- home
- Coloproctology
- Sigmoid colon cancer
- Surgery for sigmoid colon cancer
Among all malignant tumors, sigmoid colon cancer ranks 4th. The tumor, which initially does not cause any particular discomfort, gradually increases in size, a number of symptoms appear, and in the absence of timely treatment, severe consequences may develop. But the only effective treatment for sigmoid colon cancer is surgery.
Today, there are various techniques, but if in the early stages it is possible to get by with organ-preserving, low-traumatic intervention, surgery on the sigmoid colon for cancer at a later stage will be more extensive.
Types of surgical treatment
At the initial stage, when the malignant process is localized within the mucosa, tumor removal can be performed during colonoscopy. The material removed during endoscopic intervention is sent for histological examination. If there is no spread of the malignant process, the patient will continue to be observed by specialists.
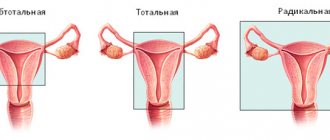
For stage I-III cancer, resection is indicated, during which the tumor is removed along with the affected area. The volume of intervention depends on which part of the tumor is located: proximal (upper), distal (lower) or middle. There are several types of resection, which can be combined for greater efficiency.
| Type of resection | Description |
| segmental | surgery to remove 1/3 of the sigmoid colon for stage 1-2 cancer - only the affected area is removed; |
| distal | removal of a tumor located in the lower part of the intestine, 2/3 of the length of the sigmoid colon is removed; |
| total | Almost the entire intestine must be removed; |
| extended | recommended in later stages, removal of the sigma is combined with left-sided hemicolectomy - the tumor located in the upper part is removed along with part of the colon. |
written consultation, in order to determine the indications for surgery, as well as choose the correct surgical treatment tactics, you can send me a full description of the colonoscopy, histology data, if possible, MSCT data of the abdominal cavity with contrast, indicate your age and main complaints. Then I will be able to give a more accurate answer to your situation.
Polycystic ovary syndrome. Treatment approaches
In general, treatment of the syndrome consists of either achieving regularity of the menstrual cycle with the help of COCs (at the same time this is the prevention of ovarian and endometrial cancer and the ability not to get pregnant, but to become pregnant), or to correct metabolic disorders (obesity, diabetes, prevention of depression, thrombosis). And, of course, we do not forget the main goal - to safely give birth to a healthy child.
A gynecologist often asks women with PCOS: “What do you want?” Women, as a rule, want everything and more: “I want to be cured so I can get pregnant! And so that there is no extra hair. And my periods are regular. And in general, can you make it faster?” The doctor responds to these and other requests by proposing and justifying a treatment regimen. Let's see what this looks like in practice.
What does a woman want: “I want regular menstruation and not have hair grow in the wrong places”
This task is quite simple if a woman is not planning a pregnancy in the next couple of years.
What the doctor suggests: hormonal treatment
Here, the first choice drugs will be combined oral contraceptives. While taking COCs, menstrual-like reactions will become regular and comfortable. At the same time, we will prevent endometrial hyperplasia with uterine bleeding and reduce the risk of developing endometrial and ovarian cancer.
It is preferable to use COCs with antiandrogenic properties. These are drugs that include cyproterone acetate, drospirenone, chromadinone acetate (Diane-35, Yarina/Yarina Plus, Midiana, Belara). The drug will have to be taken for a long time, so it is necessary to take into account existing metabolic disorders, the risk of venous thrombosis and many other factors.
If the regularity of menstruation can be dealt with immediately, then a significant reduction in hair growth in androgen-dependent areas will have to wait one to two years. During the waiting period, you can use various hair removal methods. In cases of severe hirsutism or lack of effect from 12 months of COC use, antiandrogenic drugs can be added to treatment: cyproterone acetate, spironolactone, flutamide, finasteride. It is important to understand: antiandrogenic drugs are used together with COCs, and not instead of COCs.
If COCs are contraindicated (with PCOS, the doctor should be very careful and monitor patients with obesity, high blood pressure, smokers, and cases of strokes/heart attacks in parents), then there are no easy ways. Regulation of the cycle will have to be carried out using cyclic use of gestagens, and hair growth will have to be combated using monotherapy with antiandrogens. In this case, strict contraception is necessary: pregnancy while taking antiandrogens is unacceptable.
The woman is stubborn: “I want to get pregnant, but I don’t want to lose weight”
Obesity is common in PCOS. It is these patients who most often come to us with complaints of infertility - a body mass index above 40, a waist circumference of 120 cm, but: “Help, doctor, you are the only hope. I’ve already been to all the doctors, I can’t get pregnant for five years, I’ve even done IVF twice - nothing helps.”
What the doctor says: weight loss is a must
Obesity is a recognized factor in the development of infertility and miscarriage. In patients with excess body weight, ovulatory function disorders are significantly more common. This is a protective barrier put up by Mother Nature, because pregnancy in such women is often complicated by the development of severe late gestosis, threatening the life of the mother and fetus, and gestational diabetes mellitus.
A weight loss of 5–10% of the original weight can lead to restoration of ovulatory cycles and fertility (Thessaloniki Consensus on Restoring Fertility in Women with PCOS, 2007).
You will definitely have to lose weight. You cannot plan a pregnancy if you are obese. Target parameters: BMI = 29.9, waist circumference less than 80 cm. If this is not achievable, and the spouses are of critical age, it is necessary to achieve at least normalization of blood pressure and metabolism.
Trying to get pregnant during a period of rapid weight loss, regardless of the weight loss method, is undesirable. Restricting calories, increasing physical activity, and using weight loss medications in early pregnancy can seriously harm fetal development. You should lose weight and change your lifestyle before pregnancy, ideally before starting infertility treatment.
What does the doctor want: “I want the patient to not have diabetes and cardiovascular diseases”
This task is much more difficult. First of all, because this goal worries the doctor more than the patient, and it is the woman who will have to make the effort. Unfortunately, women for the time being associate excess weight only with external attractiveness, believing that this is their personal matter.
What the doctor suggests: monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol, glucose levels
The first line of treatment for overweight and obese women is lifestyle changes. You can't get by with diets alone. You will definitely have to go to the gym so that, under the guidance of a cruel trainer, the physical activity is sufficient. It is equally important to increase general physical activity: walk up the stairs, walk to and from work (starting from 1-2 stops and gradually increasing the length of the route), get a dog and not only wander around the house with it for 15 minutes in the morning and in the evening, and start going to exhibitions and getting interested in dog sports.
Recommendations of the Society for Hyperandrogenism and PCOS, Endocrine Society:
- Blood pressure should be measured regularly. If you have high blood pressure, daily monitoring with a diary is necessary.
- Screening for impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes mellitus is recommended for all patients. A glucose tolerance test is performed once every 2 years if glucose tolerance is normal or more often if additional risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes are identified.
- A screening for “bad/good cholesterol” is also necessary. In the absence of violations - once every 2 years, in case of deviations from the norm - annually.
There is still no magic pill. Metformin, which has been tried in patients with obesity and PCOS since the mid-90s of the twentieth century, reduces the risk of developing diabetes by only 16%, and lifestyle modification - by 32%. Today, this drug is prescribed according to strict indications: for proven insulin resistance in cases where lifestyle changes were not enough.
The prognosis depends on age, weight and blood pressure: the older, fatter and taller you are, the more carefully you will have to follow the recommendations.
The patient is in a hurry: “I have already lost weight and am following all your stupid recommendations, but I can’t get pregnant. Let's do something!
If other causes of infertility are excluded, the patient is prepared for pregnancy, and you can safely proceed to active action.
What the doctor offers: three lines of therapy
The first line is stimulation of ovulation with Clomiphene. Clomiphene (clostilbegit) has been well studied, is affordable, and the risks are low. A maximum of 12 treatment cycles are carried out, but no more than 6 cycles in a row. However, after six unsuccessful attempts, it is better to move on to plan B.
Plan B, or second line of therapy, involves two approximately equivalent options: continue stimulating ovulation with more powerful means, or go to the operating room.
If the patient is more inclined to think about drug treatment, the doctor may suggest stimulation with gonadotropins (for example, Gonal-F). For patients with PCOS, stimulation is performed in small doses in order to obtain only one leading follicle.
Unfortunately, this does not always happen, and a whole group of follicles may begin to grow. This is fraught not only with multiple pregnancies, but also with the development of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, up to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal and chest cavity with abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and shortness of breath. Such patients require urgent hospitalization.
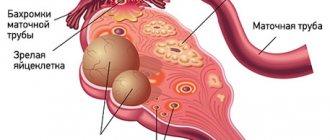
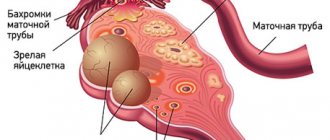
Surgical treatment of PCOS has its own traditions - 80 years ago, Stein and Leventhal successfully helped patients become pregnant by performing wedge resection of the ovaries.
Today's laparoscopic operations (electrocautery, laser drilling and multiple ovarian biopsies) are much safer and less likely to leave behind an adhesive process. However, surgical treatment is still not the main option.
It is indicated only if the first line of therapy has not worked or if there is a suspicion of tubal obstruction, adhesions in the pelvis, endometriosis in combination with PCOS and infertility.
And finally, the third line of therapy is assisted reproductive technologies. If neither lifestyle modification, nor Clomiphene, nor laparoscopic surgery helps, the only option is to use in vitro fertilization methods. With anovulatory infertility in combination with obstruction of the fallopian tubes, severe endometriosis, the need for genetic preimplantation diagnosis and/or male factor infertility, there is nothing else left.
PCOS is not a death sentence. Even with a long absence of ovulation, ovulation can “shoot” once or twice a year. I have patients with a confirmed diagnosis who easily gave birth to two children and carefully protect themselves, believing that “getting pregnant” is possible with the slightest error. Another thing is important: an unplanned pregnancy with uncompensated symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome threatens the woman and the fetus with a variety of problems. That is why it is so important to plan your life wisely, preparing in advance for desired pregnancies and carefully preventing unwanted ones.
Oksana Bogdashevskaya
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Products by topic: [product](Diane-35), [product](Yarina), [product](Yarina Plus), [product](Midiana), [product](Belara), [product](Clomiphene), [ product](clostilbegit), [product](Gonal-F), [product](metformin)
How is the operation performed?
The operation to remove sigmoid colon cancer consists of three stages: the tumor with the adducting and efferent sections is isolated, after which the intestine is cut off and all regional lymph nodes are removed.
Then an interintestinal anastomosis is applied - connecting the end sections of the intestine, as a result of which normal passage through the intestine is restored. When forming an interintestinal anastomosis, I use endoscopic staplers made in the USA, which reduces the likelihood of complications after surgery, such as suture failure or the development of stricture.
In some cases, usually with the development of intestinal obstruction, a temporary colostomy can be formed - bringing the end of the intestine to the anterior wall of the peritoneum (unnatural anus). In this case, after 2-3 months, a reconstructive operation is planned, during which the ability to naturally move intestinal contents is restored.
Treatment tactics for adhesions
When an adhesive process is detected, treatment tactics will depend on the severity and severity. If we are talking about an acute adhesive process or an intermittent form of pathology, surgical intervention will be the only effective way to solve the problem. Typically, diagnostic laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes, uterus, ovaries and simultaneous removal of adhesions are performed. This method is very effective and does not require long-term rehabilitation, and gives a pronounced effect.
In case of pronounced adhesions in the pelvis, diagnostic laparoscopy is performed with simultaneous excision of adhesions and their removal, which were identified during a complete examination of the pelvic organs. Today, pelvic adhesiolysis is considered the most effective method for eliminating adhesive disease. The procedure is minimally invasive, effective and does not require a long rehabilitation period.
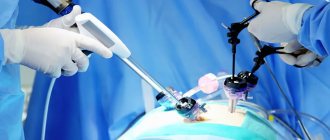
Laparoscopy for sigmoid colon cancer
Oncological disease is treated by laparoscopic surgery
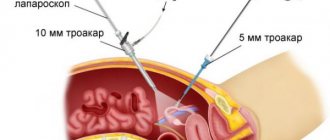
To remove the tumor, I use laparoscopic access, which has a number of advantages compared to open surgery:
- there is no extensive tissue trauma, I perform all manipulations through 3-4 small punctures;
- the risk of blood loss during surgery is minimized;
- the rehabilitation period is much shorter, the patient begins to walk on the day of surgery, which significantly reduces the risk of thromboembolism;
- pain associated with tissue trauma is practically absent;
- Hospitalization lasts about 3-5 days.
Laparoscopic surgery for sigmoid colon cancer is performed using video endoscopic equipment, which allows manipulations to be performed as carefully and accurately as possible. Thanks to the use of ultrasonic scissors and the LigaSure electrothermal tissue ligation device during the intervention, the risk of intraoperative complications is eliminated, the duration of the operation is significantly shorter, when using the Force Triad energy platform, intestinal mobilization is performed quickly and bloodlessly, and there is no need to use surgical clips and threads.
Considering the psychological state of patients when a colostomy is removed to the anterior abdominal wall, I always strive to perform the operation in such a way as to minimize possible functional impairments after surgical treatment. I try my best to maintain bowel continuity. Also, if possible, I always try to perform organ-conserving surgery.
Diagnosis of pelvic adhesions
It is difficult to suspect an adhesive process just by external signs; similar complaints and symptoms are typical for many other processes. Indirect indications of possible adhesions include previous inflammatory processes and infections of the genitals, surgical delivery, trauma to the perineum and pelvic organs, abdominal surgery, and diagnosed endometriosis.
To diagnose the adhesive process, the gynecologist conducts a detailed conversation, and then a gynecological examination. Only laparoscopic surgery - examination of the pelvic cavity using a miniature camera - can accurately determine the diagnosis.
Preparation
The operation is carried out as planned; before it, the woman must undergo a full examination in order to exclude contraindications and any health problems that require additional treatment. It is important to be examined by a gynecologist and undergo all the required tests, as well as a physician’s opinion on the possibility of surgery. You need to do:
- general blood test in combination with coagulation studies (blood for clotting), hormone levels, determination of biochemical parameters;
- urine tests to exclude urological infections;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis to determine the anatomical features of the body;
- research to exclude hepatitis, HIV and sexually transmitted infections.
2-3 days before surgery, a light diet, laxatives, and bowel cleansing are necessary. After 6 pm before the operation, it is forbidden to eat, and in the morning before the operation you should also not drink.
Contraindications for surgery
List of contraindications for laparoscopic dissection of adhesions:
- acute infections and diseases;
- exacerbation of chronic pathology;
- severe damage to the heart, blood vessels and respiratory tract (due to problems with anesthesia);
- severe damage to the kidneys, liver, digestion until the condition stabilizes;
- serious and uncorrectable metabolic problems;
- blood clotting disorders;
- pregnancy period.
After the examination, the doctor can determine other individual contraindications, for example, allergies or intolerance to anesthesia or medications, and then the issue of intervention is decided individually.
Laparoscopic adhesiolysis of the pelvis
Surgical intervention is widely used today to treat adhesions, but it is carried out mainly by laparoscopic method. Adhesiolysis is used - dissection of pelvic adhesions using special surgical instruments that are inserted through punctures in the abdominal cavity. The operation is performed in an operating room using anesthesia, but the intervention itself is not as traumatic as a full-fledged operation with incisions. Adhesions are dissected and removed in order to restore the functionality of the organs of the female reproductive system and eliminate intestinal problems. This is the safest and most effective method, after which a woman quickly recovers and can live a full life.