3 minutes Author: Lyubov Dobretsova 190
CTG is a special diagnostic branch of ultrasound (ultrasound), with the help of which, in late pregnancy, the baby’s heart rate, as well as the tone of the uterus, is recorded. The obtained data is synchronized and displayed in the form of simple graphs on the cardiotocogram tape.
Sometimes patients, upon receiving a result of a procedure that is incomprehensible to them, want to decipher it themselves, but often encounter some difficulties. In order to understand the results of CTG, it is necessary to study each indicator separately. This article will discuss such an important parameter as variability, the study of which will bring clarity to the understanding of the issue under consideration.
What is variability?
Variability is the amplitude of fluctuations that represent any deviations from the main line of the basal rate. In simple terms, it is the difference between the maximum (ascending) and minimum (descending) tines.
There are several main types of amplitude indicator (saltatory, slightly undulating, monotonic and undating), each of which requires a little explanation.
| Species name | Characteristic | Diagnostics |
| Monotonous | There are no drops or jumps on the line merging with the main straight line. | Fetal hypoxia, serious damage to the central nervous system, heart disease incompatible with life, etc. |
| Slightly undulating | The presence of microscopic waves almost adjacent to the main line. | |
| Undilating | Wavy. | Normal fetal development. |
| Saltatory | Similar to a discontinuous or broken line. |
In addition to the parameter under consideration, the cardiotocogram may contain additional indicators: STV (or short-temp variation) and LTV (or long-term variation) - short-term and long-term variability. They are decrypted only using special automated systems.
Pathological indicators of variability
The value of variability is always considered in conjunction with other indicators of cardiotocography, since only a complete picture, collected from all the fragments of the mosaic, will make it possible to create a more reliable and objective assessment of the child’s condition.
Thus, a parameter located below 5 beats per minute, together with a basal rhythm of 100–110 or 160–170 units, forms a questionable result of an ultrasound examination. In this case, an additional CTG procedure is prescribed, the readings of which will put everything in its place.
The following set of indicators should also raise suspicion:
- lack of acceleration;
- sudden outbreaks of deceleration;
- deviation of the basal heart rate from the norm;
- too high or low variability.
A complete lack of variability may indicate fetal hypoxia (lack of oxygen), serious damage to the central nervous or cardiovascular system. A more detailed analysis of CTG decoding is contained in this article.
In order to determine the exact result of an ultrasound procedure, it is necessary to entrust the interpretation of data to a specialist who, due to the necessary medical experience, will make the correct conclusion based on the obtained indicators.
Fetal cardiotocography is a study that is performed on all pregnant women after 28-29 weeks. Most often, diagnosis is made at 32-34 weeks, if there are no complications. We will tell you in this article what CTG allows you to see and what the normal values are.
The essence of the method
CTG is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods in the third trimester of pregnancy.
The tiny heart works in full accordance with the general condition of the child. If the baby is healthy and well, then the heart beats rhythmically and clearly. The small heart reacts to any disorders, diseases, or pathological conditions by increasing or decreasing its rhythm.
Cardiotocography is performed two or three times in late pregnancy, usually after 30 weeks, and then before birth at 38-40 weeks. If the pregnancy is not going very smoothly, the doctor may recommend additional CTG.
Cardiotocography is done to find out how the baby is feeling.
During childbirth, the device is also connected to the pregnant woman’s belly to monitor the baby’s well-being while she goes through a difficult but natural path.
Using two sensors, several indicators are measured simultaneously, which are considered together. This is the nature and frequency of the child’s heartbeat, contraction of the uterine muscles and fetal movements.
One of the sensors is a conventional ultrasonic recorder. Its task is to record the baby's heartbeat.
Another sensor is called a strain gauge; it is a wide Velcro belt that is used to encircle a woman. Its task is to record uterine contractions (or labor contractions, if the method is used during childbirth) based on slight fluctuations in the volume of the abdomen. The same sensor “catch” the movements of the fetus inside the uterus.
Recording of indicators is carried out simultaneously, synchronously in two graphs. One shows data on the baby’s heartbeat, the second shows uterine contractions and movements. The readings of the upper graph on the time scale completely correspond to the lower one, so all parameters are interconnected.
The examination lasts from 30 minutes to 1 hour, sometimes the procedure for recording indicators can be extended. CTG is performed in consultations at the place of residence, as well as in any clinic that provides pregnancy services.
How and why fetal CHT is performed
A routine cardiography procedure is necessary to check the health of a developed fetus. The procedure also helps diagnose oligohydramnios and fetoplacental insufficiency. The result is based on the sequence of recordings of the child's heart rate, the mother's uterine contractions, the child's movements and the influence of the environment on them.
You can get results in 15 minutes. Therefore, the analysis is considered universal: it can be performed during a routine check, during painful contractions or childbirth.
The CTG procedure and how it works
Cardiography is carried out using a special sensor that has an ultrasonic effect and is based on the Doppler effect. The device is attached to the stomach.
The sensor produces an ultrasonic wave and sends a signal towards the fetal heart. The wave is reflected from the heart, and this is the information that the device displays. It converts it into a heart rate per minute. The result is displayed with sound, light and graphics on the tape.
Preparing for CTG
The woman's main task is to wake up the baby before the procedure. This is helped by the woman being active and consuming more glucose.
Attention! If the fetus is asleep during CTG, the results will be incorrect.
There is no need to hit the stomach or apply ice, this can only cause harm. It is better if awakening is natural. To do this you need:
- workout. Light physical activity will help a lot: walking up the stairs, swimming, simple exercises;
- eat something sweet: chocolate, dried fruits, tea with sugar;
- do breathing exercises. A slight holding of breath causes a slight oxygen deficiency in the fetus, which will cause it to wake up. Not all doctors approve of this method, so use it if all else fails.
This will help wake up the child before the procedure and not harm him. If he is stressed, the results will be incorrect.
Cost of CTG

The price of the procedure depends on the city and the medical center where it is performed. The cost is also affected by the type of pregnancy (singleton or multiple), as well as the service of interpreting the results (whether it is included in the examination or not).
Prices in St. Petersburg start from 1500 to 2000 for cardiotocography of one fetus (with or without interpretation). From 2000-2500 for examination of a multiple pregnancy with interpretation of the result. In Moscow, the cost starts from about 1800 rubles.
Many medical centers often run promotions on some of their services. If you're lucky, CTG can be done for about 1000 rubles, taking into account the discount.
Is CTG dangerous for the fetus?
The procedure is absolutely safe for both the woman and the child. It takes place without injections or punctures of the skin, is completely non-invasive and painless and is mandatory, as it helps to identify complications in the early stages of pregnancy.
Modern drugs make it possible to assess the vital signs of the fetus without direct intervention in its body. Therefore, the examination should not be neglected or abandoned out of fear for the child.
Decoding and norms
With the advent of modern fetal monitors, the problem of deciphering difficult terms used in CTG has become a simpler task, because the device itself analyzes the data received and issues a conclusion. In it, a woman always sees the main thing - the cherished note “the fetus is healthy.” But such a record, alas, does not always appear.
In addition, expectant mothers really want to know as much as possible about their son or daughter. We will try to explain what the records in the cardiotocography report mean and what the standards are.
Basal heart rate
Everyone knows that the heart of a child who has not yet been born beats quickly - more than 110 beats per minute. But a woman who comes to CTG for the first time is faced with another discovery - a small heart not only beats quickly, it beats at a different pace.
Almost every second the speed changes - 145, 150, 132 and so on. It would be difficult to determine the norm for a particular child if an average value - the so-called basal heart rate.
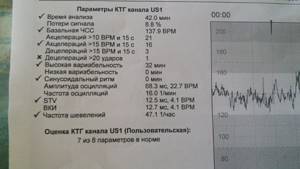
During the first minutes, the program analyzes all incoming values, and after that determines the arithmetic mean. The normal basal heart rate is considered to be between 110 and 160 beats per minute. An excess may indicate tachycardia; a heart rate below 110 beats per minute may indicate bradycardia. Both the increase and the decrease can equally be physiological, or they can indicate the child’s troubles.
What is the normal amplitude?
The normal variability is considered to be from 5 to 25 beats per minute. Moreover, their frequency should not reach more than 6 units. STV is located in the region of 6–9 ms (milliseconds). A lower value means the presence of so-called metabolic acidosis, characterized by an imbalance of the acid-base balance (pH), in which the acidity in the body increases significantly. A good LTV level corresponds to 30–50 milliseconds.
If serious pathological changes in the fetus are detected at the time of CTG, you should immediately contact competent doctors for advice
conclusions
Expectant mothers should not look for which of the parameters in her CTG report are normal and which deviate from it. All analysis is done by a special computer program. And the main indicator for a woman is PSP. In fact, it reflects the entire verdict.
If the CTG does not work, if the indicators contradict each other, the doctor will definitely ask you to come for an examination again. There is no need to worry, this is also not uncommon.
Alarming indicators of cardiotocography are not a reason to worry, but a reason to go to the hospital, where the expectant mother will undergo an examination, including ultrasound and laboratory tests, and a decision will be made about delivery.
This option for ending pregnancy, of course, cannot suit any woman. But to console them, we can say that at the time of the CTG, the child is already quite viable , and if he is born at 36, 37, 38 or 39 weeks, he will be able to cope with new circumstances.
Refusal to hospitalize due to a “bad” CTG is the risk of losing the baby completely.
To learn how to interpret a cardiotocogram (CTG), see the following video.
medical reviewer, psychosomatics specialist, mother of 4 children
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Could it be wrong?
Gynecology is an exact science, which cannot be said about cardiotography. The study is not very accurate. It is no more than 90%. Here, a lot depends on the correctness of the procedure, the qualifications of the doctor, and the emotional and physical state of the woman.
The results are interpreted the same way for all girls, but the reasons for their deterioration can be anything. Therefore, CTG is a mandatory procedure that shows whether the fetus or mother has any problems. Other tests are needed to clarify complications.
Attention! Results may change due to medications that the woman may have taken before the procedure without the knowledge of the doctor.
Usually, deciphering the CTG result is a matter for the doctor. An error may occur when parsing the chart yourself.
Problems can happen for many reasons: the CTG machine is faulty, the expectant mother suddenly develops insomnia. Inaccurate indicators are rechecked with repeated CTG and ultrasound. In case of possible complications, the woman first goes to the hospital so that, if the problem is confirmed, treatment can begin.
Values and indicators of the CTG graph, interpretation and evaluation of results
Under normal conditions, CTG ( cardiotocography)
)
a number of parameters are recorded that must be taken into account when assessing the results of the study.
CTG evaluates:
- basal rhythm;
- rhythm variability;
- acceleration;
- deceleration;
- number of fetal movements;
- contractions of the uterus.
Basal rate (fetal heart rate)
Low and high rhythm variability (heart rate range, oscillations)
As mentioned above, the basal rate is the average of the fetal heart rate. Normally, the heart rate varies from beat to beat, which is due to the influence of the vegetative ( autonomous)
) nervous system on the heart.
These differences ( deviations from the basal rhythm
) are called oscillations (
fluctuations
).
When examining CTG, the following are distinguished:
- instantaneous oscillations;
- slow oscillations.
Instantaneous oscillations
Instantaneous oscillations are expressed in the time intervals between each successive heart contraction.
For example, in each second of the study the heart can contract at a different frequency ( for example, 125, 113, 115, 130, 149, 128 beats per minute
). Such changes are called instantaneous oscillations and should normally be recorded during any CTG.
Instantaneous oscillations can be:
- Low (
low variability )
- in this case, heart rate changes by less than 3 beats per minute ( for example, 125 and 127
). - Average (
average variability )
- in this case, the fetal heart rate changes by 3 - 6 beats per minute ( for example, 125 and 130
). - High (
high variability )
- in this case, the fetal heart rate changes by more than 6 beats per minute ( for example, 125 and 135
).
It is considered normal if high instantaneous oscillations are recorded during CTG. At the same time, the presence of low instantaneous oscillations may indicate fetal damage, including the presence of oxygen starvation ( hypoxia
).
It is worth noting that
it is impossible to determine instantaneous oscillations with the naked eye This is done automatically using special computer programs.
Slow oscillations
As for slow oscillations, they are characterized as changes in the fetal heart rate within one minute. On CTG they appear as small waves with sharp teeth.
Depending on the nature of slow oscillations, CTG can be:
- Silent (
monotonic ) type
- in this case, heart rate fluctuations within a minute do not exceed 5 beats per minute. - Slightly undulating (
transitional ) type
- heart rate fluctuations ranging from 6 to 10 beats per minute. - Undulating (
wave-like ) type
– heart rate fluctuations from 11 to 25 beats per minute. - Saltatory (
jumping ) type
– heart rate fluctuations of more than 25 beats per minute.
A wavy type of cardiotocogram is considered normal, indicating good condition of the fetus. With other types of CTG, the presence of damage to the fetus is likely ( in particular, with the jumping type, the umbilical cord is likely to be entangled around the baby’s neck
).
Also, when assessing slow oscillations, their number is taken into account, that is, how many times the heart rate increased or decreased ( compared to the basal rhythm
) in a minute.
Accelerations and decelerations
During the study, more pronounced fluctuations in heart rate may be recorded on the cardiotocogram, which is also important to take into account when assessing the results.
The following can be registered on CTG:
- Accelerations.
These are increases in the fetal heart rate by 15 or more beats per minute (
compared to the basal rhythm
) that persist for at least 15 seconds (
on CTG they look like increases in the upper line visible to the naked eye
).
The presence of accelerations of different form and duration is a normal phenomenon that should be present on CTG of a healthy, normally developing fetus ( normally, at least 2 accelerations should be recorded during 10 minutes of the study
).
This also happens due to the influence of the autonomic ( autonomic
) nervous system on heart rate. At the same time, it is worth noting that accelerations of the same form and duration may indicate damage to the fetus. - Decelerations.
This term refers to a slowdown in the fetal heart rate by 15 or more beats per minute (
compared to the basal rhythm
).
Decelerations can be early ( begin simultaneously with uterine contractions and end simultaneously with it
) or late (
begin 30 seconds after the start of uterine contractions and end much later
).
In any case, the presence of such decelerations may indicate a violation of oxygen delivery to the fetus. It is also worth noting that so-called variable decelerations that are not associated with uterine contractions may sometimes be observed. If they are shallow ( that is, the heart rate decreases by no more than 25–30 beats per minute
) and are not observed often, this does not pose a danger to the fetus.
Norm of fetal movements per hour (why does the child not move on CTG?)
During cardiotocography, not only the frequency and variability of the fetal heart rate is recorded, but also their relationship with active movements ( movements)
) fruits, of which there must be at least 6 per hour of research.
However, it is immediately worth noting that there is no single norm for the number of fetal movements. Its movements in the womb can be determined by many factors ( in particular, the period of sleep or activity, the mother’s nutrition, her emotional state, metabolism, and so on
). That is why the number of movements is estimated only in conjunction with other data.
Fetal movements are detected on the bottom line of the cardiotocogram, which records uterine contractions. The fact is that uterine contractions are recorded by a sensor that measures the circumference of a woman’s abdomen. When the uterus contracts, the circumference of its abdomen changes slightly, which is determined by a special sensor. At the same time, when moving ( moving
) of the fetus in the uterus, the abdominal circumference may also change, which will also be recorded by the sensor.
Unlike uterine contractions ( which on the bottom line of the cardiotocogram look like smoothly increasing and also smoothly decreasing waves
), fetal movements are determined in the form of sharp rises or jumps. This is due to the fact that when the uterus contracts, its muscle fibers begin to contract relatively slowly, while the movements of the fetus are characterized by relative speed and sharpness.
The reason for the absence or mild fetal movements may be:
- Rest phase.
This is a normal phenomenon, since during the prenatal period the child spends most of the time in a state resembling sleep. In this case, he may not have any active movements. - Severe fetal damage.
In severe hypoxia, fetal movements may also be absent.
Is it possible to see the tone of the uterus with CTG?
Theoretically, during CTG the tone of the uterus is also assessed. At the same time, practically doing this is somewhat more difficult.
Measuring the tone and contractile activity of the uterus is called tocography. Tocography can be external ( part of CTG and is carried out using a strain gauge installed on the surface of the mother’s abdomen
) and internal (
for this, a special sensor must be inserted into the uterine cavity
).
It is only possible to accurately measure the tone of the uterus using internal tocography. However, it is impossible to perform it during pregnancy or childbirth ( that is, before the birth of the child
). That is why, when analyzing CTG, the tone of the uterus is automatically set to 8 - 10 millimeters of mercury. Subsequently, when recording the contractile activity of the uterus, indicators that exceed this level are assessed.
What do the percentages on the CTG monitor mean?
What do contractions (uterine contractions) look like on CTG?
Will CTG show training (false) contractions?
The cardiotocogram can display both real and training contractions. Training contractions can occur in the second and third trimester of pregnancy and are short-term and irregular contractions of the uterine muscles that do not lead to the opening of the cervix and the onset of labor. This is a normal phenomenon that characterizes the normal activity of the uterus. Some women do not feel them at all, while others may complain of mild discomfort in the upper abdomen, where the hardened fundus of the uterus can be felt during a training contraction.
During a training contraction, a slight contraction of the uterus and an increase in its size in the fundus are also observed, which is detected by a sensitive strain gauge. In this case, the same changes will be noted on CTG as during normal contractions, but less pronounced ( that is, the height and duration of the curvature of the lower line will be less
). The duration of a training bout takes no more than a minute, which can also be determined on the graph.
What does sinusoidal rhythm on CTG mean?
The sinusoidal type of cardiotocogram is observed when the condition of the fetus is impaired, in particular with the development of oxygen starvation or for other reasons.
Sinusoidal rhythm is characterized by:
- rare and slow oscillations ( less than 6 per minute
); - low amplitude of oscillations ( fetal heart rate changes by no more than 10 beats per minute compared to the basal rhythm
).
In order for the rhythm to be considered sinusoidal, these changes must be recorded on CTG for at least 20 minutes. The risk of intrauterine damage or even fetal death increases significantly. That is why the question of urgent delivery ( through a cesarean section)
).
What does STV (short-term variation) mean?
This is a mathematical indicator that is calculated only by computer processing of CTG. Roughly speaking, it displays instantaneous fluctuations in the fetal heart rate over short periods of time ( that is, similar to instantaneous oscillations
). The principle of assessing and calculating this indicator is understandable only to specialists, but its level may also indicate damage to the fetus in the womb.
Normally, STV should be more than 3 milliseconds ( ms
). When this indicator decreases to 2.6 ms, the risk of intrauterine damage and fetal death increases to 4%, and when STV decreases to less than 2.6 ms – to 25%.
CTG assessment by points (Fisher, Krebs scale)
For a simplified and more accurate study of the cardiotocogram, a scoring system was proposed. The essence of the method is that each of the characteristics under consideration is assessed by a certain number of points ( depending on its characteristics
). Next, all the points are summed up, on the basis of which conclusions are drawn about the general condition of the fetus at the moment.
Many different scales have been proposed, but the most common today is the Fisher scale, which is considered the most reliable and accurate.
CTG assessment according to the Fisher scale includes:
- basal rhythm;
- rhythm variability ( slow oscillations
); - acceleration;
- deceleration.
Today, the Fisher scale as modified by Krebs is most often used, which, in addition to the listed parameters, also takes into account the number of fetal movements during 30 minutes of the study.
Features of the study
CTG is usually prescribed after the 32nd week of pregnancy, since only by this period does the maturation of neuromuscular impulses occur, and the method becomes the most informative.
For example, for fetal CTG, the norm is 33 weeks - the presence of more than two accelerations on the graph. By this time, they are caused by the response of the nervous system to fetal movements or to external factors. At earlier stages, accelerations may be associated with the conditions of intrauterine existence of the fetus, so the study may lead to false results.
Also, by this time the fetus has established a cycle of activity and rest, which is of great importance for this study. When performing CTG during the fetal rest period, the results will always be positive, even if in fact there is a high degree of hypoxia. That is why the study must be carried out for at least 40 minutes. During this time, the fetus' motor activity will certainly increase, which will make it possible to record changes in heart rate during its movement.
It is very important that the woman feels calm and comfortable during the examination. An uncomfortable position or strong emotions can cause more active fetal movement, which will lead to false results. Typically, during the procedure, the woman sits in a comfortable chair or lies on her side on a couch.
In order to understand how to decipher fetal CTG, we will analyze in detail the parameters by which it is assessed.