Where and how can you get gonorrhea?
There is an opinion that gonorrhea is a disease of people who are promiscuous.
In fact, this is nothing more than a myth, because both adults and children can become infected with gonorrhea. In addition to the transmission of bacteria during unprotected sexual intercourse, the disease is also transmitted through hygiene items, and children can become infected from a pregnant mother in utero or during childbirth. You can become infected with gonorrhea:
- while visiting public baths, saunas, water parks, swimming pools;
- when using someone else’s toothbrush, towel, or utensils of a sick person;
- in a shared bathroom, shower, toilet.
Children can become infected when using a potty.
What is gonorrhea
This is a sexually transmitted disease caused by gonococci. The disease is transmitted sexually, although purely theoretically there is a possibility of infection (1% of cases of gonorrhea) through domestic means: the pathogen is practically unviable outside the human body.
Those most often infected are those who lead a promiscuous and overly active sex life, neglecting protective measures. No one who enjoys unprotected sexual intercourse is immune from such an illness. With orderly family relationships, infection with gonorrhea is excluded; the infection can only be introduced by a third party.
For people at risk, such as prostitutes, escort workers, as well as those who travel a lot, live away from home and indulge in the pleasure of sleeping with an unfamiliar partner, a gonorrhea smear should be taken at least once every six months.
Gonococcus is transmitted through all types of sexual intercourse - vaginal, anal, oral. The disease is dangerous, as it can quickly become chronic and destroy the body, affecting many organs and systems. The peculiarity of this disease is that there may be an almost complete absence of symptoms, in which case the carrier of the infection himself is not aware of it. In most situations these are women. In 80% of men with gonorrhea, symptoms appear, and quickly.
Studies show that after a single sexual contact with an infectious partner, the smear result in 85% of women will be positive, while gonococci will be found in only 35% of men. This discrepancy in statistical data is explained by the different structure of the genital organs.
Symptoms of the disease
The insidiousness of the disease is that the incubation period lasts from 3 to 30 days, so it can be quite difficult to determine when and where the patient became infected. Due to the asymptomatic course of the disease in the first period, its diagnosis at the initial stage is difficult.
The symptoms are somewhat different in men and women. Men feel pain in the urethra, yellowish or green discharge appears, and pain in the scrotum. In women, in addition to discharge and pain in the lower abdomen, there is swelling of the vulva and spotting before menstruation. Common to both sexes are fatigue, sore throat, and burning sensation when urinating.
Important! A woman may have no signs of gonorrhea infection at all, but at the same time she is a source of infection for her sexual partners and those people who use her personal hygiene items.
If you experience any of the listed symptoms and have questions about where and how to get a gonorrhea smear done in Moscow, please contact our “Polyclinic +1”.
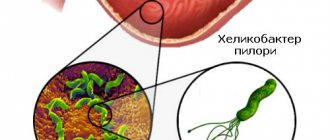
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infectious disease caused by gonococcus ( Neisseria gonorrhoeae
). According to WHO data [1, 2], up to 200 million new cases of gonorrhea are registered annually in the world. In Russia, after a slight decrease in incidence in the 90s of the twentieth century, an increase in the number of patients was again noted to 102.2 per 100 thousand population [3]. High rates of growth in the incidence of gonorrhea were simultaneously noted in Estonia, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic and a number of other countries. According to the literature [4], in 2009, the incidence in countries that register gonorrhea was: in the Russian Federation - 48.1 per 100 thousand population, in the USA - 106 per 100 thousand population, in EU countries - 9.7 (from 27.6 in the UK to 1.0 in Greece) per 100 thousand population. In the United States, about 300–350 thousand new cases of the disease are officially registered annually[5].
It is generally accepted that the incidence of the disease in the population is at least 2 times higher than officially registered, since gonorrhea is asymptomatic in 3-5% of infected people, and patients from private doctors may not be included in statistical reports [6]. Considering that making a correct diagnosis for sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including gonorrhea, directly depends on the quality of laboratory diagnostics, violations of the laboratory diagnostic algorithm, as well as, often, non-compliance with the requirements of the main regulatory documents contribute to this problem.
According to Bergey's key (1997), gonococcus belongs to the family Neisseriacae
, genus
Neisseria
, species
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
(Key guide Bergey, 1997).
The genus Neisseria
is represented by several species:
N. canis, N. cinerea, N. denitrificans, N. elongate, N. flavescens, N. gonorrhoeae, N. lactamica, N. macacae, N. meningitides, N. mucosa, N. polysaccharea, N. sicca, N. subflava
.
Of the listed species, only two are pathogenic for humans - N. gonorrhoeae
and
N. meningitides
.
Pathogenic microorganisms of various parts of the urogenital tract are presented in Fig.
1, a, b, c .
spp. is a normal microflora of the urethra, oral cavity and oropharynx, as well as the nose and skin
(see Fig. 1, d, e)
.
Figure 1. (d, e). Pathogenic microorganisms and saprophytes of various human hollow organs: saprophytes of the urethra (d), mouth and oropharynx (e).
The biomaterial for laboratory examination for gonococcal infection is discharge from the urethra, vagina, cervix, rectum, eyes, pharynx, prostate secretion, urine, blood. Antibiotics and local procedures are stopped 10 days before taking material for examination. In women, it is recommended to take material before menstruation. Before taking the material, it is necessary to refrain from urination for 3-4 hours and sexual intercourse, as well as toileting the external genitalia and douching. The test material should not contain blood impurities [8].
The legislative framework for laboratory diagnosis of gonorrhea has historically been represented by several orders. Currently, Order of the Ministry of Health of the USSR No. 1570 dated December 4, 1986 “On improving the identification of patients with gonorrhea and trichomoniasis in obstetric and gynecological departments (wards, offices), antenatal clinics and urological offices of clinics (together with methodological recommendations) has been declared invalid (Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 398 dated 12/23/02). The diagnosis of gonorrhea is regulated by Order of the Ministry of Health of the USSR No. 535 dated 04.22.85 “On the unification of microbiological (bacteriological) research methods used in clinical laboratory diagnostics of medical institutions”, Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 64 dated 02.21.2000 “On approval of the Nomenclature of Clinical Laboratory Research” , by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 415 of March 20, 2003 “On approval of the protocol for the management of patients with gonococcal infection.” At present, Order of the USSR Ministry of Health No. 936 dated July 12, 1985 “On the unification of laboratory research methods in the diagnosis of gonorrhea and trichomoniasis” is still in force.
According to the current orders, as well as in accordance with the clinical recommendations (CR) of the Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists “Management of patients with sexually transmitted infections and urogenital infections”, the list of laboratory tests for suspected gonococcal infection includes: microscopy of stained preparations and cultural examination ( KR-2010), and currently, also molecular biological methods (KR-2011). Molecular biological methods (MBM) are aimed at detecting specific fragments of DNA and/or RNA using test systems approved for use in Russia. For the first time, KR-2012 introduces these methods into the category of recommended methods for diagnosing STIs, but does not define the procedure for conducting and requirements for performing research.
From the clinician's point of view, the optimal laboratory diagnosis of gonorrhea is the use of simple screening tests. The light microscopy method best satisfies these requirements: for clinicians because of the speed of obtaining results, for clinical laboratory diagnostics doctors due to the ease of implementation, and for patients because of its affordable cost. This does not take into account the low sensitivity of the method for biomaterial from the cervical canal (pharyngeal and rectal samples are not used for microscopic examination), as well as in cases of early diagnosis of gonorrhea, asymptomatic infection and for some variants of gonococci.
Lack of understanding of the capabilities of the light microscopy method is the cause of conflict between clinicians and laboratory doctors. It is at this stage of obtaining a qualified result of a microscopic examination that the conflict flares up between clinicians and clinical laboratory diagnostic doctors, since in order to prescribe appropriate treatment, the clinician requires a conclusion from the laboratory doctor about the presence of N.gonorrhoeae
in the material under study, despite the fact that for the species identification of gonococcus it is necessary to conduct a cultural study, which makes it possible to isolate a pure culture of the microorganism and identify it by morphological and biochemical characteristics.
The answer based on the culture results is given 5 days after the sample is taken. Isolation of N. gonorrhoeae
by culture is indisputable evidence of the presence of gonococcal infection. A huge contribution to this problem was made by Orders of the USSR Ministry of Health No. 1570 of 12/04/86 and No. 936 of 07/12/85, in which the term “gonococcus” is not entirely correctly used when describing light microscopy as one of the methods for diagnosing gonococcal infection.
To diagnose gonococcal infection, several options for staining preparations for light microscopy are used: methylene blue (a survey preparation allows you to identify signs of inflammation and describe the morphotypes of bacteria) and the Gram method, to determine the gram identity of diplococci. In addition to the classical staining methods, if a gonococcal infection is suspected, in accordance with the order of the USSR Ministry of Health No. 936 dated July 12, 1985, staining with eosin with methylene blue is used (to identify, along with diplococci, morphologically similar to gonococci, trichomonads and eosinophils), as well as brilliant green (to identify Trichomonas).
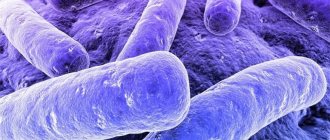
Under light microscopy, all species of the genus Neisseria
have the same morphological characteristics: cell shape - cocci, cells arranged in pairs (except for
N. elongate
, presented in the form of short chains, often diplobacilli).
Diplococci, morphologically similar to gonococci, are defined as paired cocci, shaped like coffee beans, facing each other with concave sides, negative when stained by the Gram method. Diplococci are located intracellularly (inside segmented leukocytes), in mucus, on epithelial cells. Inside the leukocyte - in pairs, groups, at different angles to each other, and on epithelial cells (extracellular) - in large numbers in rows, perpendicular to each other within the row (Fig. 2)
.
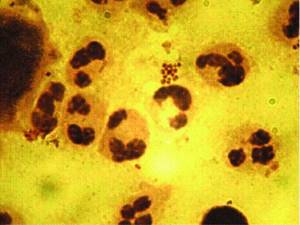
Often, clinical laboratory diagnostic doctors believe that the morphological signs of gonococcal infection are exclusively the intracellular location of gram-negative diplococci. Is it so? According to the literature [9], the causative agent of gonorrhea is characterized by the intracellular location of pathogens in segmented leukocytes at all stages of the disease. During the period of the first clinical manifestations, in the presence of scanty mucopurulent discharge, gonococci are found mainly on the surface of epithelial cells in the form of cocci, less often - tetracocci. At the height of the disease, with profuse purulent discharge, intracellular diplococci dominate. As the severity of the process decreases, the number of intracellular gonococci decreases and their number on the surface of epithelial cells increases. The frequency of intra- and extracellularly located gonococci depends on the period of the disease. Characteristic of gonorrhea is an incomplete phagocytic reaction, in which microorganisms find favorable conditions for intracellular persistence. In addition to polynuclear cells, macrophages, epithelial cells, and lymphocytes take part in phagocytosis. The latter have a migration cycle and contribute to the generalization of infection.
Consequently, with light microscopy of preparations of the urogenital tract of patients with suspected gonococcal infection, the researcher determines the morphological characteristics of the pathogen and its gram affiliation, which suggests the presence of gonococcal infection, but does not confirm it. Only three signs - shape
(diplococci in the form of coffee beans),
localization
(mainly inside leukocytes and on epithelial cells),
gram affiliation
- suggest the presence of gonococcal infection [10].
According to the literature [11], the sensitivity of the microscopy method of specimens discharged from the urethra of men using Gram staining ranges from 50 to 75% for asymptomatic infection - up to 95% for severe manifestations; in women - from 20% for material from the urethra to 37-50% for material from the genital tract. The sensitivity of primary microscopy increases to 97.3% and specificity to 99.6% when using a combination of methylene blue and gentian violet, but only for material obtained from males [12]. To reduce the likelihood of false results, repeat microscopy is recommended. Microscopy is not recommended for oropharyngeal material. The method also has low sensitivity when examining rectal smears obtained from women without signs of infection.
According to the Federal System of External Quality Assessment, during the period from 2007 to 2010, false positive results when identifying gonorrhea pathogens in preparations of the mucous membrane of the urogenital tract by microscopy were observed in 5.7% of cases, false negative results - in 0.5%. The reasons for errors at the analytical stage are the unsatisfactory quality of smears (43.4%), associated with errors in fixing the preparations, unevenness of their coloring, the presence of thick areas with unstained cells, under- or over-discoloration, as well as a violation of the methodology, when some laboratories stain preparations only methylene blue, although this type of staining does not allow differentiation of microorganisms by tinctorial properties [13].
According to the laboratory criteria for the diagnosis of gonorrhea adopted by the European Union (2002), in addition to the detection of gram-negative intracellular diplococci in urethral smears of men, N. gonorrhoeae
and detect
N. gonorrhoeae
in clinical specimens. For this purpose, a cultural study is used, including the isolation and identification of gonococci in pure cultures on special media with the obligatory performance of a cytochrome oxidase test, the study of the saccharolytic properties of the pathogen, the determination of beta-lactamase activity and sensitivity to antibiotics, and, according to clinical recommendations of 2012, also MBM. When examining grown cultures in smears stained using the modified Gram method, if the staining is correct, in the center of clusters of orange-red microorganisms, groups of cocci or individual areas of smears stained purple are observed. It is necessary to take into account the morphology, location and color of gonococci. They are mainly not paired, but individual cocci, collected in clusters with a denser center and seemingly randomly scattered around the periphery. Along with intensely orange-red colored cocci, there are pale colored forms, as well as individuals with irregular rounded shapes. Polymorphism of gonococci increases as the culture ages. Gonococci do not form chains and clusters in culture, which is characteristic of streptococci and staphylococci.
During the growth process, gonococci produce an enzyme - cytochrome oxidase. Gonococcal colonies turn pink, then red and black within minutes of exposure to dimethylparaphenylenediamine. Coloring occurs even in cases where colonies of gonococcus are located under colonies of other microorganisms.
Gonococcal colonies are always oxidase-positive, but other bacteria that produce cytochrome oxidase during their life processes can also be oxidase-positive. Therefore, such colonies of microorganisms must be examined by staining using the modified Gram method.
Errors at the analytical stage during cultural research are: reducing the algorithm for identifying gonococci to determining oxidase activity and Gram staining, as well as fermentation of glucose to acid. Despite the fact that for a number of reasons the sensitivity of a single culture may not reach 40%, in Russia a single negative response during microscopy and culture often serves as the basis for issuing a final negative response.
In the cultural diagnosis of gonococcal infection, difficulties arise at the stage of isolating strains that weakly ferment glucose, as well as sucrose-negative strains of N. subflava, N. meningitidis
and glucose-positive strains of
N. cinerea
.
Because non-pathogenic neisseria such as N. cinerea, N. sicca, N. subflava, N. mucosa
resemble the growth
of N. gonorrhoeae
, the use of chromogenic media does not help in the differential diagnosis.
Some strains of N. gonorrhoeae
(they are called auxotypes) require additional substances when cultivated on nutrient media.
To date, about 30 of them are known. The most common is the auxotype AHU
, since it requires arginine, hypoxanthine and uracil. This type is characterized by high sensitivity to penicillin and often causes asymptomatic infection in men [6].
The molecular biological methods recommended for diagnosing gonorrhea (KR-2012) also have a number of limitations: polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for detecting DNA or rRNA cannot be used when examining material from the pharynx and rectum, as well as for making a diagnosis in children and monitoring treatment ; a false negative result is given by strains that produce β-lactamases. False-positive results have been reported when testing samples containing N. subflava
[14].
The nucleic acid amplification test (NAT) is superior in sensitivity to PCR and is characterized by equally high sensitivity (more than 96%) both in the presence of symptoms and in asymptomatic infection in men and women [15]. The ANC method is used to search for pathogens, including in urine, mainly in men. In addition, its effectiveness has been proven for the simultaneous detection of gonococci and chlamydia. To exclude false negative results due to the presence of amplification inhibitors in the material, controls are required. A positive test result in extragenital material with a low incidence of gonorrhea in the territory requires confirmation by another method.
Analysis of the results of a cultural study of the discharge of the urogenital tract and material from the pharynx in patients of the City Clinical Hospital No. 14 named after. V.G. Korolenko showed over 7 years that out of 18 samples in which Neisseria were identified, pathogenic strains of N. gonorrhoeae
identified in 10 cases (localization: urethra - 5, cervical canal - 2, vagina - 2, pharynx - 1),
N. menengitidis
- in 2 cases (localization in the urethra).
Non-pathogenic species of Neisseria were identified in 6 cases: N. mucosa
- 1 (urethra),
N. perflava
- 3 (urethra),
N. flava
- 1 (vagina),
N. elongate
- 1 (urethra). Consequently, the method of light microscopy of Gram-stained preparations cannot be used as the only method for diagnosing gonorrhea, since it does not provide species identification of the microorganism.
There are two possible answers about the results of a microscopic examination recommended by the European Association for Sexual and Reproductive Health (2012). According to the first, the conclusion indicates: gram-negative intracellular and/or extracellular diplococci, morphologically similar to gonococci, were found. According to the second: gram-negative intracellular and/or extracellular diplococci morphologically similar to gonococci were not found.
Anamnesis, clinical picture and positive microscopy results are sufficient to establish a diagnosis of gonorrhea only in men with clinical symptoms of urethritis (European Union Guidelines, 2002). When studying biomaterial from women, children, in cases of sexual violence, when studying material from the oropharynx, conjunctiva, rectum, it is necessary to conduct a bacteriological study to identify N. gonorrhoeae
.
Laboratory criteria for the diagnosis of gonorrhea, adopted by the European Union (2002), include the detection of gram-negative intracellular diplococci in smears from the urethra of men, the isolation of N. gonorrhoeae
N. gonorrhoeae
antigen or nucleic acid . If gram-negative diplococci are detected, the preparations are stored for 3 months.
Since there are no tests with 100% sensitivity and specificity, a comprehensive laboratory examination of patients is necessary to diagnose gonococcal infection. Considering that most laboratories use only bacterioscopy, the quality of gonorrhea diagnosis is low.
conclusions
1. For mass screening for gonorrheal infection, today it is optimal to use a combination of laboratory methods: microscopy of material with Gram staining and cultural examination, subject to in-laboratory quality control.
2. Light microscopy can only suggest the presence of Neisseria
spp.
in the test sample, but does not allow species identification of N. gonorrhoeae
.
3. Identification of diplococci that are morphologically similar to gonococci by light microscopy, in combination with anamnesis data and the clinical picture, makes it possible to diagnose gonorrhea in the presence of clinical symptoms of urethritis only in men.
4. Species identification of N. gonorrhoeae
is possible only with bacteriological and molecular biological research.
Types of tests for gonorrhoea
Laboratory testing of biological material for gonorrhea is carried out by specialists at our clinic as soon as possible.
Many people are interested in whether it is possible to take a blood test for gonorrhea in men and women. Unfortunately, our clinic does not take blood samples due to the fact that neither antibodies nor the pathogen are diagnosed in it. This method is called RSK; in medicine it is classified as serological - it belongs to the auxiliary group and is rarely used. It is prescribed if bacteriological examination does not allow diagnosing the disease, and the doctor has doubts (which is extremely rare) or the disease is in a complex advanced form and proceeds with complications.
The methods are as follows:
- PCR (polymer chain reaction) - the result will be available in a day;
- microscopic examination - it takes only 20-30 minutes to get the result;
- sowing - production time will be 5–9 days.
Microscopic examination is performed by staining the discharge with special dyes - Gram or methyl blue. Examination allows you to identify a high content of pus and binuclear bacteria - gonococci - in the smear. PCR analysis for gonococci is good because it allows you to identify not only this bacterium, but also other diseases - trichomoniasis, chlamydia. It can be performed in two ways: to determine the presence or absence of gonococcus, and the second option is to determine its concentration.
The sowing method is recommended in the following cases:
- the treatment was ineffective;
- only one partner has the disease;
- transition of the disease to the chronic stage;
- the appearance of complications.
The good thing about this method is that it allows you to identify the concentration of the pathogen, as well as determine the patient’s sensitivity to antibiotics.
Get tested for the causative agent of gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a disease caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Refers to sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Clinically manifested by mucopurulent discharge from the genital tract, but can be asymptomatic. Gonorrhea is often accompanied by complications, the most dangerous of which are infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and pelvic adhesive disease. Detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA is the basis for diagnosing gonorrhea and prescribing treatment. Qualitative DNA determination of Neisseria gonorrhoeae can also be used to monitor treatment.
Gonorrhea is one of the most common STDs. It should be noted that its diagnostics indicate the opposite. It is extremely rare for doctors to detect gonorrhea. But this does not mean that the infection has decreased. This only means that the frequent use of antibacterial agents for the treatment of various diseases (not the genitourinary system) leads to a blurred clinical picture and false negative results. Most often, the disease occurs in patients 16-30 years old who are sexually active. There is a possibility of infection through household contact, but in the vast majority of cases the disease is transmitted during unprotected sexual contact. Symptoms of gonorrhea differ between males and females. In men, symptoms appear within 3-4 days after infection. Characteristic manifestations include pain during urination and discharge from the urethra. Swelling may also occur. If the infection becomes chronic, the discharge is often insignificant and is not paid attention to. If the disease is not treated for a long time, various complications may develop. These include disruption of the reproductive system, damage to the kidneys and bladder. The infection can also affect the joints and cause infertility.
In women, the disease often occurs without significant symptoms. The appearance of pronounced clinical manifestations, as a rule, indicates the development of complications. Therefore, the disease is often detected by chance, and not when a woman goes to the doctor with complaints. Gonorrhea can be suspected if the patient complains of painful urination, discharge, bleeding between menstruation, itching of the external genitalia, pain in the lower abdomen or perineum. But it should be noted that gonorrhea is very often not the only infection. For example, the disease develops against the background of bacterial vaginosis. In this case, the woman will notice symptoms of dysbiosis - an unpleasant odor, grayish discharge, itching or burning. It is with these symptoms that women go to the doctor, after which, during a PCR examination, the causative agent of gonorrhea is detected. Most often, this study is included in a comprehensive examination for STIs.
Indications for the study:
· Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections, including the diagnosis of gonorrhea. · If infection is confirmed during treatment monitoring · Routine examination to assess vaginal microflora
It should be noted that if gonorrhea is confirmed in one of the sexual partners, then this study is recommended for the second partner. The same goes for treatment. If the partner's infection is confirmed, the couple should undergo treatment at the same time. Patients with gonorrhea are at increased risk of contracting other STDs.
Particular attention is paid to the nonspecificity of the symptoms of the disease, which does not allow making a diagnosis without laboratory confirmation. For example, the manifestations of chlamydia and gonorrhea may be similar. The treatment is completely different. Therefore, to resolve the issue of a complex of therapy, the results of the study are first obtained. Note that the number of copies of the bacterium does not matter, since the causative agent of gonorrhea is an absolute pathogen that, in any quantity, causes infection. Therefore, it is sufficient to carry out PCR diagnostics of gonorrhea using a qualitative method. The main risk factors for contracting gonorrhea: unprotected sex, frequent change of sexual partners.
How to take a smear
The most accurate test to identify this sexually transmitted disease is a smear test. This is a procedure for taking biomaterial from the mucosa. Most people assume that a smear is taken only from the genital mucosa. However, this is not entirely true - a venereologist can take a smear from the anus, throat, and also the mucous membrane of the eyes.
For proper preparation, we recommend that women adhere to the following tips:
- avoid sexual intercourse one to two days before the examination;
- stop taking medications a week before taking a smear;
- do not use perfume products 2-3 days in advance - only water is allowed;
- Do not wash your face on the day of the procedure.
Men should prepare in the same way. 24 hours before taking a smear, it is recommended to perform thorough genital hygiene without cosmetics and soap.
If a woman is having her period, it is necessary to wait until it ends, otherwise the results will be incorrect. Or take a smear test before your period.
If the disease has entered a chronic stage, the doctor can provoke the release of gonococcus onto the mucous membrane. This will help you get the right results.
If at least one of these requirements is violated, the test results will not be accurate, which the patient should tell her doctor about.
Gonococci in a smear
Types of smear examination for gonococcus
After taking a smear, depending on the capabilities of the laboratory, it can be examined for the presence of gonococci using several methods:
- 1.Bacterioscopy. Allows you to see gonococci in a smear using microscopy. This study is a preliminary diagnostic technique. Since it does not make it possible to accurately identify the type of causative agent of the infectious process. During this examination, gonococci are detected less frequently in a smear in women. Since the pathological process in them tends to be chronic without active release of the pathogen. In the acute course of gonorrhea, gonococci in a smear in men are determined in the form of paired bean-shaped formations located under one capsule.

- 2. Bacteriological study. The taken material is sown on a special nutrient medium. If gonococci are present, colonies of the microorganism grow on it. Then the identified Neisser gonococci in the smear are identified and their sensitivity to antibiotics is determined. Bacteriological research is quite lengthy; it takes 3-7 days to get results.
- 3.PCR. A modern laboratory research technique in which direct genetic identification of the pathogen is carried out using a polymerase chain reaction.
To obtain a reliable result, it is enough to find a DNA fragment of an infectious pathogen in the material being tested.
Smear for gonococci in women
Gonococci provoke the process of inflammation of the female reproductive system.
They penetrate the vaginal mucosa, where they multiply in large numbers.
The process is accompanied by copious discharge of pus.
Gonococcus is most often found in young girls under the age of 32.
What to do if there is gonococcus in the smear?
If a gonorrhea pathogen is detected in a woman’s smear, this indicates that she has been infected with a sexually transmitted disease.
It is necessary to begin treatment of the disease immediately.
A woman can become infected through promiscuous intimate relations or using other people's personal hygiene items.
The first symptoms can be detected 7 to 10 days after contact.
There are cases when gonococci do not show signs of disease and the disease is asymptomatic.
It should be noted! Both partners should be tested for gonococcus.
This will prevent the recurrence of gonorrhea.
Important! Promptly undergo laboratory tests for gonococcus.
All women should have a smear test for flora regularly.
Delayed treatment may cause the development of gonococcal sepsis.
How can a woman prepare for a gonococcus test?
In order for the research to be reliable, you should know the rules for preparing for collecting material.
The main condition is the abolition of antibacterial drugs 1-2 weeks before the study.
If it is impossible to stop taking medications, you should inform your doctor.
There are a number of other rules for preparing for smear collection:
- A couple of days before the test, stop having sexual intercourse.
- Do not urinate two hours before the smear
- Carry out hygiene, without soap, in the evening, the day before collecting the material.
- Do not use vaginal suppositories or creams
Taking a smear during menstruation is strictly not recommended.
It is better to reschedule the analysis for the first days after menstruation.
How is a smear taken from women?
The doctor makes a smear during the examination.
The material is taken from the walls of the mucous membranes of the vagina or cervix.
The sampling is carried out using a sterile spatula.
The material taken from the patient is placed on a glass slide and sent to the laboratory.
The procedure is absolutely painless.
Sometimes there may be slight discomfort.
After receiving the result, you should contact a gynecologist.
A specialist will help you decipher the result and, if necessary, prescribe a course of treatment.
When gonococcus is detected in a woman’s smear, this is a sign of a serious disease that requires mandatory drug treatment.
Normally, there should be no gonococcus in the organs of the genitourinary system.
Smear for gonococci in men
Men should be tested for gonorrhea as part of a routine check-up or when symptoms are present.
In women, gonorrhea most often occurs without visible symptomatic manifestations.
Without knowing about the presence of gonococcus, a woman can cause infection to her partner.
Transmission of the gonorrhea pathogen can occur through unprotected intimacy.
If suspicious symptoms appear, you should definitely be examined by a doctor.
In men, gonococcal flora most often affects the bladder and urethra.
In this case, the following symptoms may begin to bother you:
- 1.Frequent urge
- 2.Hyperemia of the head of the penis
- 3.Swelling of the genital organ
- 4. Specific discharge with an unpleasant odor
In some cases, men may have no symptoms of the disease.
How is a smear taken from men?
In order to confirm the presence of gonococcus, laboratory diagnostics should be performed.
In such cases, the doctor takes a swab from the urethral canal.
A special sterile probe is used to collect a smear.
The probe is inserted into the urethra to a depth of several centimeters and rotated for several seconds.
Afterwards, the material is sent to the laboratory for further study.
When taking a smear, you may experience discomfort.
As a rule, such pain is tolerable.
Important! If you want to have a painless smear test, please contact our clinic.
The procedure does not cause complications and is well tolerated by all patients.
The following laboratory diagnostic methods are used to examine a smear:
- Bacteriological culture
- Microscopic studies
- PCR diagnostics
Taking a smear for Neisser's gonococcus with provocation
With an asymptomatic course of the disease, it is quite difficult to determine the presence of the infectious agent.
Therefore, for an accurate diagnosis, a smear with provocation is used.
Most often, this method is used for chronic gonorrhea.
The causative agent of gonorrhea in a chronic course is capable of encapsulating.
For provocation before taking an analysis, use:
- 1.Introduction of chemical reagents
- 2. Mechanical irritation of the mucous membranes of the genital organ
- 3. Drinking alcohol or fatty foods
Under the influence of irritating factors, intensive release of gonococcus occurs.
The smear is examined in a laboratory.
A smear for gonococcus should be negative, which indicates the absence of the pathogen.
Interpretation of smears for gonococcus
When visiting a venereologist, one of the types of tests is a smear for gonococcus.
Such a smear is taken if complaints and a corresponding symptomatic picture are detected.
The result can be either negative or positive.
If the microscopic examination of the smear is positive, the presence of epithelium and mucus will be indicated.
The leukocyte count will be increased in the smear.
If the number of leukocytes in the field exceeds 5, then this is a sign of severe inflammation.
When staining the specimen according to Gram, diplococci will be noted.
Normally, the smear should not contain Neisser's gonococcus.
If there is infection, the smear may contain gonococci and trichomonas.
When studied using the polymerase chain reaction method, the result will indicate the presence or absence of the gonorrhea pathogen.
Bacteriological culture for gonococcus is carried out using a special nutrient medium.
As a result, the type of causative agent of the inflammatory process is indicated.
The sensitivity of pathogenic strains to antibacterial agents is determined.
If the smear was taken from a pregnant woman, the readings will be slightly different.
There will be an increase in epithelial cells.
Possible presence of coccal flora.
Remember! An increase in the number of cocci may indicate the presence of an inflammation process.
If the presence of gonococcus in a smear has been laboratory confirmed, treatment of the disease should be started as soon as possible.
If gonococci are found in the smear, the venereologist has the opportunity
After a laboratory test, if gonococci are found in the smear, the venereologist has the opportunity to carry out adequate etiotropic therapy.
It is aimed at their destruction.
Therefore, even if the characteristic symptoms of gonorrhea appear, you cannot treat it yourself.
Effective therapy is possible only after examining a smear for gonorrhea.
If you suspect or detect gonococci in a smear, contact the author of this article - a venereologist, a urologist with 15 years of experience.
How to get tested for gonorrhea in women
You can take a smear at different times - pregnancy will not be a contraindication. Before donation, the patient needs to ask where the biomaterial will be collected from and when the results can be found out. In women, sampling is carried out in places where mucus accumulates - this is the cervix, vagina, and less often - the urethra. To facilitate the collection of biomaterial, the nurse uses a gynecological speculum. The collection procedure will be easier if the woman relaxes and does not move. Taking an analysis most often does not cause any discomfort. However, some particularly sensitive women experience pain in the lower abdomen and vaginal discharge may appear. Painful symptoms disappear on their own a couple of hours after collection. If the situation does not normalize on its own, our specialist is ready to help you.
For smears, use plastic spatulas or cotton swabs. The smear is applied to a glass slide and sent to the laboratory. You can usually see results within 2-3 days.
Important! If gonorrhea is suspected during pregnancy, gonococci culture is routinely performed three times: when the pregnant woman is registered, at the 30th week and on the eve of childbirth.
Culture for gonorrhea
How is a tank culture performed for gonorrhea?
The material for this type of laboratory test is a smear from the urethra.
In women, an additional smear can be taken from the mucous membrane of the vagina, as well as the cervix.
Then the material is added to a sterile tube with a buffer solution and sent to a bacteriological laboratory, where it is inoculated on special nutrient media.
After a period of incubation at a certain temperature, colonies of microorganisms grow on the medium (provided they are present in the material under study).
They are identified by morphological, biochemical and antigenic properties, which makes it possible to determine their species.
If it is necessary to determine sensitivity to antibiotics, re-seeding is carried out on nutrient media with the addition of antibacterial agents.
The absence of colony growth indicates the sensitivity of gonococci to a particular antibiotic.
How to prepare: tank culture for gonorrhea
As a result of improper preparation of the patient before the test, a false positive result may be obtained.
Therefore, it is necessary to comply with a number of conditions before the procedure:
- Avoid sexual intercourse 2 days before the test.
- Do not urinate for 2 hours.
- Toileting the genitals without intimate hygiene products.
- Avoid taking antibacterial drugs during the study.
Sample collection for chronic gonorrhea
Often, chronic forms of gonorrhea are asymptomatic.
To increase the reliability of laboratory test results, medical provocation methods have been developed:
- Biological
- Chemical
- Mechanical
- Nutritional
- Physiotherapeutic
- Physiological.
Let's look at each method in more detail.
To carry out biological provocation, a gonococcal vaccine, plasmol or pyrogenal is administered intramuscularly.
The method of chemical provocation is the instillation of a 0.5% solution of silver nitrate, Lugol's solution, into the urethral canal.
Eating spicy, salty, sweet foods is a method of nutritional stimulation.
One of the methods of physiotherapeutic stimulation is the use of inductometry to increase the temperature of the pelvic organs in women.
Taking a test during menstruation in women is called physiological provocation.
It is believed that these methods help to increase the inflammatory process in the tissue and facilitate the identification of the pathogen.
Time frame for preparing cultures for gonorrhea.
The disadvantage of tank seeding is the length of time it takes to wait for results.
As a rule, the average analysis time is 7-10 days.
Interpretation of tank culture results for gonorrhea
The results of the study are deciphered by a venereologist.
Based on them, he makes a conclusion about the presence or absence of an infectious process.
And also, if necessary, prescribe etiotropic antibiotic therapy aimed at destroying gonococci.
The result of this study can be positive (gonococci are detected in the smear) and negative (gonococci are not present in the test material).
When determining sensitivity to antibiotics, the analysis results in a list of antibacterial agents, as well as the sensitivity of the isolated gonococci to them.
Gonorrhea culture is a specific and reliable laboratory test method.
The advantage of this technique is the ability to determine the sensitivity of gonococci to antibiotics.
This is especially important in the case of chronic pathology.

The only drawback of the inoculation tank is the rather long period of research time required for the growth of a colony of microorganisms.
Results can be obtained only after a few days.
Culture for gonorrhea: price
Let's consider the cost of this procedure.
In Moscow, depending on the specific clinic, prices for this study vary from 1000 to 2500 rubles.
It should be understood that sowing alone is not enough.
You can pay for other diagnostic methods, provocative tests, and control tests.
Doctor's consultation is usually paid separately.
In our clinic you can get quality services at the most reasonable prices.
The cost of sowing is 1600 rubles.
Based on the results, you can consult a doctor.
Culture for gonorrhea: where to go
In order to get results quickly and efficiently, we recommend contacting our clinic.
Our own laboratory allows us to perform analyzes quickly.
If the disease is detected, the doctor will prescribe an effective course of treatment.
If you need to take a culture test for gonorrhea, contact the author of this article - a venereologist, a urologist in Moscow with 15 years of experience.
How to take a smear test for gonorrhea in men
The procedure for taking biomaterial from men is somewhat different. In a doctor's office, a man washes his penis with water, then wipes it thoroughly. The healthcare provider inserts a special probe into the urethra. To obtain a smear, the nurse performs rotational movements at a depth of several centimeters. This procedure may cause discomfort. The more advanced the inflammatory process, the more discomfort the man experiences. However, according to our patients, they tolerate the procedure without any problems.
After removing the probe, the smear is applied to glass and sent to the laboratory. For a certain period after collection, a man may feel discomfort that intensifies during urination.
If the discomfort is severe, we recommend:
- drink anti-inflammatory chamomile decoction;
- take a comfortable shower, bath;
- wear natural, loose-fitting underwear.
In case of severe pain, analgesics are recommended. If your condition worsens, you should consult a doctor.
If you still have questions about how to take a smear for gonorrhea in women and men and how to prepare, call or contact our clinic!
Gonorrhea (gonorrhoea) - symptoms and treatment
Gonococcal infection, if untreated, almost always causes various local and extensive, early (acute) and late (chronic) complications.
Local complications are limited by the spread of the inflammatory process and its consequences within the genitourinary system and its neighboring organs.
Complications of gonorrhea in men
Orchiepididymitis - inflammation of the testicle and its epididymis - is the most common complication of gonorrhea in men. In acute gonorrheal orchiepididymitis, sharp pain occurs in the scrotum and perineum, spreading to the rectum, and difficulty urinating. The scrotum swells, the level of blood flow to it increases, and palpation reveals a compacted and sharply painful appendage. In a chronic process, pain is less pronounced. Gonorrheal orchiepididymitis is a serious complication leading to male infertility due to scarring of the epididymis and vas deferens.[21]
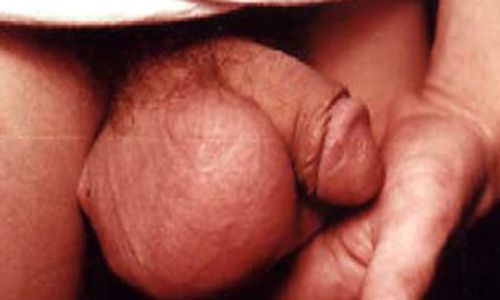
Urethral stricture is a pronounced narrowing of the urethra. Previously, this complication of gonorrhea occurred quite often in men.[22] Lately, this has rarely occurred. The main symptom is difficulty urinating and weakening of the urine stream.
Much less frequently in men, cases of inflammation of the paraurethral glands ( paraurethritis ), damage to the seminal vesicles ( vesiculitis ) and inflammation of the prostate gland ( prostatitis ) occur.[15]
Complications of gonorrhea in women
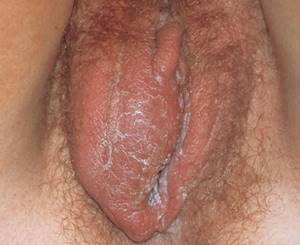
Pelvic inflammatory diseases (salpingoophoritis, endometritis, pelvioperitonitis) are common and serious complications of gonorrhea in women. Their main symptoms are cramping pain in the pubic area and lower abdomen, as well as purulent or mucopurulent discharge from the genital tract. In the acute process, fever and chills are noted. The development of peritonitis with a fatal outcome is possible. In a chronic course, the symptoms are less pronounced.
This type of complications due to adhesions and cicatricial changes in the fallopian tubes is considered the main cause of tubal infertility in women and the development of ectopic pregnancy. With chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvis, women quite often experience spontaneous abortions and premature births, and children are often born with low birth weight.[16]
Rarer local complications of gonorrhea in women include inflammation of the vaginal vestibule ( vestibulitis ), damage to the paraurethral ducts and glands ( paraurethritis ), abscess of the Bartholin gland ( bartholinitis ) and damage to the bladder ( cystitis ).[5]
Disseminated gonorrheal infection (DGI) develops when gonococci spread hematogenously from the genitourinary organs to the skin, joints and other organs. It manifests itself as a sharp increase in temperature, often skin rashes and other symptoms depending on which organ is affected.[23] In disseminated gonorrhea, cases of sepsis [24], meningitis[25], epidural abscess[26], liver abscess[27], endocarditis[28], myopericarditis[29], pneumonia[30], tenosynovitis[31], arthritis[32] have been described. ], perihepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome).[33]
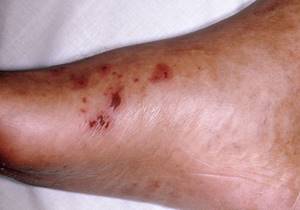
Visible symptoms of the spread of the process are hemorrhagic skin rash, arthritis and palmoplantar keratosis.
Hemorrhagic rash occurs most often in the area of the extremities above the joints of the feet and hands. Initially, small red spots appear, quickly increasing in size, turning into pustules or blisters with hemorrhagic contents and necrosis in the center.[34]
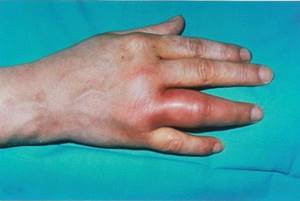
With gonococcal arthritis, 1-2 joints are affected. The process is always one-sided. Most often, the metacarpophalangeal, interphalangeal joints of the hands, knee, elbow, ankle, shoulder and hip joints are affected. Characteristic symptoms are pain, hyperemia, fever, and swelling of the joint.[32]
Gonorrheal keratosis occurs 2-3 weeks after the onset of the disease. Keratosis lesions are located on various parts of the skin, but most often on the soles and palms, and are characterized by sharply circumscribed callous-like horny plaques located on an infiltrated base.[34]
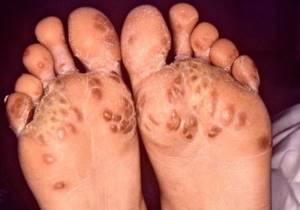
Gonococcal and HIV infection - gonorrhea increases the risk of contracting HIV infection by 3-5 times; with rectal gonorrhea, this risk increases tens of times.[5]
How are smears tested for gonococci?
In this section, we will take a closer look at how different types of biomaterial research are carried out.
Important! Gonococcus, which is located outside the human body, is unstable, so after taking the material, the study is carried out within 15 minutes.
Analysis using the Gram method, or bacterioscopy in other words, is performed, as we have already said, using the method of staining with special means. To identify Neisser gonococcus, the nurse examines the biomaterial under a microscope. Thanks to the bright coloring of gonococci, they are easy to see against a pink background. Bacterioscopy is good because the results can be found out almost immediately, but for women it is not entirely accurate - when taking material from the cervix, the gonorrhea may not be detected. Therefore, the absence of gonococci in a smear does not guarantee the absence of the disease itself.
In addition to bacterioscopy, our specialists use other types of tests to identify gonorrhea. The seeding of the material is among the most reliable. It is often used when other test results are negative and the doctor has doubts about their accuracy. The patient's biomaterial is placed in a special environment supplied with nutrients. Observation of the growth of the gonococcus colony is carried out for 5–7 days. If the colony increases, the diagnosis is confirmed.
The advantage of bacterial culture is that it not only guarantees the reliability of the data obtained with high accuracy, but also allows you to select the right antibiotics. The method makes it possible to identify the resistance of microorganisms to different types of drugs, which facilitates subsequent treatment.
Results of smear test for gonorrhea
Decoding the analysis results is quite simple. Based on the results of the bacteriological study, they write: gonococci were detected (not detected). Alternatively, the conclusion may say: gram-negative diplococci were detected (not detected), which means the same thing. Gram-negative diplococci are a descriptive characteristic of the pathogens.
The conclusion after the cultural examination should contain information about which microbe was identified and in what quantity (massiveness of its growth), to which antibiotics this infectious pathogen is sensitive.
Deciphering a smear for gonorrhea should be done exclusively by a specialist, since the correct interpretation of the results is very important. The slightest inaccuracies and inattention can lead to an erroneous diagnosis and the prescription of the wrong course of treatment for gonorrhea.
Thus, a smear test for gonorrhea is performed during a gynecological examination. It is often performed easily and does not cause any complications. A gonorrhea smear test is necessary if you have symptoms or are at risk of the disease.
We also invite you to watch a video on how to properly prepare for the upcoming tests for sexually transmitted infections:
Interpretation of examination results
The venereologist deciphers the received data. Normally, the biomaterial is completely free of gonococcal bacilli.
If a gonorrheal infection is confirmed, the results will be as follows:
- the number of leukocytes reaches 10–20;
- extracellular diplococci are detected;
- the amount of mucus exceeds 1+, which indicates the presence of infection;
- the amount of epithelium is higher than normal.
Often the clinical picture is such that the symptoms of gonorrhea overlap with other sexually transmitted diseases. Therefore, a comprehensive study is necessary to identify other bacteria. The presence of trichomonas or chlamydia in the body can be quite difficult to identify.
Advantages of visiting our clinic
If you feel any of the symptoms we listed above or are unsure about your sexual partner, to avoid worries, take a gonorrhea smear at our clinic.
The advantages of contacting us are as follows:
- the analysis is performed anonymously - we do not require the presentation of a passport;
- experienced nurses will perform the collection procedure quickly, with minimal pain;
- laboratories are equipped with modern high-precision equipment - obtaining analysis results within half an hour;
- Venereologists have more than 20 years of experience - we guarantee the accuracy of the diagnosis;
- there is an opportunity to undergo a comprehensive test for sexually transmitted diseases;
- convenient location: the clinics are located in the center of the capital, a 5-minute walk from the Krasnopresnenskaya / Barrikadnaya, Tretyakovskaya / Novokuznetskaya metro stations (there is parking next to the clinic).
Remember that timely testing will allow you to avoid the development of the disease and its progression to the chronic stage - subject to a course of treatment.
The consequences of inattention to health lead to the following complications: prostatitis, impotence, peritonitis, infertility, purulent sepsis. To avoid such unpleasant complications of the disease, contact us if you have the slightest suspicion of gonorrhea - the test costs only 900 rubles. Half an hour of your time will allow you to avoid long-term worries and start treatment on time! We wish you good health!
Smear test for gonorrhea during pregnancy
In the case when a woman is pregnant, there are several ways to smear for gonorrhea. For preliminary diagnosis, a smear of flora is taken from the urethra or cervical canal, but the accuracy of such a study is only 30–70%.
The next method is the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) swab, but this can often give a false result. The most reliable method is bacteriological culture, which makes it possible to detect gonorrhea in 95% of cases.
There is a certain risk group:
- infected with gonorrhea before pregnancy;
- the presence of any other infections transmitted through sexual intercourse;
- girls who are sexually active before the age of 25;
- having an active sex life from an early age;
- girls who refused the barrier method of contraception.
At his own discretion, the gynecologist may prescribe any additional research.
We will tell you whether it is possible to become infected with AIDS and HIV through saliva.
How long after infection does syphilis appear? Read here.
The first signs of AIDS in men and women: https://venerolog-ginekolog.ru/venereology/spid/pervyie-priznaki-spida.html