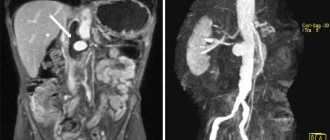
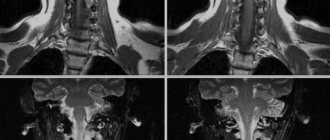
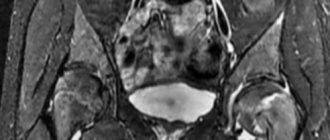
The first place among malignant neoplasia in young women is precancer and cervical cancer. Over the past two decades, this disease has been rapidly growing younger. Now the manifestation occurs at 25-30 years. Every year, 200,000 cases result in the death of the patient. The main principle of screening for this and other pathologies of the female reproductive system is early diagnosis. It includes imaging and biopsy followed by histological examination. The most informative today is MRI with contrast of the uterus.
How are the internal genital organs arranged in women?
Sexual dimorphism determines not only morphological similarities, but also significant differences in the structure of this group of organs. Many physiological processes in the lives of female representatives depend on their correct functioning. The main function of the system is procreation. It is located in the pelvic area. Comprises:
- Vaginas are tubes made of muscle tissue, which are the receiver of male seed and the birth canal;
- Uterus. It consists of smooth muscles covered with a layer of endometrium, permeated with blood vessels;
- Fallopian tubes, responsible for the advancement of a mature egg during ovulation;
- Ovaries - female reproductive glands responsible for endogenous and exogenous secretion. They release sex hormones into the bloodstream and form eggs.
Functional disorders and structural abnormalities may not manifest themselves for a long time. Moreover, in 13% of cases they become the main etiofactor of infertility, in 18% - the cause of premature birth and in 15% - loss of pregnancy.
What does the study show?
During pregnancy, MRI of the uterus provides information about:
- position of the fetus (type of presentation, relative position of body parts);
- the location of the umbilical cord and placenta inside the uterus;
- presence of defects in the child;
- oxygen saturation of the fetal brain;
- condition of the muscle tissue of the uterus.
A resonance examination makes it possible to assess the patient’s condition, readiness for childbirth and identify some indications for a cesarean section. Based on the results of MRI, the uterus is sent for observation in the maternity ward, delivery is stimulated, or it is prepared for surgery.
In non-pregnant women, MRI of the uterus and ovaries allows to identify gynecological diseases, clarify the preliminary diagnosis and refer for appropriate treatment.
What symptoms require testing?
The clinical picture signaling trouble includes:
- Dysmenorrhea;
- Amenorrhea;
- Uterine bleeding;
- Chronic or acute pain syndrome localized in the lower abdomen;
- Pelvic pain;
- Dyspareunia;
- Menorrhagia;
- Opsomenorrhea;
- Hypomenstrual syndrome;
- Infertility of unknown origin;
- Galactorrhea;
- Hirsutism;
- Uremia;
- Painful urination;
- Hematouria;
- Hyperthermia with febrile or subfebrile values;
- General weakness;
- Fever;
- Unexplained weight loss.
Diagnostics is necessary during the preoperative preparation period. It allows you to minimize intervention, significantly reducing the load. If there is a history of cesarean section after 14 weeks of a new pregnancy, imaging is required to assess the condition of the scar and determine the mode of delivery. In the postoperative period, the study allows you to check the effectiveness of the operation and monitor the recovery period.
Advantages of MRI
In addition to high sensitivity, this technique has a number of advantages:
- The main advantage is the absence of radiation exposure. This is especially important when examining the reproductive organs during pregnancy planning. In addition, this eliminates the recovery period. This means scanning is carried out as often as necessary for dynamic monitoring.
- Another positive aspect is the complete virtuality of the procedure. It is non-invasive and does not require trauma to the skin or mucous membranes. This completely eliminates iatrogenic risks.
- Diagnostics is a painless method that does not cause discomfort to patients.
- It is indicated during pregnancy, starting from the second trimester. It is not advisable to schedule an examination during the first 12 weeks, since at the moment there is insufficient high-level evidence on its safety for the fetus during the period of active embryogenesis.
- The complexity of scanning becomes an important point. It covers the entire pelvic region, allowing you to assess the condition of adjacent structures and exclude pathologies associated with their diseases.
Indications for MRI of the uterus
Indications for MRI examinations are divided into two main groups: pregnant women and those not pregnant.
For pregnant women, examination is indicated if there is a suspicion of pathological conditions occurring in the mother and fetus.
In particular, it is diagnosed:
- intrauterine hypoxia;
- severe chromosomal abnormalities;
- fetal malformations;
- placenta previa in the uterus;
- umbilical cord entanglement.
Nuclear resonance is also used to evaluate the condition of the fetus and internal organs after injuries, for example, bruises in the abdominal area.
For women who are not preparing for childbirth, a uterine examination is performed in order to exclude or clarify gynecological disorders. Benign and malignant tumors, ectopic pregnancy, chronic miscarriage. Often, the ovaries and fallopian tubes are examined at the same time, where inflammatory processes or persistent adhesions occur that interfere with the passage of eggs.
A referral for an MRI of the uterus and ovaries is issued by the attending physician or urgently by a specialist at the medical center where the diagnosis is carried out.
Briefly about
Address: Moscow, metro st. 1905, no. 7, building 1
Working hours: seven days a week, from 7 am to 2 am
Equipment: Powerful Philips 1.5 Tesla
Specialists: All employees have at least 5 years of experience
What diseases does scanning verify?
With its help they discover:
- Endometriosis;
- Endometritis;
- Erosion;
- Cysts and polycystic disease;
- Polyps;
- Piovar;
- Sactosalpinx;
- Salpingo-oophoritis;
- Abscess;
- Vaginal-vesical fistulas;
- Hyperplasia;
- Injuries;
- Congenital structural anomalies: bicornuate uterus, septum, duplication, rudimentary horn, and so on;
- Adhesive processes;
- Precancerous conditions;
- Dysplasia;
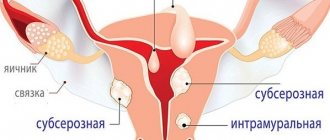
- Neoplasia of malignant and benign nature: fibroids, fibromas
- Metastases;
- Loss and prolapse of an organ;
- Hyperanteflexia;
- Atresia;
- Foreign bodies;
- Leukoplakia;
- Retroflection;
- Oophyte;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Thrombosis of the ovarian vein.
Why do you need contrast?
Paramagnetic contrast agents are made from gadolinium. It is a soft rare earth metal with a silvery color. Its solution has ferromagnetic properties. Once in the bloodstream, it increases the clarity of images. Allows you to identify areas with impaired hemodynamics or normal blood supply. Such vascular growths are characteristic of cancerous tumors.
How tomography is done
You must arrive for the procedure 20 minutes before the scheduled time, since you will first need to fill out a health questionnaire and talk with a diagnostician.
After this, the patient will have to remove all wardrobe items made from sports stretch fabrics with metal threads or with metal elements. This is necessary to avoid injury, because under the influence of a magnetic field the metal heats up to high temperatures or is attracted to the radiation source. All jewelry, watches, electronic devices and bank cards will have to be placed in a special locker. To save time, it is better to dress in advance in comfortable clothes made of natural fabric that do not restrict movement.
Immediately before the procedure, the woman lies down on a mobile tomograph table. A nurse injects Gd into a vein in the elbow. After this, the table is pushed under the emitter of the open apparatus or into the tomograph tube. It is installed in such a way that the entire patient is exposed to a high-intensity magnetic field. This is absolutely safe for the body, since the radiation only has a short-term effect on the hydrogen atoms in the human body. After the procedure is completed, it disappears and does not cause harm to health.
Any pain or discomfort should be reported to the radiologist. This can be done through a two-way intercom or by pressing the signal bulb, since medical personnel are located in a separate shielded room.
The procedure takes 40-60 minutes. After completion, you can wait for the results or go straight home, since additional medical supervision is not required.
Contraindications
Since uterine examination is also carried out in pregnant women, pregnancy is not a contraindication. In fact, MRI of the uterus and ovaries is absolutely safe for the patient. It also does not harm the fetus inside the uterus.
The only caution concerns the presence of metal objects in or nearby the body of the woman being examined. Removable items are removed in preparation for an MRI of the uterus. These include earrings, rings, bracelets, buckles, dental braces, partial and complete dentures.
If you have non-removable ones (dental crowns, internal dentures, pacemakers, bullets and shrapnel), a doctor’s consultation is necessary. Depending on the location of metal inclusions and the composition of the metal, a decision is made whether MRI is possible. Even inclusions located far from the uterus are affected by an intense magnetic field.
Who is the study contraindicated for?
There are few absolute contraindications to the study. These include:
- The presence of metal particles in a woman’s body. These can be fragments, bone knitting needles, pins, vascular clips, extensive tattoos applied with metallic paint.
- The use of complex medical devices that are recommended for constant wear. These are pacemakers, insulin pumps, ferromagnetic middle ear implants. Violation of their performance can provoke deterioration and even death of the patient.

All other obstacles are considered relative:
- Unusual height and weight. The technical characteristics of the device do not always allow checking the health of very tall or overweight girls. Open type devices have a greater load capacity.
- A tendency to claustrophobia, panic attacks, VSD, hyperkinetic syndrome requires the use of sedation or anesthesia.
- Examinations under anesthesia are also indicated for newborns and young children.
- A state of alcohol or drug intoxication prevents the radiologist from following the recommendations, so the examination is not carried out at this time.
Contradictory studies are not conducted:
- For renal dysfunction, liver dysfunction, hemodynamic disorders. If the function of removing foreign substances from the body is affected, gadolinium can accumulate in the tissues. In kidney failure, there is a risk of a rare complication called systemic contrast-induced fibrosis.
- Bronchial asthma during exacerbation, to avoid an attack of suffocation.
- Hemolytic anemia;
- Severe forms of diabetes mellitus;
- Pregnancy. Gd is able to penetrate the placental barrier. Recent studies show that it accumulates in the cerebellum and pituitary gland. There is not yet sufficient information about the presence or absence of clinical significance of this process.
- During breastfeeding, lactation must be interrupted for two days. This is the complete period of removal of contrast from the body.
- If you are intolerant to the components of paramagnetic contrast.
Preparing for the study
No special preparation is required, regardless of which organs are being examined. The intestinal loops located almost next to the uterus do not interfere, the same applies to the ovaries. Therefore, both planned and emergency MRI of the uterus is performed without first following a diet.
Since MRI excludes the presence of metal objects that react with the device, they must be removed in advance. While the MRI is taking place, the patient's relatives or accompanying persons should not approach the machine. It is better to completely refrain from visiting the room where the equipment is installed, assigning all responsibilities to medical workers.
Wheelchair users arriving at medical centers for an MRI are transported directly to the machine on a stretcher. The stroller should be left in another room so that the strongest magnets do not affect the metal if the diagnostic chamber is accidentally opened.
Typically, MRI of the uterus and ovaries is performed in the supine position. This is a comfortable diagnostic method that is not associated with painful sensations.
Where to get examined in St. Petersburg
To do this, just contact our portal, which was created to help patients choose medical institutions. All services of the service are free. With its help it is easy to find out in advance:
- What tomographs are used for diagnostics? All significant technical characteristics are indicated here: type of tunnel, load capacity of the couch, magnetic field power.
- Cost of the native procedure and prices for the introduction of paramagnetic agents;
- Name of contrast agents;
- Qualification and experience of medical personnel;
- Clinic infrastructure: availability of parking for motorists, accessible environment with wheelchairs, ramps, freight elevators;
- Directions for public and private transport;
- Provided payment methods;
- Reviews from visitors and a rating based on them;
- Availability of discounts, benefits, current promotions.
If you register through the portal, MRI will cost 1000 rubles less. In order to book a ticket, just contact the operators. They accept calls from 8:00 to 24:00. The staff is able to talk in detail about the upcoming study and answer questions. They will recommend medical centers within walking distance and warn you what documents you need to have on hand.
Advantages of MRI in gynecology
MRI allows you to obtain complete images of human organs and tissues at any level and in any given plane with an assessment of their functional integrity. If necessary, you can obtain layer-by-layer series of images with slice thicknesses from 4-5 mm to 0.8 mm. MRI with contrast provides a more accurate verification of the tissue identity of tumors, identifying small metastases at the earliest stages of development. In addition, tomography allows you to assess the structure and condition of bones, soft tissues, blood vessels, ligaments, and cartilage.
How to get the result
The transcript is prepared by a diagnostician after a detailed study of the images. In it he states:
- Sizes and anatomical features of organs;
- Their topography and homogeneity;
- Number of follicles in the ovaries;
- Patency of the fallopian tubes;
- Condition of adjacent organs: rectum, bladder, regional lymph nodes, blood vessels, muscles and bones (limited) of the pelvis;
- Pathological changes in any of these structures.
The diagnosis is not written in the study protocol, since its formulation is not within the competence of the radiologist. He also does not prescribe treatment.
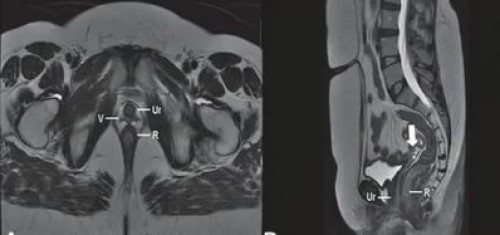
The finished results in the form of a disc with a recording, photographs and a conclusion are given to the patient or sent by e-mail. They should be contacted by your doctor for further treatment.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Literature on the topic:
- Gynecology: national. hands / Ross. Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists; ed.: V. I. Kulakov, I. B. Manukhin, G. M. Savelyeva. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2007. - 1072 p. — (National guidelines).
- Mikhalevich Stanislava Iosifovna. Treatment and prevention of threatened miscarriage in women with a history of infertility: textbook. -method. allowance / S. I. Mikhalevich, N. L. Andreeva. - Minsk: BelMAPO, 2008. - 26 p.
- Sinitsyn, Valentin Evgenievich. Magnetic resonance imaging: textbook. allowance / V. E. Sinitsyn, D. V. Ustyuzhanin. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. - 202 p. — (Pocket atlases on radiation diagnostics / ed. S.K. Ternovoy).