What does expansion of the heart to the left mean?
The average weight of this cone-shaped hollow muscular organ in an adult man is approximately 300 grams, in a woman - 250 grams. Its dimensional characteristics are comparable to the size of a clenched fist: longitudinal size - 12 centimeters, transverse - 8-9 centimeters, anteroposterior - 6 centimeters.
An expansion or increase in the volume of an organ is called cardiomegaly. If it is expanded on the left, this is a symptom of transformation of the left ventricle, which means hypertrophy of the heart muscle. This sign means that it has become larger in diameter.
As a rule, the increase in volume occurs on the left side. This may be a manifestation of hypertension (hypertension), blood stagnation in the systemic circulation, and other pathologies. Sometimes this phenomenon is called “bull’s heart”.
Causes of pathology in adults
Provoking factors for cardiomegaly can be:
- diabetes;
- hypertension;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- the onset of pregnancy;
- anemia (anemia) – a decrease in the level of hemoglobin protein in the blood, which is responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood;
- renal failure;
- alcohol abuse;
- rheumatism – inflammation of the connective tissue structures of the cardiovascular and musculoskeletal systems;
- ischemia – impaired blood supply to the myocardium;
- Myocardial infarction – damage to the heart muscle. It develops with an acute lack of oxygen. Occurs due to blockage of a blood artery by a blood clot. Subsequently, the damaged areas die off. The process of their death is called necrosis;
- athletes with enlarged heart muscle undergoing irregular training;
- genetic predisposition;
- cardiomyopathy - thickening of the walls of the ventricles, stretching of the cavities of the heart.
The described pathology does not manifest itself in any way at first, but over time, with increasing loads, the following symptoms may appear:
- a condition characterized by shortness of breath, fatigue;
- swelling in the lower extremities;
- the appearance of a feeling of heaviness on the right under the ribs;
- cephalalgia, tinnitus;
- causeless cough.

Enlarged heart in children
An increased volume of an organ in children can be a congenital pathology, which will subsequently cause serious health problems. It is important to identify such deviations from the norm immediately - from the first days of a child’s life to six months.
Cardiomegaly in children can occur due to the presence of an inflammatory process of connective tissue in the body - rheumatism. This disease, in turn, can appear as a complication after a sore throat, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, or with some types of caries. It is acquired and develops regardless of the child’s age.
Signs of the described pathology in children may be:
- weakness;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the sternum area;
- fever 1-2 weeks after recovery from tonsillitis;
- sweating;
- increased fatigue;
- pain in muscles, joints.
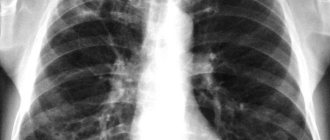
The reasons for the appearance of signs of an enlarged heart on a fluorography image may also be:
- hypertrophic cardiomyopathy - manifests itself in thickening of the wall of the ventricle, most often the septum between the ventricles;
- myocarditis is an inflammatory process in the heart muscle. It can be of viral, fungal, bacteriological origin, or may appear due to autoimmune problems or improper use of medications;
- endocarditis – inflammation of the endocardium (inner lining);
- pericarditis is an inflammatory process in the serous membrane.
The last two pathologies in minor patients are quite rare.
If the described symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor; it is highly undesirable to leave this situation without proper attention.
Right ventricular hypertrophy
The right ventricle allows blood to pass through and pushes it deep into the vessels connecting to the lungs. It is enriched with oxygen. Due to the fact that the right side of the heart and lungs are connected, various difficulties with the respiratory system lead to cardiomegaly.
The right ventricle is 3 times smaller in volume than the left, therefore the electrical activity of the latter is higher. The increase can be pronounced when the mass of the right one exceeds the left one. With moderate expansion, the sizes of the ventricles do not vary. Insignificant excitement is noted. At the initial stage of the disease, symptoms are mixed or absent at all. If there is a tendency towards stable expansion, symptoms are expressed in difficulty breathing, a feeling of heaviness in the chest, and the appearance of painful discomfort.
In addition to these signs, the patient experiences fluttering or freezing and delayed heartbeat. Possible dizziness and unconsciousness.
What additional diagnostic measures are taken?
To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment, the following types of examinations are required.
- X-ray of the sternum area. You can notice an expanded shadow of the heart group and determine congestion in the circulatory system.
- Electrocardiography (ECG).
- Echocardiography (EchoCG). Allows you to determine the parameters of the heart muscle, the size of the chambers, identify necrosis (death of cells/tissue areas) or ischemic disease (impaired blood supply to the myocardium due to damage to the arteries).
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the heart muscle.
- Computed tomography (CT).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Immunological and biochemical blood tests. They determine the levels of hemoglobin, bilirubin, protein, hormones and urea.
The doctor will be able to prescribe adequate treatment only after making a diagnosis. And to determine the disease, the doctor carefully examines not only the data of hardware examinations, but also the results of clinical tests, as well as the clinical picture.
Treatment
For almost any disease with a symptom of heart enlargement to the left on fluorography, doctors recommend leading a healthier lifestyle, adhering to a special diet, which means avoiding spicy, fatty and salty foods. Patients are advised to give up bad habits and may be prescribed special exercises.
As a rule, medications from the following groups are prescribed for cardiomegaly:
- angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors;
- angiotensin receptor blockers;
- beta blockers;
- diuretics.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
Such drugs dilate blood vessels and lower blood pressure, reducing the workload on the cardiovascular system. The drugs have the following names: Enalapril, Captopril, Lisinopril. A side effect is often a dry cough.
Angiotensin receptor blockers
Being analogous to ACE inhibitors in terms of pharmacological effect, these drugs do not cause a dry cough as a side effect.

Beta blockers
The use of beta blockers helps reduce heart rate and normalize blood pressure. However, such drugs are only auxiliary in treatment.
Diuretics
Diuretics (diuretics) can improve blood flow to the heart and help lower blood pressure. The names of these drugs: Chlorthalidone, Hydrochlorothiazide.
It is not recommended to resort to self-medication; only a doctor can make a diagnosis and determine an effective drug therapy regimen.
Surgery may also be required. It consists of restoring or completely replacing the arterial valve. In severe cases, a whole organ transplant is necessary.
Prevention
Prevention of cardiomegaly can be a change in lifestyle. One of the main factors in the occurrence of heart pathologies is obesity. It is recommended to maintain a normal body mass index. Losing weight if you are overweight, against the background of an already enlarged heart, helps stabilize the condition.
A special diet is recommended to prevent cardiovascular diseases. It is advisable to consume fish, soybean, flaxseed, corn or olive oil at least twice a week. To strengthen the heart muscle, you need to eat cranberries, cabbage, viburnum, eggplants, peaches, dried apricots, apples, pomegranates, walnuts, melon. To normalize blood pressure, you need to avoid excessive consumption of salt and salt-containing foods. In addition, it is advisable to reduce the consumption of alcoholic beverages or completely abandon them.

Although an increase in heart volume may be caused by intense physical activity, in moderate doses, sports activities can only benefit the patient. Thus, yoga, Pilates, and walking will help strengthen the heart. If hypertrophy has already been identified, it is better to consult a physiotherapist. He will help you choose a set of therapeutic exercises, designed for about half an hour. Regularly performing this set of physical activities will reduce the volume of the heart muscle.
Eight hours of sleep and avoidance of excessive physical and emotional stress are helpful. In addition, regular walks outside are recommended.
Thus, a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition will help minimize the risk of complications with an enlarged left ventricle.
Clinical manifestations
To understand what an enlarged heart means, it is necessary to identify its manifestations. The most common symptom indicating changes inside the left ventricle is angina. It develops against the background of compression of blood vessels that provide nutrition to the myocardium. As a result, its expansion in size and its consumption of a significant amount of oxygen in parallel with nutrients are noted. In addition to these symptoms, atrial fibrillation appears, signs of atrial flutter and starvation of the heart muscle are observed. Often a pathology occurs during which the organ freezes for 3-5 seconds and the beat is not visible, which leads to an unconscious state. In certain situations, shortness of breath may indicate the presence of cardiomegaly. The following symptoms are considered additional:
- high blood pressure;
- unstable blood pressure;
- headache;
- disturbances in heart rhythm;
- disturbed sleep;
- poor condition and general malaise;
- painful discomfort in the heart area;
- painful discomfort in the chest.
Dilatation of the right ventricle is not accompanied by any complaints. Only its causes and adverse effects can be demonstrated in the laboratory:
- dilatation of the right ventricle;
- disturbances in heart rhythm;
Symptoms of pulmonary hypertension:
- shortness of breath during light physical exertion and at rest, dry cough;
- lethargy, apathy, dizziness and fainting;
- increased heart rate, swelling of the veins in the neck;
- coughing up blood;
- arrhythmia;
- anginal pain that is associated with hypoxia of the heart muscle (pressing and squeezing pain in the chest area during exercise, often associated with cold sweat, subsiding after consuming nitroglycerin).
Symptoms of heart failure, which is caused by decreased contractility of the dilated right ventricle:
- a feeling of heaviness near the hypochondrium on the right;
- formation of enlarged veins on the skin of the peritoneum;
- swelling of the lower extremities and the anterior wall of the peritoneum.
Congenital heart defects in childhood can mean cyanosis of the skin, shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat, rhythm disturbances, and slow growth and development.
Risks and possible complications
There are various prognoses that are directly dependent on the diagnosis made when the heart expands to the left.
- For arterial hypertension (hypertension, high blood pressure), the prognosis is considered favorable. After taking the medications prescribed by the doctor, the patient’s condition returns to normal, the heart returns to its normal parameters and does not enlarge again.
- If a ventricular septal defect is observed, surgery is necessary. Otherwise, the pathology will lead to aortic valve insufficiency, serious rhythm disturbances will occur, and left ventricular dysfunction is possible. All of the above can cause death. After the operation, the patient’s condition returns to normal, and he no longer faces such heart problems.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy (stretching of the heart cavities) is characterized by a poor prognosis. Full recovery becomes possible only after a heart transplant.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (thickening of the walls of the ventricles) - the prognosis is relatively unfavorable, the disease may be asymptomatic. Without proper and timely treatment, there is a risk of death. When undergoing treatment procedures, the likelihood of death becomes lower.
- Metabolic cardiomyopathy is a non-inflammatory myocardial lesion of various etiologies. It can cause insufficiency of cardiac functions, in particular contractile function. The prognosis is favorable. If you establish proper metabolism, complete recovery will occur.
- Myocarditis. Characterized by a favorable prognosis. Complete recovery is possible within 1-2 months in nine out of ten cases, after 1 year in the remaining patients.
- Aortic stenosis (the mouth of the aorta becomes narrow, as a result of which blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta is impaired) - without treatment, the life expectancy will be from 1 to 4 years from the time the disease is detected. With proper treatment, the prognosis is relatively favorable.
- Exudative pericarditis (inflammation of the serous membrane of the heart) has a favorable prognosis, all patients recover.
Left ventricular hypertrophy
This pathology is a typical heart lesion for those suffering from hypertension. Dilatation of the left ventricle is considered a rather unsafe phenomenon, which is characterized by high mortality. This process involves structural adaptation of the organ regarding metabolism and changes that occur in hemodynamic data.
Cardiomegaly causes significant thickening of the walls. Often it leads to a significant change in the septum, which is located between the 2 ventricles. Due to the expansion that occurs, the elasticity of the walls is lost. Thickening can be either uniform or in certain areas of localization. This specificity directly affects the course of the disease.