile accumulates. The liver constantly synthesizes bile, but it is not always necessary. Therefore, first of all, bile accumulates in the gallbladder, and then enters the duodenum.
What will an ultrasound of the spleen show?
If the ultrasound readings of the spleen are outside the normal range, the doctor should suspect the presence of pathology, for example:
- hematological syndrome;
- anemia;
- leukemia;
- Congenital heart defect;
- typhoid fever;
- tuberculosis.
An enlarged spleen in childhood occurs with impaired liver function and leukemic infiltration. If in an adult the size of the spleen is not enlarged, the edge of the organ is pointed, there is an excessively convex contour, there is an increased density of parenchyma and inflammation of the lymph nodes at the gate of the organ - all this indicates a splenic abscess. Transformation of the echo structure is a sign of the appearance of a cyst. Signs of a hematoma on ultrasound will be a mixed or anechoic echo structure. Uneven borders of the organ contour may be symptoms of a ruptured spleen. Signs of a splenic infarction on ultrasound are the appearance of fluid in the abdominal cavity or under the diaphragm and an irregular shape, an uneven, deformed contour of the organ. Unfortunately, not all spleen diseases can be seen using ultrasound. For example, oncological pathologies will require a CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity with contrast. However, if the medical center has an expert-class ultrasound machine, the doctor can identify tumor formations by the area of the largest section. To do this, the doctor multiplies the largest linear dimension by the smallest. In a healthy organ, the figure is 15.5 - 23.5 cm2. If there are deviations from the norm, education should be suspected.
| Ultrasound service | Price according to Price, rub | Promotion price, rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach) | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of one organ (liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, bladder, adrenal glands) | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the bladder | 2000 rub. | |
| Kidney ultrasound | 800 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland) | 2400 rub. | 1999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
Classification, stages
“Spleen cancer” is not quite the correct term. Strictly speaking, cancer refers to tumors that originate from epithelial tissue. In the spleen, malignant neoplasms develop from other types of tissue. Their classifications have changed over time and differ among different authors. Currently, doctors are often guided by the L. Morgenstern classification, developed in 1985. In accordance with it, all malignant tumors of the organ are divided into three large groups: vascular, lymphoid and non-lymphoid:
| Examples of vascular tumors |
|
| Examples of lymphoid tumors |
|
| Examples of non-lymphoid tumors |
|
Lymphomas most often occur in the spleen. However, primary organ damage is a rare occurrence. It is known that in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma the spleen is involved in 50–80% of cases, and this often occurs in Hodgkin's disease.
The most common vascular malignant tumor in the spleen is angiosarcoma. However, it is a very rare disease - it affects 1-3 people in ten million. Angiosarcoma originates from the tissues of the vascular wall, is highly aggressive, and quickly metastasizes.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
results
After the screening is completed, the patient receives a research protocol, which will indicate the location of the spleen, its shape and size, tissue structure, condition of the capsule, diameter of the vessels, and the calculated area of the maximum oblique cut. The doctor's report will contain a list of all identified pathologies. With the ultrasound results obtained, the patient should be referred to the attending physician for a final diagnosis and treatment.
Alternative Research
In medicine, there are many methods for examining the spleen:
- Ultrasound.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging.
- Radionuclide scanning.
- Puncture.
Ultrasound of the spleen has many advantages over other methods.
- Painless – the study does not require invasive procedures. Then, like a biopsy (tissue sampling for further analysis), although it is carried out with anesthesia, the procedure is still unpleasant.
- Short duration - obtaining the necessary information about the condition of the organ and making a preliminary diagnosis takes only 15 minutes.
- It has no contraindications, which allows the procedure to be performed many times. And this is very convenient for monitoring the course of the disease and adjusting treatment.
- Affordable cost – ultrasound has the lowest price among all methods.
Ultrasound or MRI of the spleen - which is better?
In addition to ultrasound, there are other non-invasive methods for studying the spleen - these are CT and MRI of the abdominal organs. The main advantages of spleen ultrasound compared to tomography are:
- no contraindications;
- inexpensive and generally available.
However, the information content of MRI of the spleen is certainly higher than ultrasound examination. Therefore, if alarming signs of inflammation or tumor lesions are detected, the patient will be referred for further examination to an MRI of the abdominal cavity.
Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience
Indications for ultrasound diagnostics
The content of the article
The spleen (splen) is the largest lymphoid parenchymal organ. It has a peculiar shape of a flat hemisphere. The spleen is located in the upper left part of the abdominal cavity, behind the stomach.
Despite the fact that the organ is not considered vital, it performs the most important functions, which, by the way, are still not fully understood:
- Lymphopoiesis
- the production of antibodies and circulating blood lymphocytes - a kind of filter for bacteria, foreign particles and protozoa. - Destruction of damaged red blood cells and platelets
. The spleen, through the destruction of blood elements, participates in the formation of bile and iron metabolism. - Platelet accumulation
. The organ stores a third of all platelets. - Production of lymphocytes and monocytes
. - Hormonal regulation of bone marrow function
.
The procedure is carried out both for individual indications, in which case the doctor examines this particular organ, and for standard diagnostics of the abdominal cavity. The circulatory system of the spleen is interconnected with the vessels of other organs, and its tissues react to any abdominal pathology, so the organ must be examined during an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Ultrasound of the spleen is prescribed for the following disorders:
- All groups of blood diseases.
- Increased size of the spleen.
- Oncological diseases or suspicion of their presence. Determination of the location and degree of localization of metastases.
- Improper development of the organ. Congenital anomalies (absence of an organ, “wandering” spleen, several spleens, etc.).
- Abdominal injuries.
- Numerous infectious diseases, including sexually transmitted infections (syphilis, malaria, sepsis, typhus, etc.).
- Liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis, etc.). Determination of foci of purulent processes.
- Monitoring the results of prescribed treatment.
Abdominal injuries, falls from heights, and traffic accidents are especially important indications for examining the spleen, since rupture of the organ, accompanied by blood loss, can be fatal.