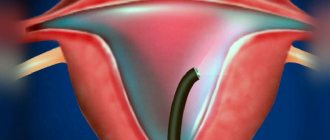
Hysteroscopy is a therapeutic and diagnostic procedure during which a doctor, using a hysteroscope, examines the uterine cavity and cervical canal through the vagina, and, if necessary, performs minimally invasive surgical procedures (removal of polyps, endometrial curettage, etc.).
The medical doctor has already talked about in what cases and how hysteroscopy is performed. Meanwhile, the technical side of the procedure is of little interest to patients. The possible consequences of hysteroscopy are of much greater interest to women. This publication is devoted to a detailed analysis of this issue.
What is hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a method of examining the uterine cavity using a special optical system that is inserted into the cavity through the cervix. It can be diagnostic and surgical (hysteroresectoscopy). Diagnostic is a low-traumatic method, carried out under the full supervision of a doctor, using an optical system that transmits to the monitor an enlarged image of the uterine cavity several times. This magnification allows you to see the smallest changes in the inner layer of the uterus, perform surgical procedures to remove small polyps, small adhesions, membranes, and make a diagnosis. Treatment of disorders using surgical hysteroscopy allows for the removal of endometrial polyps, myomatous nodes, septa and dense adhesions, and other formations. Hysteroscopy allows women with a benign tumor in the inner layer of the uterus to undergo surgery more easily, recover quickly after surgery, and increases the chance of pregnancy.
The procedure is prescribed 7-10 days from the start of the menstrual cycle. The endometrial layer is still small, changes and formations in the uterine cavity are clearly visible. To improve visibility, the uterine cavity is expanded - liquid or gas is injected into the uterus under pressure through a hysteroscope. The device contains a light sensor that illuminates the uterine cavity, and the camera on it transmits what is happening to the monitor. Using the device, the doctor can carefully examine the cervical canal of the cervix, the opening of the fallopian tubes, and the inner layer of the uterus. With the help of hysteroscopy, the doctor can detect the reason for the failure of pregnancy, which could not be detected by other means. Very often, the cause of non-pregnancy is synechiae, which forms in the cervical canal or uterine cavity. Subtle synechiae cannot always be seen using other research methods. Endometrial hyperplasia is also not always detected by ultrasound. A symptom of endometrial hyperplasia is heavy menstruation, which may be the reason for prescribing hysteroscopy. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is used to examine the condition of the uterine cavity in postmenopausal women to exclude the development of cancer. For postmenopausal women, hysteroscopy is prescribed any day. Diagnosis can take about 30 minutes, the use of surgical hysteroscopy takes from half an hour to two hours. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed without the use of anesthesia, surgical hysteroscopy is performed under general anesthesia. After the manipulation, a few hours later the woman can go home.
Hysteroscopy: indications and contraindications, possible complications
Hysteroscopy is an endoscopic examination used in the field of gynecology. The essence of this method is the introduction through the cervix into the uterine cavity of a special optical device - a hysteroscope, at the end of which a camera is mounted, thanks to which the doctor assesses the condition of the uterine cavity and the patency of the fallopian tubes. Hysteroscopy can be prescribed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Indications for hysteroscopy
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is prescribed if a woman is suspected of having the following pathologies:
• infertility and miscarriage; • dysfunctional bleeding; • tumor processes; • neoplasia (pathological changes in tissue); • adhesions and septa in the uterine cavity; • abnormalities in the structure of the uterus.
This research method is also carried out to identify the remains of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity after a frozen pregnancy, an intrauterine device, and also as a control examination of the uterus after surgical interventions, curettage and hormonal therapy.
Indications for therapeutic hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy for therapeutic purposes is prescribed for the following pathologies:
• endometrial polyps; • hyperplasia of the uterine mucosa; • intrauterine synechiae (adhesions) and septa; • submucosal myoma; • narrowing of the mouth of the fallopian tubes.
Hysteroscopy is also performed to perform sterilization and remove the intrauterine device.
Contraindications to hysteroscopy
Like any method of instrumental research, hysteroscopy has its contraindications. This method does not apply in the following conditions:
• in case of intrauterine pregnancy (progressive): before the procedure, patients of reproductive age must take a pregnancy test (determine the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood or urine) in order to exclude the possibility of pregnancy; • in acute inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs: after hysteroscopy, performed for acute inflammation, the infection can spread to other organs, chronic pain in the pelvis and infertility may appear; • with heavy uterine bleeding; • in case of widespread cancer of the cervix or uterus: the technical possibility of conducting research in oncological processes exists, however, after hysteroscopy, cancer cells can spread into the abdominal cavity; • for cardiovascular pathologies; • for diseases of the nervous and respiratory systems; • for severe pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
Hystroscopy technique
To perform hysteroscopy, a special device is used - a hysteroscope, which is inserted into the uterine cavity. A hysteroscope is a dense tube at the end of which there is a camera and a light connected to a computer monitor using cables. A real image, magnified 20 times, is transmitted to the monitor screen via a fiber optic cable, allowing the doctor to examine in detail the uterine cavity and the area where the fallopian tubes exit. The data obtained is recorded or images of areas with pathological changes are taken, after which their condition is assessed by other specialists.
Hysteroscopy process
Despite the complexity of the procedure and the need for preparatory measures, it is considered relatively safe compared to other methods of instrumental research.
The procedure is scheduled for 6-10 days of the menstrual cycle; if a non-standard examination is necessary, hysteroscopy can be scheduled for any day after menstruation.
Before hysteroscopy, the patient must undergo laboratory tests: blood for the presence of infectious pathogens, a general blood and urine test, a smear for vaginal microflora.
A few days before hystroscopy, it is necessary to avoid sexual intercourse, not to use vaginal suppositories, tampons, or douching.
The study requires short-term intravenous anesthesia, since during hysteroscopy a woman may experience quite unpleasant and painful sensations.
To insert the apparatus tube, the cervix is in some cases dilated to 10-12 mm.
The average duration of hysteroscopy is 10-30 minutes, which depends on the goals of the study and what manipulations will be performed (routine examination or tissue sampling for histological analysis, etc.).
Complications after hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is an invasive procedure in which the device is inserted into the uterine cavity, so after hysteroscopy a number of complications may occur, especially if the rehabilitation period is disrupted.
Hysteroscopy is fraught with the development of the following negative consequences:
• endometritis: inflammatory processes in the uterine cavity, the appearance of which is caused by infection. They are manifested by increased temperature, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, purulent and bloody vaginal discharge, and are characterized by gradual development; • perforations of the uterus associated with gross violations of the procedure: perforation of the walls of the uterus (violation of tissue integrity) with a hysteroscope. Accompanied by sharp pain in the abdominal area, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, fainting; • uterine bleeding: occurs during medical procedures. The nature of the bleeding is profuse, duration is more than two days.
When the study is carried out correctly by a qualified specialist, the development of serious complications is reduced to a practical minimum.
Pain after hysteroscopy
After hysteroscopy, a woman may experience minor short-term pain in the pelvic area caused by instrumental intervention. Normally, pain is noted in the lumbosacral region. Patients with different pain thresholds tolerate pain differently. In cases of severe pain, a woman may be prescribed painkillers.
In order to minimize the likelihood of complications, after hysteroscopy a woman should not use sanitary tampons, avoid douching, sexual intercourse, active physical activity and overwork.
A signal to see a doctor is pain that does not stop within a week after hysteroscopy.
Discharge after hysteroscopy
The appearance of bleeding after hysteroscopy, lasting from two to three days, is considered normal, which is explained by the natural cleansing of the uterus after the intervention. After hysteroscopy performed for diagnostic purposes, the discharge is less abundant than after hysteroscopy, during which certain therapeutic measures were performed.
The appearance of discharge is due to traumatization of mucous tissues by devices inserted into the uterine cavity, which can occur during any surgical intervention, which includes hysteroscopy. These discharges do not pose a threat to the woman’s health, however, if their intensity increases or blood clots appear in them, the woman should consult a doctor.
Menstruation after hysteroscopy
The menstrual cycle after hysteroscopy, as a rule, is not disrupted, menstruation occurs as scheduled. However, in some cases, curettage of the walls of the uterus, carried out for medicinal purposes, can trigger the beginning of a new cycle, due to which menstruation occurs immediately after the procedure. A woman should pay special attention to the nature of menstrual flow: intensity, color and consistency. If your periods become more abundant or have an unusual color, which may indicate the presence of certain pathological processes, you should consult a doctor.
Pregnancy after hysteroscopy
Despite the fact that this study does not interfere with a woman’s reproductive function, and is sometimes even carried out as a method of treating infertility, it is recommended to start planning a pregnancy no earlier than six months after hysteroscopy.
If pathologies that cannot be corrected by traditional methods are identified, in order to treat infertility, a woman may be recommended to undergo in vitro fertilization - a modern method of assisted reproductive technologies, the popularity of which is growing every year.
After hysteroscopy, the woman is prescribed a course of antibacterial therapy in order to exclude the development of inflammatory processes. If, as a result of a diagnostic study, any diseases are discovered, measures are taken to eliminate them: with the help of anti-inflammatory therapy, hormonal treatment and stimulation of ovarian activity.
Indications for hysteroscopy
The following symptoms and diseases are indications for the procedure:
- Heavy, painful menstruation
- Uterine bleeding
- Infertility
- Endometriosis
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- Suspicion of synechia
- Myoma
- Polyps
- Inability of a woman to carry a pregnancy to term
- Suspicion of cancer
- Clarifying the location of the intrauterine device and its removal
- Examination of the uterus after surgery
- Removing the remnants of the fertilized egg after termination of pregnancy
Is menstruation a contraindication or not?
During menstruation, routine hysteroscopy is not performed. It is usually prescribed on days 5-7 of the cycle to identify neoplasms, fibroids, and polyps (in the first phase of the cycle, the endometrium is thinner, which allows you to see even tiny defects). But foci of inflammation are easier to detect when the endometrial layer is thicker (in the second half of the menstrual cycle, on days 20-24). Hysteroscopy of the uterus with biopsy before IVF is prescribed immediately after the end of menstruation. Two or three weeks are often enough to restore and renew the endometrium, which allows the patient to enter the protocol already in the next cycle.
However, if emergency hysteroscopy is indicated (in case of intense bleeding, suspicion of the presence of a dead fertilized egg or foreign objects in the uterus), it can be performed on any day of the cycle. It doesn’t matter whether you’re menstruating or not.
Pain after hysteroscopy
The pain occurs most often in the lower back and abdomen. Hysteroscopy is performed using a device whose diameter is no more than 3 mm. The insertion of the hysteroscope probe is almost painless, but after the manipulation, slight nagging pain will appear. If it hurts after hysteroscopy, which was performed for diagnostic purposes, then such pain goes away a few hours after the manipulation. Minor discomfort may be felt for several days. If the pain does not go away within several days, if severe pain occurs, this is a reason to consult a doctor for help. To avoid pain after this procedure, you should refrain from sexual intercourse for several days, do not lift anything heavy, do not take a hot shower, bath, or go to the sauna or bathhouse.
Main contraindications to surgery
A patient suffering from an acute infectious disease (pneumonia, pyelonephritis, influenza, etc.) will not be allowed to undergo the procedure. Hysteroscopy will not be prescribed for a woman diagnosed with acute inflammation of the genital organs. If the test results reveal a grade III or IV purity of the gynecological smear, the patient will also be denied minimally invasive surgery, since there is a high risk of infection in the uterus.
In case of renal or liver failure (both acute and chronic), hysteroscopy is not performed. Disruption of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems is also considered a contraindication. General exhaustion of the body, shock or coma is a good reason for postponing the operation (it is performed under anesthesia, which can aggravate the patient’s condition).
Another contraindication is a blood clotting disorder. During surgery, bleeding may occur, which can be fatal.
Discharge after hysteroscopy
As after any intervention in which the instrument comes into contact with the mucous membrane, discharge appears due to injury to the mucous membrane of the cervical canal and uterine cavity. After such an operation, discharge is considered normal. The discharge is bloody, not profuse, and lasts for several days. If the discharge is profuse, painful, or the color of the discharge has changed, you should immediately consult a doctor. If diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed, the discharge is most often scanty and passes quickly. If surgical hysteroscopy is performed, the discharge will be more abundant for several weeks. Often after such an intervention, hemostatic drugs are prescribed. The doctor is often asked the question: “When will menstruation occur if hysteroscopy is performed?” Discharge after the procedure may smoothly transition into menstruation, but in most cases, menstruation occurs on schedule for every woman. In rare cases, it is slightly delayed.
Hysteroscopy: consequences and their cause
In most cases, negative reactions develop after surgical hysteroscopy, and serious and life-threatening complications are diagnosed extremely rarely. All arising consequences of hysteroscopy can be divided into the following groups:
- Surgical;
- Anesthetic (such consequences of hysteroscopy are often associated with an allergic reaction to the anesthetic, so it is important to undergo a full examination before the procedure);
- Complications associated with expansion of the uterine cavity;
- Consequences caused by prolonged positioning of the patient.
You can undergo a full examination and get all the information about hysteroscopy and possible risks from the specialists of the IVF Center clinic in Kursk.
After hysteroscopy, the polyp grew again
What to do if the polyp grows again after surgery? Polyps often appear due to hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. Removing a polyp does not guarantee the cessation of their formation elsewhere in the uterine mucosa. Endometrial polyps are a disease characterized by the proliferation of the basal (inner) layer of the endometrium. The most common cause of the development of polyps is an excess of estrogen, a lack of progesterone; abortion, premature termination of pregnancy, and childbirth with incomplete delivery of the placenta can also cause the growth of polyps. It is possible to develop polyps after stress, with diseases: diabetes, thyroid disease, hypertension. Chronic inflammatory processes in the female genital area and a sharp drop in immunity play a negative role. If the polyp has grown again, you should be tested for sex hormone levels. When hormone levels are disrupted, polyps will reappear even after surgery. In this case, treatment with OCs (oral contraceptives) is prescribed, which will affect hormonal levels and stop the development of polyps. If hysteroscopy was used to remove a polyp, bloody discharge will persist for several days. You should monitor the condition of the discharge - it should not be abundant, change color, or have an unpleasant odor. If such symptoms appear, consult a doctor immediately.
Where is hysteroscopy used?
Hysteroscopy can be used to try to determine the cause of various problems, such as:
- Heavy or irregular bleeding that is not controlled by medications you are taking.
- Bleeding between periods.
- Bleeding after menopause.
- Irregular bleeding while you are taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
- For surgery to make your periods less severe (such as endometrial removal).
- Unexplained miscarriages.
It is also used to investigate the cause of various problems:
- Removal of polyps - small pieces of tissue growing on the lining of the uterus.
- Removal of scar tissue in the uterus.
- Removing adhesions (areas where the walls of the uterus are stuck together).
- Removal in the uterus (non-cancerous tumors in the uterus).
- Finding a "lost" or stuck contraceptive device, such as an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD) - also known as a "coil".
Before your doctor talks to you about the test.
Your doctor may discuss a number of different treatment options with you. This is necessary to immediately find out the cause of your symptoms using a hysteroscope. In order to have a hysteroscopy, you must agree (consent) to the treatment. Only you can decide which treatment option is best for you.
Consequences of the procedure
Despite the fact that hysteroscopy is considered a gentle method of treatment, complications also develop with its use. After this, the consequences are as follows:
- Perforation of the uterus
- Bleeding
- Side effect of anesthesia
- Endometritis
Consequences in the form of uterine perforation rarely occur; most often, such a complication arises due to the low qualifications of the doctor, as a result of perforation of the uterine wall with a hysteroscope.
Consequences in the form of bleeding occur due to various causes and factors; if heavy discharge occurs, a woman should urgently consult a doctor.
Consequences in the form of endometritis or inflammation of the uterus arise due to an infection introduced during the procedure, due to an inflammatory process that was not treated before the procedure.
Consequences in the form of a hematometer develop due to uterine spasm during the procedure.
Also, a complication after the procedure is considered to be an incompletely removed polyp, a myomatous node, which is rare.
Complications of hysteroscopy caused by expansion of the uterine cavity
Since normally the uterine cavity is a small closed slit, it is expanded with special media for manipulation. If the medium supply regime is violated, negative consequences may develop:
- Arrhythmia;
- Gas embolism (when using carbon dioxide);
- Nausea;
- Dizziness;
- Change in pressure;
- Pulmonary edema;
- Hemolysis, etc.
The nature of the violations is directly related to the drug administered; all consequences are eliminated conservatively.
Examination to remove a polyp
Examination before removal of cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp, endometrial polyp includes
- examination by a gynecologist;
- extended colposcopy;
- clinical blood test, platelets, blood test for sugar (glucose);
- blood test for class G antibodies (Ig G) to chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma;
- microscopic examination of the flora of a smear from the urethra, vagina and cervix;
- cytological examination of smears and scrapings of the cervix and cervical canal;
- examination of smears from the cervical canal using PCR (PCR smears) for chlamydia, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, gardnerella, trichomonas, human papillomaviruses of high oncogenic risk.
The cost of the examination is 10,730 rubles.
The cost of removing a polyp of the cervix and cervical canal using the microwave method is 1,750 rubles.
You can perform the examination at your place of residence or at the Women's Health Resort Clinic by appointment.
The results of the examination are valid for 3 months from the date of completion in the absence of a change of sexual partner.
Causes of polyp
The causes of cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp, and endometrial polyp are NOT KNOWN.
The question of the cellular source of polyp development (the primary cell) has not been resolved.
Cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp, endometrial polyp can form at ANY AGE. Even during the period of “serene” CHILDHOOD and youth! However
Cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp, endometrial polyp are statistically more often detected after 39 YEARS.
The cause of cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp and endometrial polyp is believed to be immune, HORMONAL and metabolic DISORDERS, leading to a defect in the natural control of apoptosis (natural cell death). Disruption of the mechanisms of APOPTOSIS leads to an increase in the life span of cells and the formation of a polyp in the uterus.
Psychiatrists note that cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp, and endometrial polyp more often occur in women with a stable psyche (“workhorses”), who have independently taken on an ENORMOUSLY LARGE burden of duties and responsibilities in everyday life, personal life, and at work. In other words,
A polyp in the uterus, a polyp of the cervix, a polyp of the cervical canal is a manifestation of internal excessive tension against the background of the unrealization of the feminine principle...
The reason for the formation of a cervical polyp, a cervical canal polyp, or an endometrial polyp is not the lack of orgasms during sexual intercourse.
The reasons for the formation of a polyp are not masturbation and the use of a dildo.
Polyps in the uterus (cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp, endometrial polyp) are not a contraindication to sexual intercourse (sexual intercourse), visiting the gym, swimming pool, bathhouse, sauna, swimming in the sea, river and other bodies of water.
If you have a cervical polyp, a cervical canal polyp, or an endometrial polyp, it is advisable to refrain from sunbathing in natural conditions and in a solarium.
Treatment of polyps in the uterus
Removal of cervical polyp and cervical canal polyp WITHOUT PAIN in 3 seconds at the Women's Health Clinic. There is EXPERIENCE, there are RESULTS, there are ways to ACHIEVE.
A polyp of the cervix, a polyp of the cervical canal, when confirming the oncological well-being of the situation in the Resort Clinic for Women's Health, AT THE SAME TIME (“in one go”), WITHOUT PAIN, is removed without contact using the radio wave method with coagulation of the polyp bed.
The cost of removing a polyp of the cervix and cervical canal using the microwave method is 1,750 rubles.
Removal of a cervical polyp, a polyp of the cervical canal CONTACTLESS radio wave method lasts 3 SECONDS. Anesthesia or anesthesia (general or local anesthesia) is not required even for sensitive girls and women.
We perform coagulation of the polyp bed (radio wave treatment of the base of the cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp) in order to prevent relapse (recurrence) of the polyp.
Thanks to the effect of radio waves, no burn surface remains and no scar changes occur, i.e. Narrowing of the cervical canal does not occur and a SCAR does not form.
An initial appointment with a gynecologist and examination are possible on ANY DAY of the menstrual cycle, except days of menstruation.
Removal of cervical canal polyp, cervical polyp, endometrial polyp in the Women's Health Resort Clinic is performed 1 day before the start of menstruation or immediately after the end of menstruation, ideally during the waning moon.
Removal of a polyp in the uterus during a given period of the menstrual cycle according to the phase of the lunar cycle allows us to take into account the biorhythmological characteristics of the female body and the activity of the polyp cell division processes.
Removal of a polyp in the cervix, removal of a polyp of the cervical canal using the radio wave method does not prevent the dilation of the cervix during childbirth.
We send all biological material for histological examination for further study. Read more about the radio wave method of treatment on our website in the article “Treatment of diseases of the cervix with the radio wave device “Surgitron”.
In order to prevent relapse (re-formation) of a polyp of the cervical canal, a polyp of the cervix, an endometrial polyp, we pay great attention to the correction of the psycho-emotional state and attitude of a girl, a woman towards herself, her feminine principle, production and educational activities, we pay great attention to the normalization of immune activity systems.
This comprehensive approach to the problem of the occurrence of cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp and endometrial polyp is a feature of the scientific and practical activities of the Women's Health Resort Clinic.
To normalize the activity of the immune system, the Clinic widely uses medicines based on natural raw materials according to prescriptions from doctors at the Women’s Health Resort Clinic.
Our experience in sanatorium-resort treatment shows that the use of medicines based on natural mineral and plant raw materials is an important physiological (corresponding to human physiology) component in the prevention of relapse (re-occurrence) of cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp, endometrial polyp.
AFTER REMOVAL of a cervical polyp, a cervical canal polyp, or an endometrial polyp, for 7 days it is advisable to abstain from sexual intercourse, swimming in the sea, lake, pond, pool, bath (it is advisable to wash in the shower), to refrain from heavy psycho-emotional and physical stress at work, in everyday life and in the gym, avoid lifting and/or carrying things, children, food, etc. weighing more than 3 kg, sunbathing in natural conditions and in a solarium.
There are no restrictions or nutritional features during the period and after removal of the cervical canal polyp, cervical polyp and endometrial polyp. Dry, semi-dry white and red wine, light and dark beer are allowed.
Immediately after removal of a cervical polyp, cervical canal polyp, or endometrial polyp, air travel, travel by rail and road transport are NOT CONTRAINDICATED. The style of behavior is ordinary, the rhythm of life is gentle.
After removal of a polyp in the uterus, pregnancy is possible after the cessation of sanguineous (bloody) discharge. However, it is wiser to become pregnant after assessing the results of histological examination.
The spa clinic for women's health facilitates the accommodation and accommodation of women, women with children and couples during examination and treatment.
About living conditions and transfer from Mineralnye Vody airport and Pyatigorsk railway station in detail in the article “Accommodation”.
If you need to book accommodation, please coordinate your arrival date no later than 7 days in advance.
Reception only by appointment by phone 8 (calls within Russia are free) or.
The resort clinic for women's health operates both for paid services and in the voluntary health insurance system.