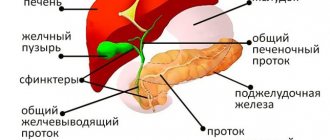
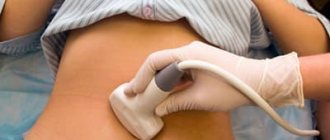
The gallbladder is classified as an auxiliary organ of digestion. Its main task is the accumulation of bile, which is produced by the liver. Our body needs bile to digest animal fats. Therefore, disturbances in the functioning of the bladder are accompanied by digestive disorders and pain in the right hypochondrium. In this case, the patient undergoes an ultrasound of all abdominal organs, during which the gallbladder is examined.
- What it is?
- Who is prescribed an ultrasound of the gallbladder?
- How should you prepare for an ultrasound?
- How is the procedure done?
- What are normal indicators for the gallbladder?
- What pathologies of the gallbladder can be detected on ultrasound?
Indications
An ultrasound scan of the gallbladder and bile ducts can be performed either upon the direction of the attending physician or on personal initiative. The following symptoms may suggest the advisability of checking this body:
- regular feeling of nausea;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth after eating;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- regular heaviness in the stomach after eating;
- sudden loss of appetite;
- jaundice;
- acholic stool;
- biliary colic;
- palpable formation;
- heartburn.
You should undergo a diagnosis if you begin to gain excess weight, severe poisoning or injury to internal organs occurs. If you decide on your own initiative to examine your gallbladder, it is best to start your diagnostic journey with a comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, which includes a scanning protocol for this organ.
Classification of techniques
Typically, patients undergo a standard ultrasound examination, which does not take much time, providing extensive results. The most important advantage of this method is its harmlessness, making the study possible for children under one year old and pregnant women.
Content:
- Classification of techniques
- Dynamic echo-choledochography
- Indications for use
- Proper preparation
- Diagnosed diseases
It does not carry radiation exposure, as happens when using modern analogues such as computed tomography or radiography.
In the absence of a primary diagnosis, in case of discomfort or other ailments in the abdominal area, the patient will be recommended to undergo an ultrasound of all abdominal organs.
If a chronic gastrointestinal disease is known, then an ultrasound scan of a specific organ is possible.
If necessary, according to the results obtained, to confirm or refute a particular disease, they resort to more accurate examinations performed on a magnetic resonance or computed tomograph.
For most potential patients in the gastroenterology department, a so-called simple ultrasound is sufficient. It involves the use of a standard apparatus together with a highly sensitive sensor. For better contact of the signal converter sensor with the skin during the study, a special gel is used. It does not cause an allergic reaction and is safe even for people with hypersensitive skin.
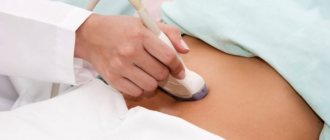
To prepare for the procedure, you must take care in advance to come to the examination in comfortable clothing so that you can free up the area being examined for examination. During the procedure, the diagnostician moves the sensor along the abdominal wall, contacting the organs through ultrasonic waves, displaying their image on the monitor.
It often happens that the bottom of the bladder is covered with intestinal loops. To improve your visibility, you will need to take a deep breath and then hold your breath. Next, the patient turns over onto his left side to open the organ from a different viewing angle.
If necessary, check the functional ability of the gallbladder, perform an ultrasound with a load on the gallbladder. In this procedure, after a simple ultrasound examination on an empty stomach, the patient is offered a choleretic breakfast consisting of sour cream 20-25% fat, cream or a sandwich with butter. This fat load promotes the synthesis of bile, and the contractility of the gallbladder will be visible during the study.
What will an ultrasound of the gallbladder show?
Ultrasound examination data will detect signs of the following diseases:
- chronic and acute pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- cholelithiasis;
- “porcelain gallbladder” syndrome;
- cholangiocarcinoma and Courvoisier's sign;
- gallbladder carcinoma;
- gallbladder polyps;
- cysts of the gallbladder and common bile duct;
- calcification of the gallbladder walls.
Unfortunately, ultrasound images are not accurate enough to definitively judge the malignant or benign potential of a mass, so if the ultrasound yields alarming results, the patient will be sent for further evaluation with MRI or CT cholangiography. If gallbladder polyps are detected on ultrasound, a repeat examination is usually prescribed after 2-3 weeks. If there are signs of rapid growth, then there is a possibility of their development into a malignant formation. Ultrasound scanning of the gallbladder in children reveals developmental anomalies, atypical location, double gallbladder or no gallbladder at all. Any deviations from the norm will require a repeat scanning procedure after 15-20 days to monitor the dynamics of the process or a more high-tech study - CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity for final diagnosis.
| Ultrasound service | Price according to Price, rub | Promotion price, rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach) | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of one organ (liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, bladder, adrenal glands) | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the bladder | 2000 rub. | |
| Kidney ultrasound | 800 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland) | 2400 rub. | 1999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
Dynamic echo-choledochography
A similar procedure with a choleretic breakfast to assess the functional activity of the common bile duct - common bile duct. After waiting at intervals of half an hour after breakfast, the examination is carried out again to determine the difference in tone that has arisen.
At the same time, the laboratory assistant must write down all the patient’s incoming complaints regarding:
- intensity of pain attacks;
- features of the disease state;
- increase in pain;
- duration of the attack.
How is an ultrasound of the gallbladder performed?
There are two directions for performing ultrasound of the gallbladder - abdominal and ultrasound of the gallbladder with a functional test.
Abdominal ultrasound of the gallbladder
An abdominal ultrasound of the gallbladder is a simple scanning method. It takes place in one stage and requires less time. The patient will have to remove clothing from the abdominal area and lie down on the couch. The diagnostician lubricates the device's sensor and the patient's examination area with a water-based gel. This will make it easier to glide during the examination and will prevent the formation of an air gap between the body and the sensor, which in turn will increase the passage of ultrasonic waves to the organ. The ultrasound procedure usually takes place in the supine position, but if the examination is interfered with by intestinal loops that may cover the organ, the sonologist asks the patient to take a deep breath and not exhale for as long as possible. In cases where the patient needs to be checked for the presence of stones or sand, the diagnostician asks the patient to bend forward several times from a standing position.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder with functional test
The second research method is carried out to determine the function of the gallbladder in real time. This method is called ultrasound of the gallbladder with a functional test, ultrasound with a choleretic breakfast, or echocholescintigraphy. This scanning is carried out in two stages. The first, the basic stage, includes a simple abdominal examination on an empty stomach. After it, the patient eats a choleretic breakfast (250 grams of cottage cheese, 2 egg yolks), and the diagnostician repeats the scan with a time interval of 5-10-15 minutes. This gives a chance to track and analyze the contractile function of the organ.
Ultrasound after gallbladder removal
If a patient's gallbladder has been removed, ultrasound diagnostics also takes place in several steps. The first step, on an empty stomach, the doctor assesses the condition of the bile ducts and their diameter, and the second step carries out diagnostics after a food load. First, the subject drinks a sorbitol solution, and then the doctor performs an ultrasound scan half an hour and an hour after taking the drug. During the second stage, the doctor records all the patient’s complaints about pain, type and characteristics, duration, intensity or complete absence of pain.
Method of implementation
A sensor is used to determine the condition of the organ with further diagnostics. It is adjusted to the abdominal wall to make the ultrasound procedure easier. In order for the research to be carried out efficiently, it is necessary to free up space where the sensors will be installed. It is also necessary to get rid of the air that has formed between the body and the sensor so that there are no failures. In this case, the accuracy of the readings increases.
There are times when loops in the abdomen interfere with the correct diagnosis. You need to take a deep breath, or turn on your side. Ultrasound examination of internal organs is often necessary, since it is difficult to determine the extent and main nuances of the disease just by symptoms.
Contraindications
This diagnostic method has no contraindications, with the exception of diseases or injuries of the skin in the abdominal area. For high-quality ultrasound diagnostics, good contact of the sensor with the patient’s skin is necessary. The presence of tuberosity of the skin does not allow this to be achieved. As a result, image quality decreases and ultrasound data may be uninformative.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the gallbladder?
Preparation for an ultrasound of the gallbladder is required, but it is simple and does not differ fundamentally from the organizational issues associated with preparation for any other type of ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space. Diet. 3 days before the scan, you should start by changing your usual diet to a special diet that excludes foods that cause gas formation in the intestines. You should not eat yeast-based baked goods, carbonated and alcoholic drinks, kefir, milk and other fermented milk products, peas and legumes, raw fruits and vegetables, and coffee. Boiled foods, porridge cooked without milk, lean meat, chicken or fish are suitable for the menu these days. Drugs. On diet days, you should start taking activated carbon at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of weight. You can take charcoal at once or divide it into several servings. As an alternative to activated carbon, such drugs as Smecta, Mezim-Forte, Espumisan, and Motilium are suitable. The choice of enzyme preparations in pharmacies is large. Colon cleansing. It is advisable to cleanse the intestines naturally on the day of screening. Only in case of constipation, a small enema can be used for cleaning. Starvation. An ultrasound scan of the gallbladder is performed strictly on an empty stomach, since even a small amount of water drunk will cause the gallbladder to contract, and this will significantly complicate the diagnostic process. If the scan is scheduled in the morning, then breakfast should be canceled; if in the afternoon, a small snack is allowed 6 hours before the procedure. This can be unsweetened tea and a small cracker.
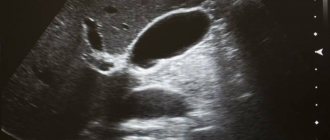
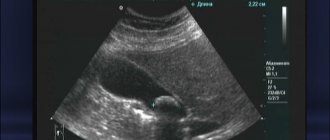
Decoding and norm
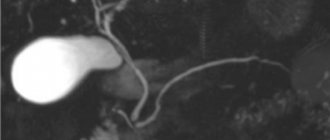
Normally, on ultrasound, the gallbladder should have a pear-shaped or oval shape with smooth and clear contours.
Any deformation of the shape or contour of an organ will indicate pathology. For example, acute cholecystitis will manifest itself as increased blood flow, thickening of the walls, multiple internal partitions and enlargement of the organ itself. In chronic cholecystitis, the size of the gallbladder will be smaller than normal, the walls are thickened and deformed, the contours are not clearly visible, and there are small inclusions. If a bend in the gallbladder and increased wall tone are visualized, this indicates dyskinesia. The final diagnosis based on the screening results can only be made by a specialized specialist. It is to him that the patient should go after the sonologist gives him the examination protocol.
Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience
Service cost*
| NAME | PRICE (Kolomenskaya) | PRICE (Vidnoe) |
| Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder and ducts (using a Voluson, Mindray, Logiq device) | 1200 rubles | 1200 rubles |
| Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder with determination of its contractility (on the device Voluson, Mindray, Logiq) | 1900 rubles | 1900 rubles |
We accept payment:
*Attention! The indicated prices are provided as reference information and do not constitute a public offer. Check current prices by phone and directly in clinics.